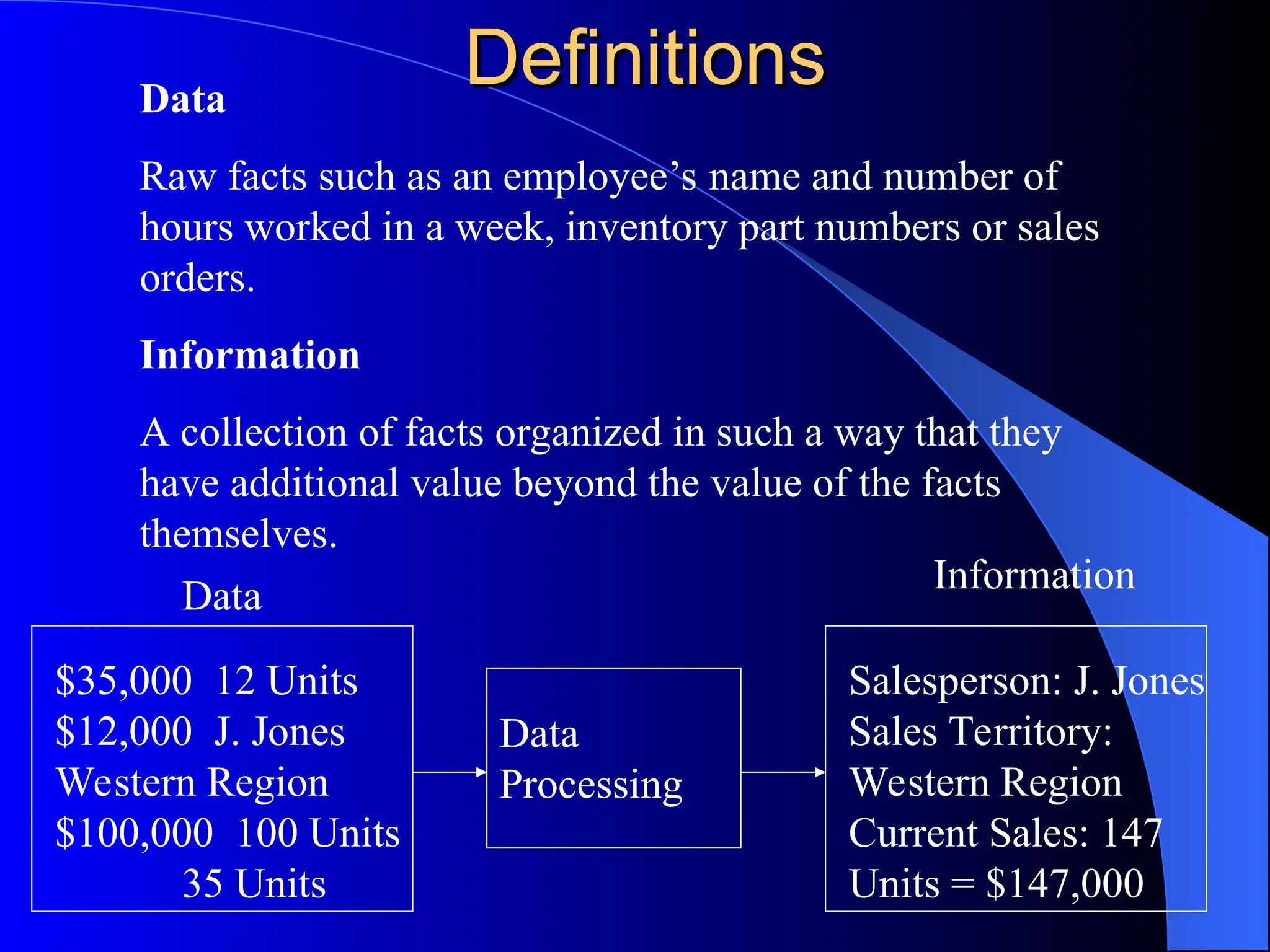
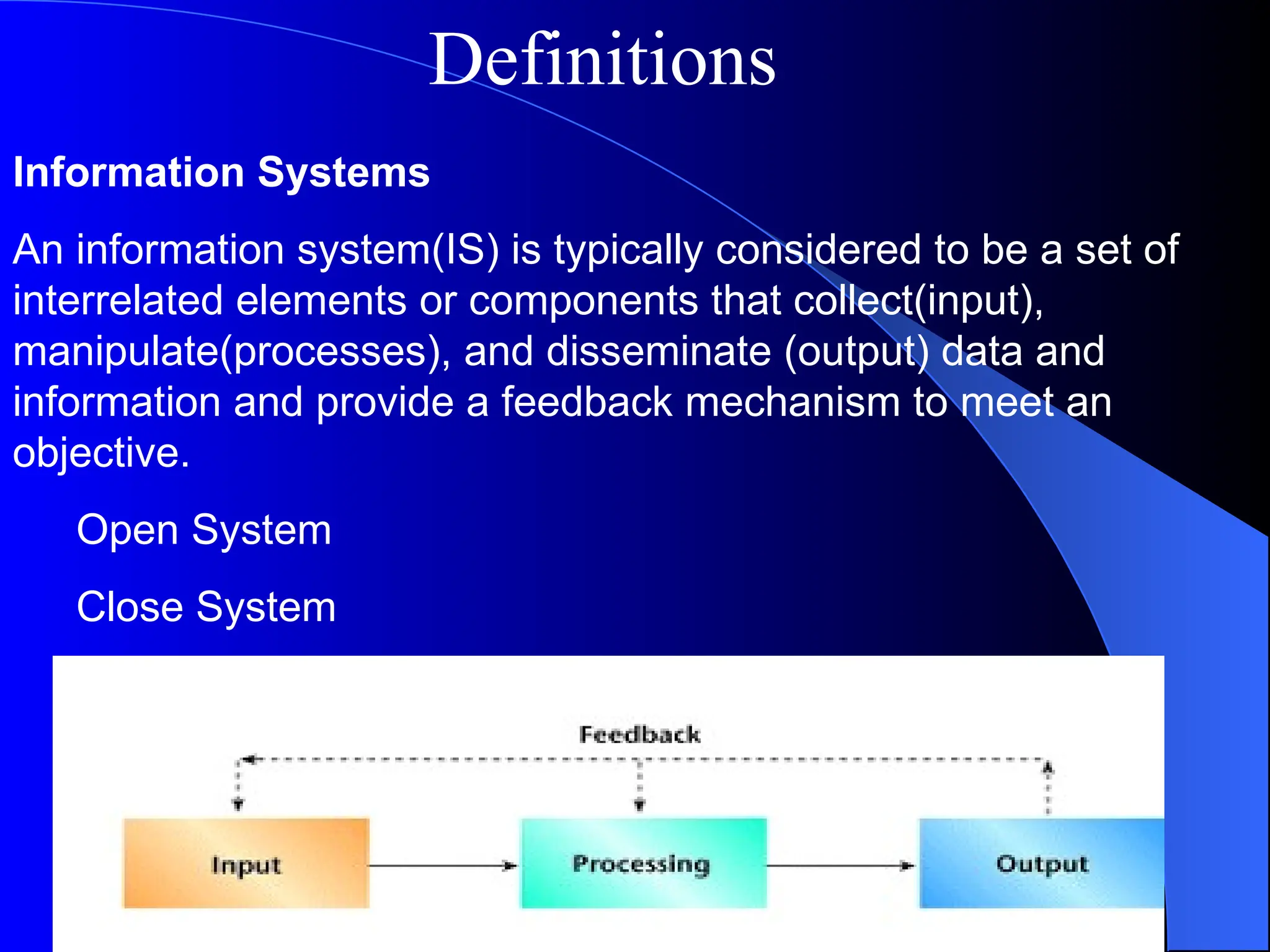
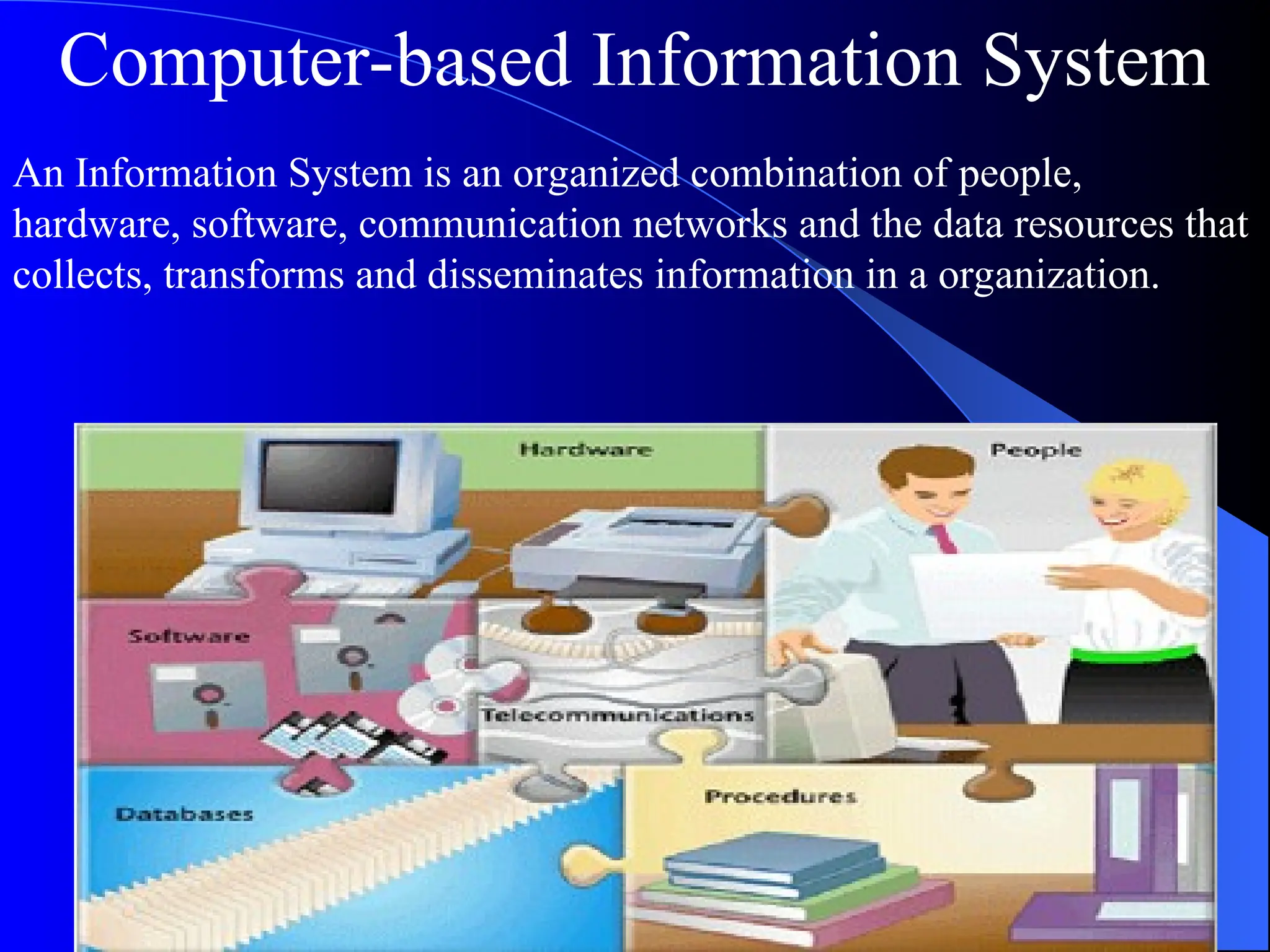
