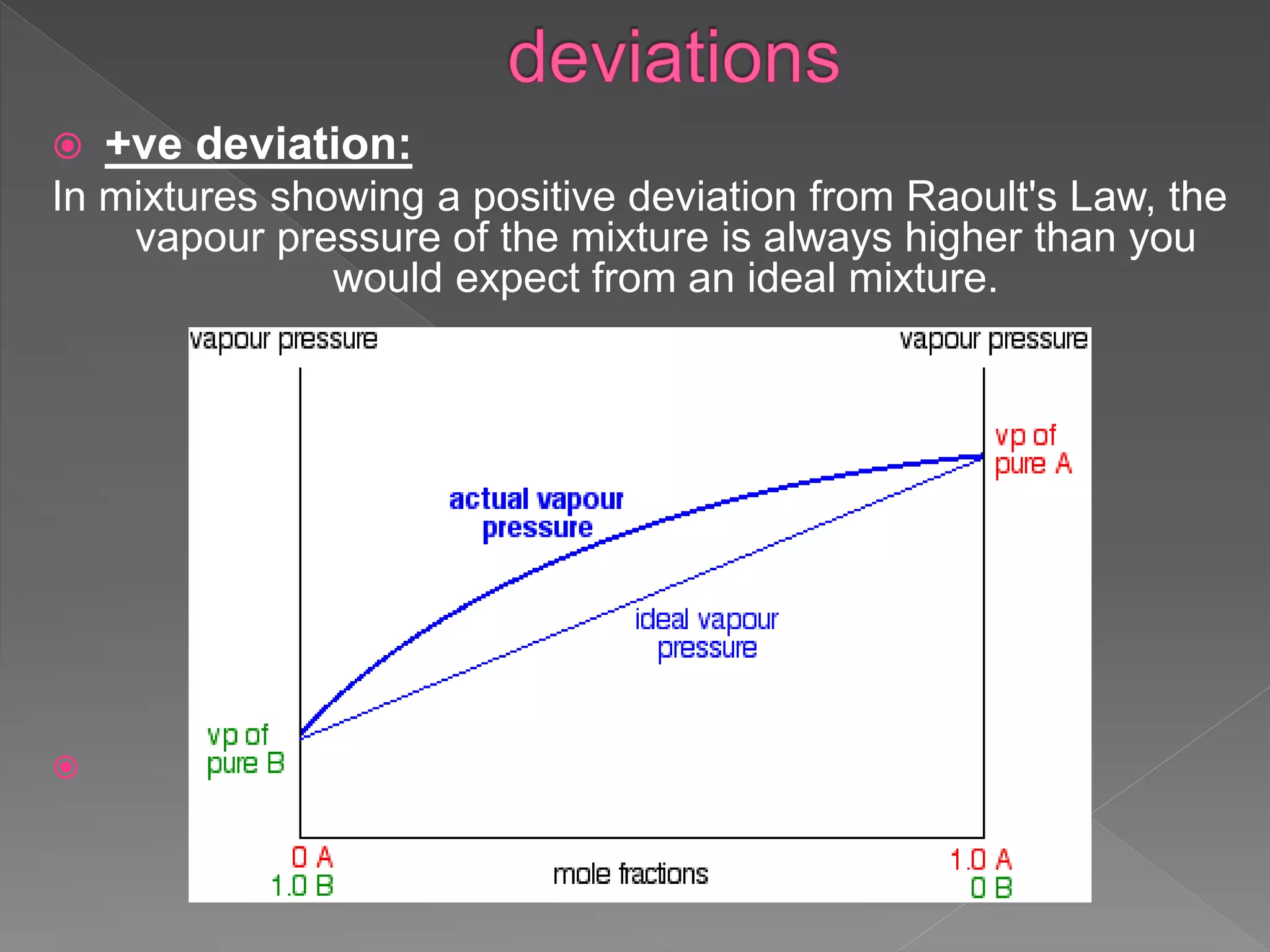
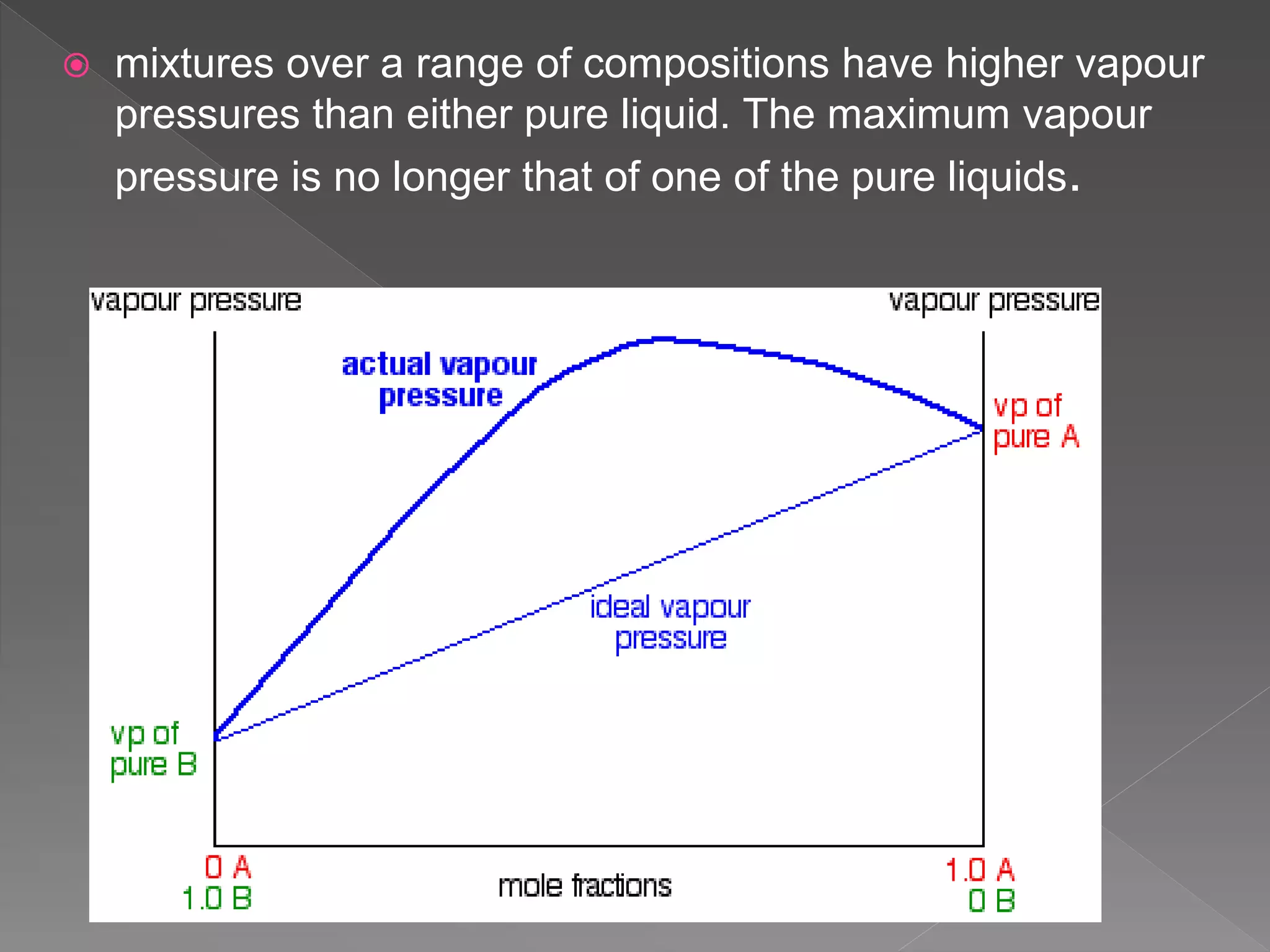
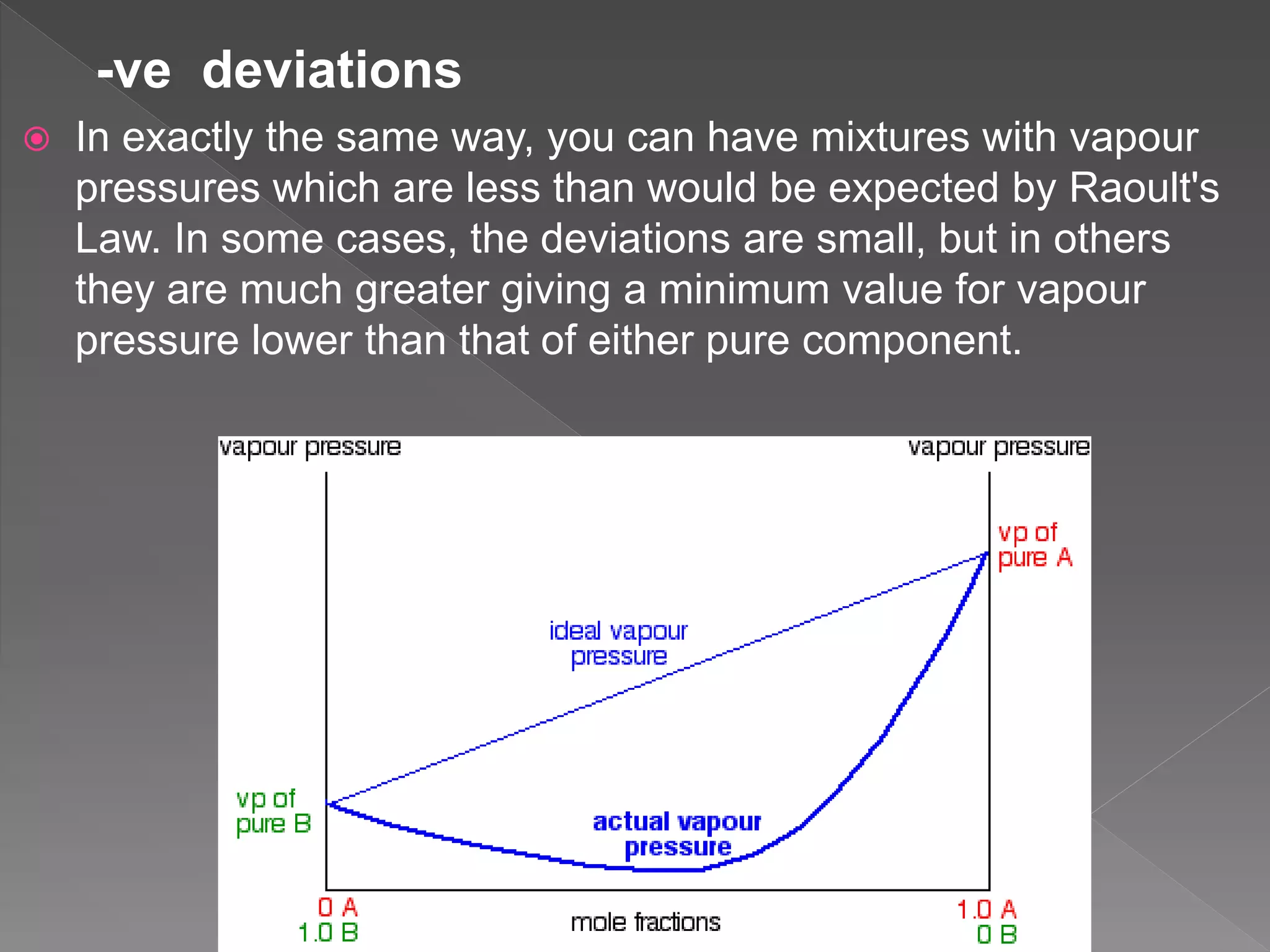
This document discusses ideal gases, Raoult's law, ideal solutions, and deviations from Raoult's law. It explains that an ideal gas is composed of randomly moving particles that only interact during elastic collisions. Raoult's law describes ideal solutions. Non-ideal solutions show either positive or negative deviations from Raoult's law due to differences in intermolecular forces between solvent-solute and pure components. Positive deviations occur when these interactions are weaker, while negative deviations occur when they are stronger.