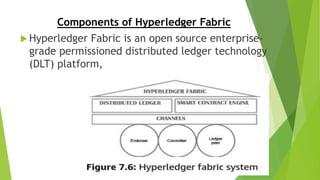
Hyperledger is an open source project from the Linux Foundation that develops blockchain frameworks. It includes distributed ledger projects like Fabric and Sawtooth, as well as libraries, tools, and domain-specific projects. Hyperledger Fabric is an enterprise-grade distributed ledger that uses smart contracts in common programming languages. It has a permissioned network where participants are known and authenticated through a membership service provider. Identity services manage member identities and roles to control access privileges on the network.














![ [First is identity, that provides authorization,
identification, and authentication services under
membership services.
It defines which CA is trusted to define members in
the network
It not only defines who can be on the network but
also defines their roles and sets access privileges to
each member of the network so as to who can
access what inside the network.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hyperledgerfabric-240208140700-5cc4c2ff/85/HYPERLEDGER-FABRIC-pptx-16-320.jpg)