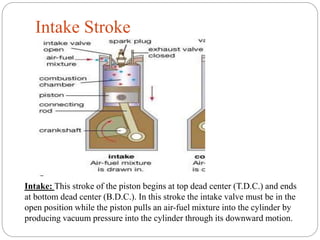
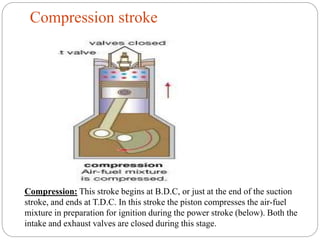
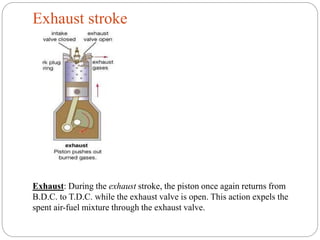
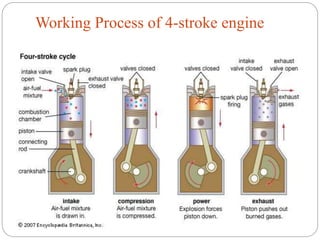
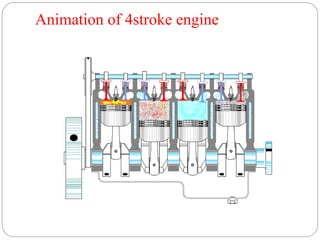
The document discusses internal combustion (IC) engines. It begins by defining a heat engine as a system that converts heat or thermal energy into mechanical energy. It then distinguishes between external combustion engines, where combustion occurs outside the engine, and internal combustion engines, where combustion occurs inside the engine. The document goes on to classify IC engines based on their application, design, operating cycle, and whether they use a four-stroke or two-stroke cycle. It provides examples of each and describes the four strokes of a four-stroke engine: intake, compression, power, and exhaust. Advantages of IC engines are also listed.