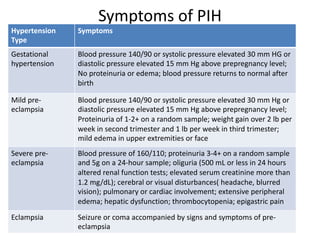
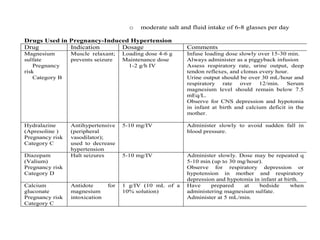
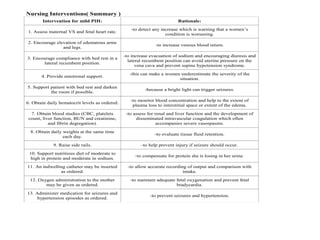
This document discusses hypertension during pregnancy. It begins by defining high blood pressure and the different types of hypertension that can occur during pregnancy, including chronic hypertension, gestational hypertension, and preeclampsia. Mothers with hypertension during pregnancy are at higher risk for complications. The document then covers risk factors, symptoms, diagnostics, potential complications, treatment including medications like magnesium sulfate, and nursing considerations for managing hypertension during pregnancy.