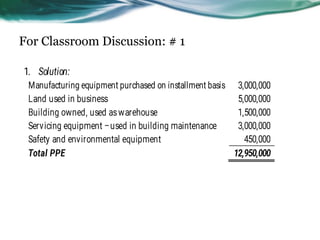
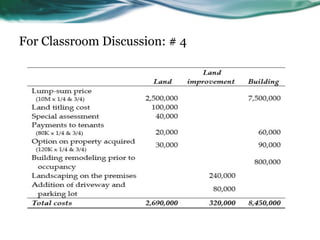
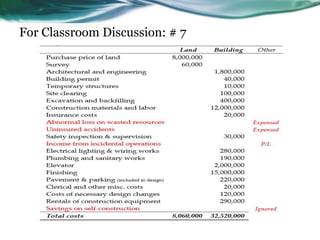
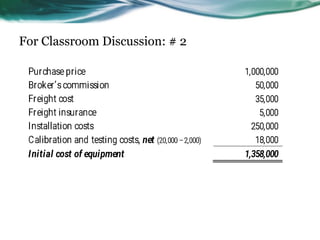
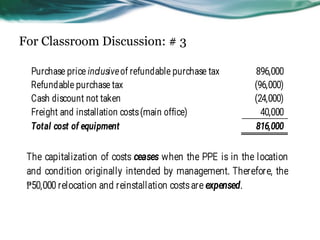
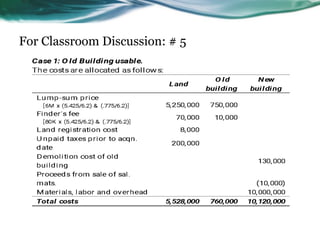
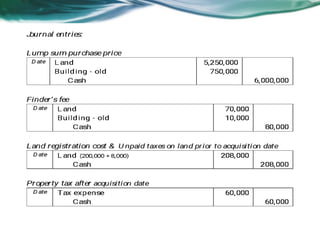
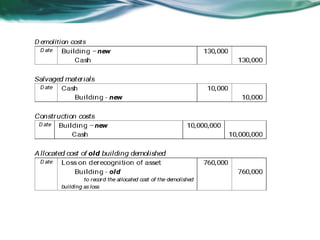
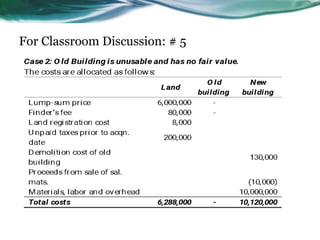
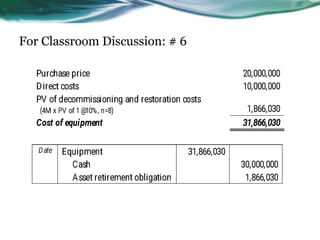
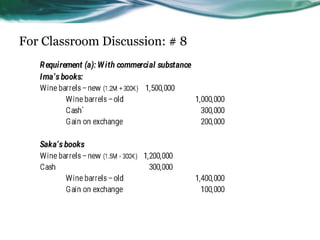
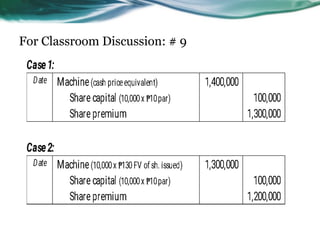
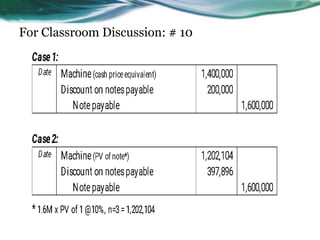
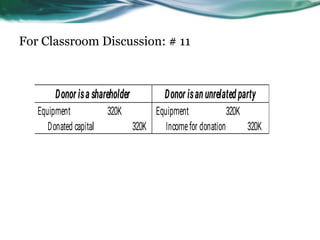
This document provides an overview of accounting for property, plant, and equipment (PPE) based on Philippine Financial Reporting Standards (PFRS). It discusses the initial recognition and measurement of PPE, including the components of cost, cessation of capitalization, and methods of acquisition. The initial cost of PPE includes the purchase price, costs to prepare the asset for use, and estimated restoration costs. It provides examples of costs that are included in or expensed from the cost of common PPE assets like land, buildings, equipment. The document also discusses accounting for various modes of acquisition such as exchange, equity/debt issuance, donation, and includes related discussion questions.