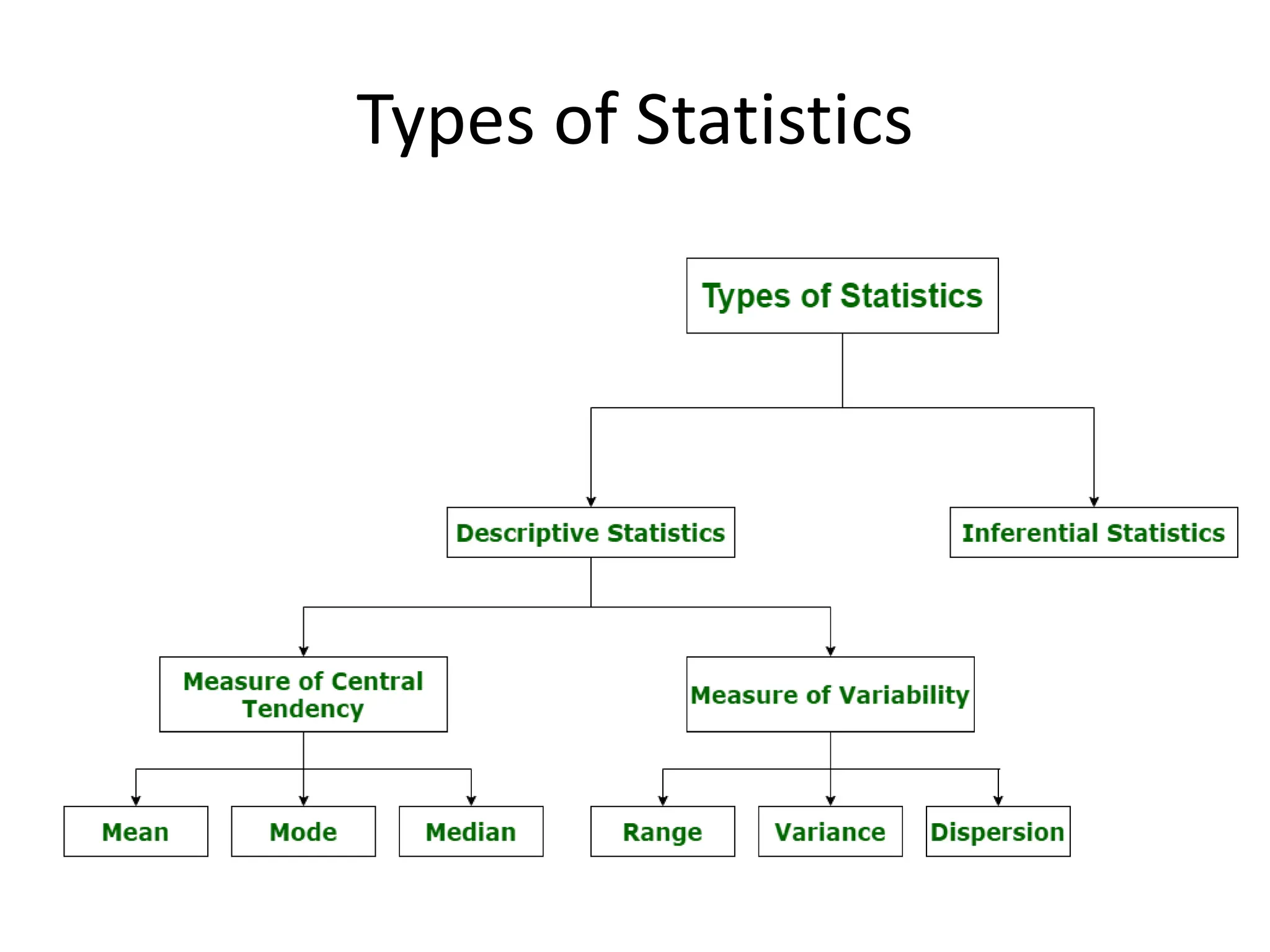
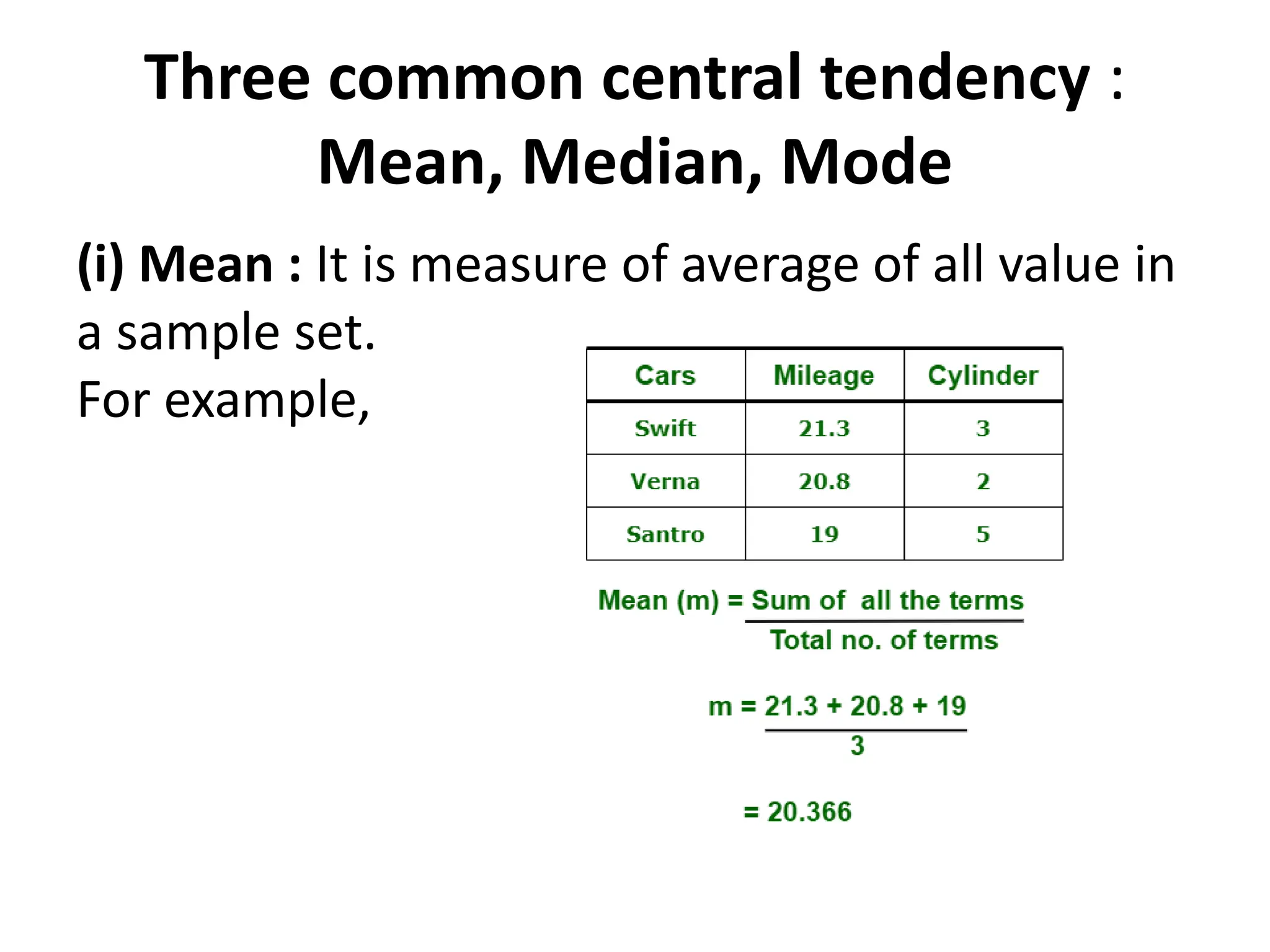
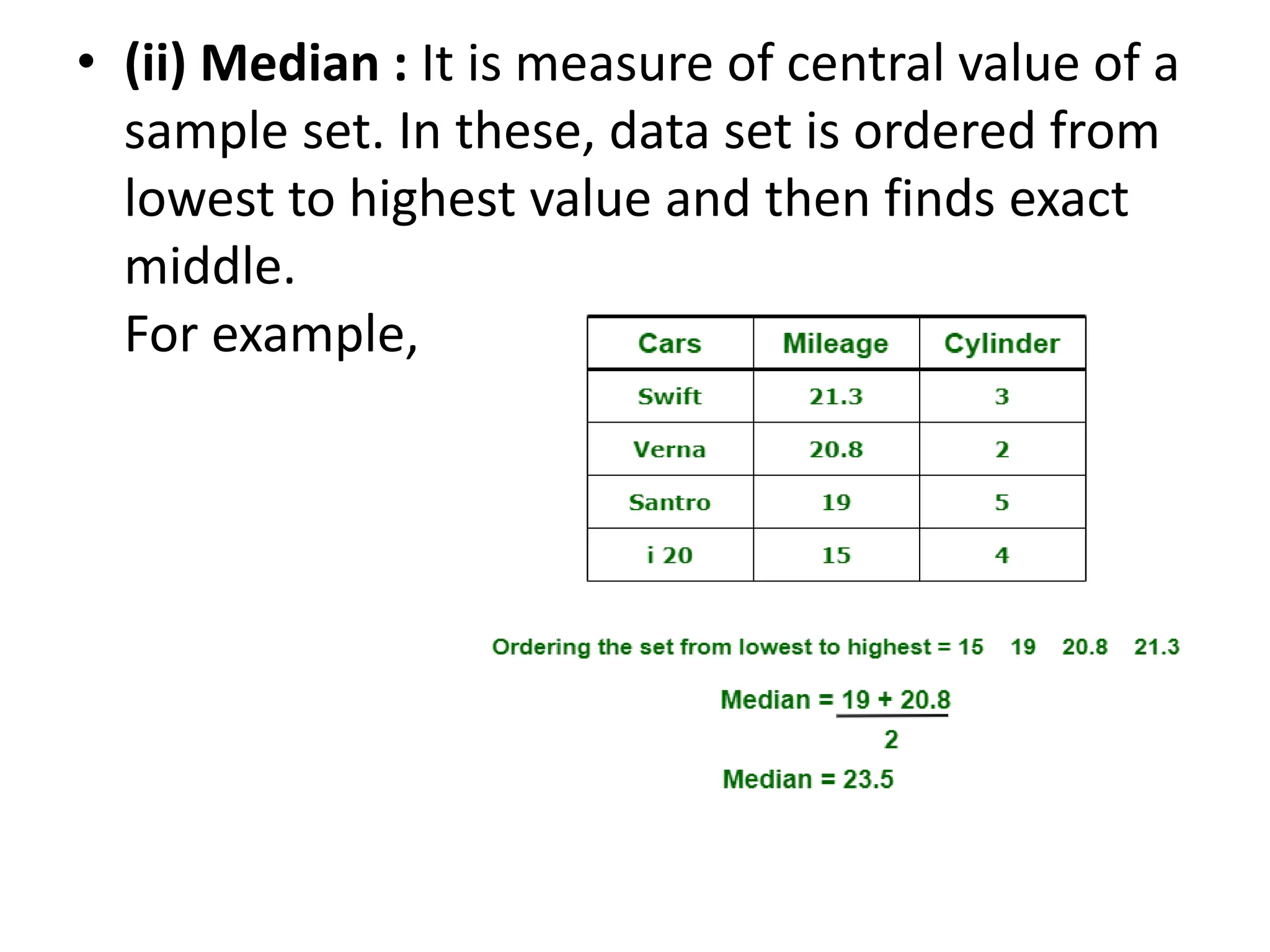
