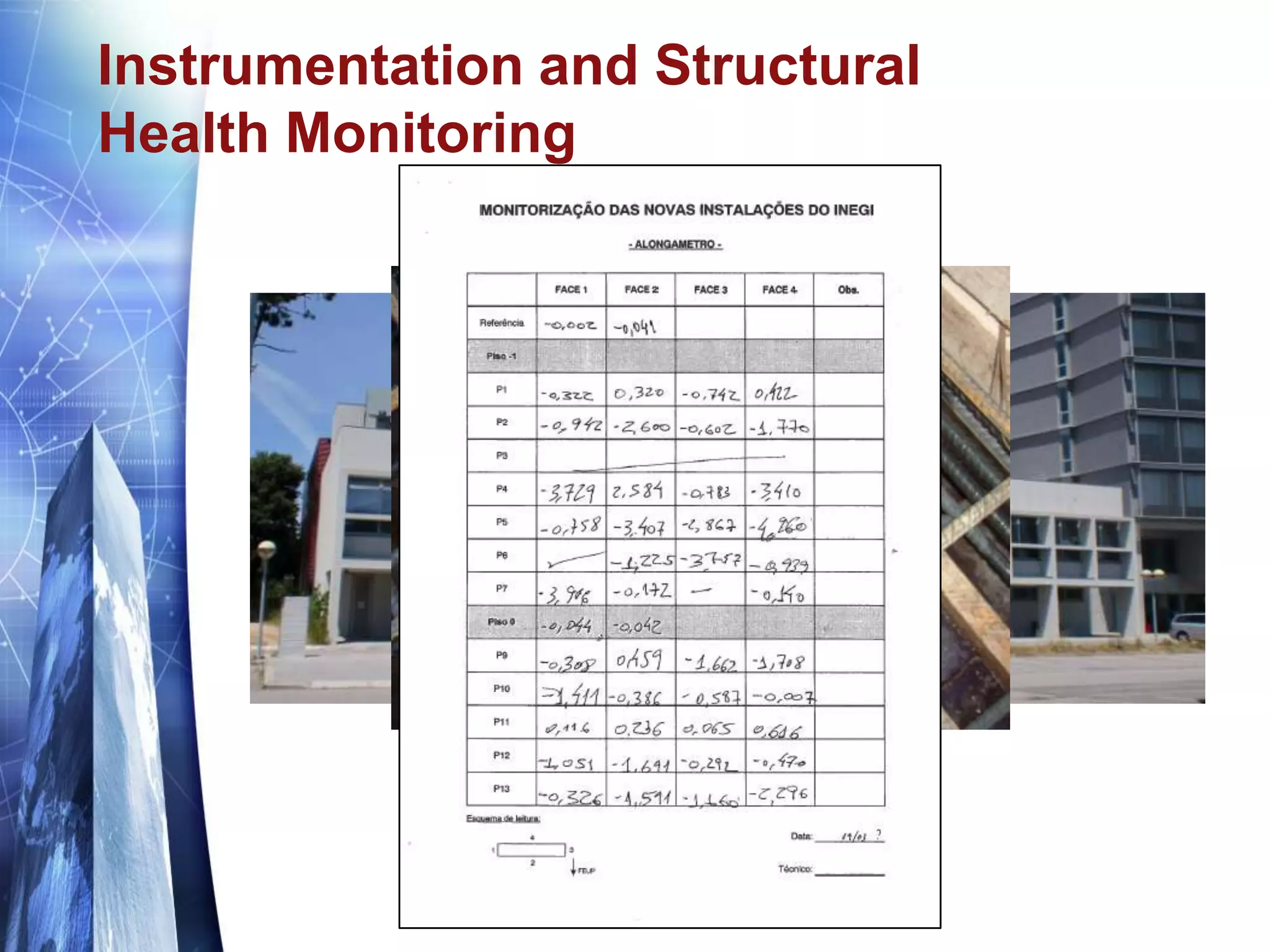
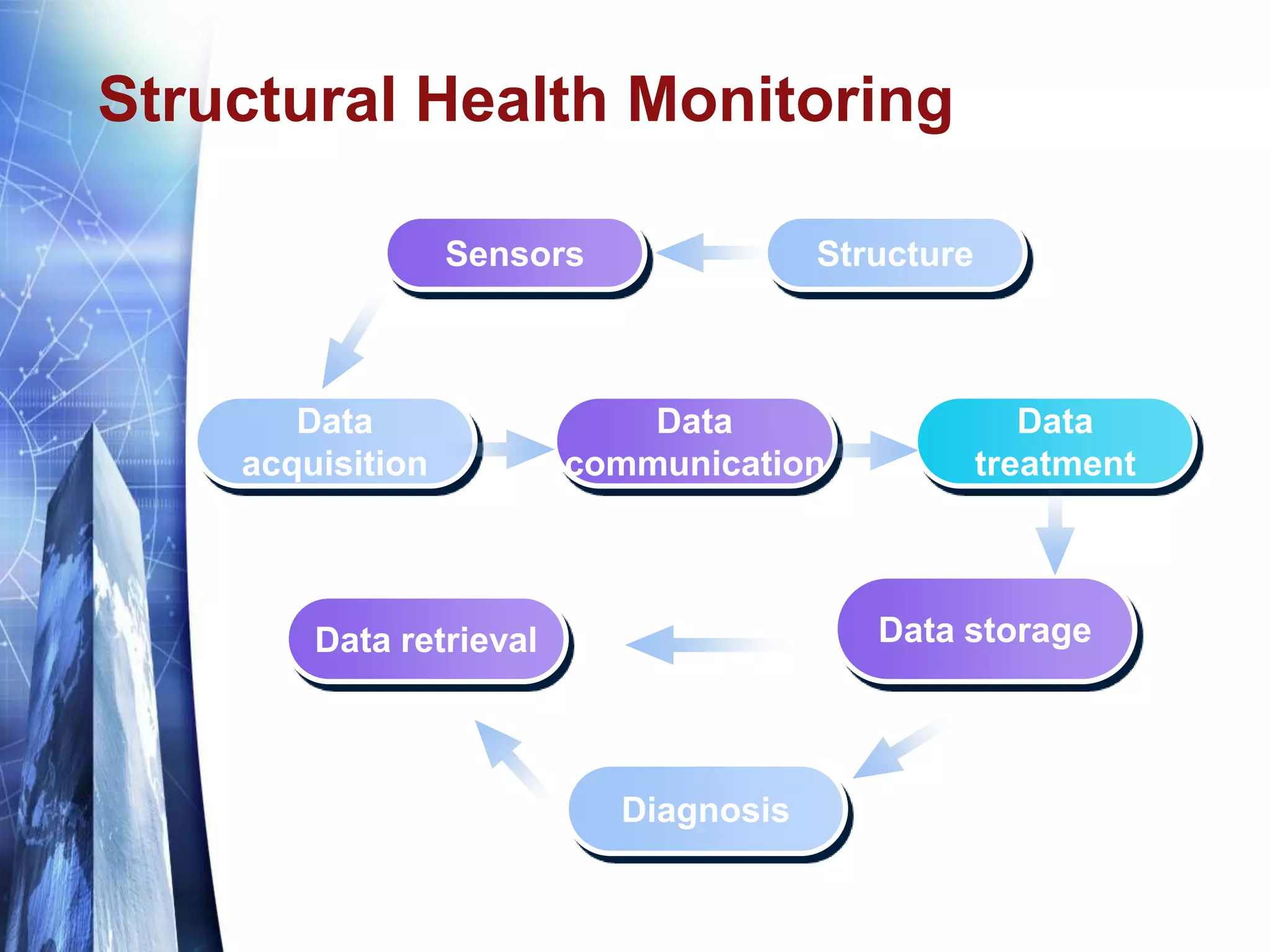
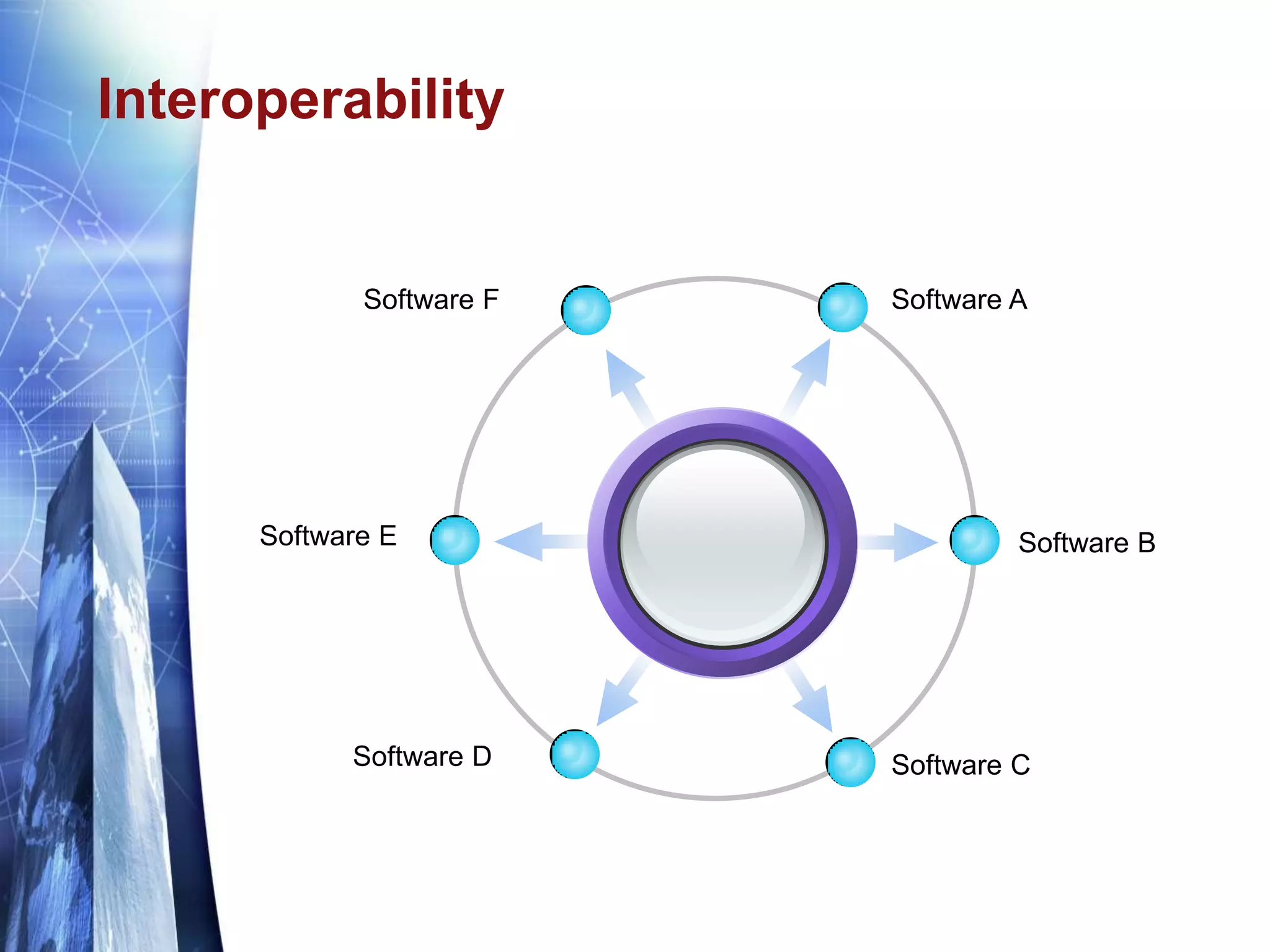
