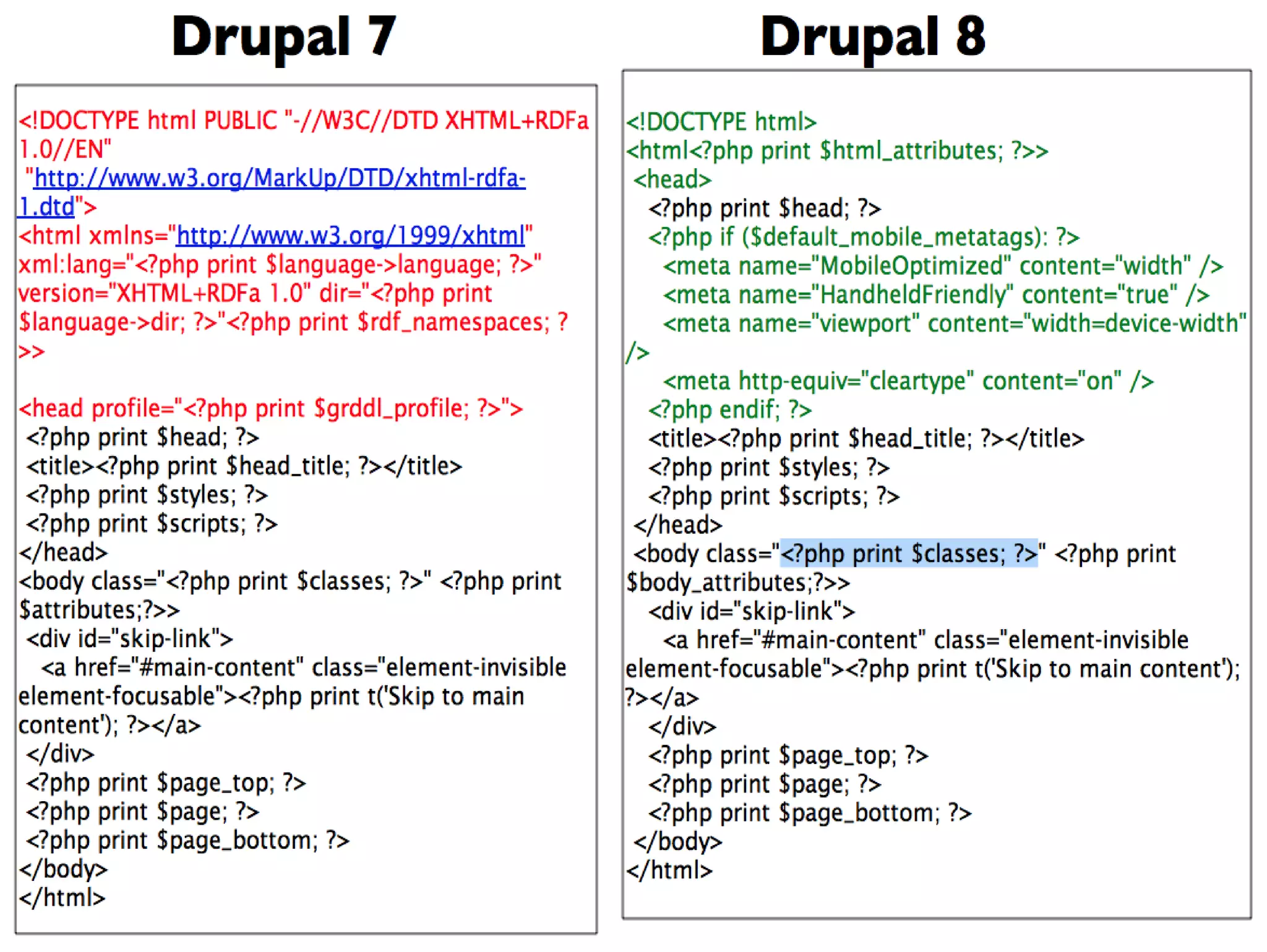
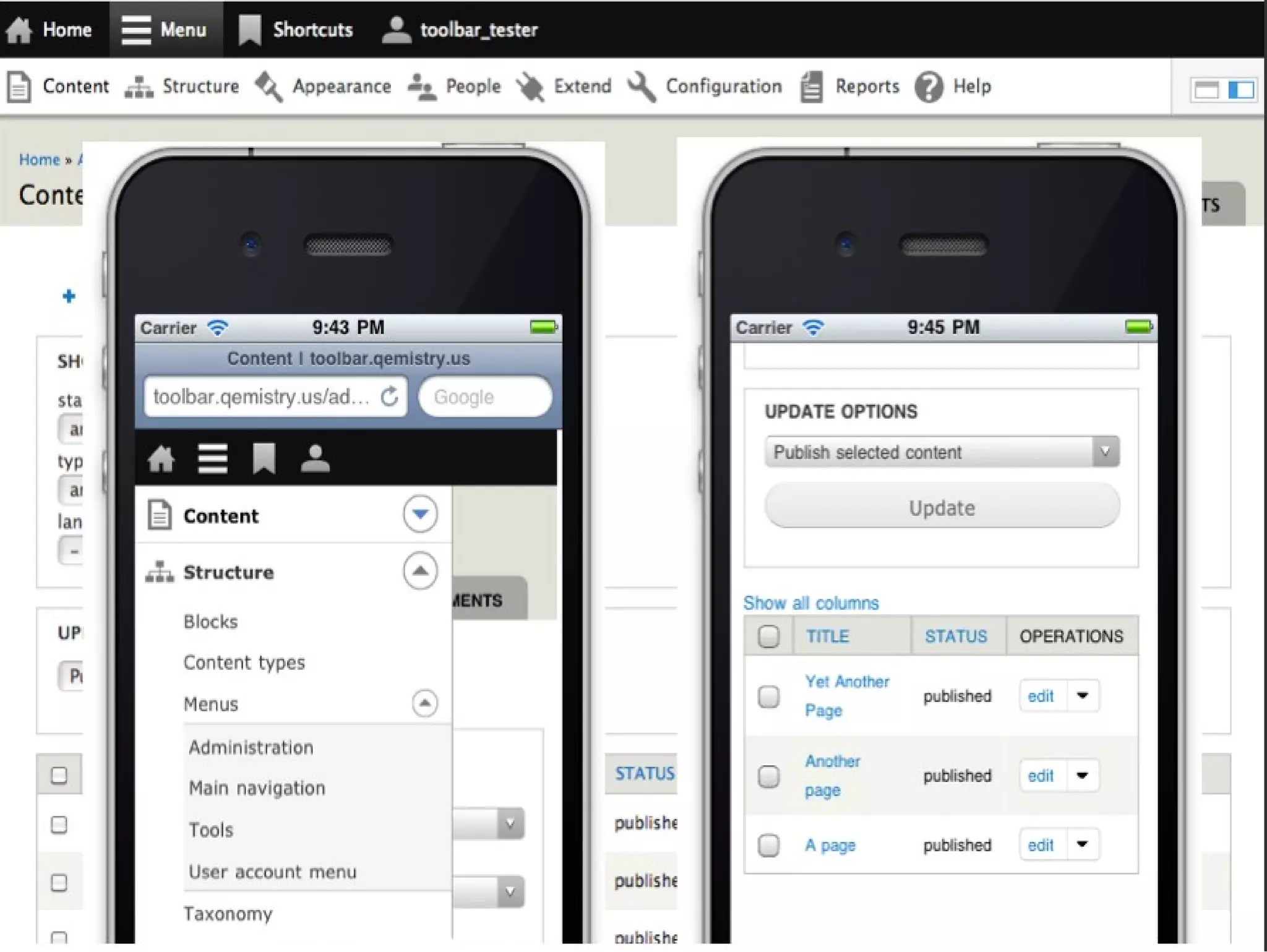
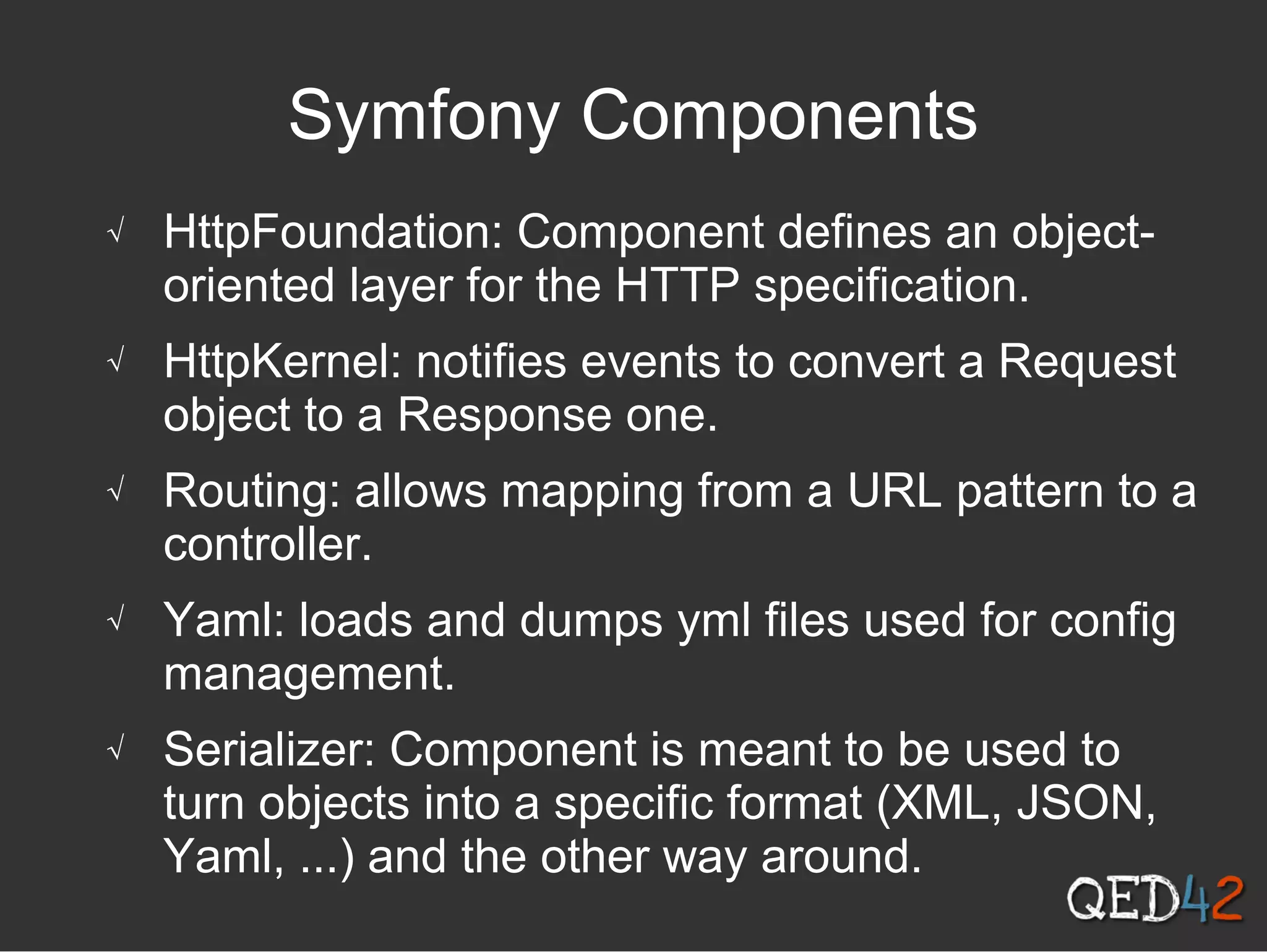
