This document summarizes the process of creating molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) and non-imprinted polymers (NIPs) for the detection of celecoxib. It describes the materials, synthesis, and testing methods used. The polymers were created using acrylamide as the functional monomer and ethylene glycol dimethacrylate as the cross-linker, with celecoxib as the template molecule. The binding capacity of the resulting MIPs and NIPs was tested through serial dilution binding experiments measuring absorbance with a NanoDrop spectrophotometer. The goal was to develop an imprinted polymer sensor for celecoxib detection.



![DMPA (Dimethoxy-2-phenylacetophenone) : 0.0088 mmol
CELEC (Celecoxib): 0.025 mmol
Tol (Toluene) : 1920 mg
For first vial, I put all above reagents, but for second vial put all above, without Celecoxib.
Solution prepared in four seperate vials, to start the reaction vials were placed at UV cabine for
18 hour.
WASHING STEP
The polymers obtained were transferred into the falcons with a spatul. After, in another beaker
20 ml acetic acid and 80 ml of methanol solution was prepared. This solution was prepared, it
was placed on the polymer in the tube to be 10 milliliters. It was stored on the shaker for one
hour and after that, it was centrifuged for 10 minutes, 5000 rpm. The liquid portion remaining
on the top, the bottom was evacuated to collapsed polymers. This step was performed 4 times,
respectively. Fourth washing, after centrifugation received 1 milliliter of the supernatant, the
