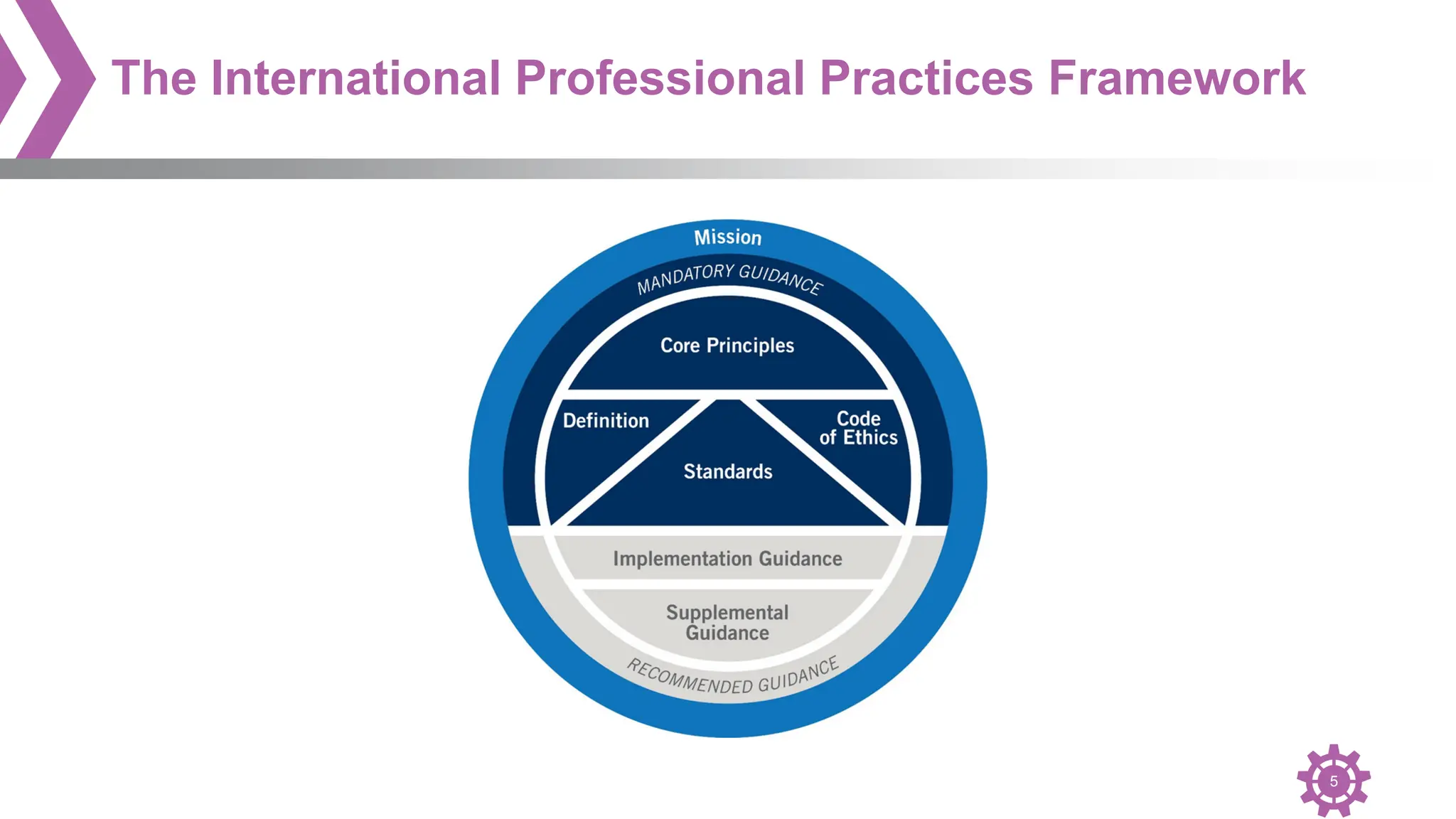
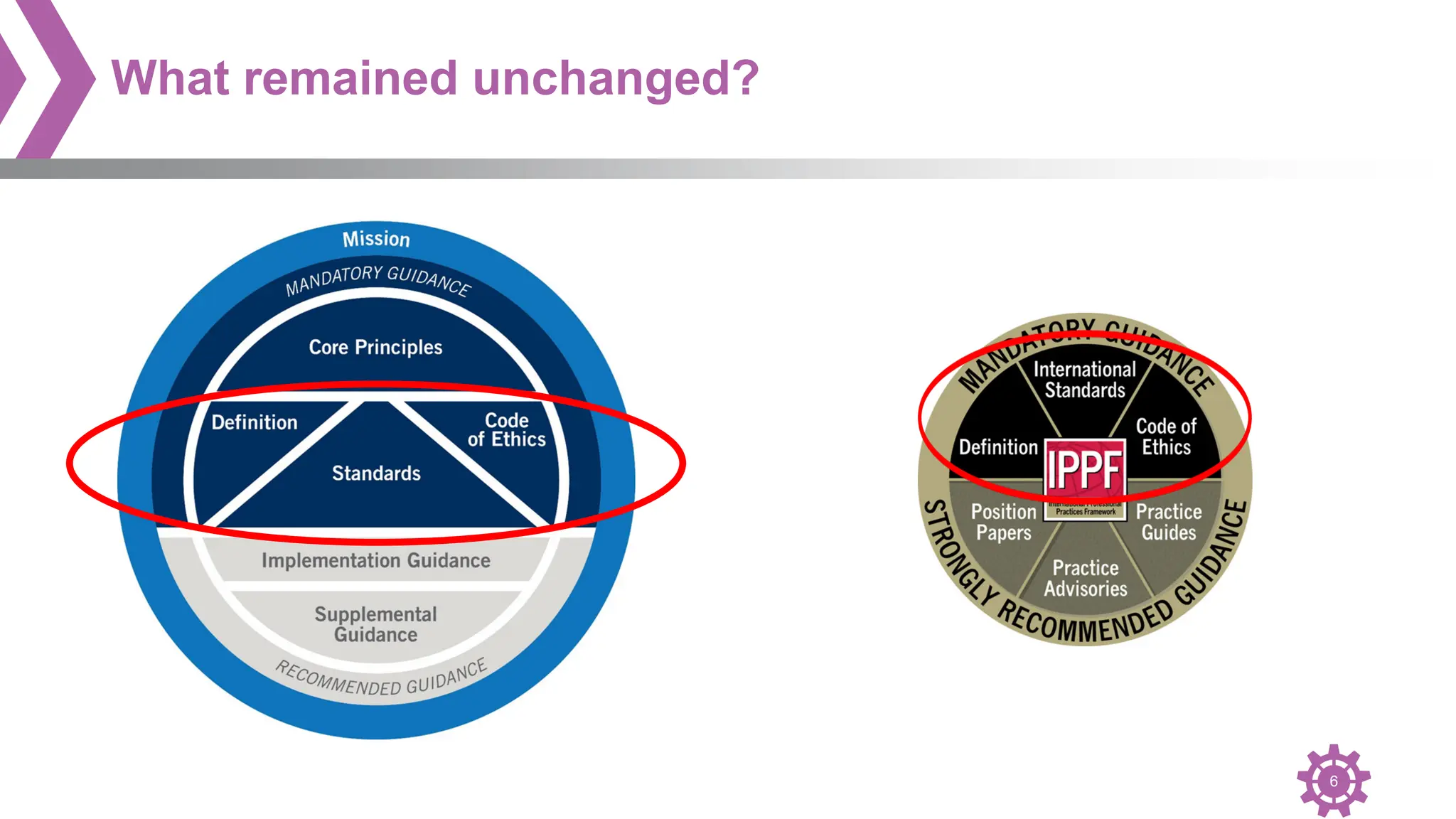
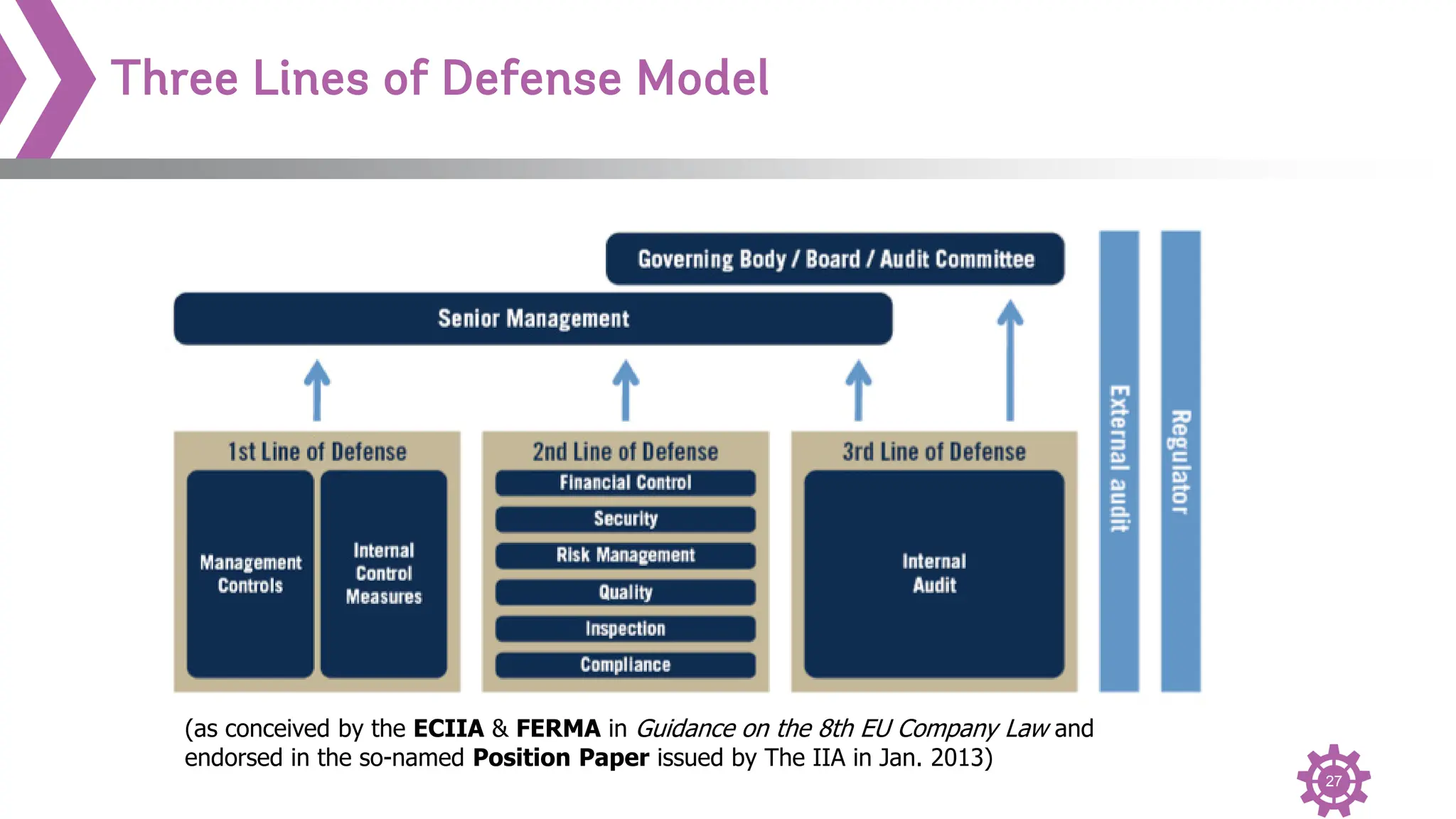
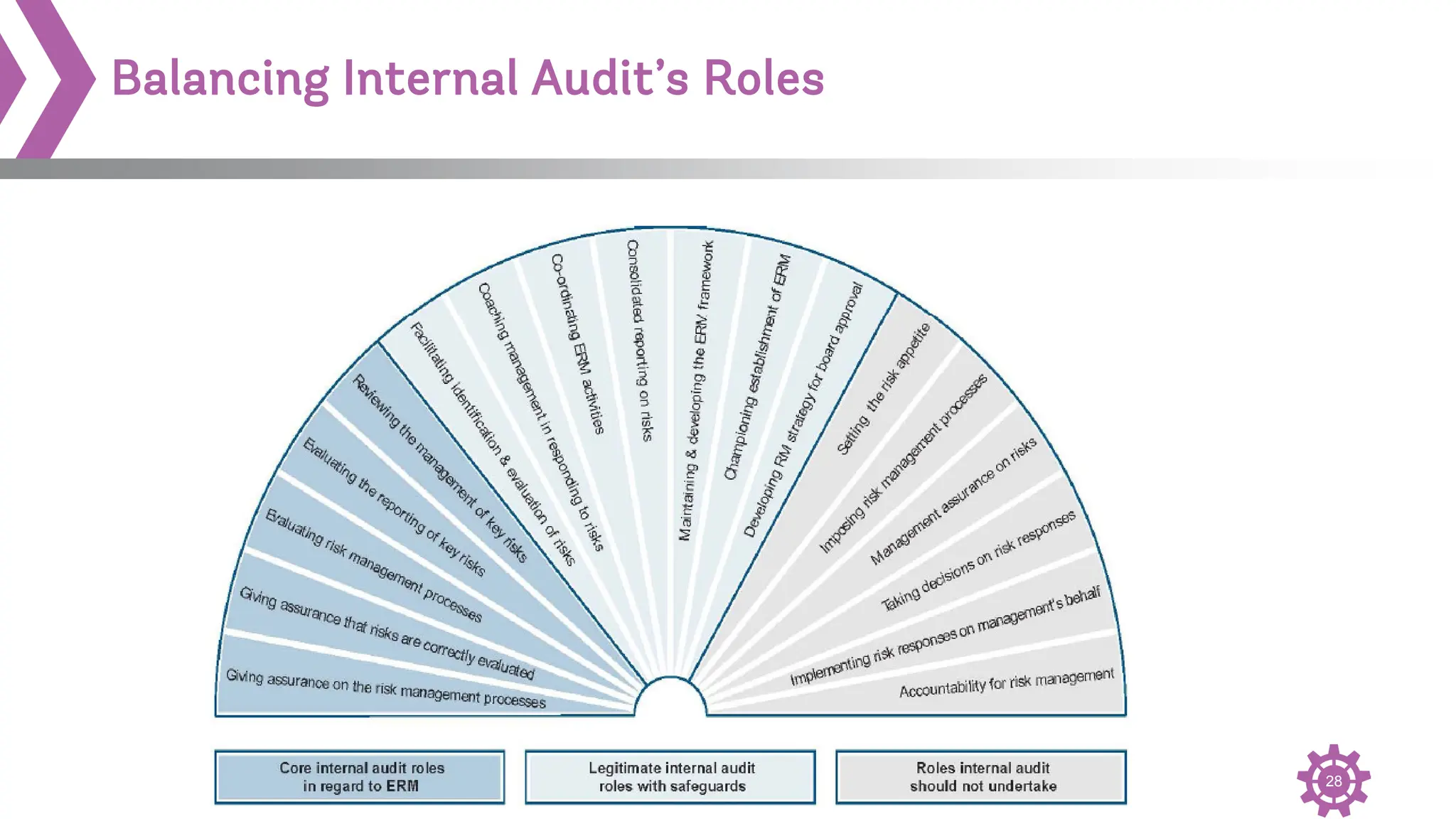
The document provides an overview of the International Professional Practices Framework (IPPF) which provides authoritative guidance for the internal audit profession. It discusses the key components of the IPPF including the Mission, Core Principles, Definition of Internal Auditing, Code of Ethics, Standards, and changes that were made to the Standards. The IPPF is established and overseen by the Institute of Internal Auditors (IIA) and represents global standards and best practices for internal auditors.