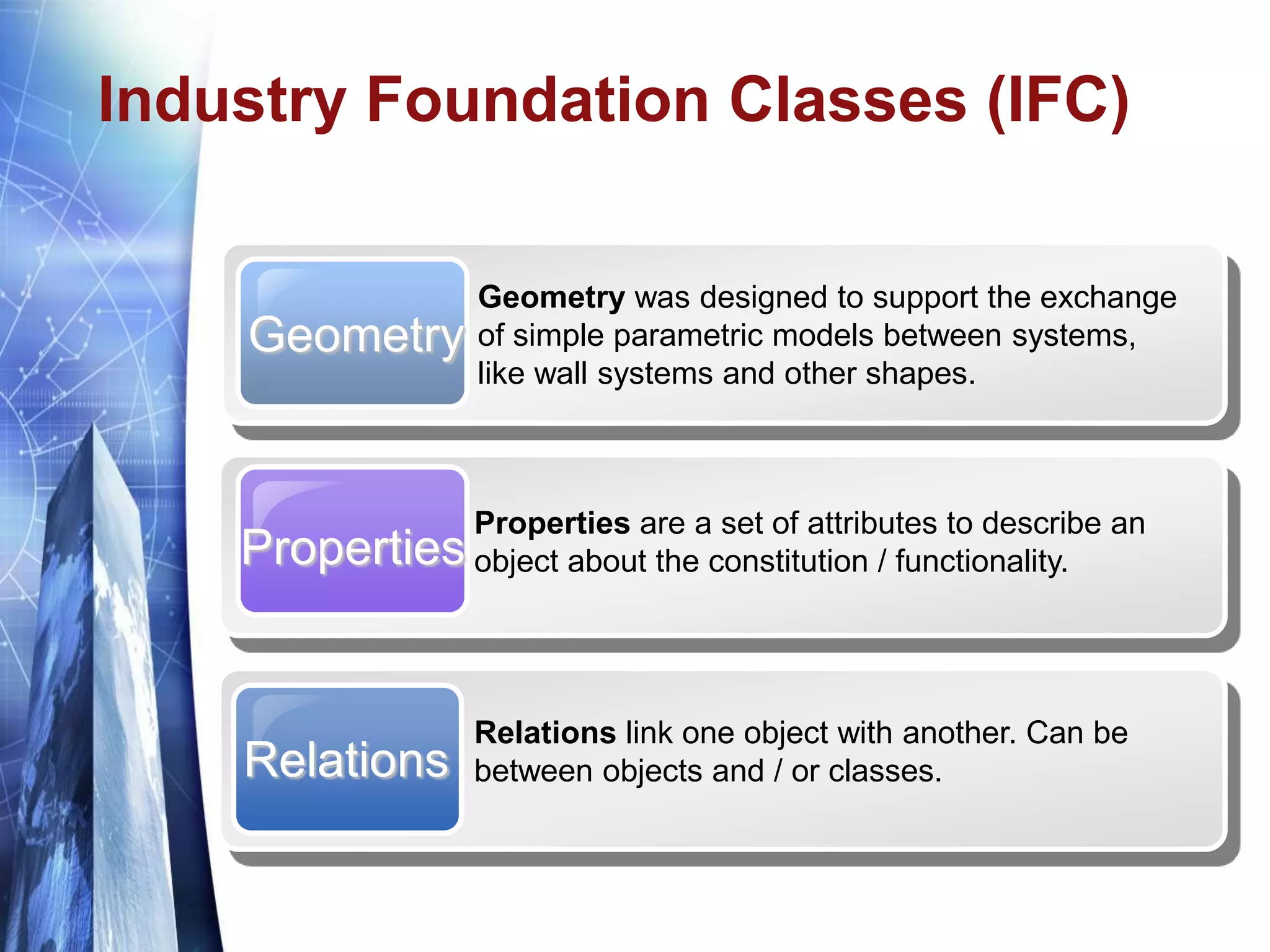
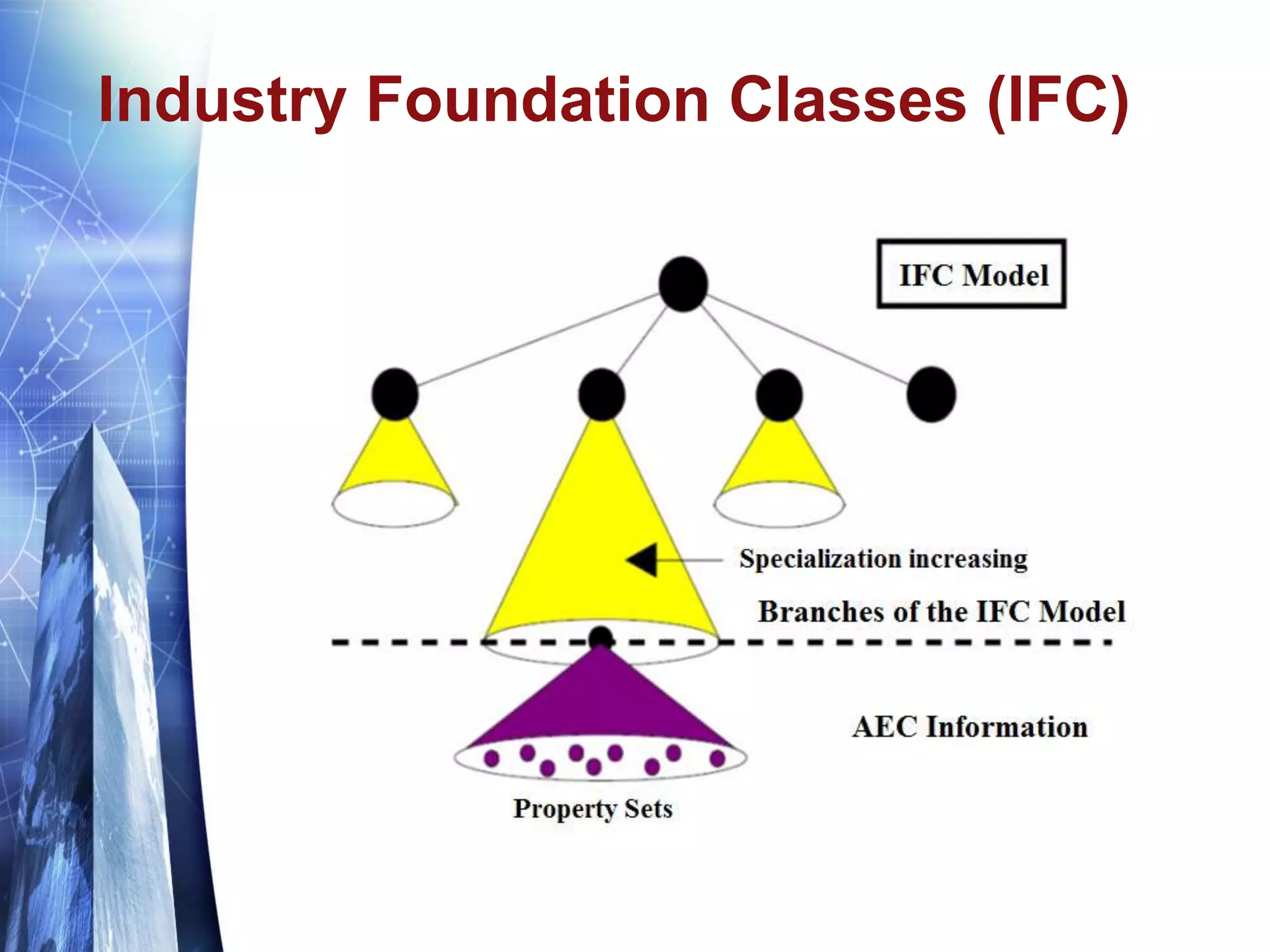