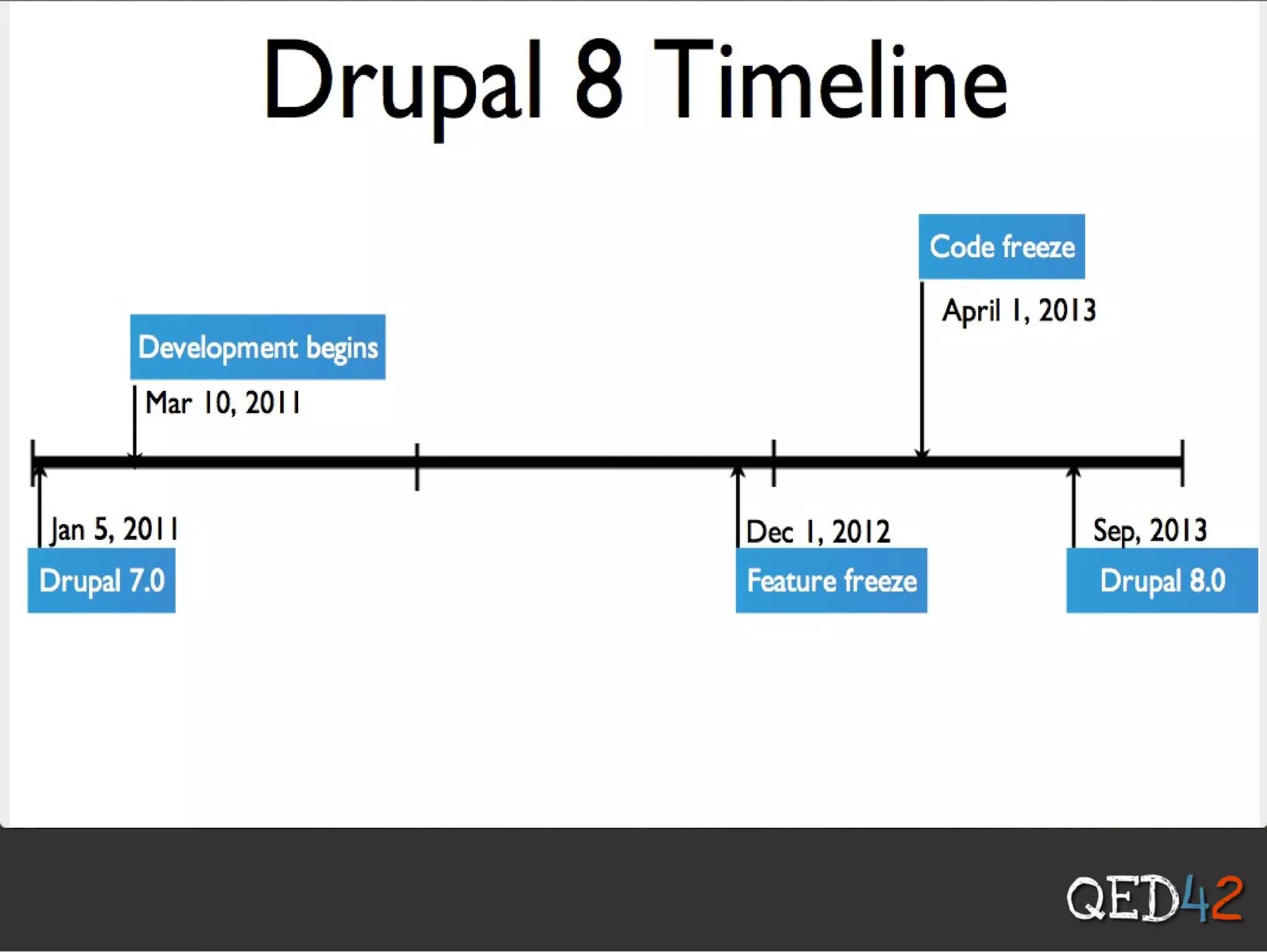
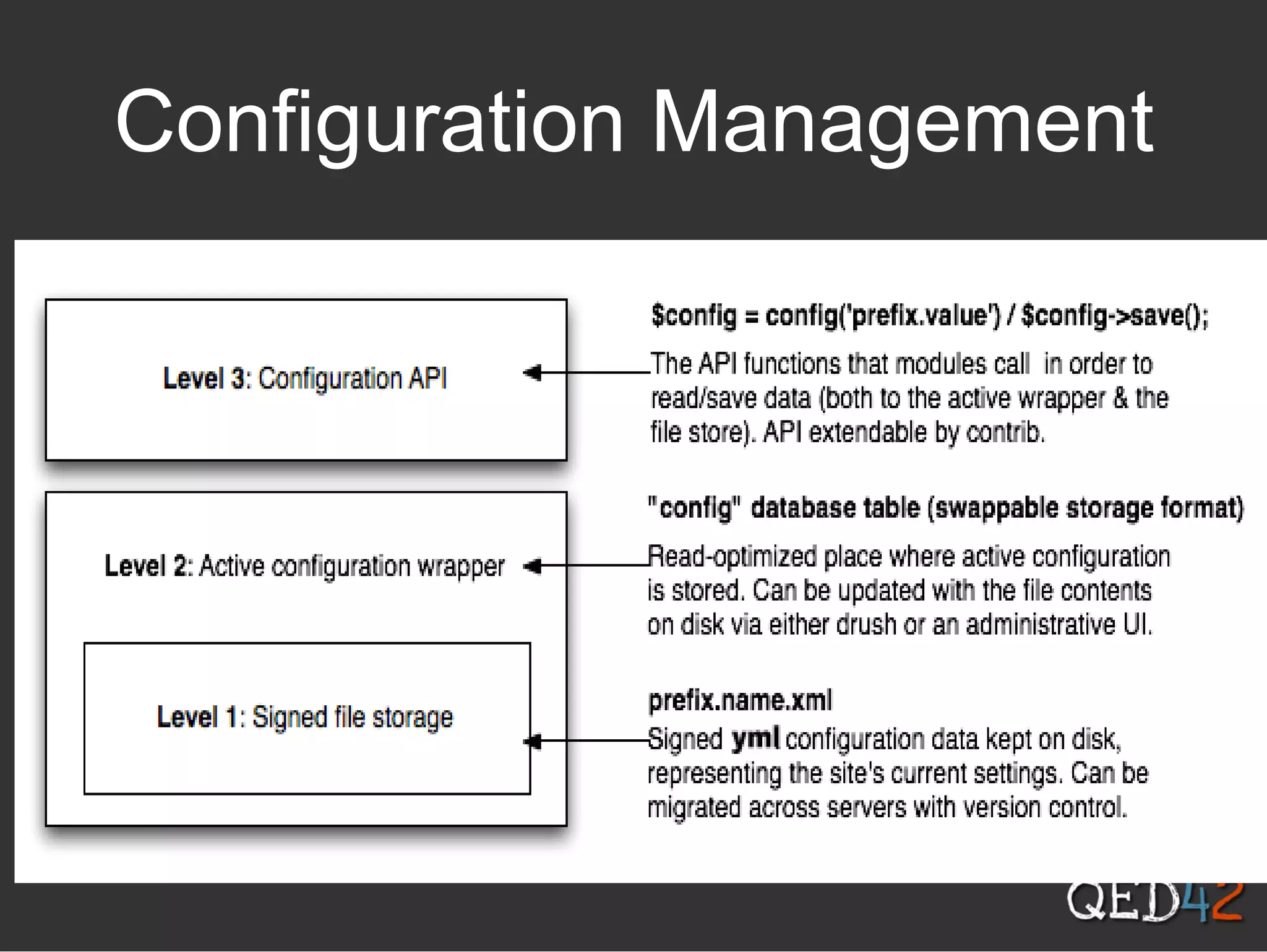
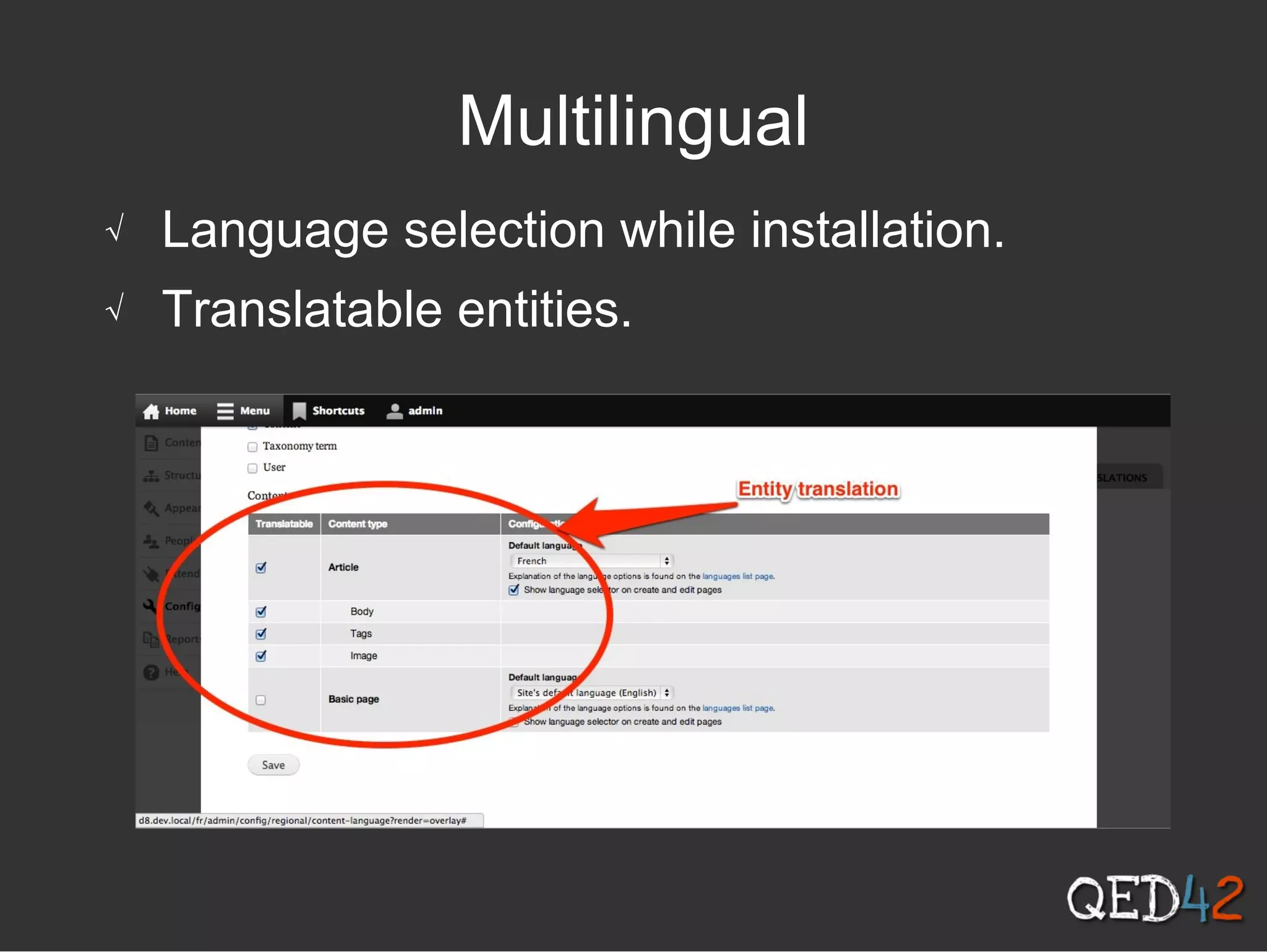
Drupal 8 uses Symfony components and introduces new initiatives like configuration management, web services, and multilingual support. It has a new directory structure and uses the Symfony class loader, dependency injection, routing and other components. Configuration is now managed through a configuration API and stored in the active config store and codebase for easier migration. Web services allow Drupal to act as a RESTful API. The system supports multilingual content out of the box.







