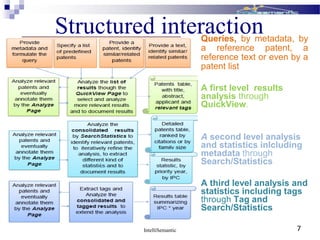
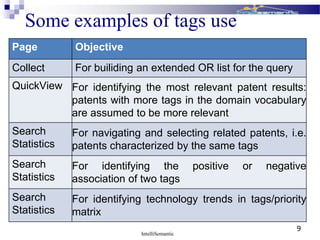
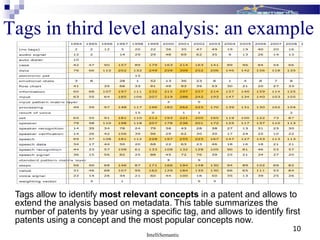
The document discusses IntelliSemantic and their patent analysis solution called MyIntelliPatent. MyIntelliPatent uses natural language processing and intelligent language technologies to automatically extract relevant information from patent documents, including identifying key entities and passages. It provides a structured approach for patent analysis tasks and allows users to build custom vocabularies and taxonomies. MyIntelliPatent aims to deliver smarter patent analysis tools that help professionals focus on higher value work by automating some initial analysis steps.