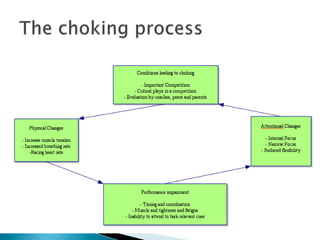
The document discusses mental imagery and simulation techniques used by athletes. It states that mental imagery involves visually picturing events in the mind and allows athletes to strengthen muscle coordination through thought processes. Simulation aims to recreate competition situations for training. Both techniques improve neural pathways and allow athletes to mentally rehearse movements and prepare for events. The document also discusses different types of focus athletes can employ, such as internal focus on thoughts or external focus on environmental cues, and how attention shifts are important for performance in different sports situations.