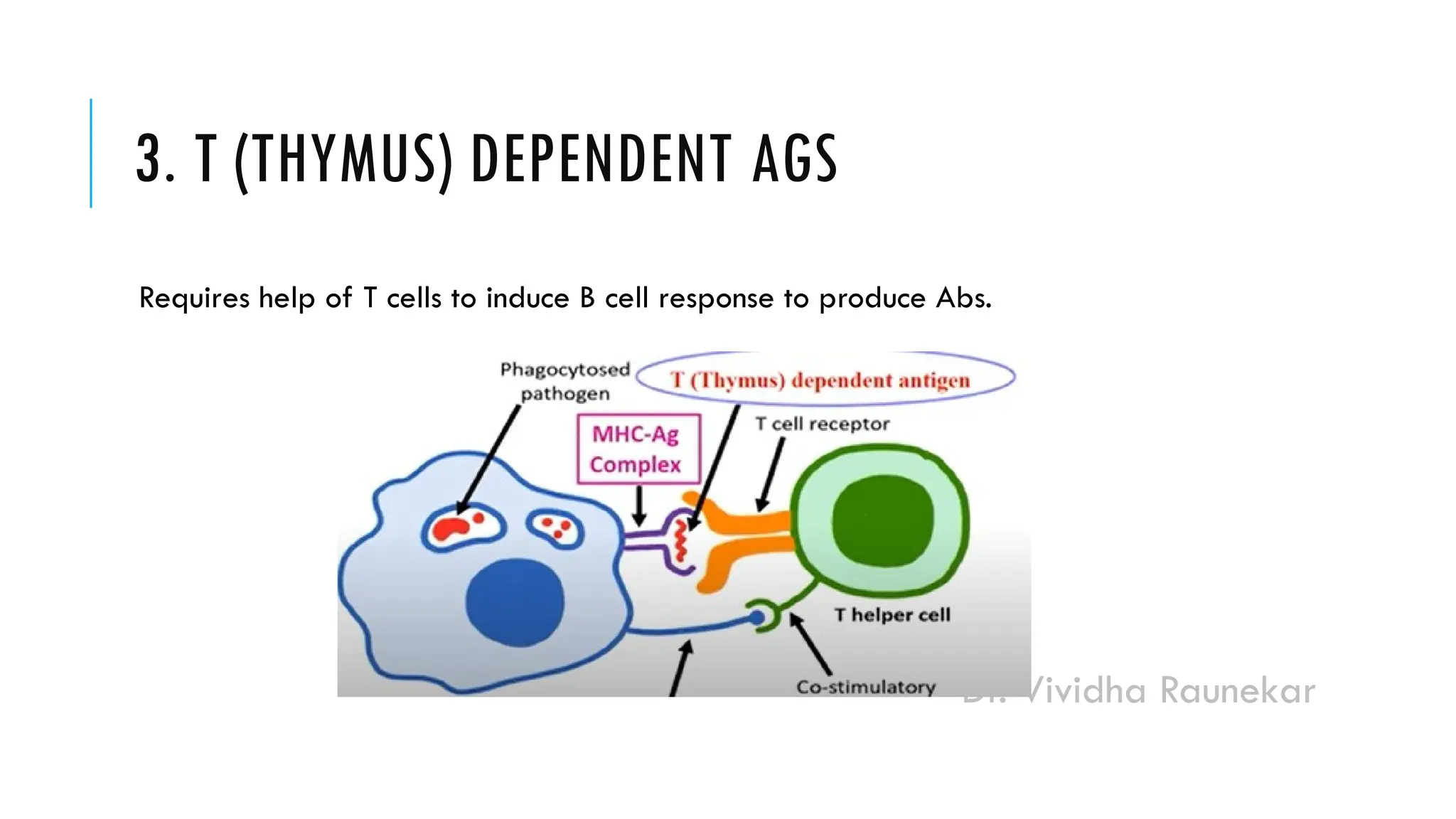
The document discusses the concepts of immunity and the organs of the immune system, defining antigens and their classification based on origin and immune response types. It explains the differences between immunogens and haptens, as well as T cell-dependent and independent antigens. Additionally, it covers the terms immunogenicity and antigenicity, highlighting their roles in the immune response.