absorbance value was measured in the NanoDrop. (1 ml was taken from each tube.) By the way
methanol was used to blank the NanoDrop.
To remove acetic acid, methanol was introduced into the falcons containing the polymer (to be
10 ml). It was stored on the shaker for 45 minutes and after that, it was centrifuged for 10
minutes, 5000 rpm. The liquid portion remaining on the top, the bottom was evacuated to
collapsed polymers. This step was performed 3 times, respectively.
After all these operations, cover of the tubes were opened, they were covered with napkin. It
was placed in a vacuum oven overnight.
[To give you some information about the reagents used: AAm: Functional Monomer ;
EGDMA:Cross-Linker ; DMPA: Initiator ; CELECOXIB: Template ; ACN: Solvent ; Tol :
Solvent]
FOR CALIBRATION STAGES:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/internshipnotebook-170720191305/75/Internship-notebook-4-2048.jpg)
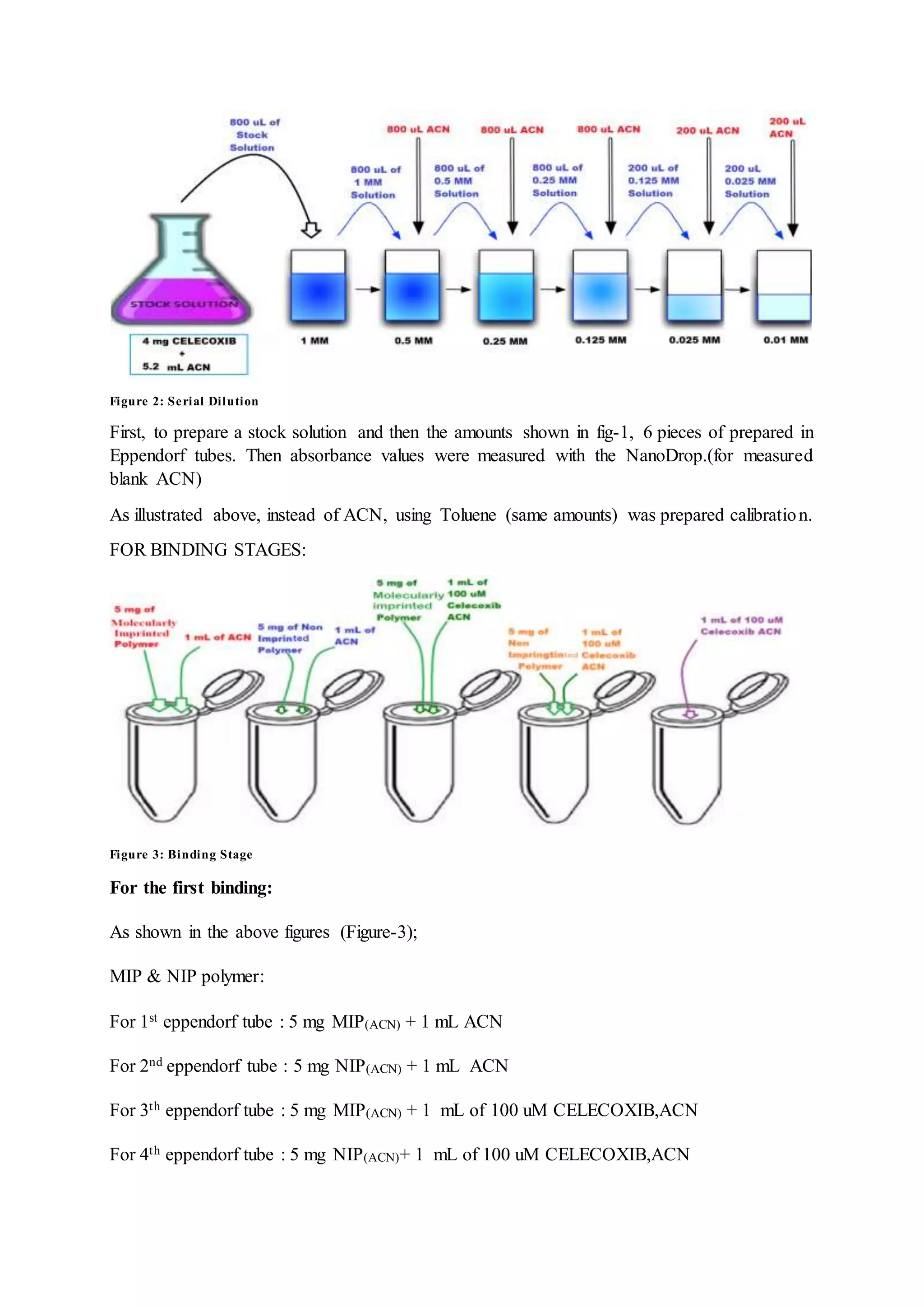
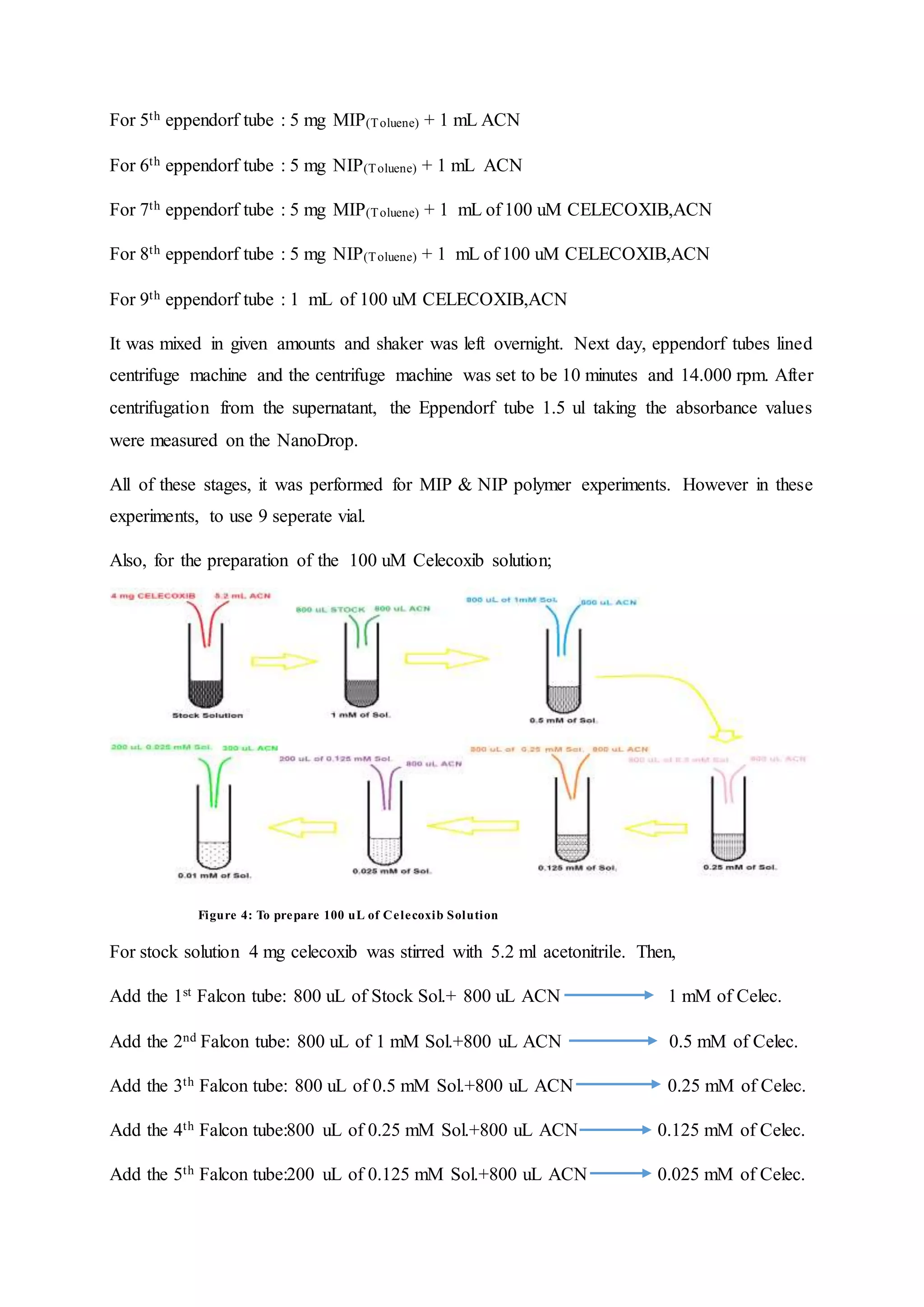

![For 4th eppendorf tube : 5 mg NIP(ACN)+ 1 mL of 100 uM CELEC,Toluene(5% Asetic Acid)
For 5th eppendorf tube : 5 mg MIP(Toluene) + 1 mL Toluene(5% Asetic Acid)
For 6th eppendorf tube : 5 mg NIP(Toluene) + 1 mL Tolene(5% Asetic Acid)
For 7th eppendorf tube : 5 mg MIP(Toluene) + 1 mL of 100 uM CELEC,Tolene(5% Asetic Acid)
For 8th eppendorf tube : 5 mg NIP(Toluene) + 1 mL of 100 uM CELEC,Toluene(5% Asetic
Acid)[not 100 uM, calculation error was made.So 500 uM was used.]
For 9th eppendorf tube : 1 mL of 100 uM CELECOXIB,Toluene(5% Asetic Acid) [not 100 uM,
