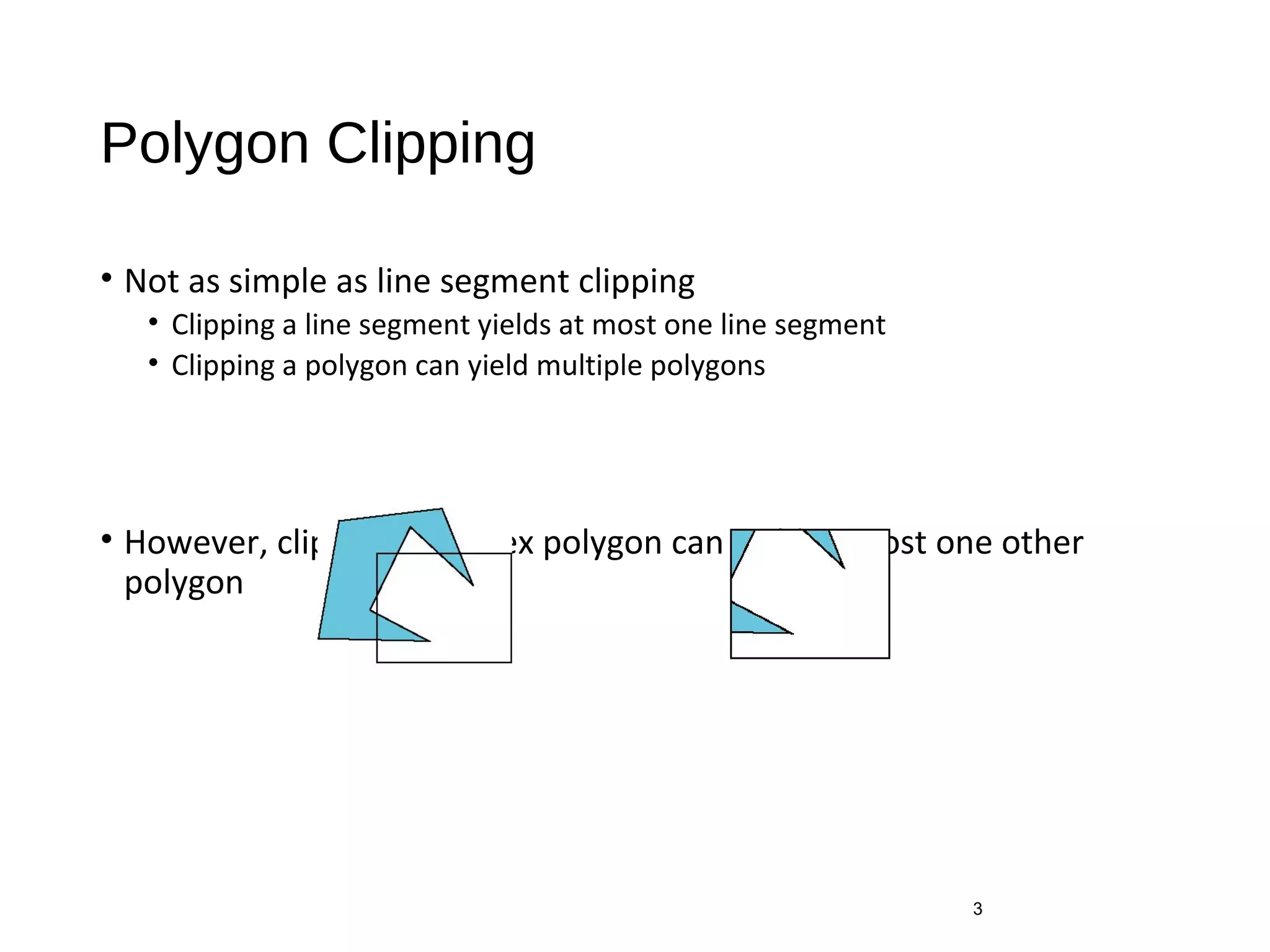
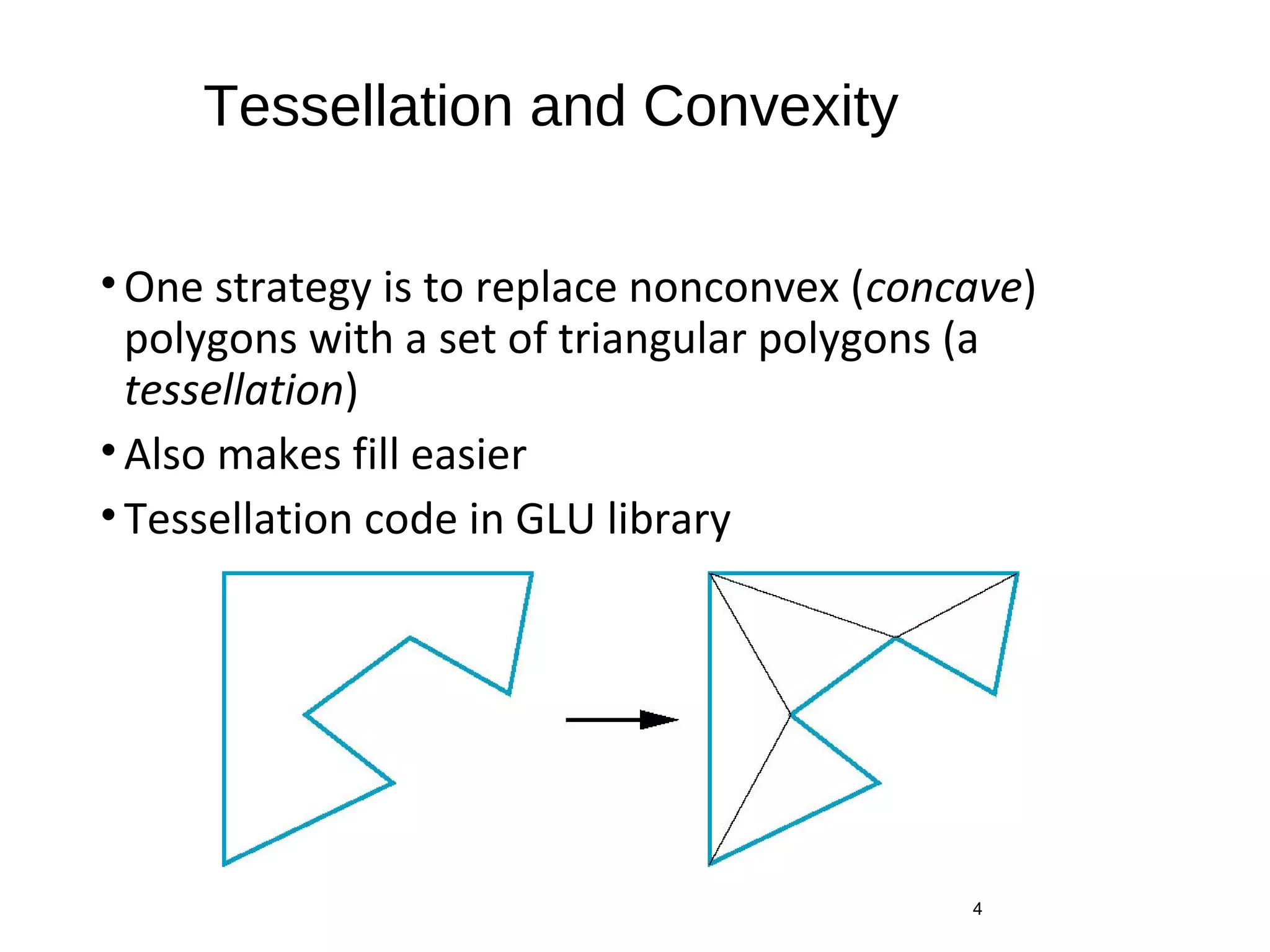
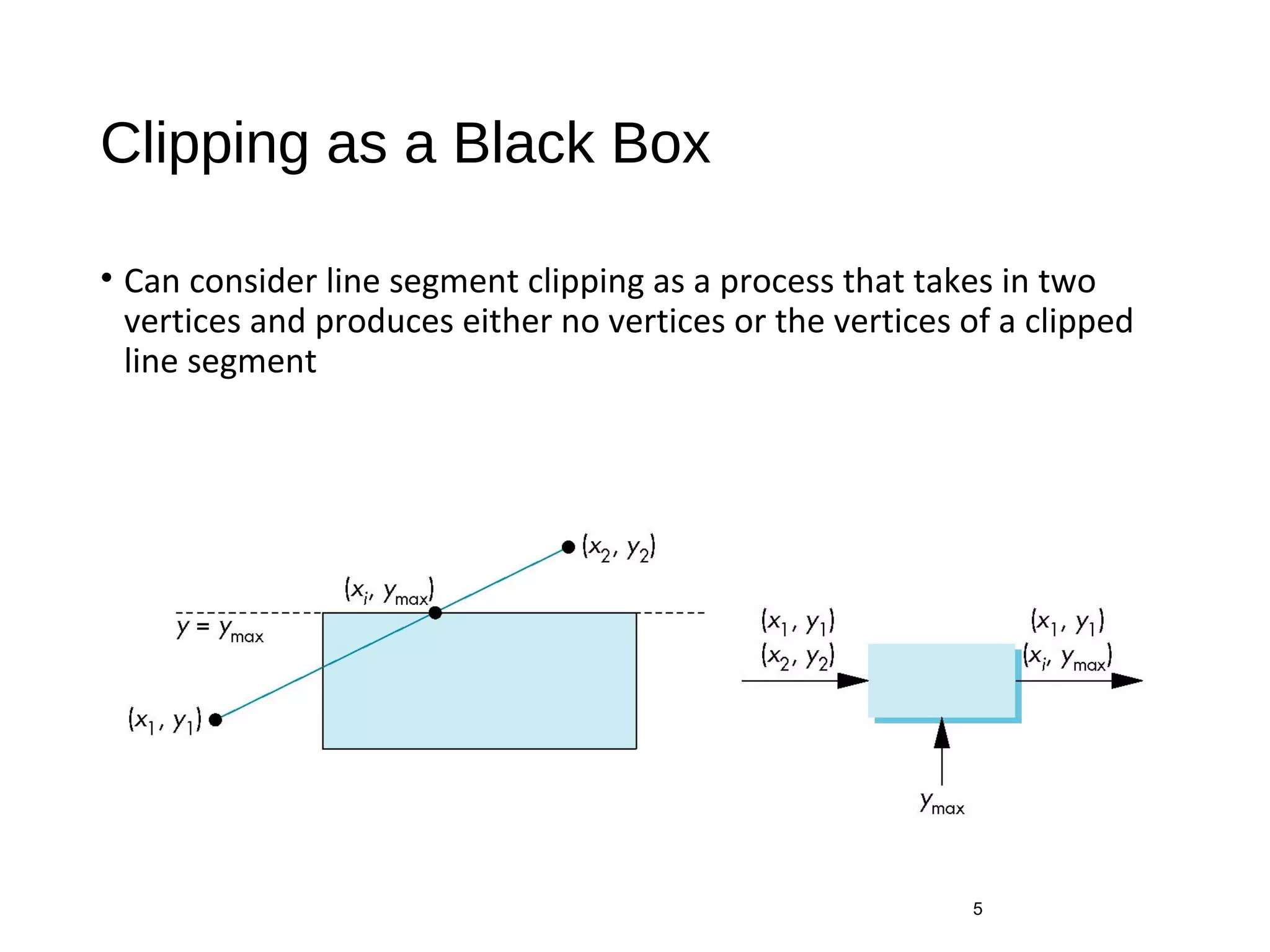
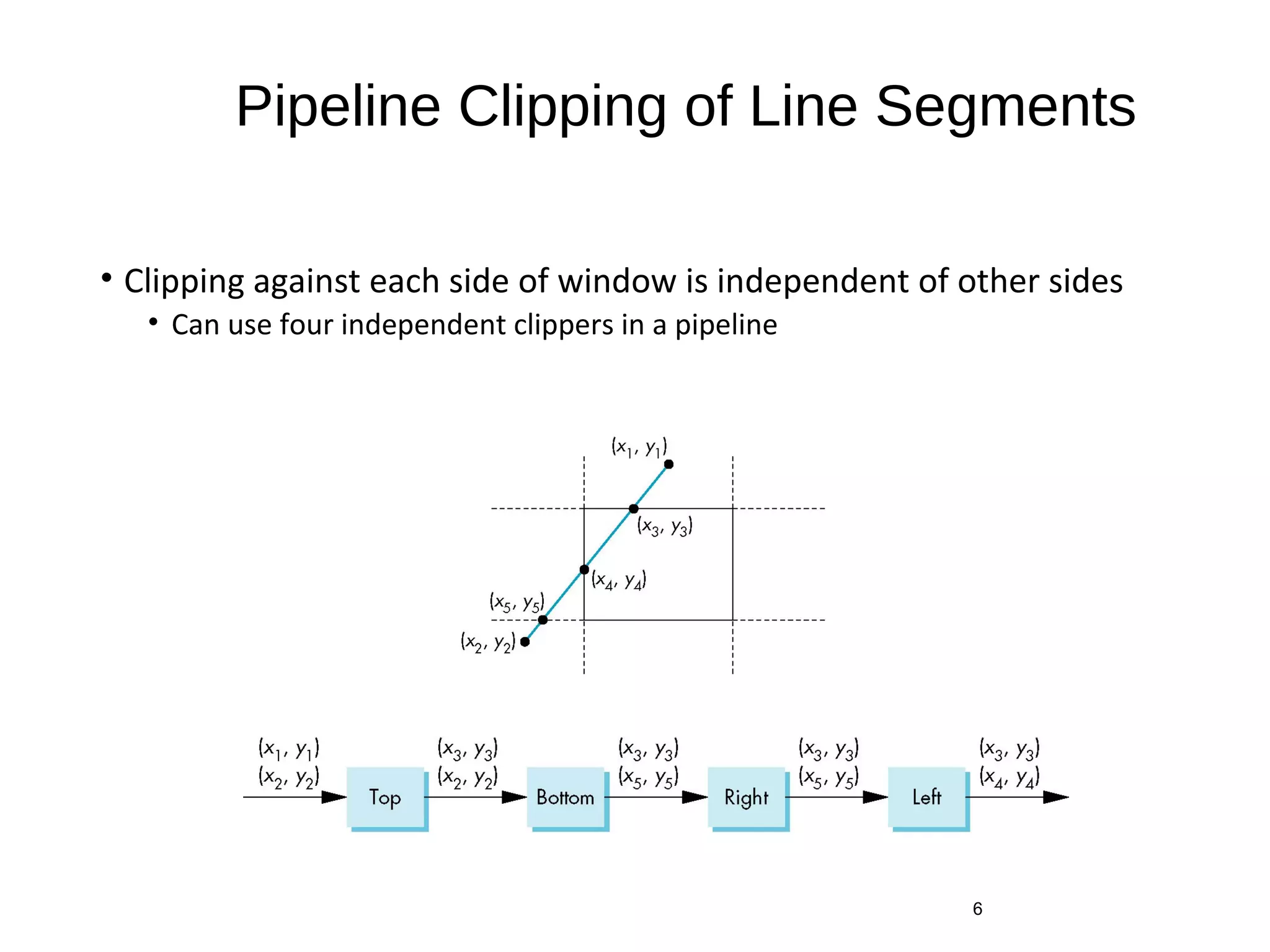
