The document discusses unit testing and mocking in Python, emphasizing the importance of automated tests and code coverage for ensuring software correctness. It covers various aspects of writing unit tests, integrating testing within CI pipelines, and the use of the unittest.mock library to simulate behavior of real objects. Additionally, it highlights common scenarios for utilizing mock objects to avoid side effects during testing and provides code examples demonstrating these practices.






![unit testsmatlib.py:
def div(dividend, divisor):
if divisor != 0:
result = dividend / divisor
else:
print('not defined')
result = float('NaN')
return result
$ pytest -v
collected 1 item
test_div.py::test_div PASSED [100%]
=== 1 passed in 0.01 seconds =====================================](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/howtofakeproperly-190508174755/75/How-to-fake_properly-7-2048.jpg)

![code coverage
$ pytest --cov -v
collected 1 item
test_matlib.py::test_div PASSED [100%]
----------- coverage: platform linux, python 3.7.2-final-0 -----------
Name Stmts Miss Cover
------------------------------------
matlib.py 6 2 67%
test_matlib.py 4 0 100%
------------------------------------
TOTAL 10 2 80%
========== 1 passed in 0.03 seconds =====](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/howtofakeproperly-190508174755/75/How-to-fake_properly-9-2048.jpg)

![code coverage
testmatlib.py:
import math
from matlib import div
def test_div():
assert div(4,2) == 2
def test_div_by_zero():
assert math.isnan(div(4,0))
$ pytest --cov -v
collected 2 items
test_matlib.py::test_div PASSED [ 50%]
test_matlib.py::test_div_by_zero PASSED [100%]
----------- coverage: platform linux, python 3.6.6-final-0 -----------
Name Stmts Miss Cover
------------------------------------
matlib.py 6 0 100%
test_matlib.py 6 0 100%
------------------------------------
TOTAL 12 0 100%](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/howtofakeproperly-190508174755/75/How-to-fake_properly-11-2048.jpg)