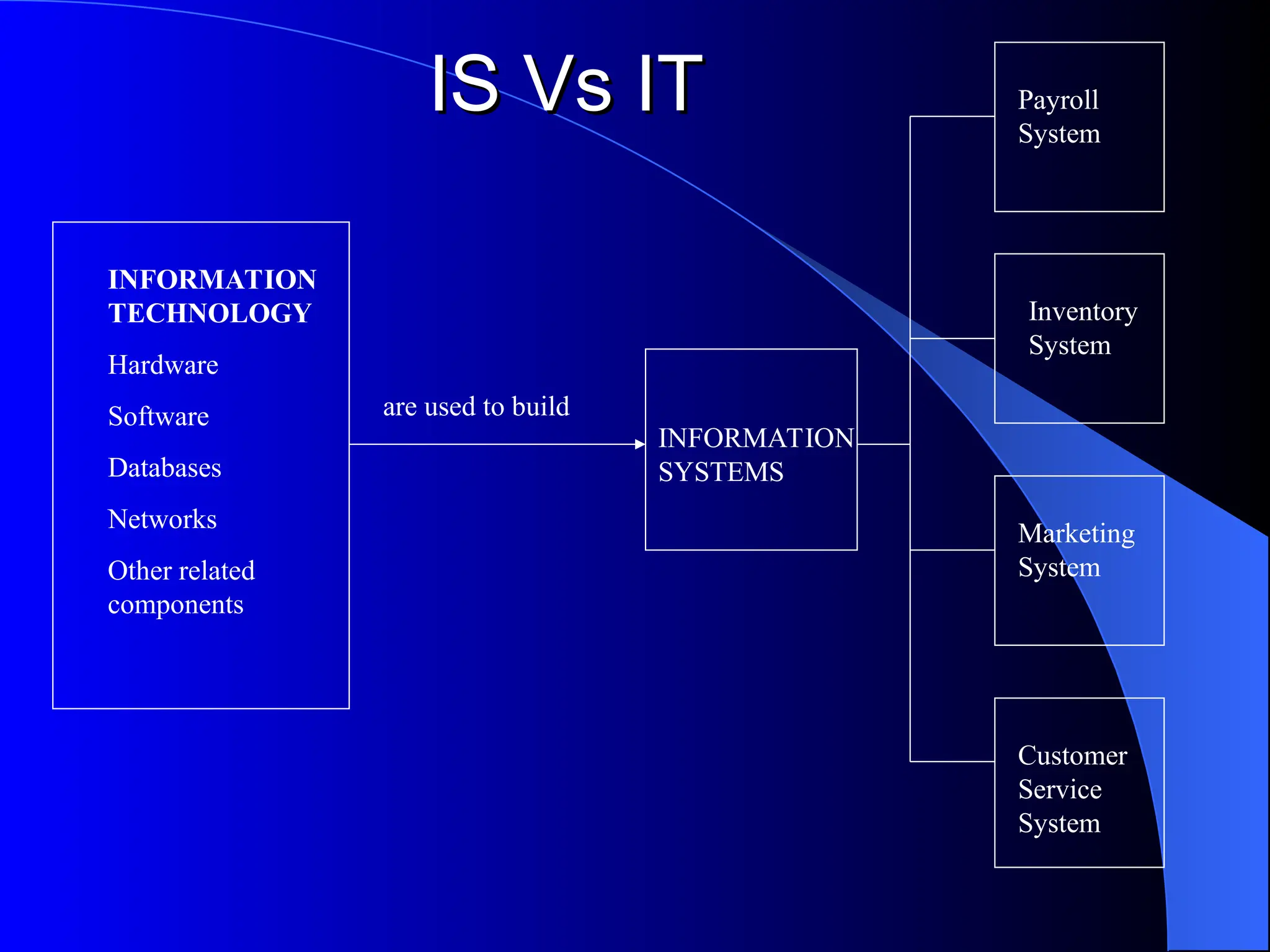
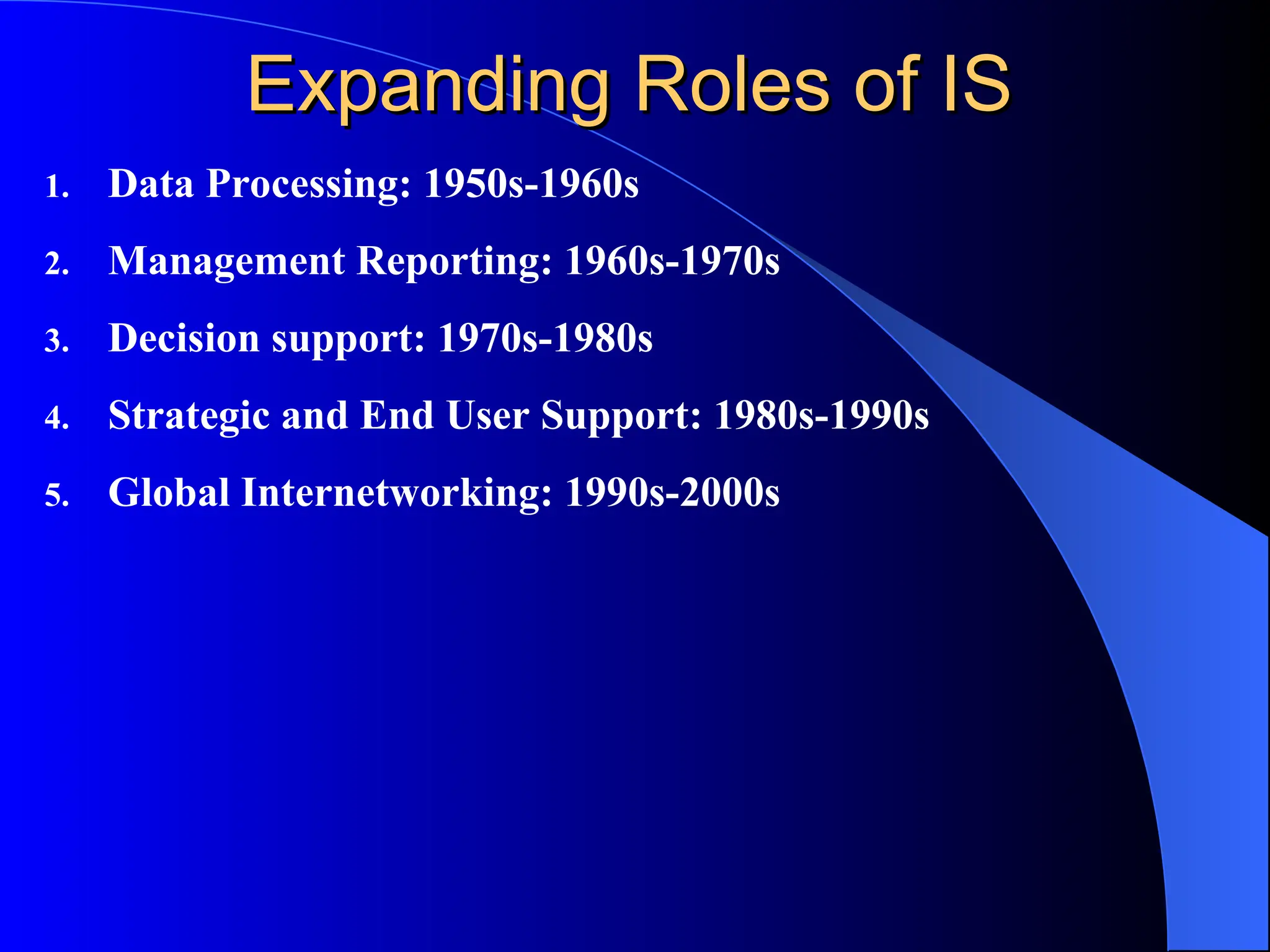
