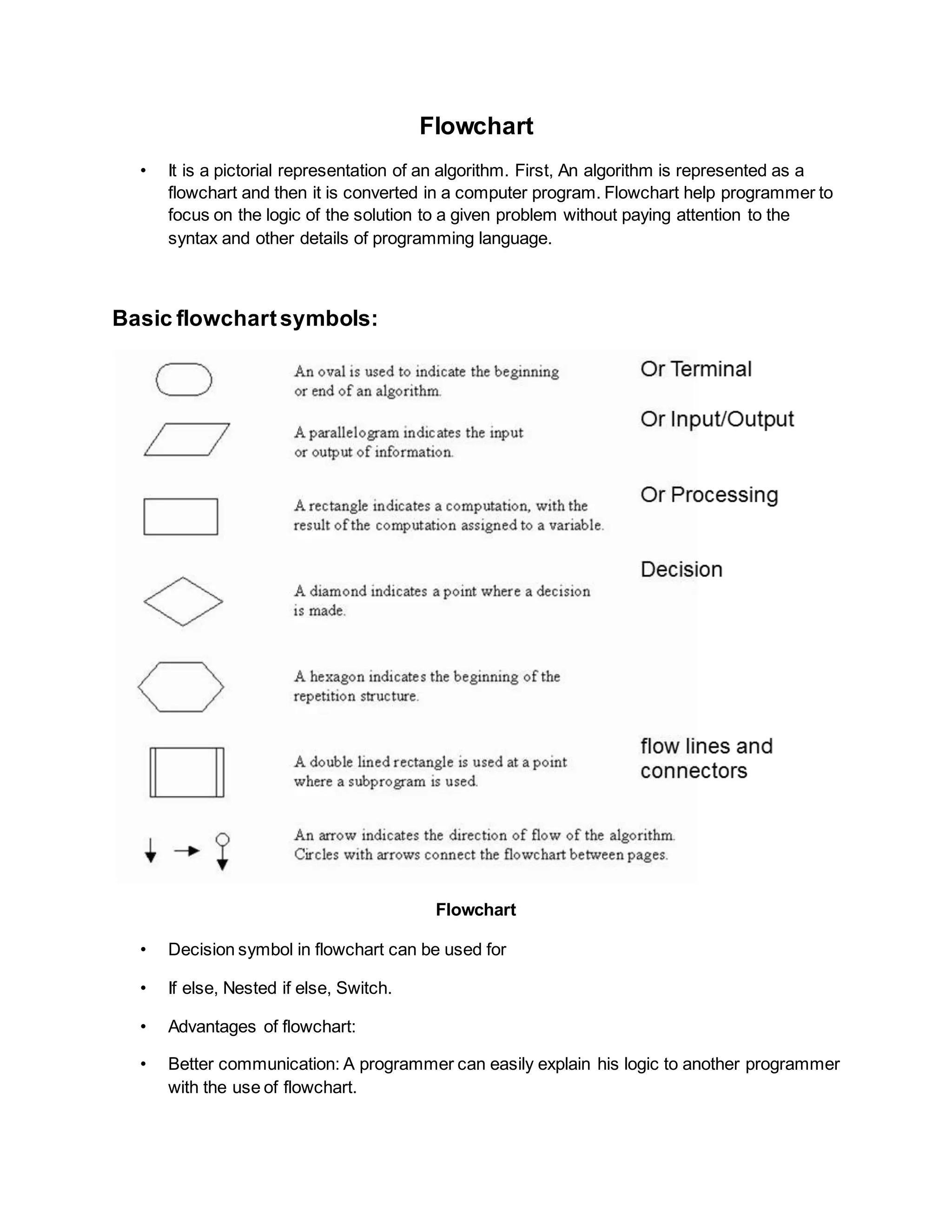
The document provides information on different types of computer software and programming concepts. It discusses system software and application software, giving examples of each. It also covers programming languages from machine language to assembly language to high-level languages. Other topics summarized include algorithms, flowcharts, pseudocode, decision tables, operating systems, and functions of an operating system.