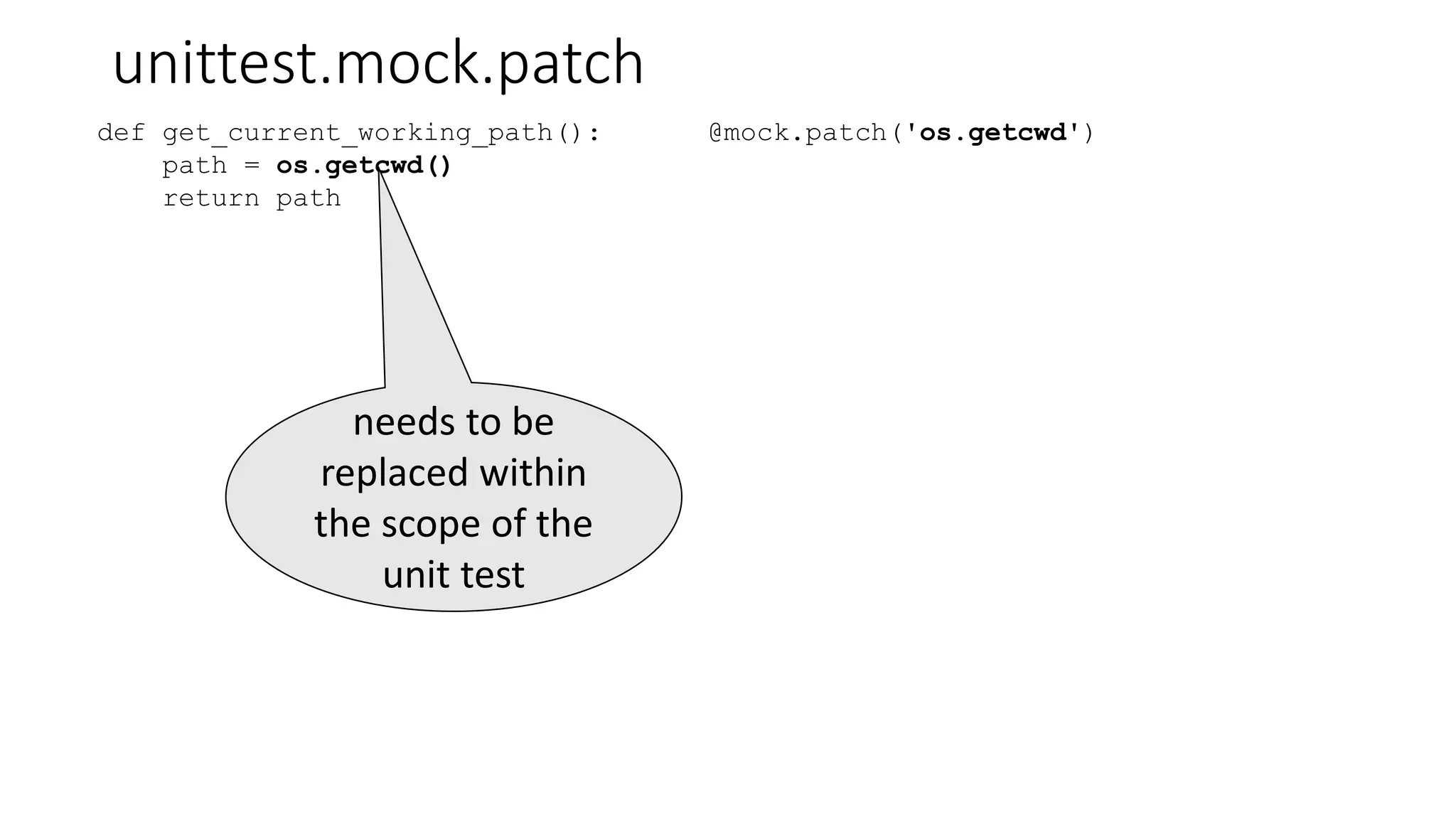

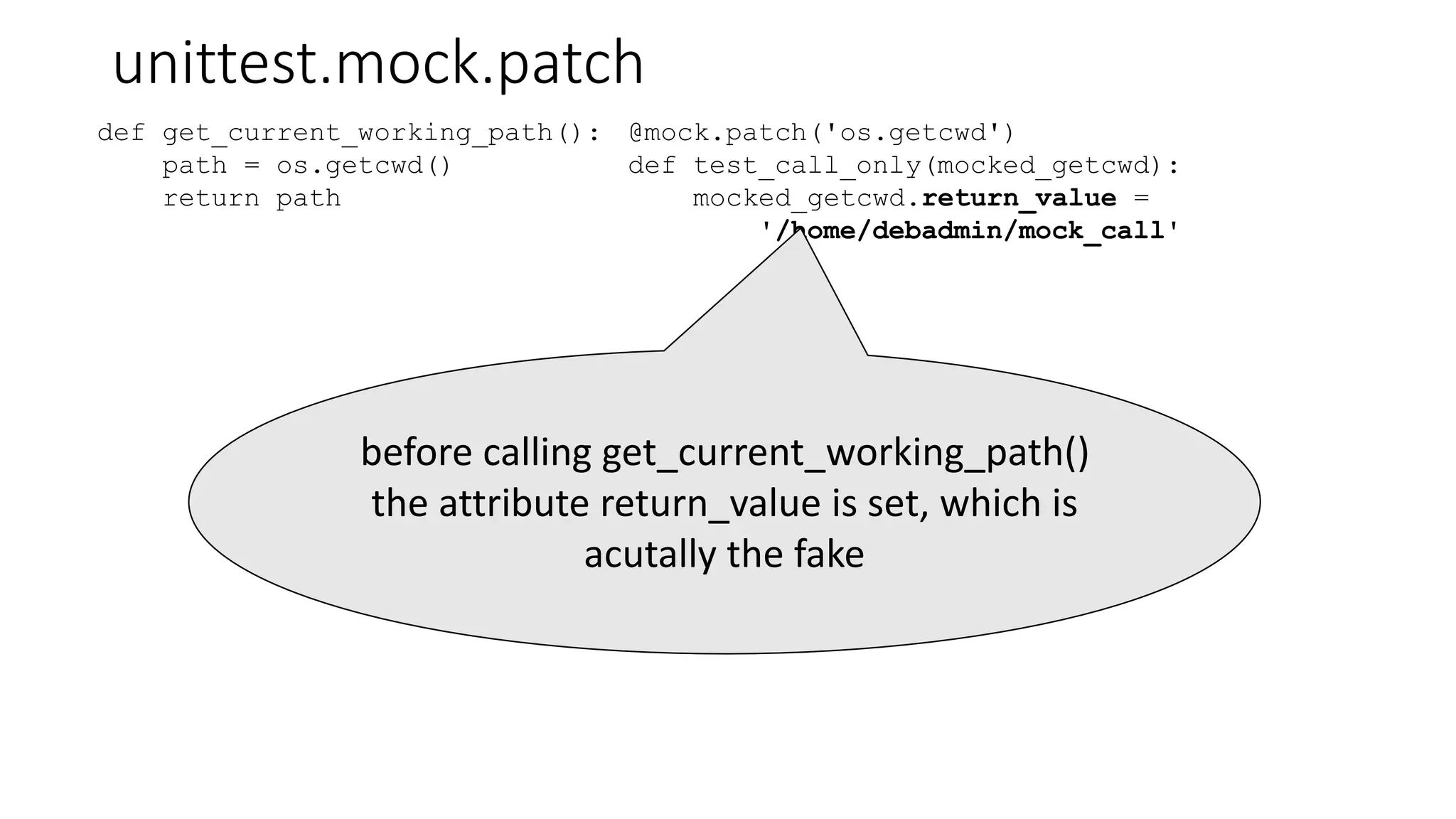





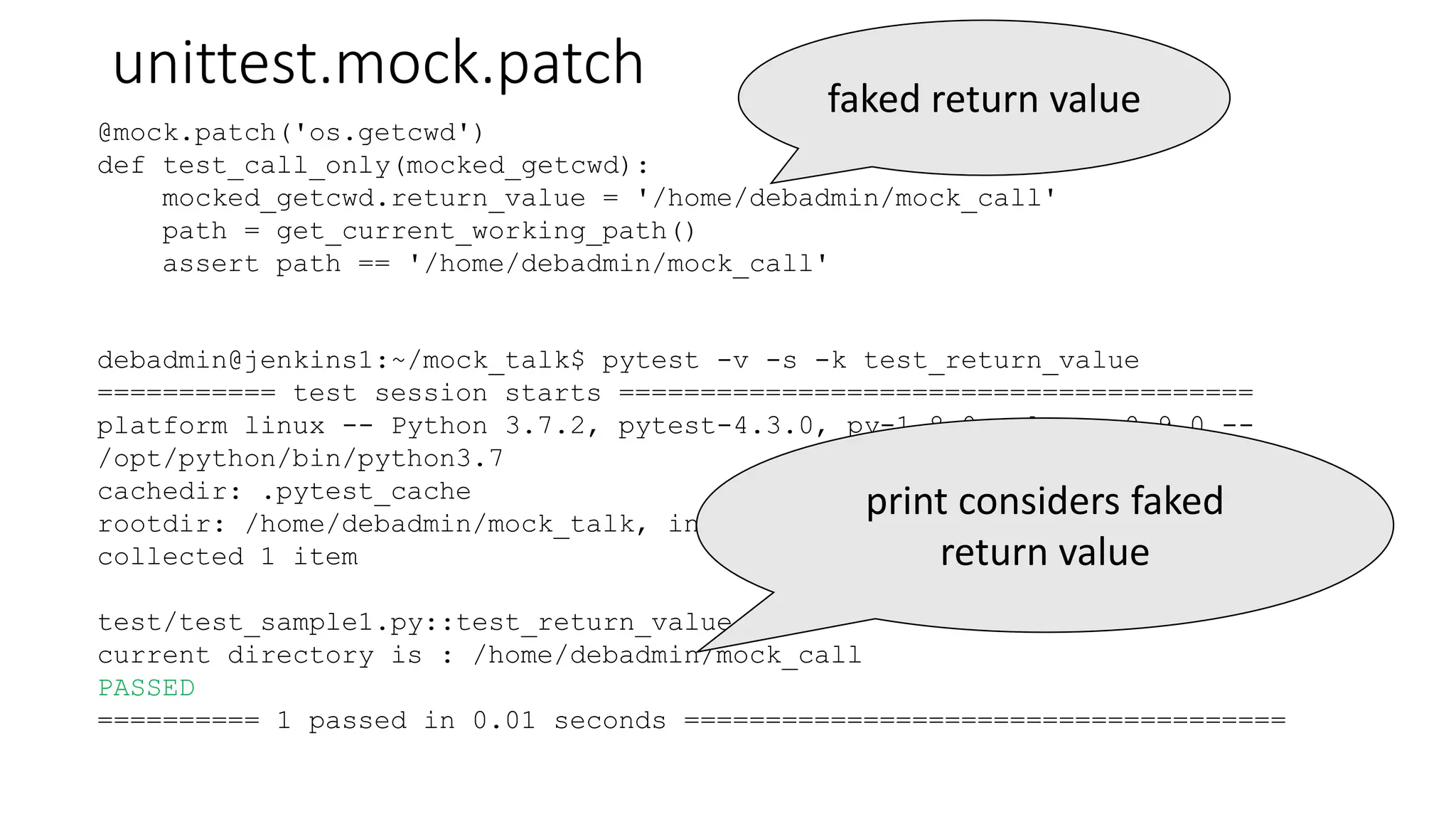
![unittest.mock.patch
>>> from unittest import mock
>>> with mock.patch('os.getcwd') as mocked_getcwd:
... dir(mocked_getcwd)
...
mocking out os.getcwd by
means of an context
manager
possible assertions about
mock object usage
['assert_any_call', 'assert_called', 'assert_called_once',
'assert_called_once_with', 'assert_called_with', 'assert_has_calls',
'assert_not_called', 'attach_mock', 'call_args', 'call_args_list',
'call_count', 'called', 'configure_mock', 'method_calls',
'mock_add_spec', 'mock_calls', 'reset_mock', 'return_value',
'side_effect']