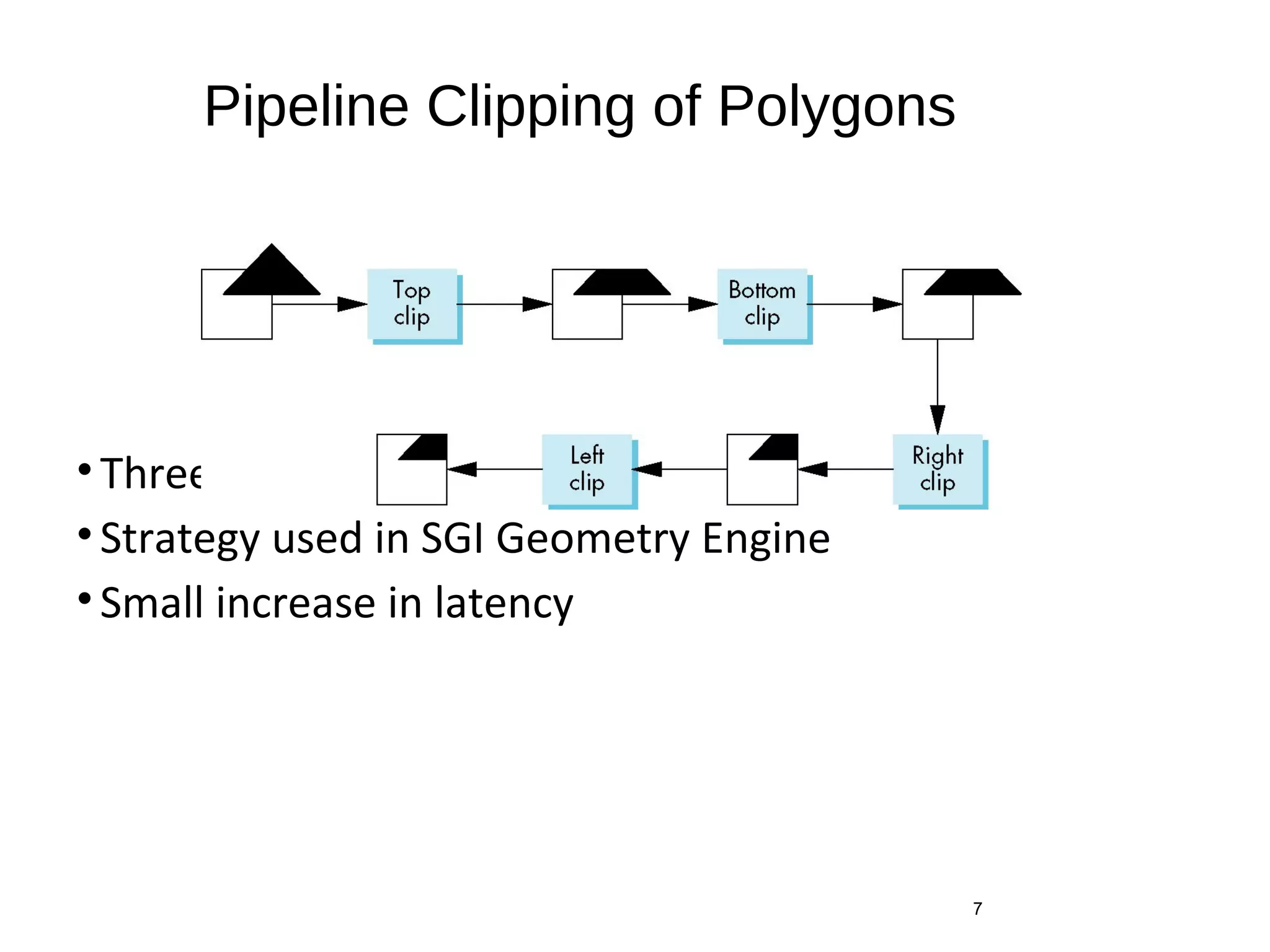
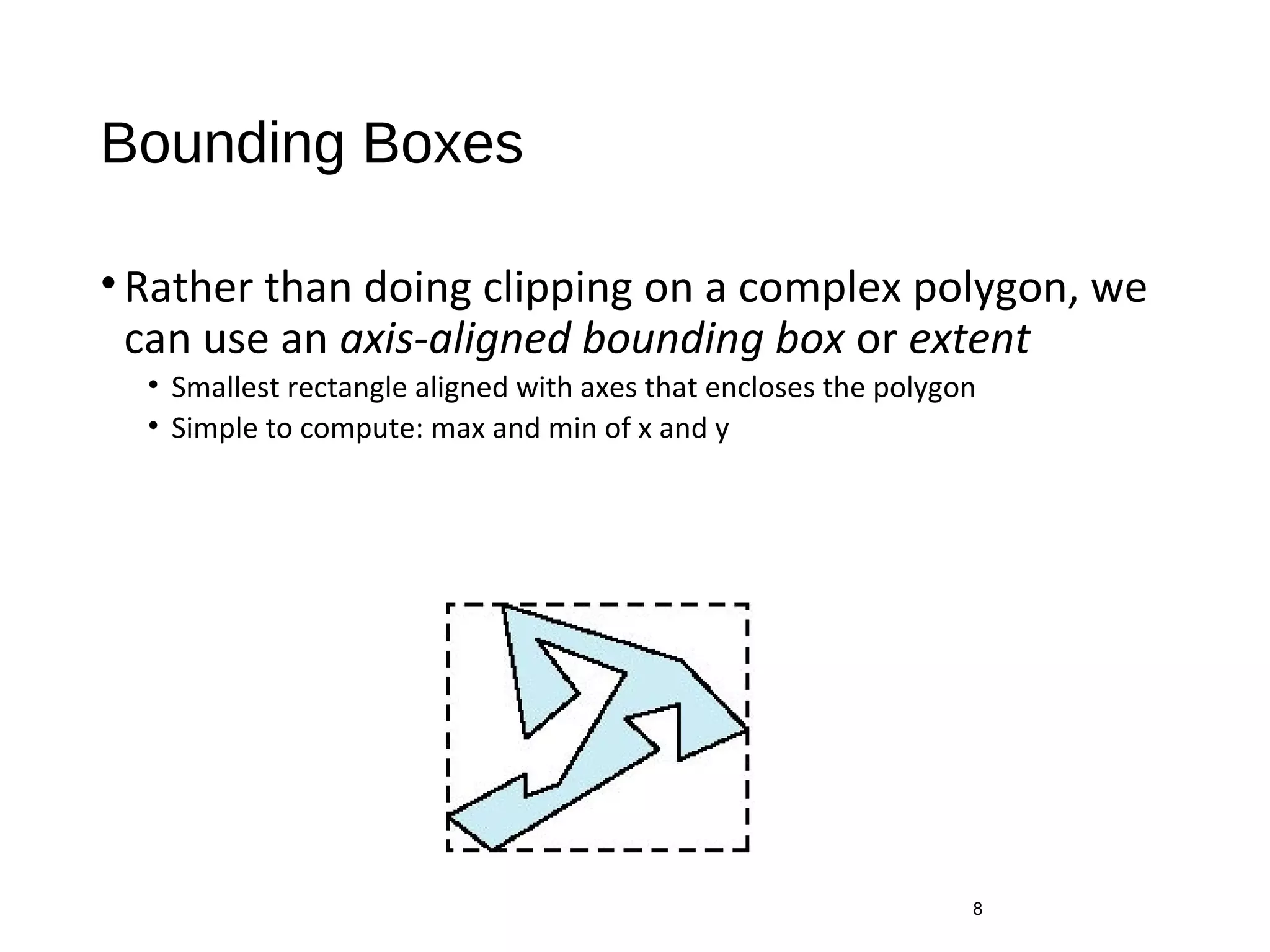
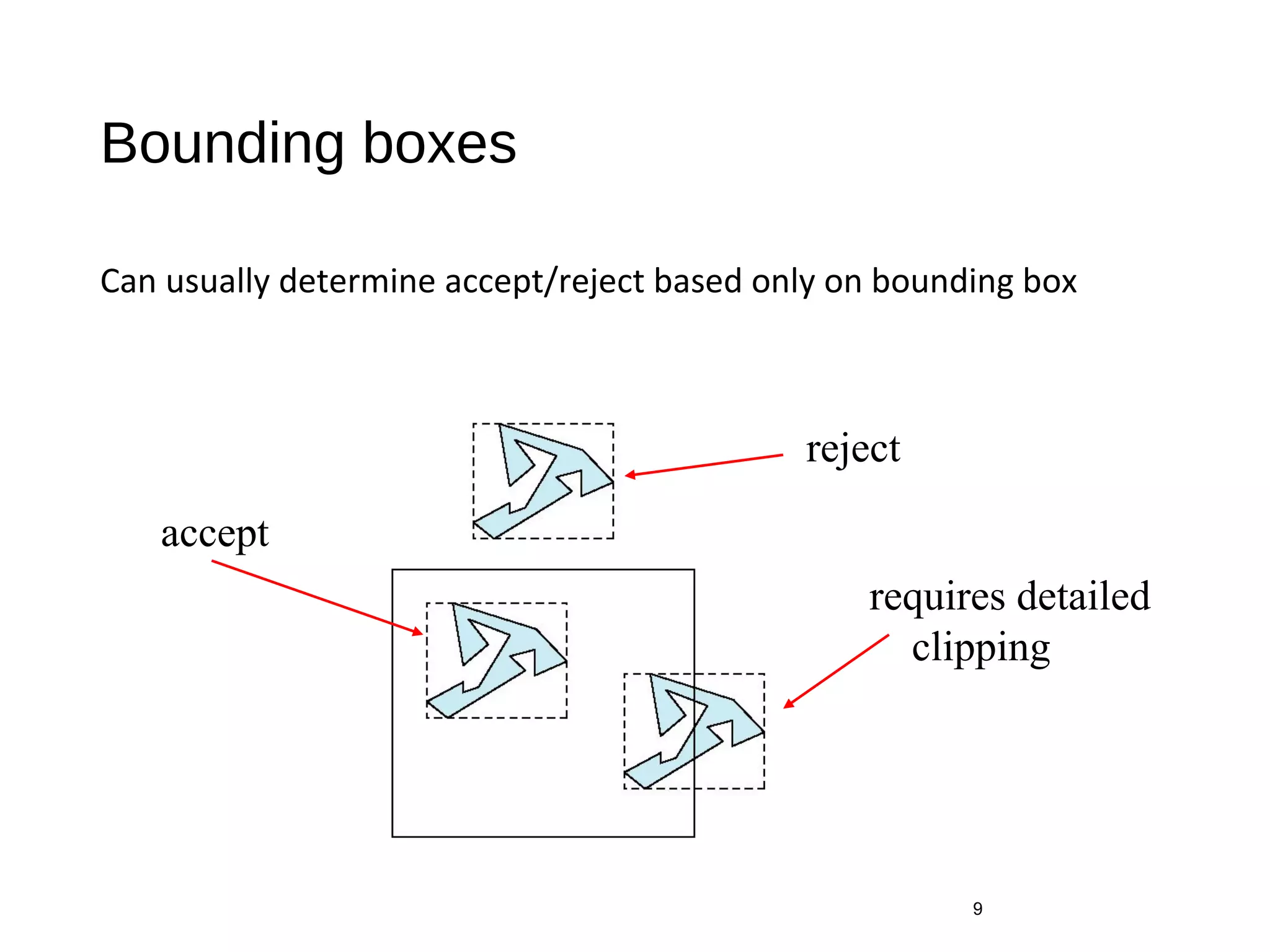
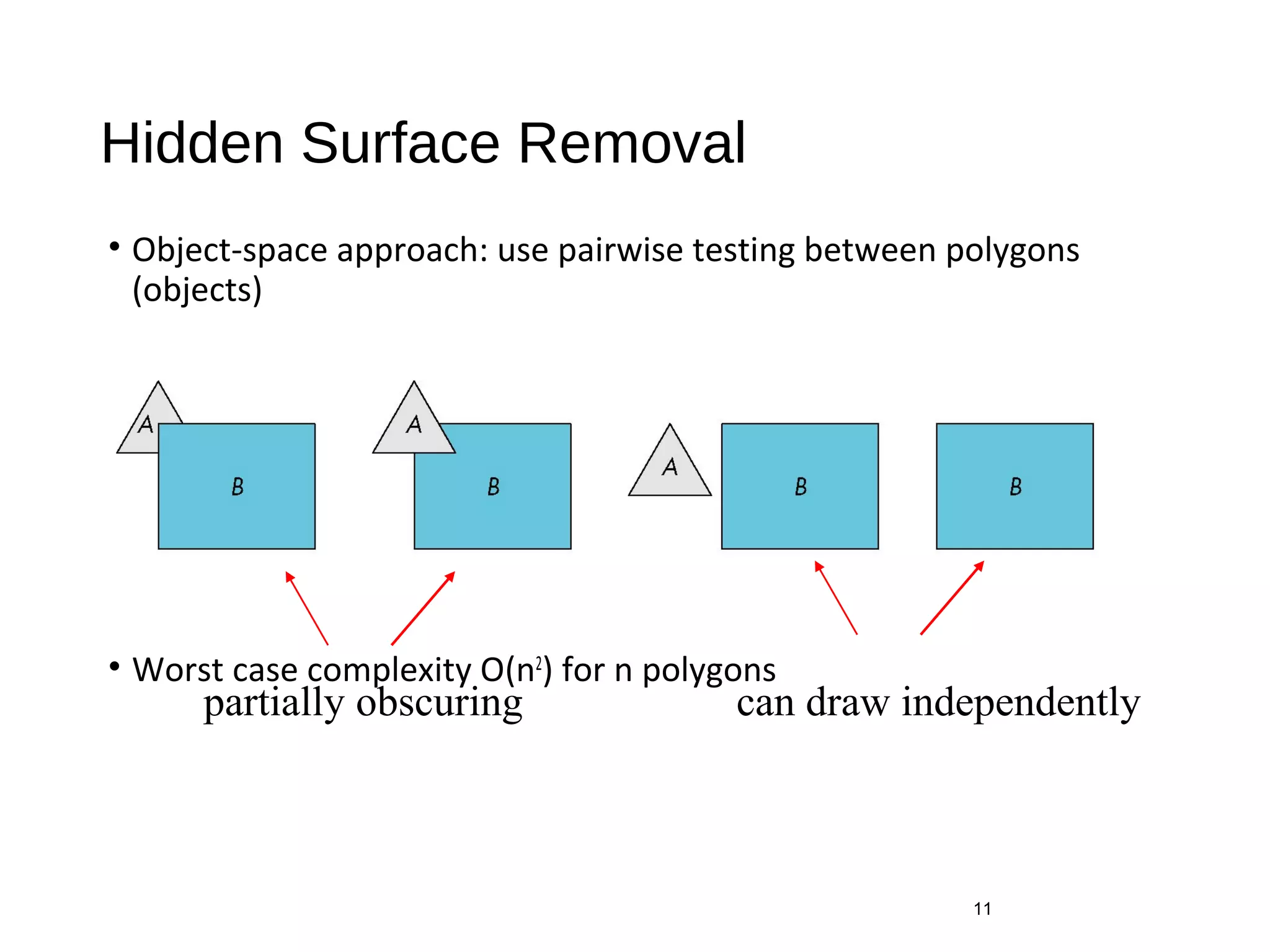
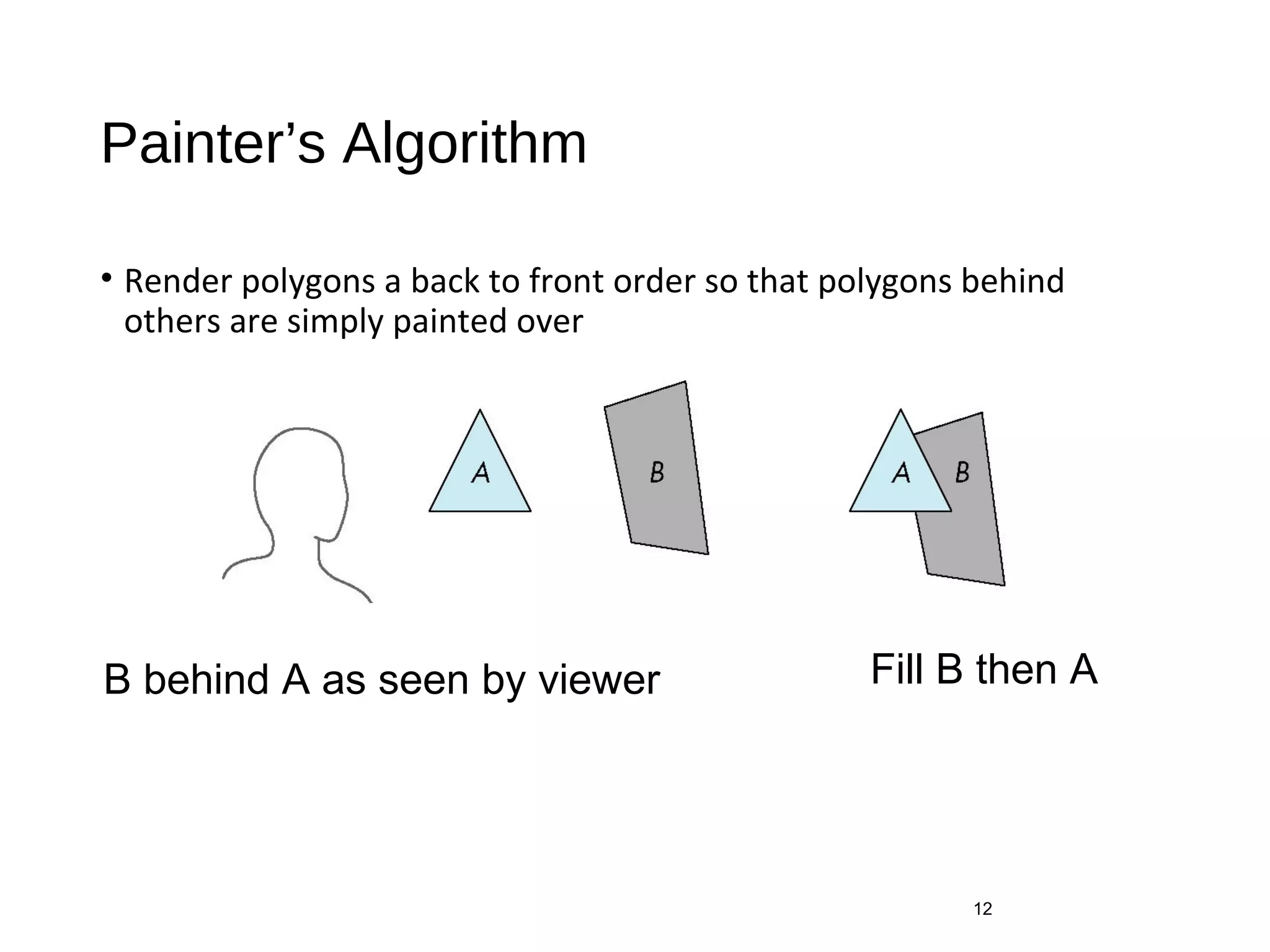