calculation error was made.So 500 uM was used.]
The obtained result of absorbance value in the NanoDrop, to calculate Binding Calculation.
For the fourth binding;
For starters, 2 MM stock solution was prepared.
3.8 mg CELECOXIB + 5 ml ACN
Afterwards, was made dilutions:
0.5 MM 2 ml of 2MM stock solution + 6 ml ACN
0.250 MM 4 ml of 0.5 MM solution + 4 ml ACN
0.125 MM 4 ml 0f 0.250 MM solution + 4 ml ACN
0.025 MM 2 ml of 0.125 MM solution + 8 ml ACN
0.001 MM 2 ml of 0.025 MM solution + 3 ml ACN
Subsequently, for the binding process
NIP (ACN):
For the 1st epp.tube: 1 ml of 0.5 MM Solution + 5 mg polymer
For the 2nd epp.tube: 1 ml of 0.25 MM Solution + 5 mg polymer
For the 3 th epp.tube: 1 ml of 0.125 MM Solution+5 mg polymer
For the 4th epp.tube: 1 ml of 0.025 MM Solution + 5 mg polymer
For the 5th epp.tube: 1 ml of 0.01 MM Solution + 5 mg polymer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/internshipnotebook-170720191305/75/Internship-notebook-8-2048.jpg)
![For the 6th epp.tube: 1 ml of ACN + 5 mg polymer
MIP (ACN):
For the 1st epp.tube: 1 ml of 0.5 MM Solution + 5 mg polymer
For the 2nd epp.tube: 1 ml of 0.25 MM Solution + 5 mg polymer
For the 3 th epp.tube: 1 ml of 0.125 MM Solution+5 mg polymer
For the 4th epp.tube: 1 ml of 0.025 MM Solution + 5 mg polymer
For the 5th epp.tube: 1 ml of 0.01 MM Solution + 5 mg polymer
For the 6th epp.tube: 1 ml of ACN + 5 mg polymer
Also, to draw the calibration curve[2nd Calibration]; 6 piece of each tube, the solution was
added.