>>>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/howtofakeproperly-190508174755/75/How-to-fake_properly-27-2048.jpg)

![unittest.mock.patch
@mock.patch('subprocess.check_call')
def test_stop_database(self, mock_check_call):
fb = Flashback(
restore_point_name='TEST1',
oracle_home='/opt/oracle/product/12.1.0.2.180417/db_test',
oracle_sid='TTEST1'
)
fb._stop_database()
mock_check_call.assert_called_with(
['/opt/oracle/product/12.1.0.2.180417/db_test/bin/srvctl',
'stop',
'database',
'-d',
'TTEST_XD0104',
]
def _stop_database(self):
LOG.info('stopping database %s ...', self.db_unique_name)
subprocess.check_call(
[self.srvctl_command, 'stop', 'database', '-d', self.db_unique_name]
)
srvctl deals with stopping
a cluster database, which
is not available for the
test system
testing the srvctl command is
out of scope, however,
determining that is has been
called with appropriate
parameters is of interest](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/howtofakeproperly-190508174755/75/How-to-fake_properly-30-2048.jpg)

![references
• Kent B. (1999). Extreme Programming. Addison-Wesley.
• unittest.mock – mock object library. [online] Available at:
https://docs.python.org/3/library/unittest.mock.html
• What the mock? – A cheatsheet for mocking in Pyhton. [online] Available at:
https://medium.com/@yeraydiazdiaz/what-the-mock-cheatsheet-mocking-in-
python-6a71db997832](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/howtofakeproperly-190508174755/75/How-to-fake_properly-32-2048.jpg)