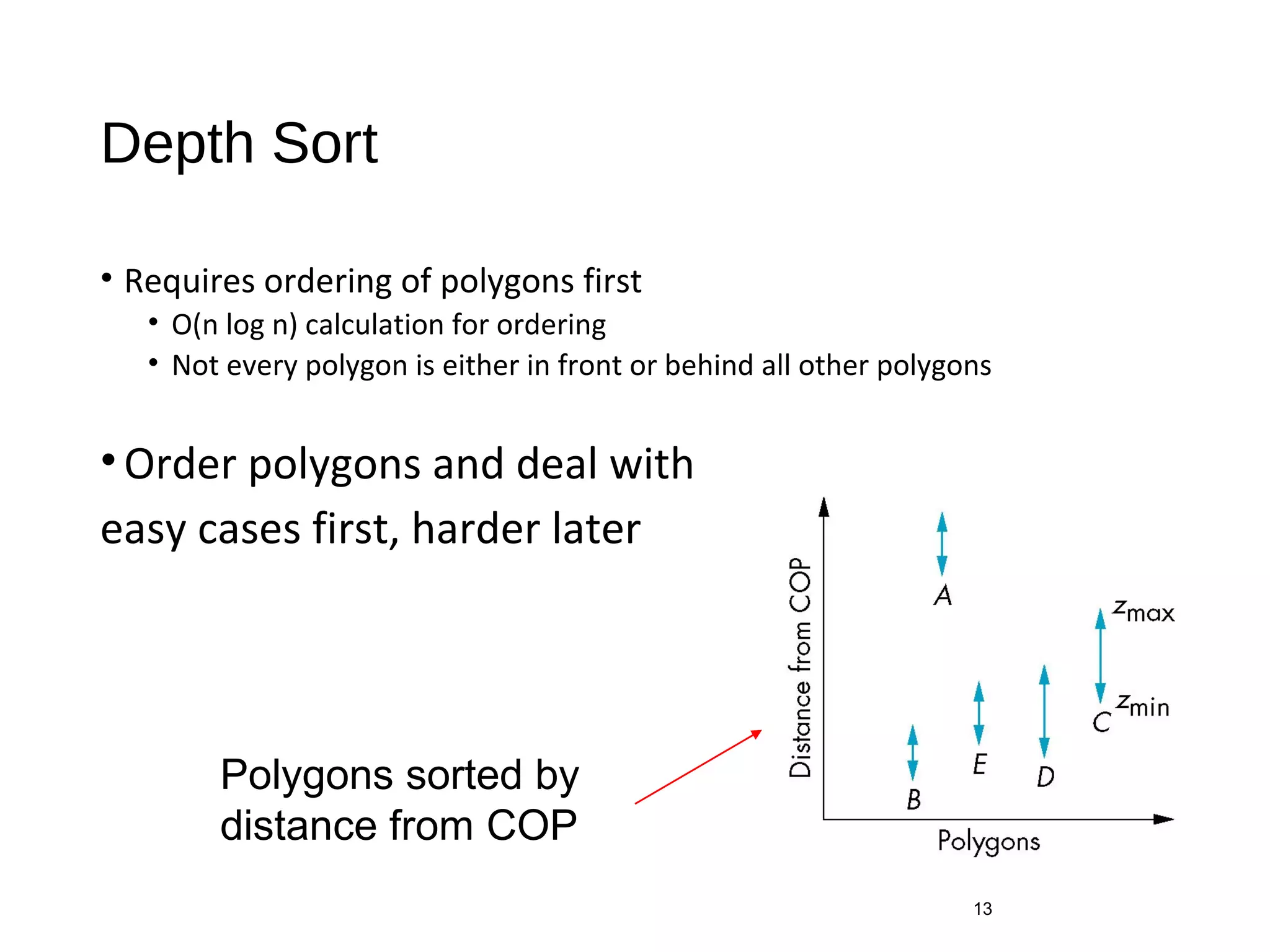
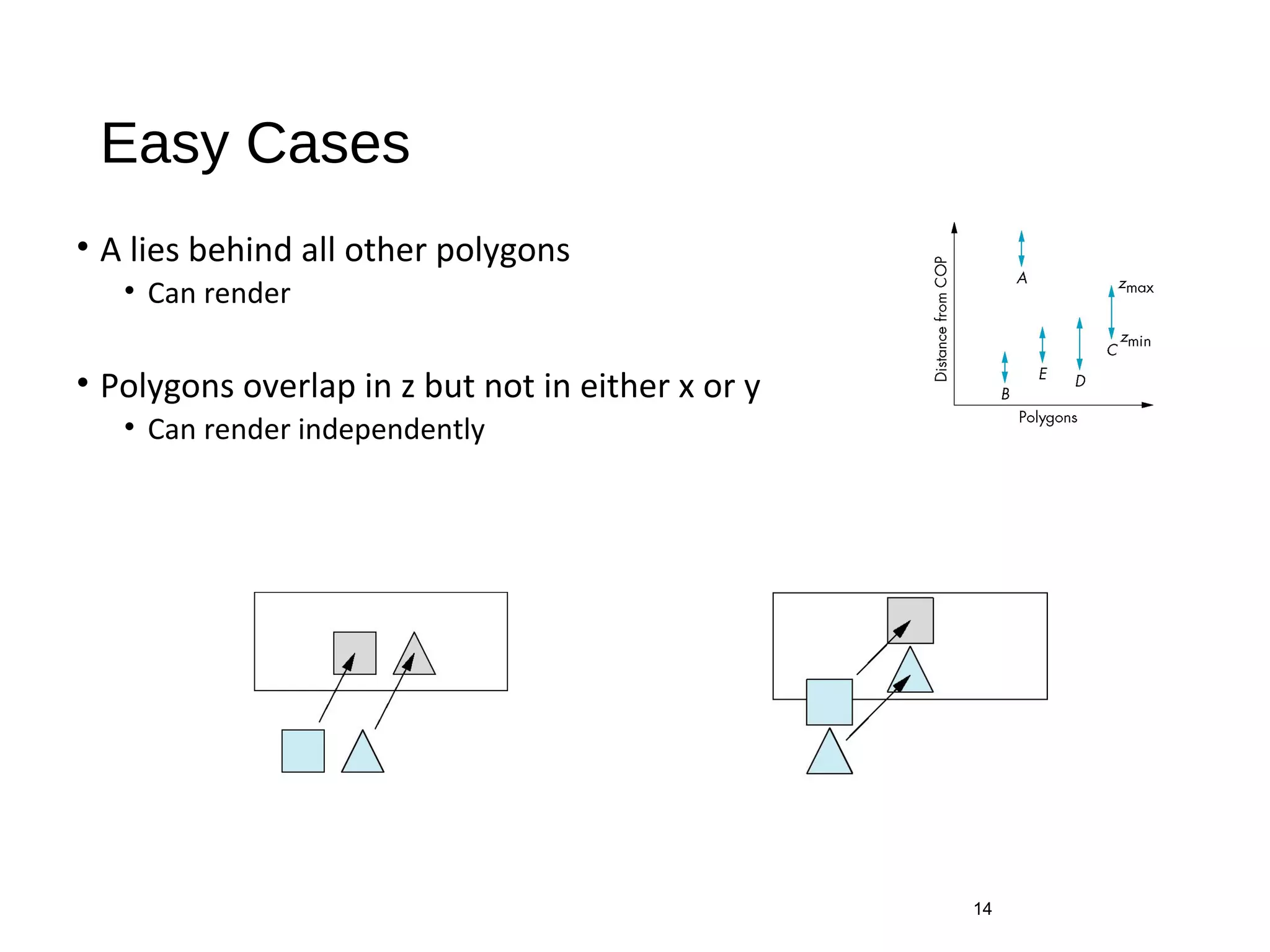
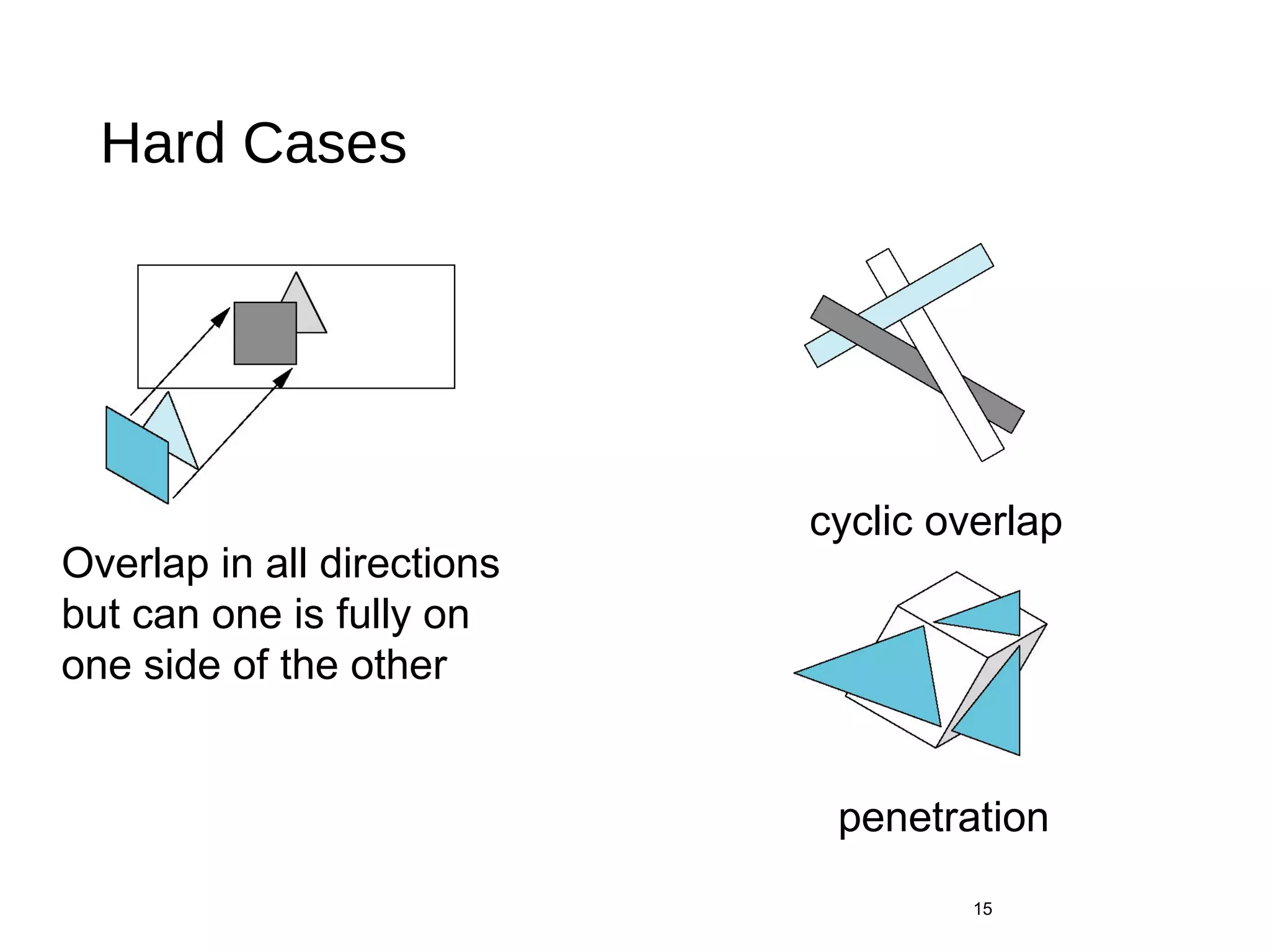
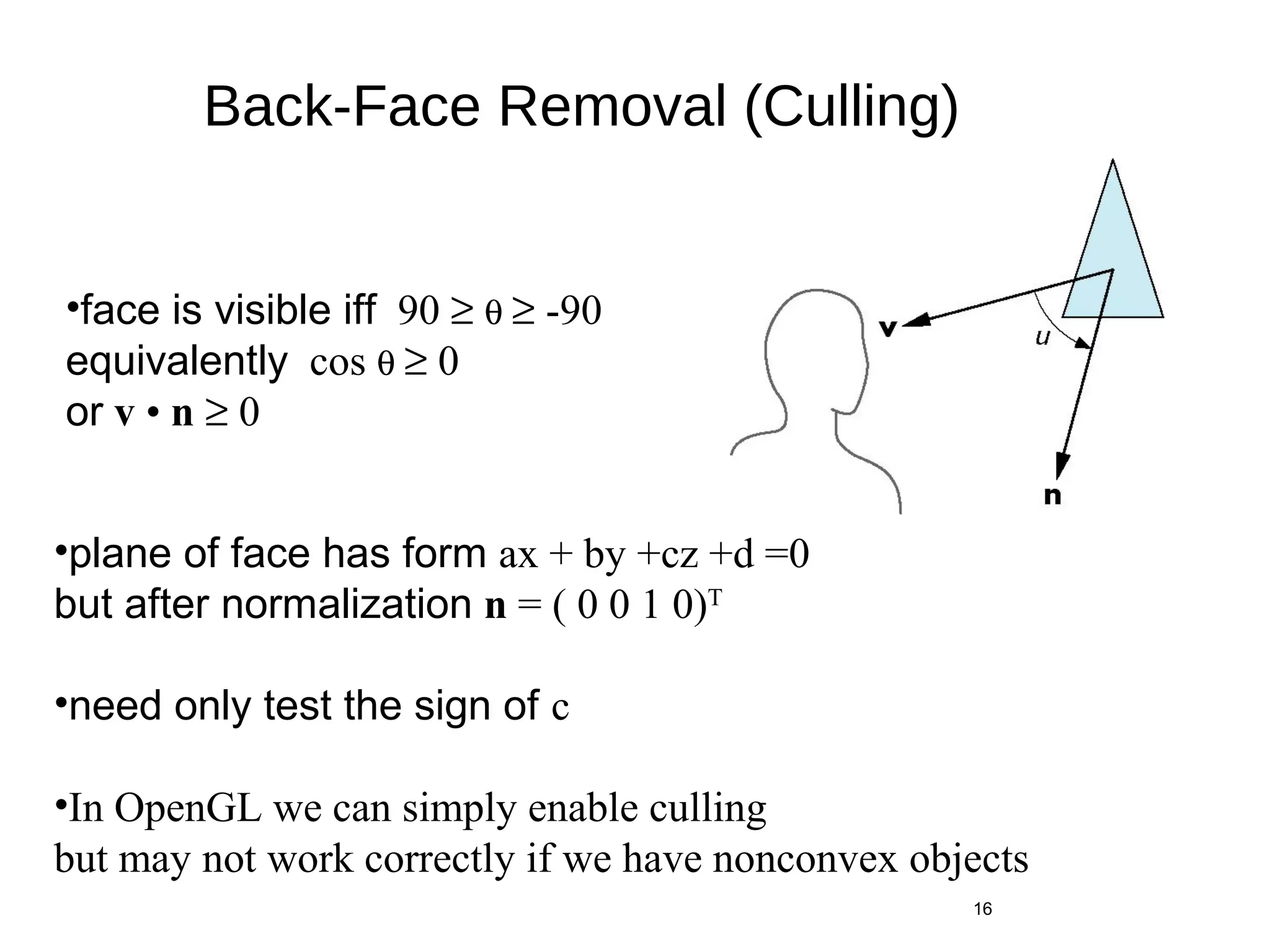