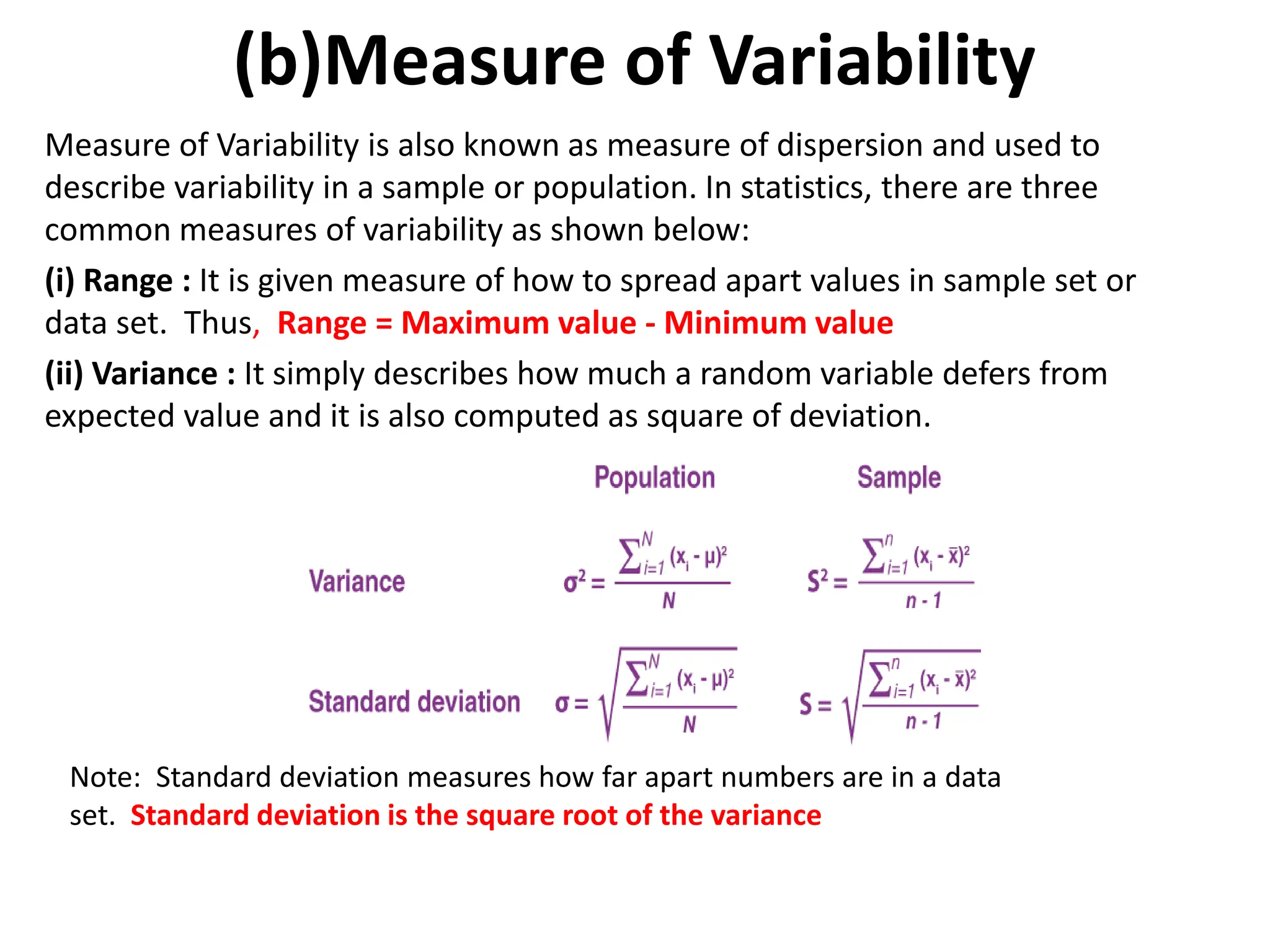
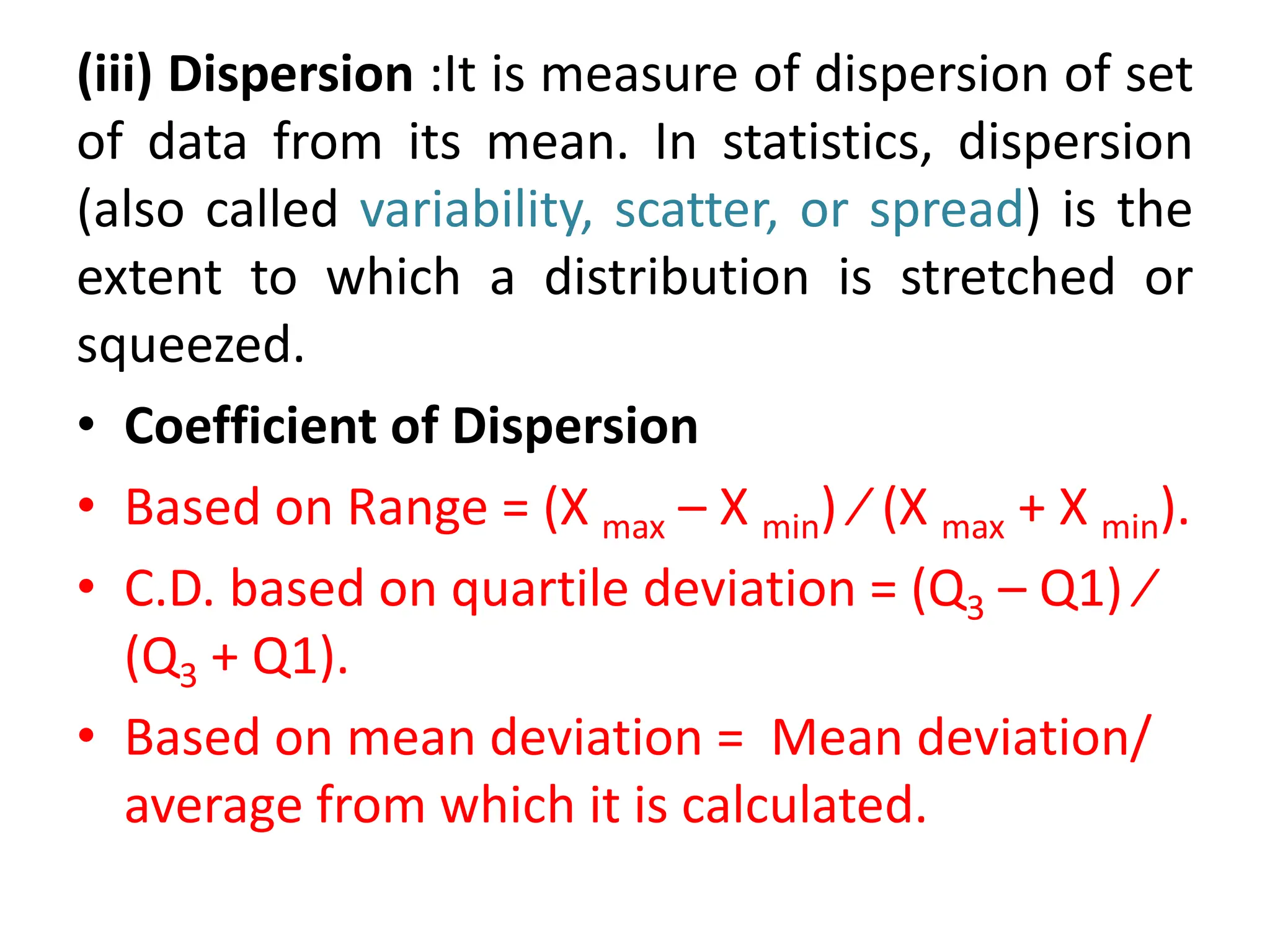
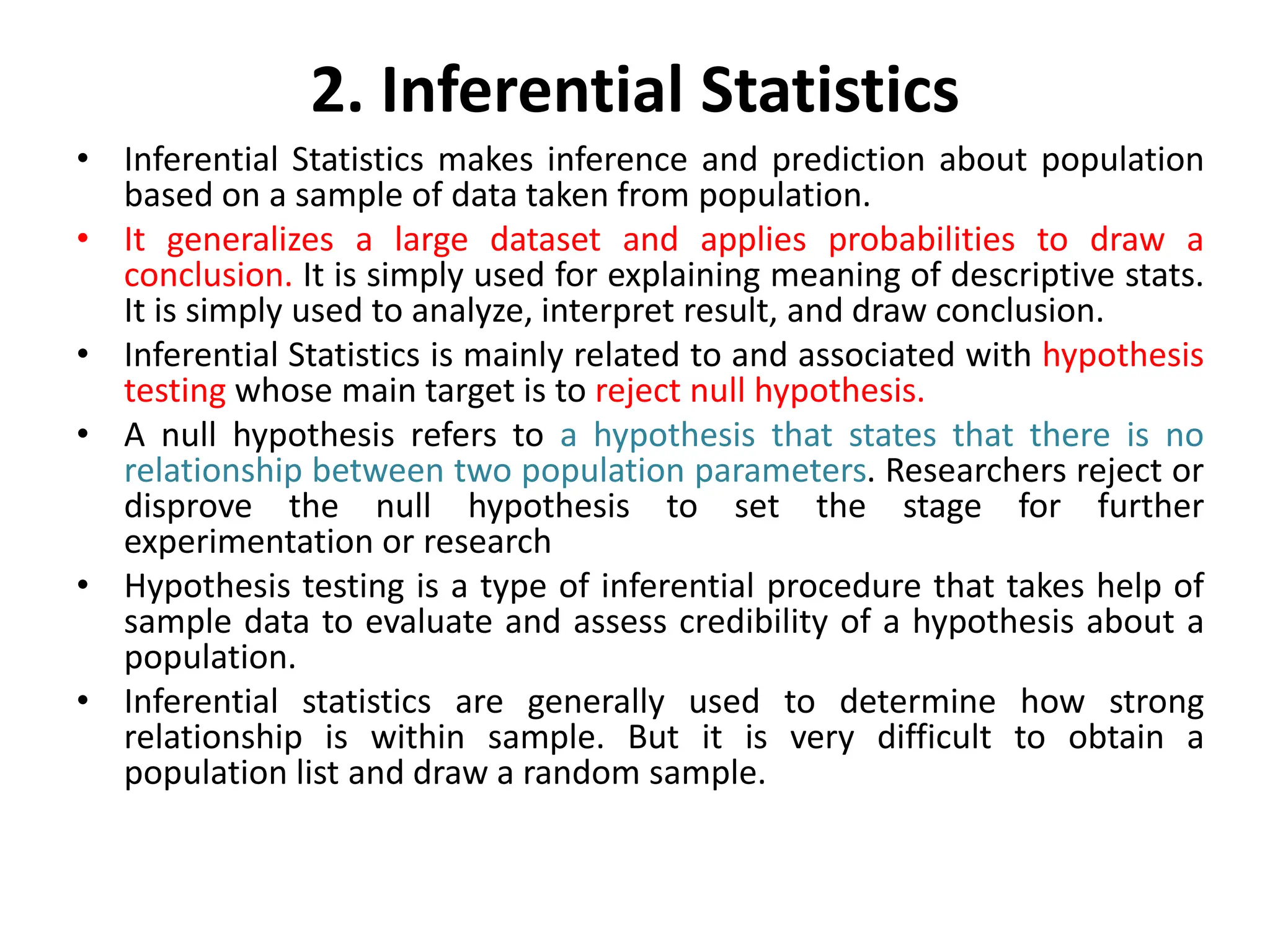
