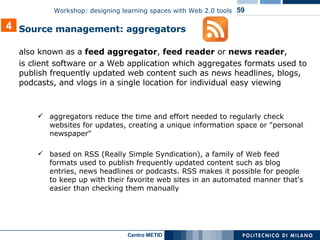
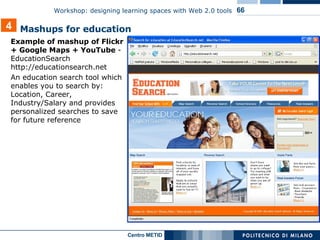
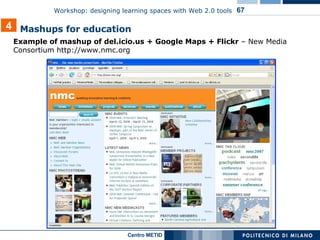
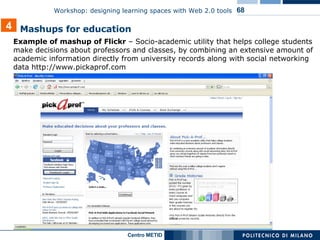
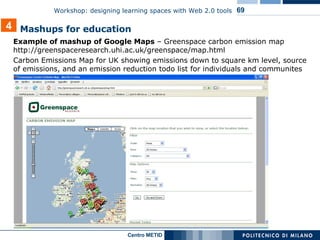
The document describes a workshop on designing learning spaces with Web 2.0 tools. The workshop aims to provide an overview of how Web 2.0 tools can be integrated into formal, non-formal and informal learning environments. The agenda includes case studies of Web 2.0 tool integration, a discussion of various Web 2.0 tools and models of their use in education, and a question and answer session.

![General info Duration: 1h 30 min Contact data: Ada Giannatelli [ada.giannatelli@polimi.it] Simona Azzali [simona.azzali@polimi.it] METID Centre – Politecnico di Milano [http://www.metid.polimi.it] Workshop material available online at http://pipes.yahoo.com/pipes/pipe.info?_id=e427f142893fb773dc60704d5bfa74eb Aim of the workshop: giving an overview of design of Web 2.0 tools for learning environments (education and training, formal and informal learning) totally online, blended, and web-enhanced](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/i-learn-workshop-01-1201863704317321-2/85/I-Learn-Workshop-01-2-320.jpg)






























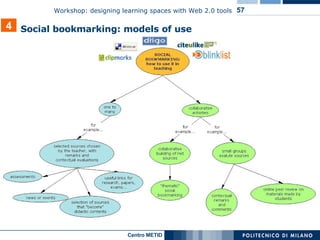
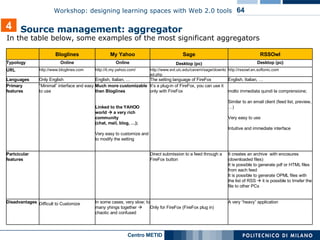
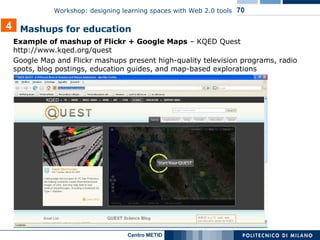
![In the table below, some examples of the most significant social bookmarking 4 Source management: tools saving “clips” as private or public voting clips sending clips by email or posting them in a blog searching by keywords in links, clips, tags or descriptions added by users it is possible to add a comment directly on the tagged pages and to share comments, Highlights and Sticky-Notes More “social” and intaractive then delicious: groups can modify remarks and notes from Diigo or directy on the clipped website Private or public bookmarks It is possible to share bookmarks as a list, in blogs, by email or feed Tags can be stored in folders Public or private bookmarks it is possible to share bookmarks Bundle tags: to group together several tags Tagrolls: to show my own tags on my own blog/website Links for you: to suggest links to other people from your network Other features People all over the world can clip the best parts of web pages (few sentences, images or videos) instead of the entire web page "Social Annotation": it is possible to the save a link with some remarks or highlighting only some part of the page (Highlight).. It is possible to insert Sticky-Note e tagging videos, images (Clip) or other multimedia elements. Created in 2003 First social bookmarking application The Most used instrument In 2005, bought by Yahoo! Del.icio.us Guide for Educators [http://pedersondesigns.com/2006/11/24/delicious-guide-for-educators-part-1-tools-tagging/] Primary features http://www.clipmarks.com/ http://www.diigo.com/ http://del.icio.us/ URL Clipmarks Diigo del.icio.us](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/i-learn-workshop-01-1201863704317321-2/85/I-Learn-Workshop-01-58-320.jpg)