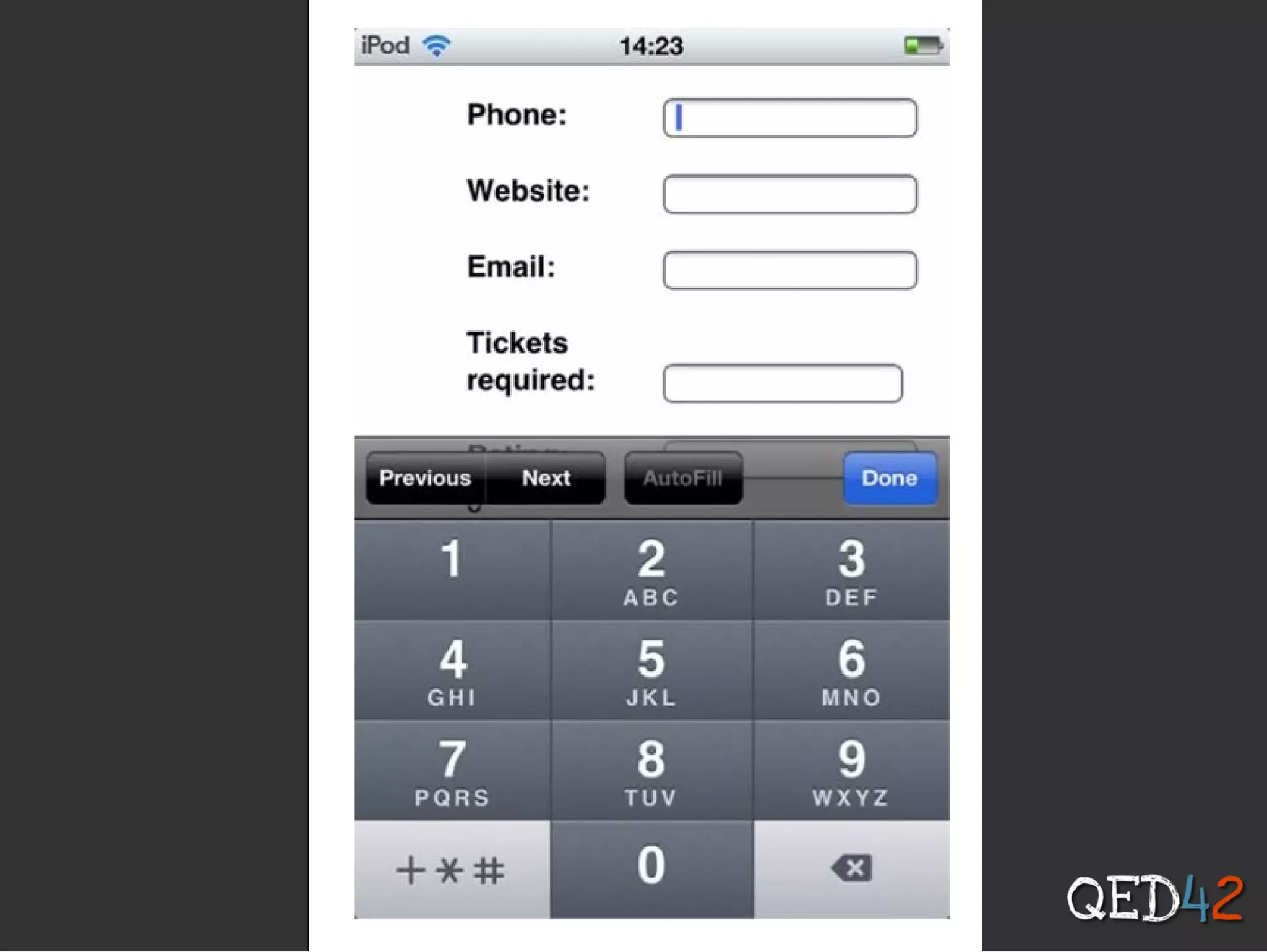
![HTML5
$form['telephone'] = array(
'#type' => 'tel',
'#title' => t('Phone'),
);
$form['website'] = array(
'#type' => 'url',
'#title' => t('Website'),
);
$form['email'] = array(
'#type' => 'email',
'#title' => t('Email'),](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intotodrupal8-130601041957-phpapp02/75/Into-to-drupal8-13-2048.jpg)