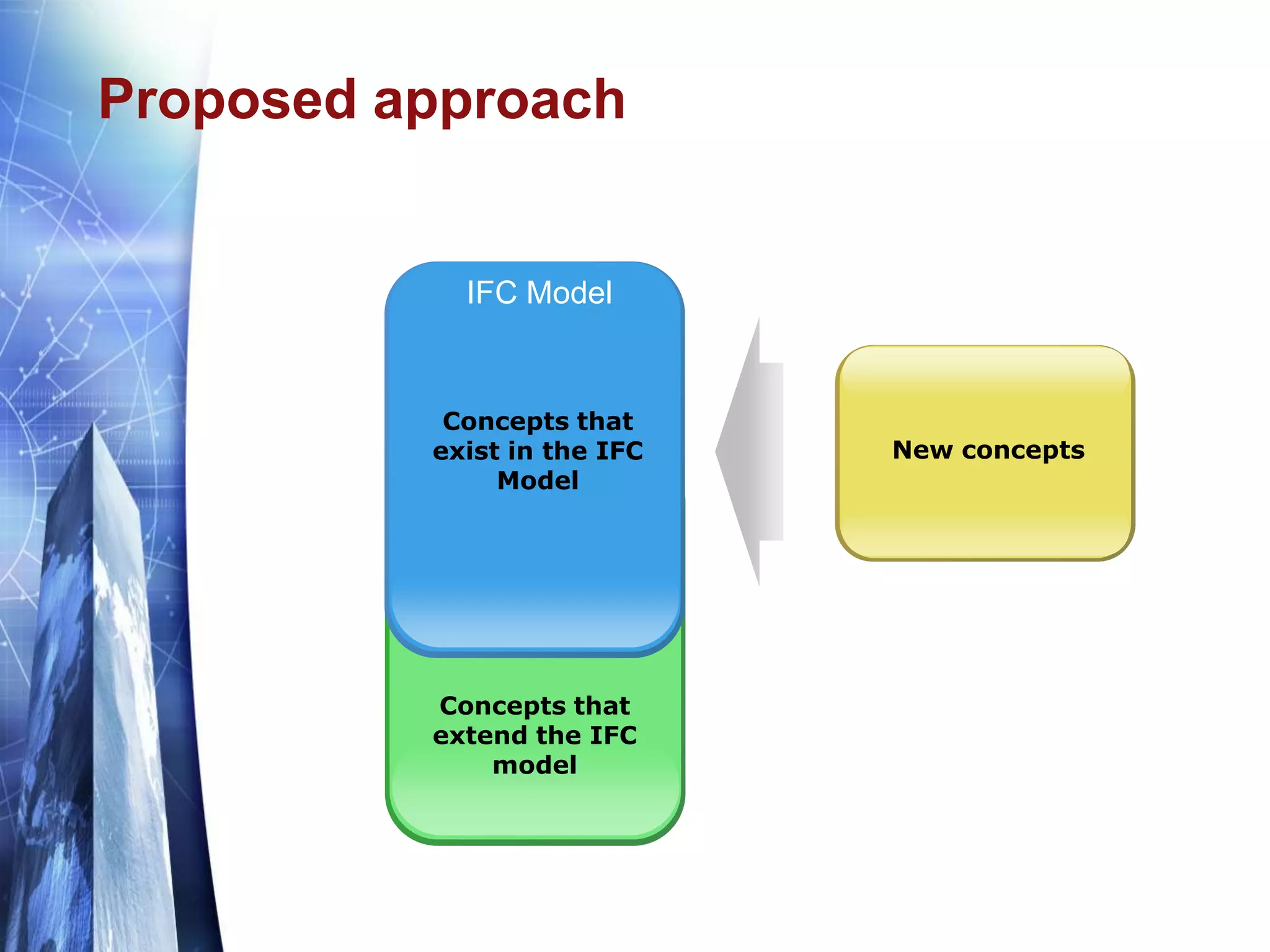
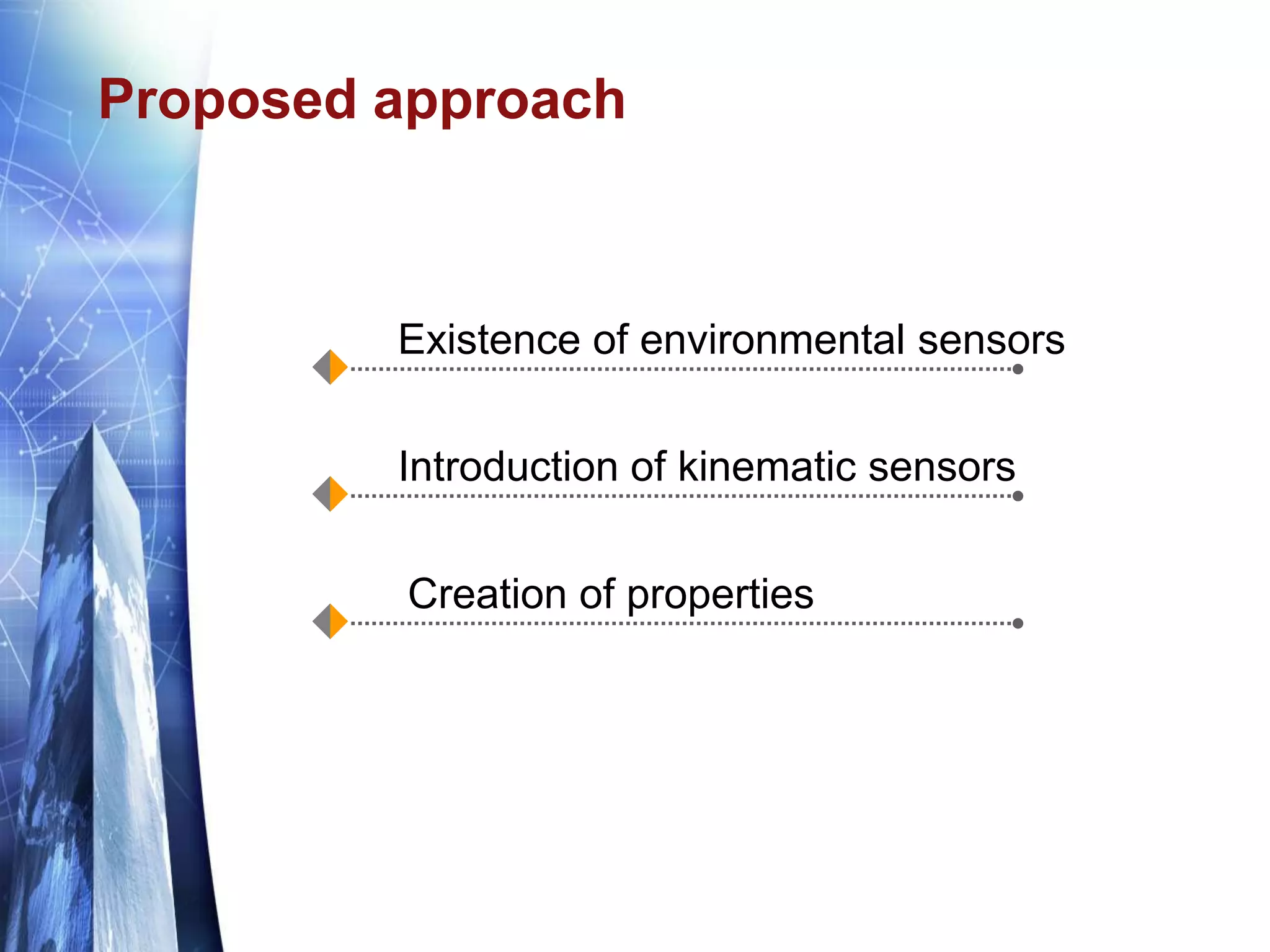
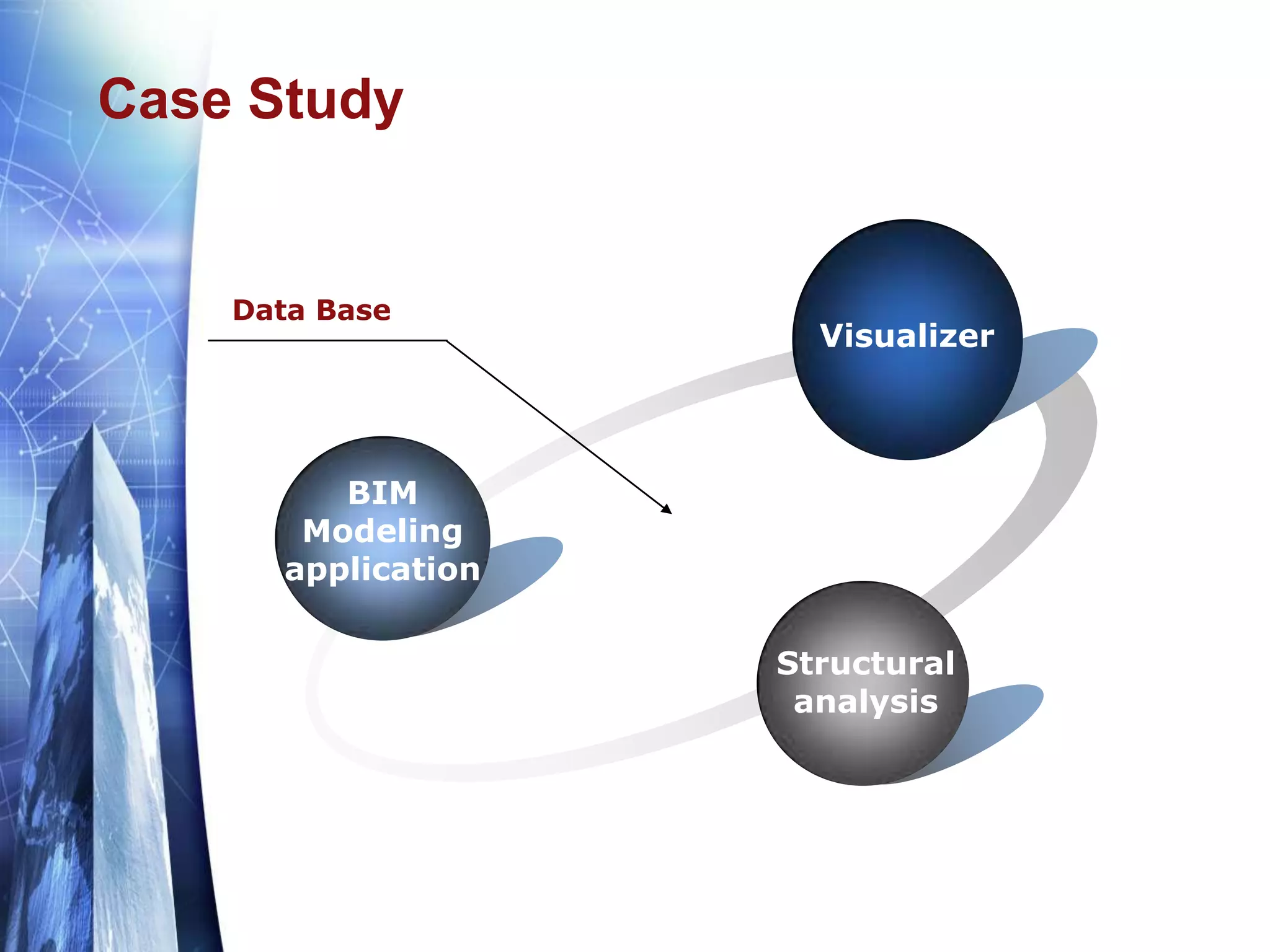