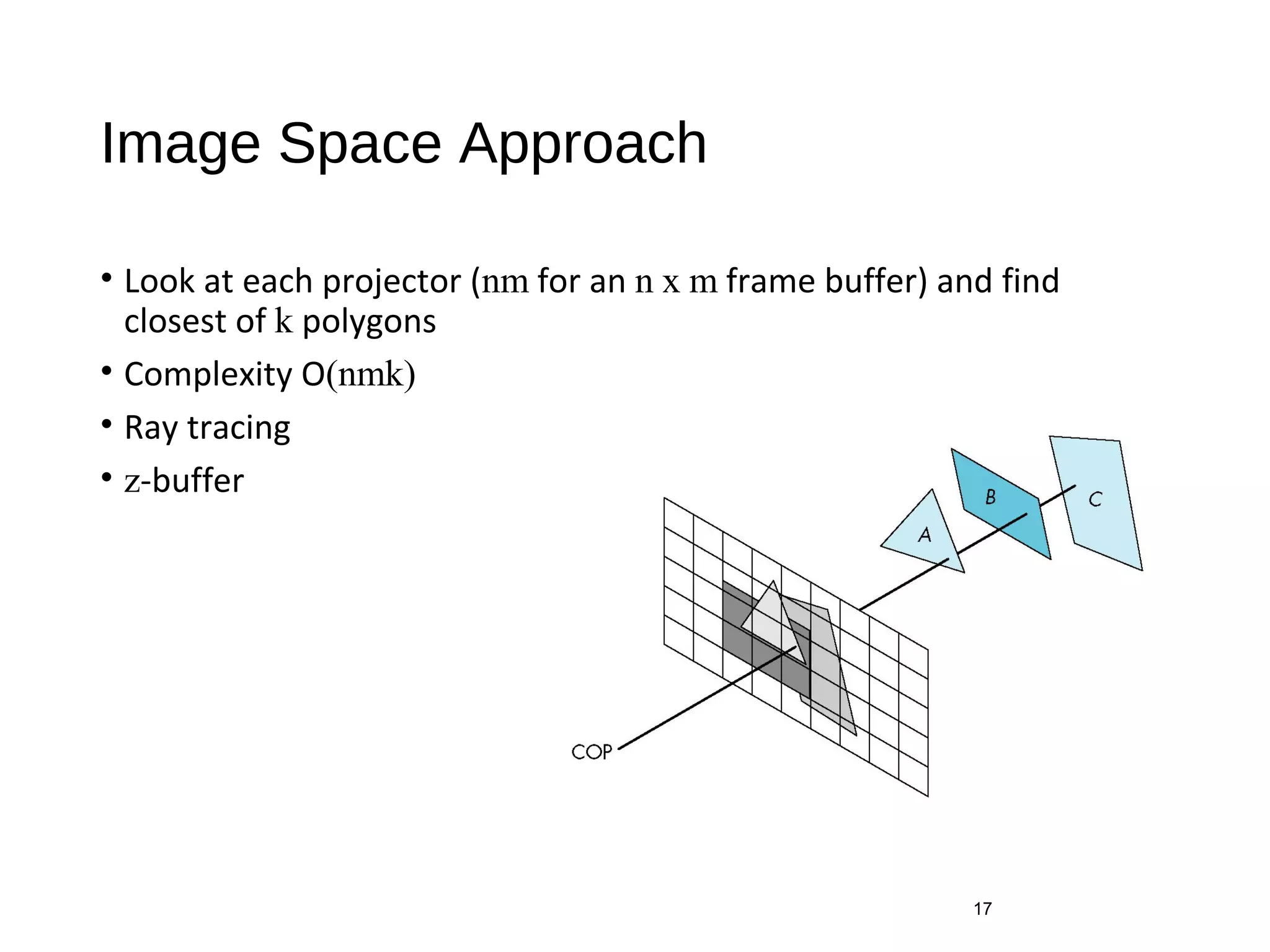
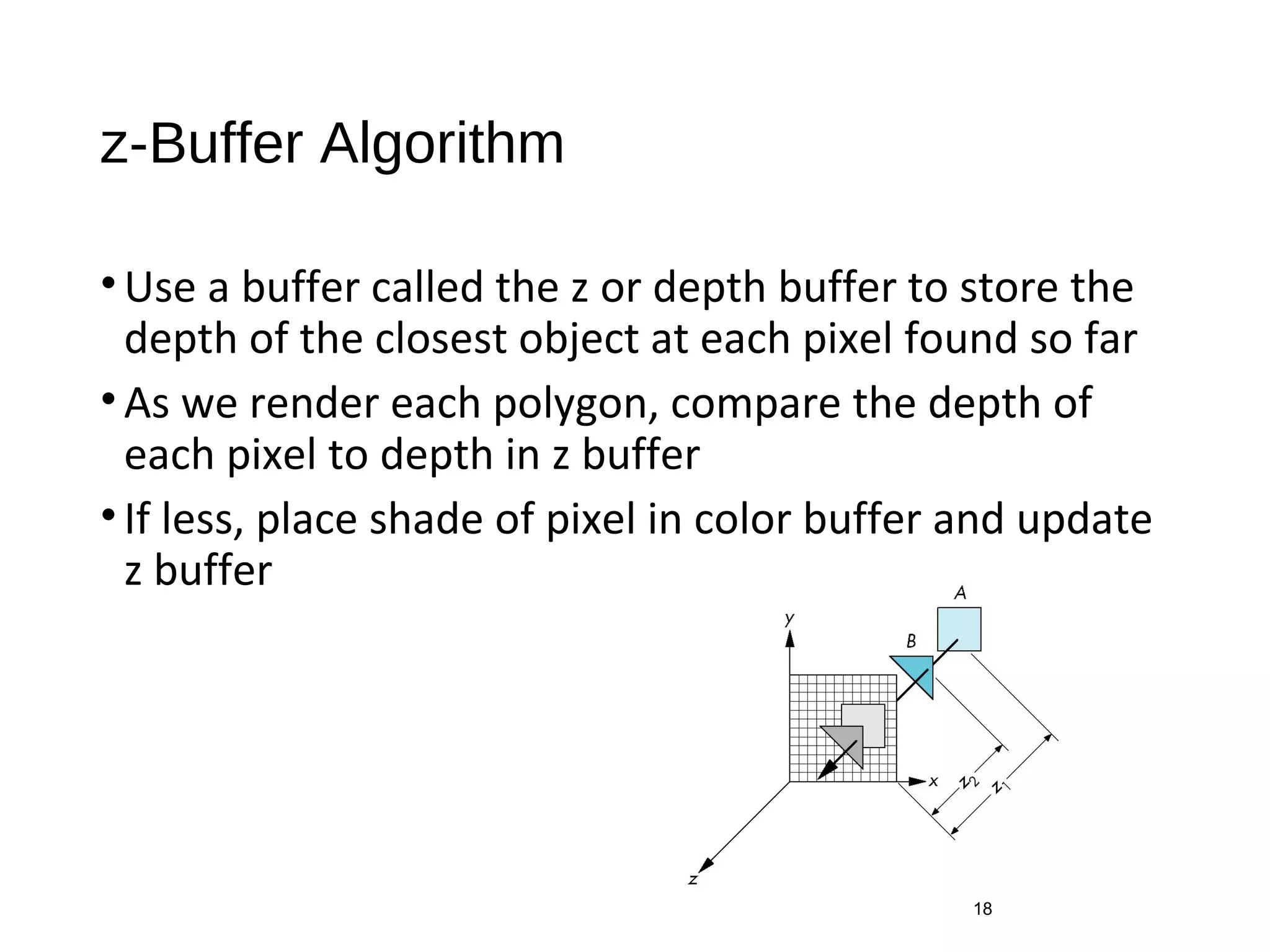
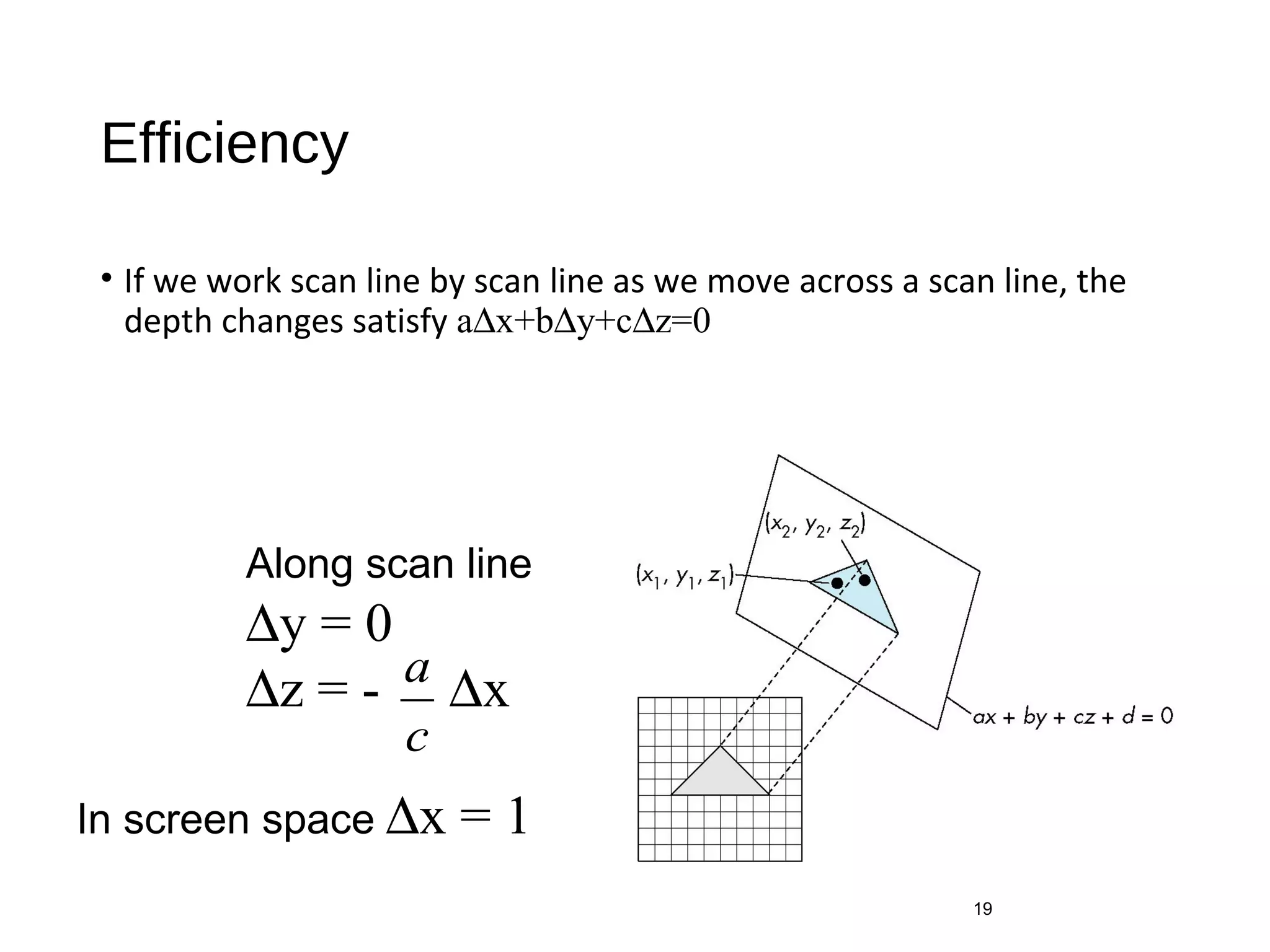
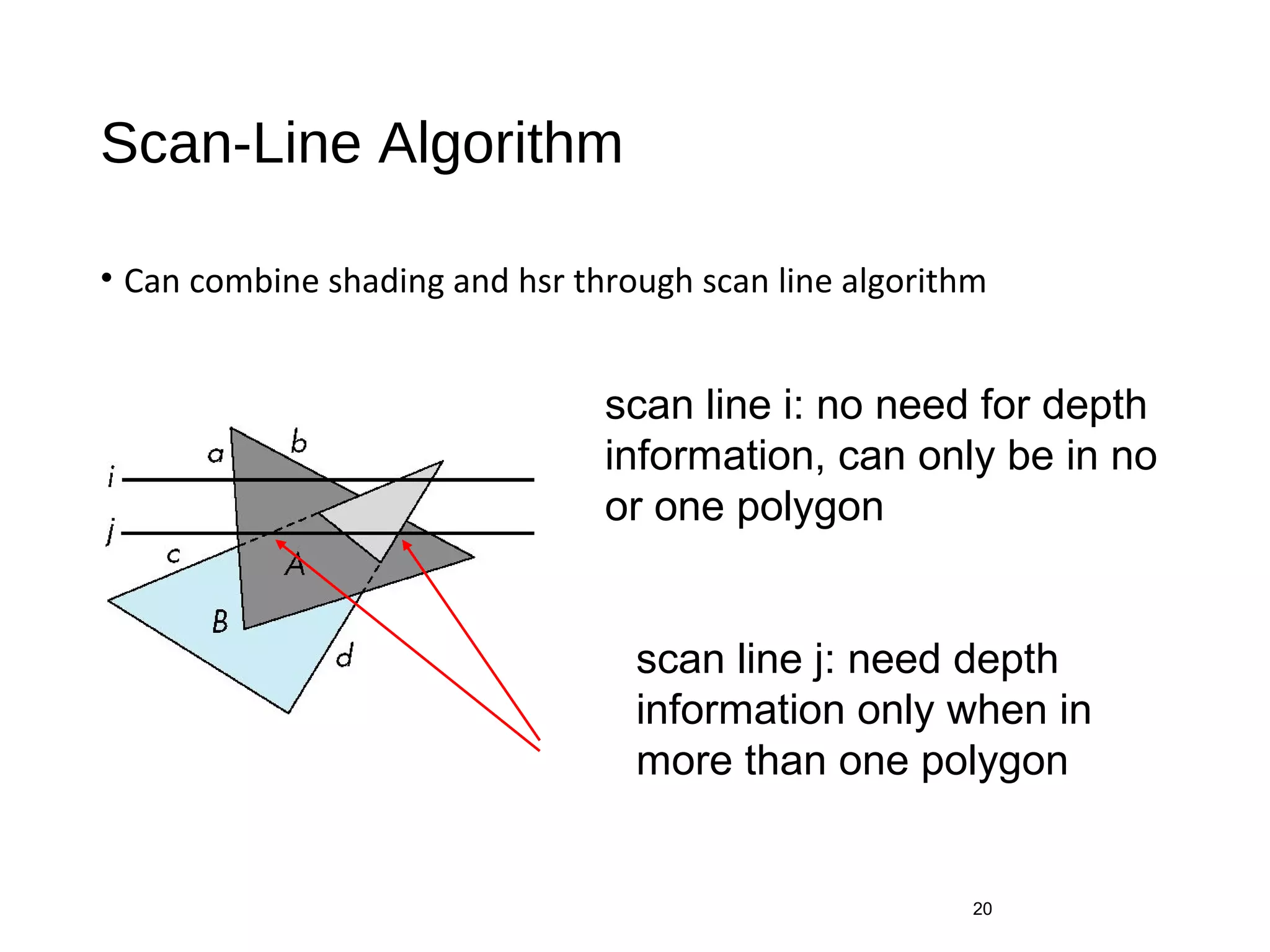
