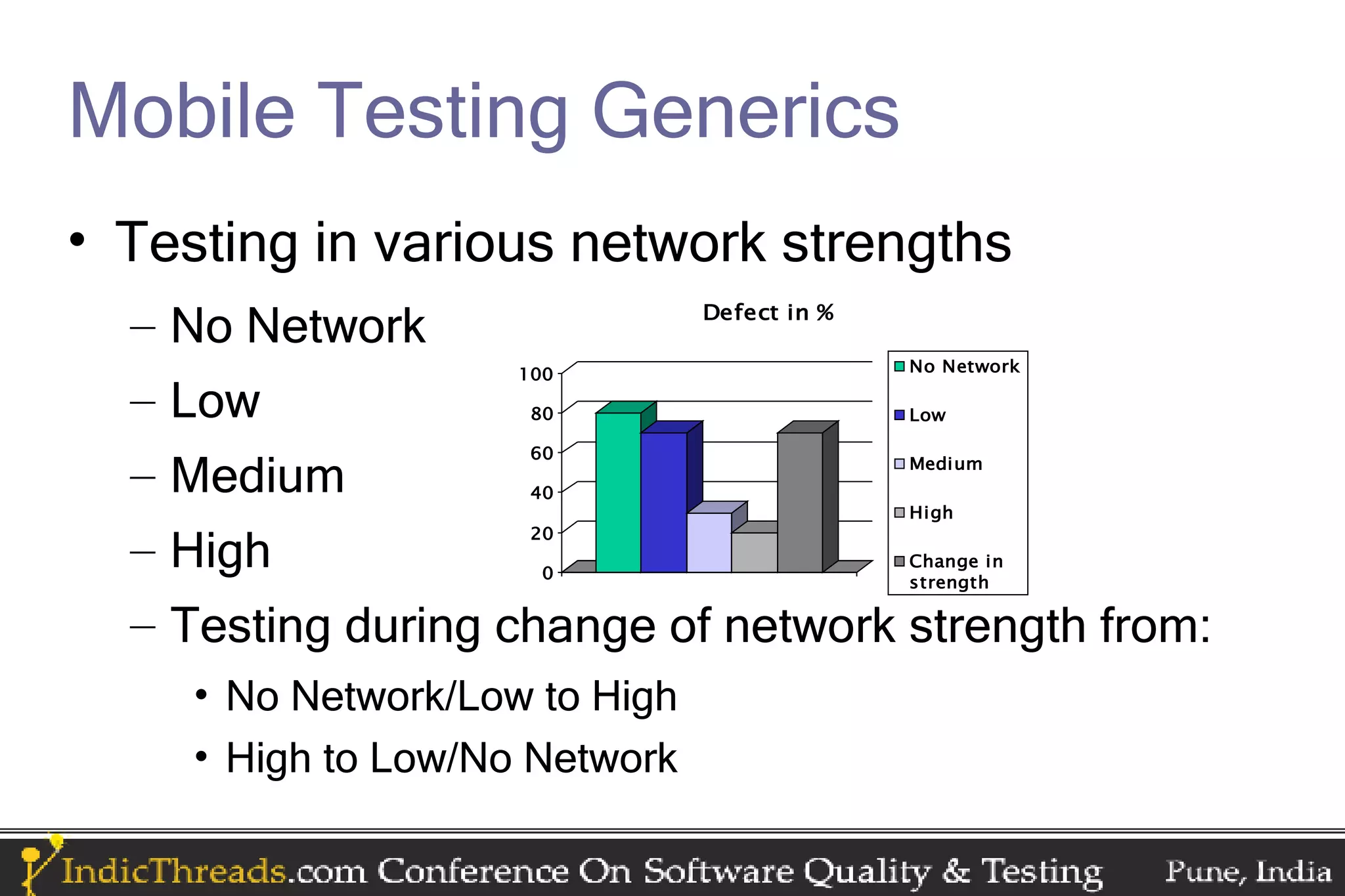
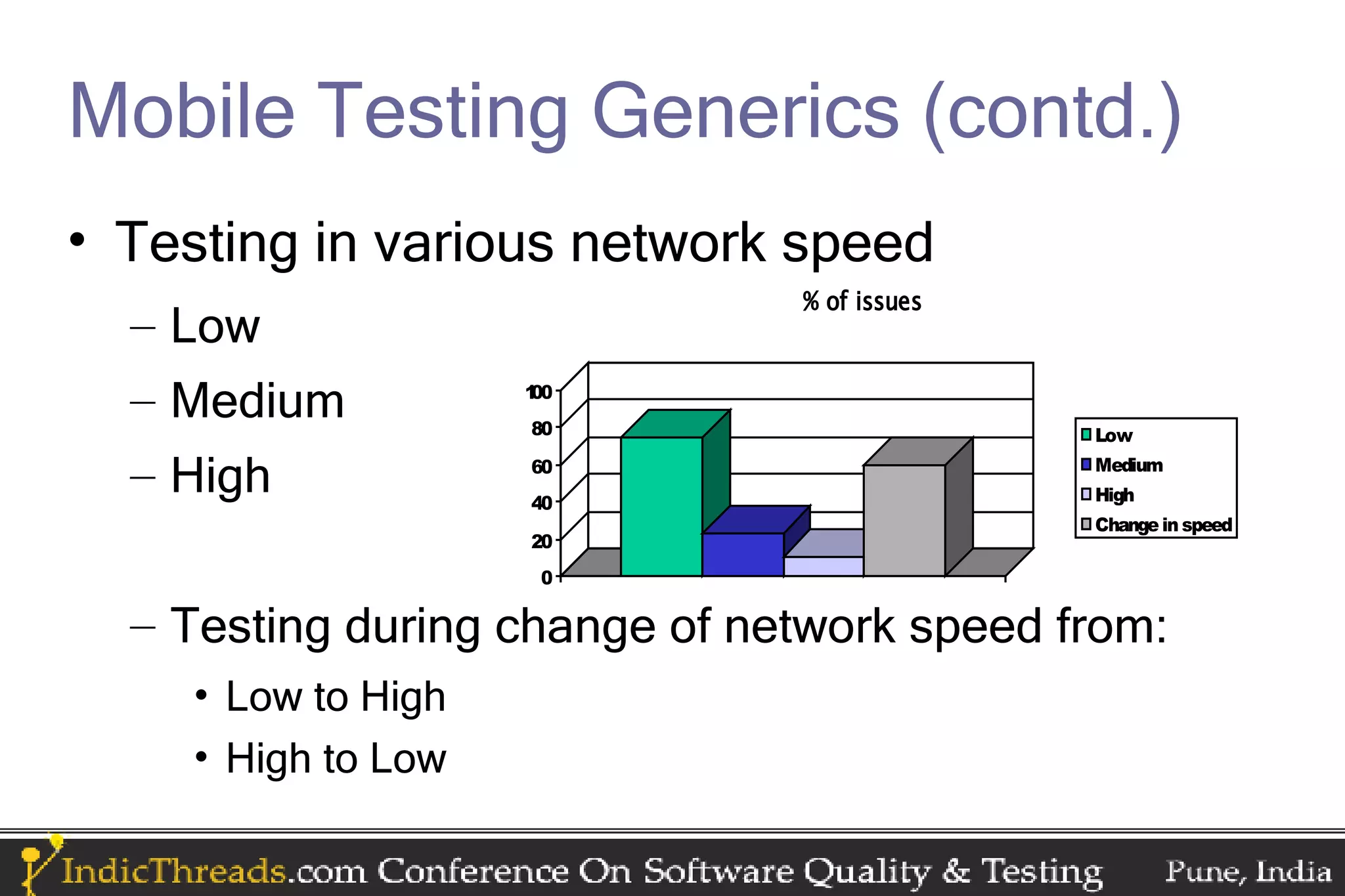
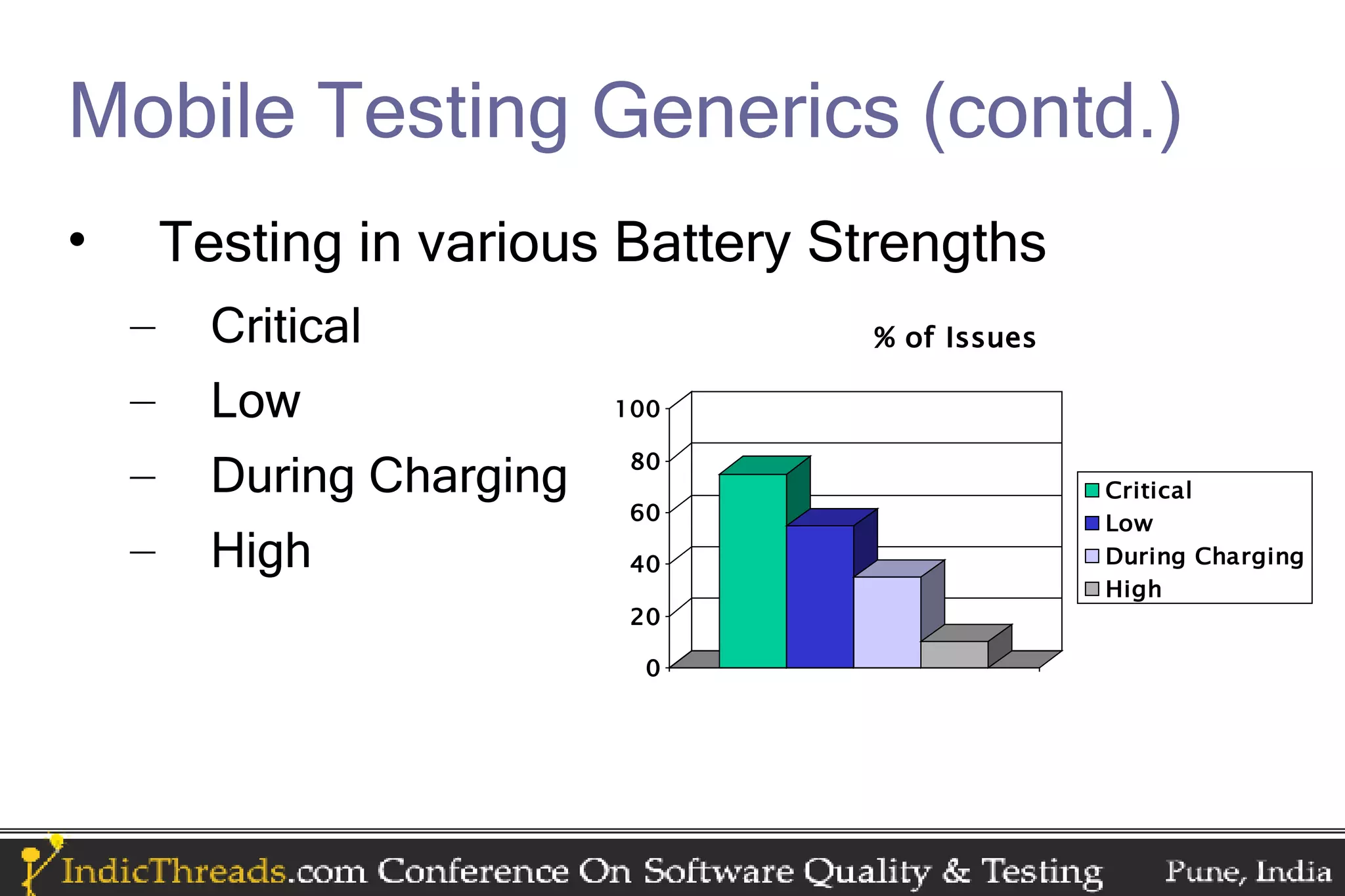
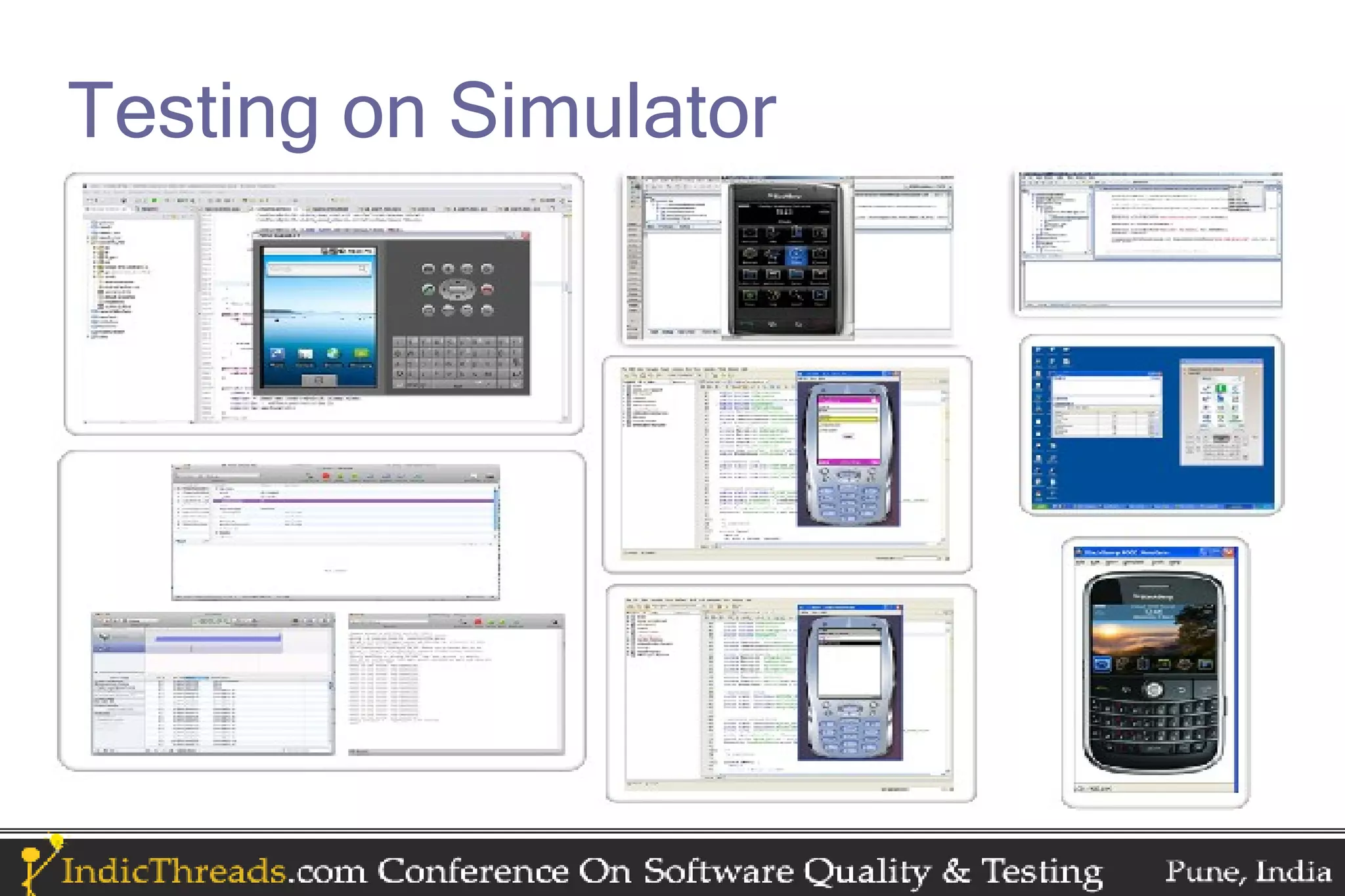
The document discusses testing techniques for mobile applications, highlighting the different types of applications (browser-based, pre-installed, and installable) and their respective testing challenges. It emphasizes the importance of considering various factors such as network strength, speed, battery consumption, and memory usage patterns specific to mobile environments during testing. Additionally, it outlines platform-specific testing practices for iPhone, Android, Blackberry, Symbian, Windows Mobile, and J2ME applications.