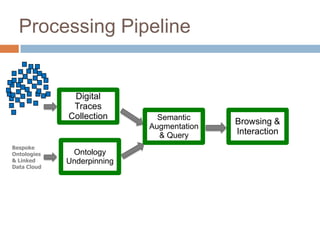
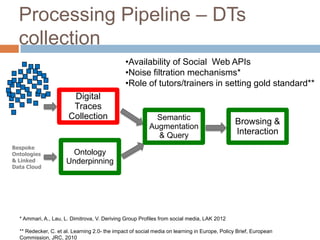
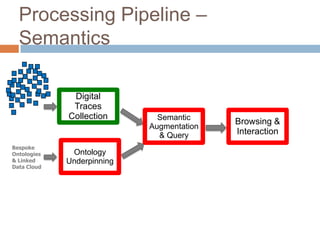
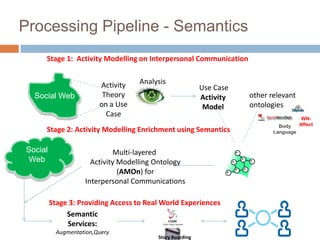
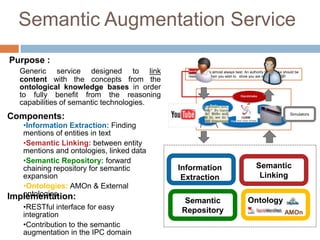
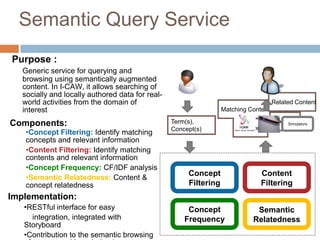
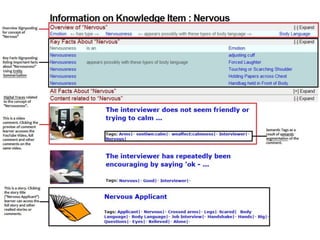
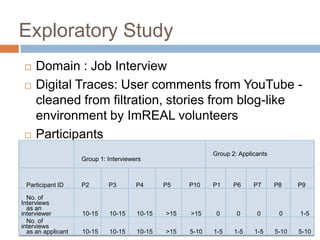
The document discusses integrating digital traces from social media into a semantic-enriched data cloud for informal learning. It outlines a processing pipeline that collects digital traces, semantically augments them using ontologies, and allows browsing and interaction through a semantic query service. An exploratory study on job interviews found that authentic examples from digital traces were useful learning stimuli but could be mistaken as norms without context. Semantic technologies provide opportunities to organize digital traces for informal learning but further work is needed to fully realize this potential.





![Exploratory Study: Good things about
DTs
Participants particularly liked the authenticity
of the content:
“Examples are the beauty of system – I will learn from examples [p10]”
“Anything that facilitates the preparation of training material and provides real
world examples to backup training is very helpful [p5]”
Which probed them to:
Further reflect on their experiences, and in some
cases help articulate what they had been doing
intuitively
Provide their viewpoints (due to culture,
environment, tacit knowledge) – acted as stimuli
Sense the diversity or consensus on the selected
topic](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/integratingdigitaltracesintoasemantic-enricheddata-120417031845-phpapp02/85/Integrating-digital-traces-into-a-semantic-enriched-data-17-320.jpg)