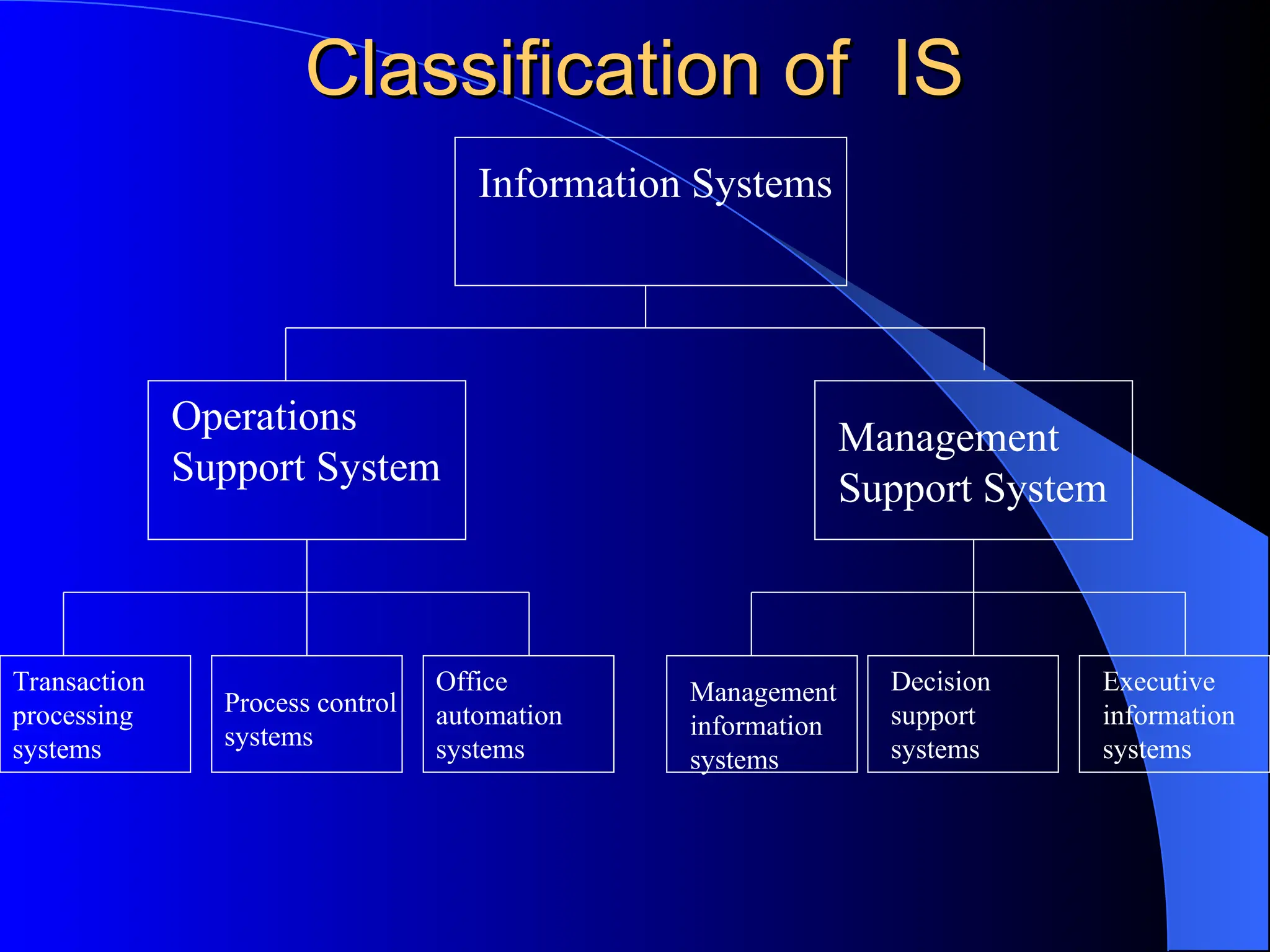
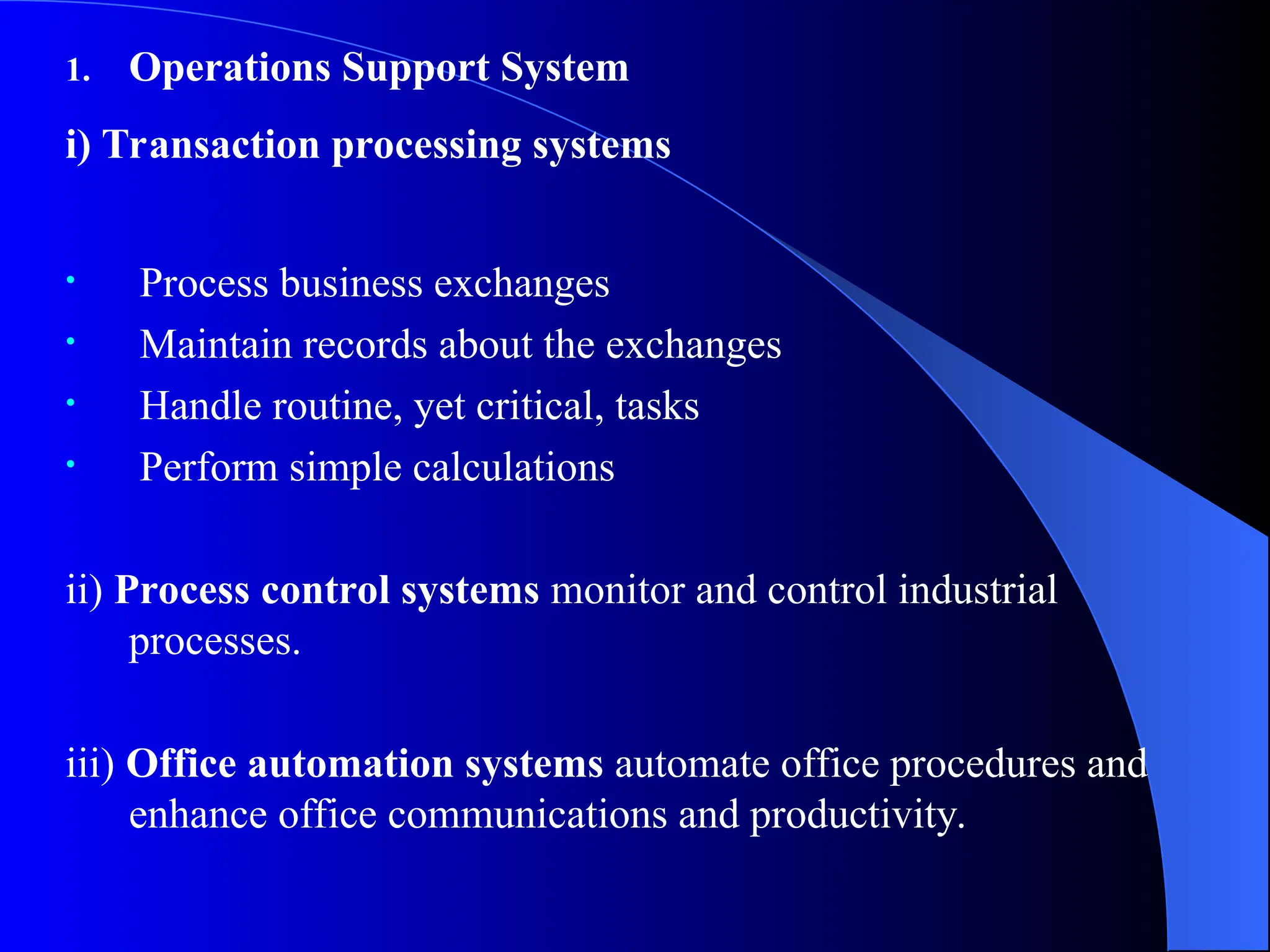
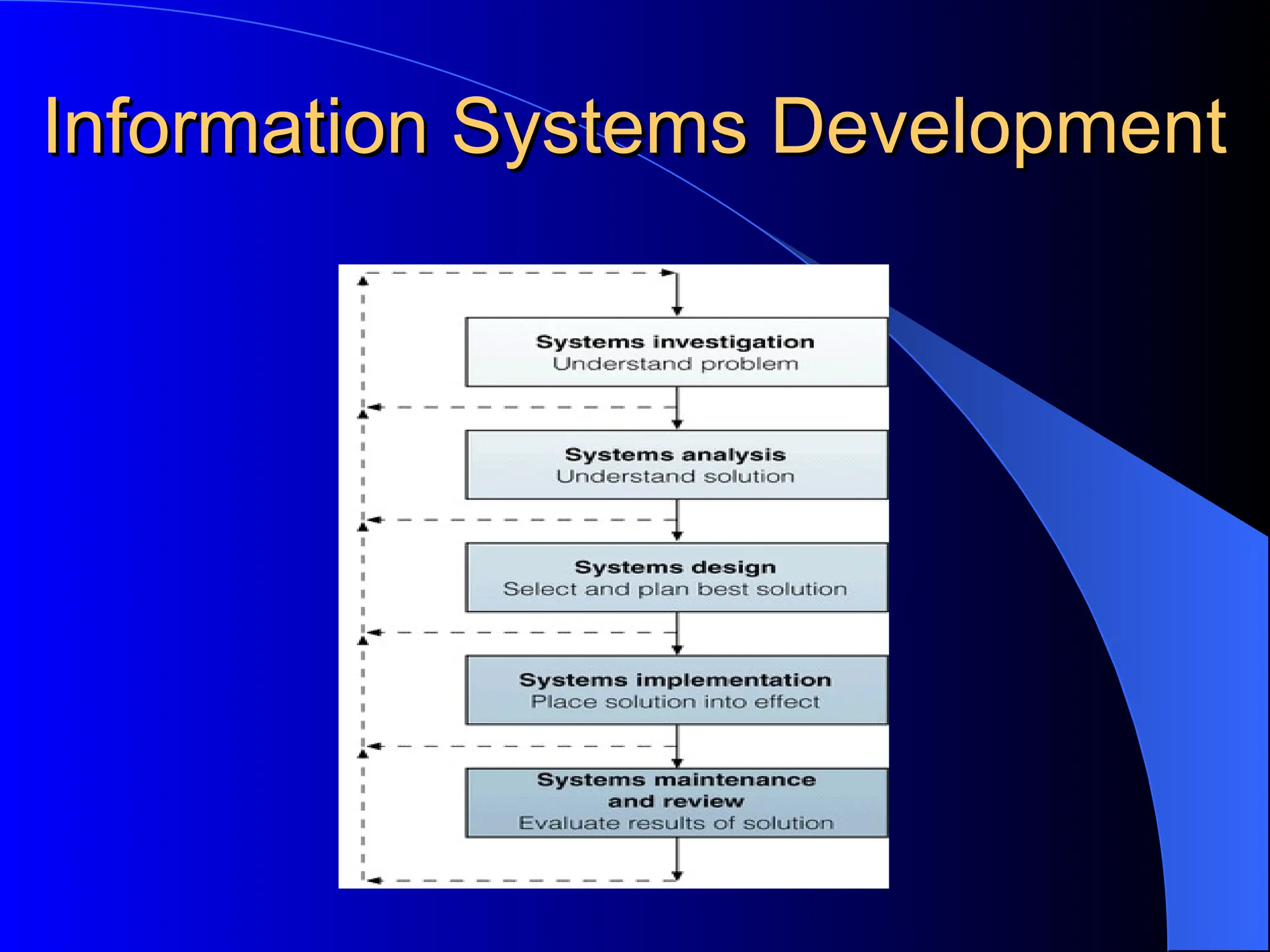
The document discusses information systems (IS), defining them as organized combinations of people, hardware, and software that collect and disseminate information. It outlines various types of IS, their expanding roles from data processing to strategic support, and details classifications such as operations support and management support systems. Additionally, it highlights challenges and opportunities in IS development, emphasizing their importance in enhancing global competitiveness and productivity.