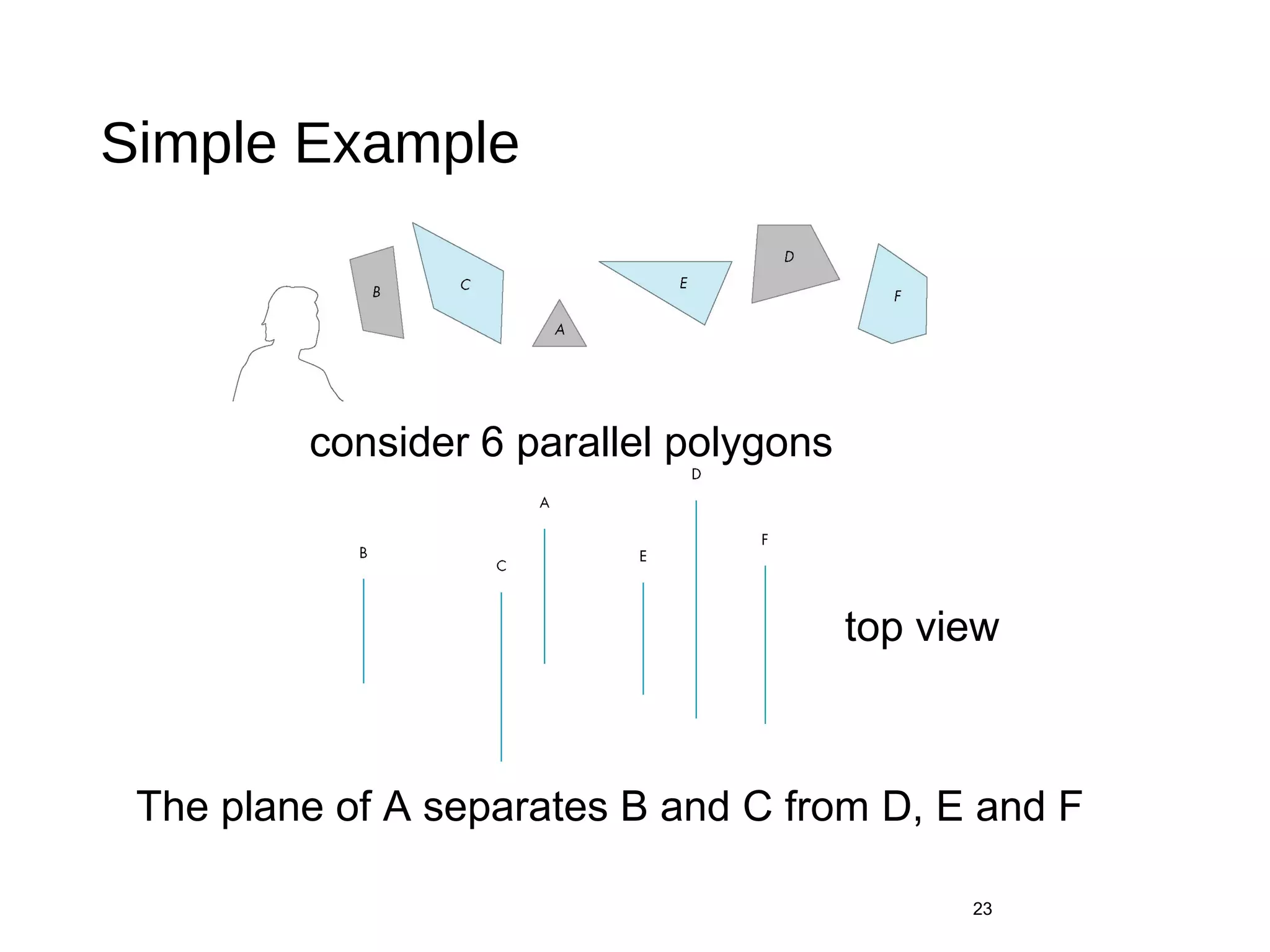
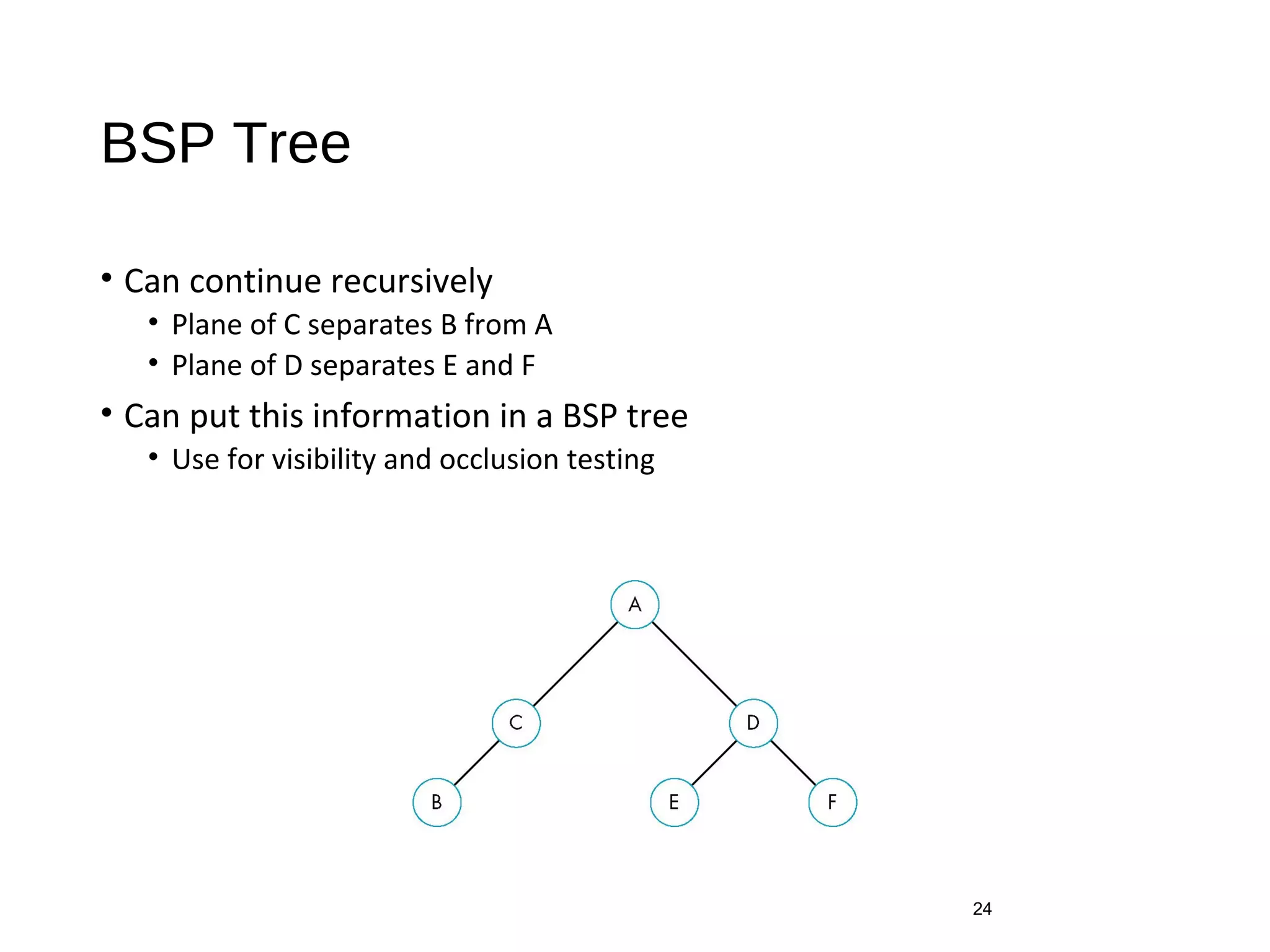
Polygon clipping algorithms can yield multiple polygons when clipping non-convex polygons, but clipping a convex polygon yields at most one other polygon. Tessellation replaces non-convex polygons with triangular polygons. Clipping can be done independently for each side of the window using a pipeline approach. Bounding boxes can determine if detailed clipping is needed. The painter's algorithm and depth sorting are common hidden surface removal techniques. The z-buffer algorithm compares depth values to determine visibility at each pixel. Binary space partitioning trees can partition space hierarchically for visibility and occlusion testing.