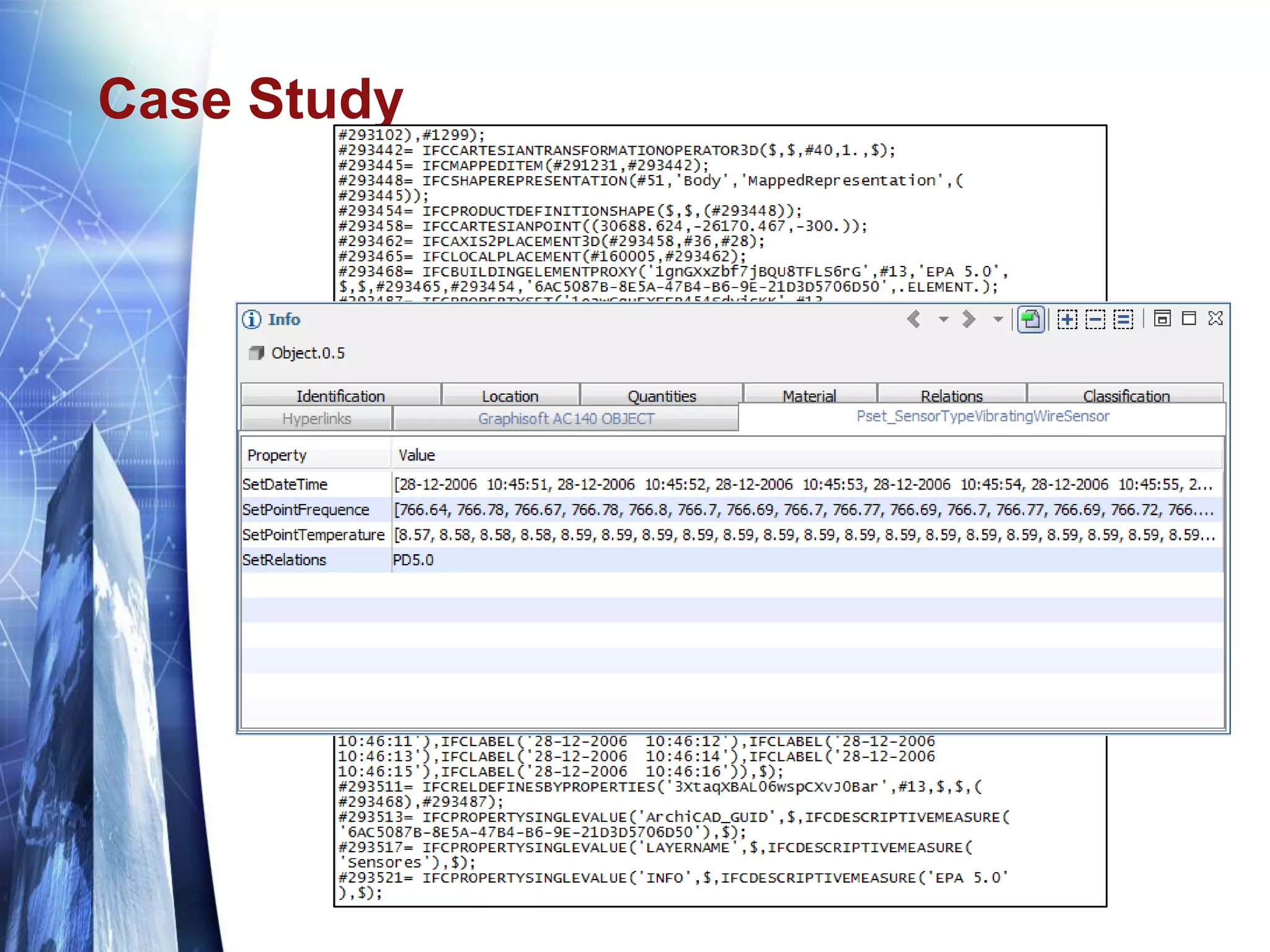
The document discusses the expansion of the Industry Foundation Classes (IFC) data model to include kinematic sensors for structural health monitoring in buildings. It highlights the importance of integrating sensor data into Building Information Modeling (BIM) and emphasizes that while the IFC model supports interoperability, it requires further enhancements for specific use cases. The conclusions drawn suggest that robust models alone do not ensure successful information exchange within the construction industry.