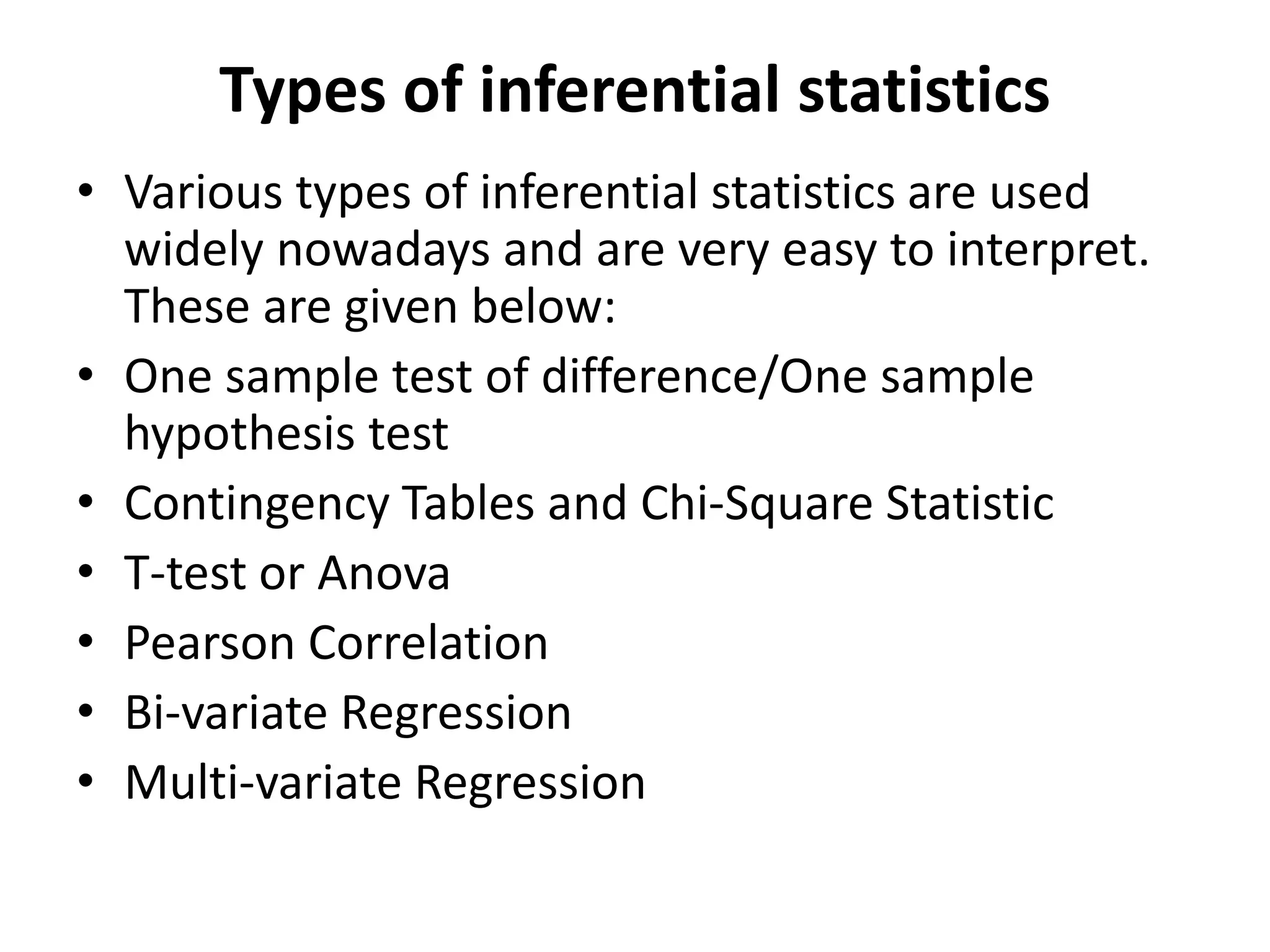
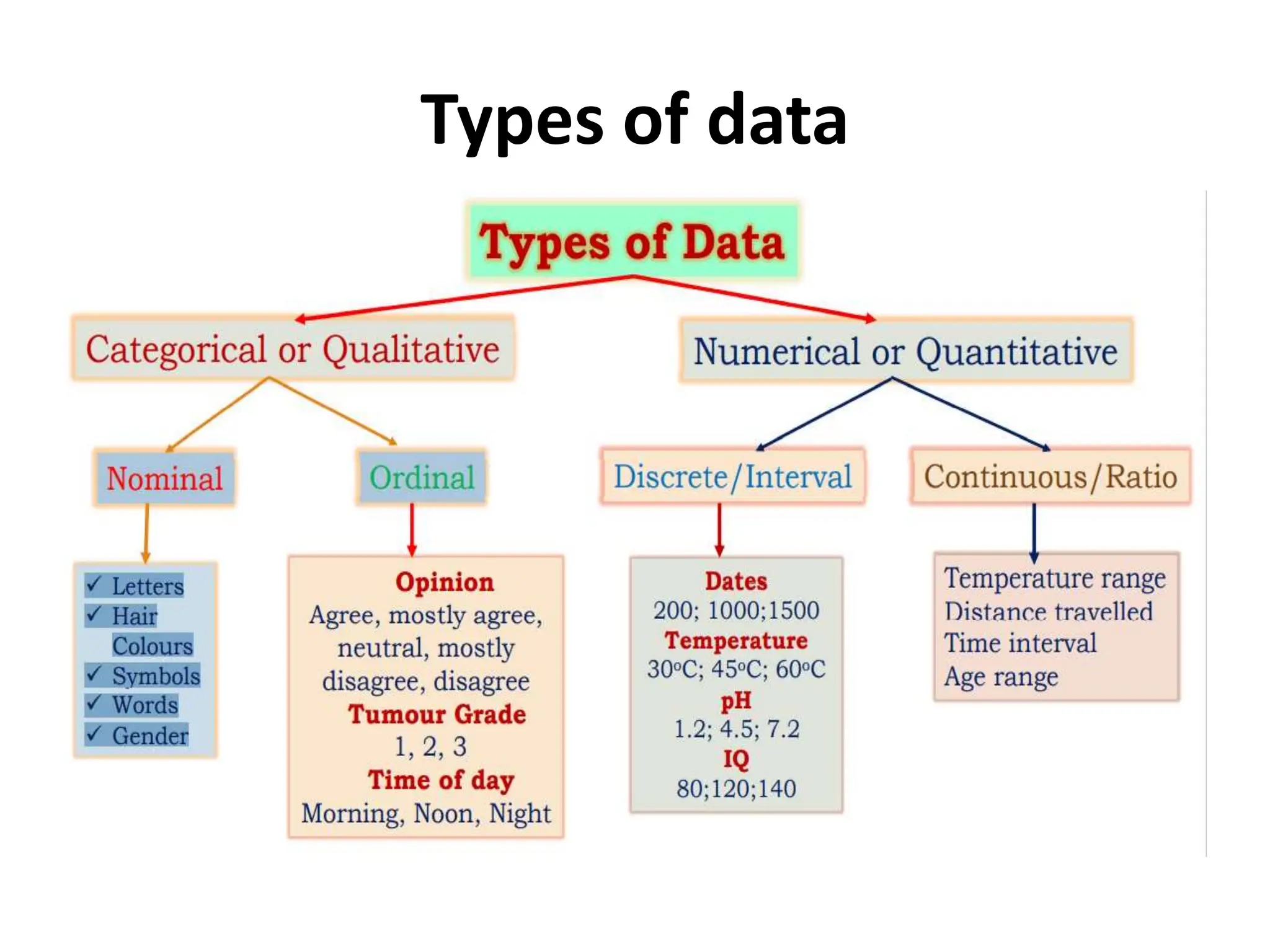
This document provides an introduction to statistics for data science. It discusses why statistics are important for processing and analyzing data to find meaningful trends and insights. Descriptive statistics are used to summarize data through measures like mean, median, and mode for central tendency, and range, variance, and standard deviation for variability. Inferential statistics make inferences about populations based on samples through hypothesis testing and other techniques like t-tests and regression. The document outlines the basic terminology, types, and steps of statistical analysis for data science.