For the first epp.tube: Add 1 ml of 0.5 MM
For the second epp.tube: Add 1 ml of 0.250 MM
For the third epp.tube: Add 0.125 MM
For the fourth epp.tube: Add 0.025 MM
For the fifth epp.tube: Add 0.001 MM
It was mixed in given amounts and shaker was left overnight. Next day, eppendorf tubes lined
centrifuge machine and the centrifuge machine was set to be 10 minutes and 14.000 rpm. After
centrifugation from the supernatant, the Eppendorf tube 1.5 ul taking the absorbance values
were measured on the NanoDrop.
The obtained result of absorbans value in the NanoDrop, to calculate Binding Calculation.
For the fifth binding;
Firstly, 2 MM stock solution was prepared.
3.8 mg CELECOXIB + 5 ml ACN
Subsequently, dilution was made.
0.5 MM 2 ml of 2MM stock solution + 6 ml ACN
0.250 MM 4 ml of 0.5 MM solution + 4 ml ACN](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/internshipnotebook-170720191305/75/Internship-notebook-9-2048.jpg)
![0.125 MM 4 ml 0f 0.250 MM solution + 4 ml ACN
0.025 MM 2 ml of 0.125 MM solution + 8 ml ACN
0.001 MM 2 ml of 0.025 MM solution + 3 ml ACN
After, for the binding process
NIP (Toluene):
For the 1st epp.tube: 1 ml of 0.5 MM Solution + 10 mg polymer
For the 2nd epp.tube: 1 ml of 0.25 MM Solution + 10 mg polymer
For the 3 th epp.tube: 1 ml of 0.125 MM Solution+10 mg polymer
For the 4th epp.tube: 1 ml of 0.025 MM Solution + 10 mg polymer
For the 5th epp.tube: 1 ml of 0.01 MM Solution + 10 mg polymer
For the 6th epp.tube: 1 ml of ACN + 10 mg polymer
P 172-2 MIP (Toluene)
For the 1st epp.tube: 1 ml of 0.5 MM Solution + 10 mg polymer
For the 2nd epp.tube: 1 ml of 0.25 MM Solution + 10 mg polymer
For the 3 th epp.tube: 1 ml of 0.125 MM Solution+10 mg polymer
For the 4th epp.tube: 1 ml of 0.025 MM Solution + 10 mg polymer
For the 5th epp.tube: 1 ml of 0.01 MM Solution + 10 mg polymer
For the 6th epp.tube: 1 ml of ACN + 10 mg polymer
In addition, to draw the calibration curve[3th Calibration]; 6 piece of each tube, the solution was
added.
For the first epp.tube: Add 1 ml of 0.5 MM
For the second epp.tube: Add 1 ml of 0.250 MM
For the third epp.tube: Add 0.125 MM
For the fourth epp.tube: Add 0.025 MM
For the fifth epp.tube: Add 0.001 MM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/internshipnotebook-170720191305/75/Internship-notebook-10-2048.jpg)
![It was mixed in given amounts and shaker was left overnight. Next day, eppendorf tubes lined
centrifuge machine and the centrifuge machine was set to be 10 minutes and 14.000 rpm. After
centrifugation from the supernatant, the Eppendorf tube 1.5 ul taking the absorbance values
were measured on the NanoDrop. The obtained result of absorbans value in the NanoDrop, to
calculate Binding Calculation.
RESULT& DISCUSSION:
Graph-1: Graph of Calibration Celecoxib+ ACN [first calib.]
Graph-2: Graph of Calibration Celecoxib+ ACN [second calib.]
The result of first binding:
MIP(ACN): -4% ; NIP(ACN): -8.4% ; MIP(Toluene): 19.802% ; NIP(Toluene): -5.9%
The result of second binding:
MIP(ACN): 42.28% ; NIP(ACN): 45.14% ; MIP(Toluene): 44.19% ; NIP(Toluene): 46.66%
The result of third binding:
MIP(ACN): %17.08 ; NIP(ACN): 21.79% ; MIP(Toluene): 28.27% ; NIP(Toluene): 22.53%
y = 2.339x
R² = 0.9993
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
1.4
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6
Abs.Value@251nm
Concentration of Celecoxib+ACN
CALIBRATION
y = 0.9582x + 0.0002
R² = 0.9976
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6
ABS.VALUE@281nm
Concentration of Celecoxib+Toluene
Calibration](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/internshipnotebook-170720191305/75/Internship-notebook-11-2048.jpg)
