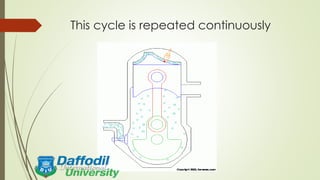
This presentation discusses the two-stroke engine. A two-stroke engine completes the combustion process in one crankshaft revolution, obtaining one power stroke per revolution. It has fewer parts than a four-stroke engine and is lighter in weight. The basic parts are the piston, piston ring, spark plug, connecting rod, and crankshaft. The working principle is that the intake and exhaust are controlled by piston movement, with the fresh charge entering due to pressure differences and being compressed by the pumping action of the piston. Applications include dirt bikes, lawn mowers, outboard engines, and others.