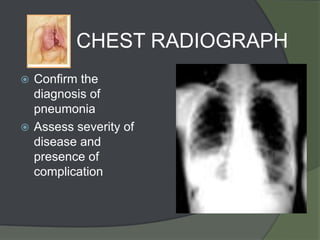
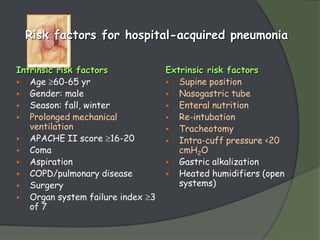
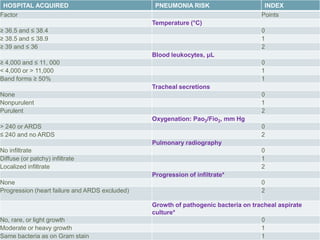
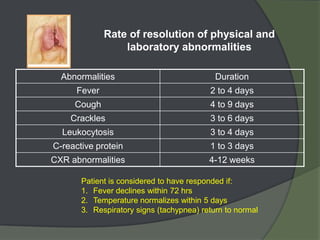
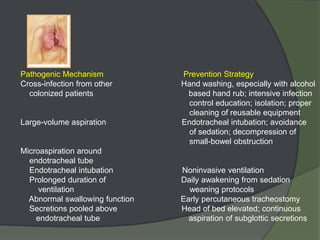
This document discusses hospital acquired pneumonia (HAP). It defines HAP as pneumonia occurring 48 hours or more after admission. It notes HAP is the second most common hospital infection and has high mortality and increased treatment costs. Risk factors include mechanical ventilation, underlying diseases, and factors compromising defenses. Common causes are gram-negative bacteria from oropharyngeal secretions. Diagnosis involves tests of sputum, blood and imaging. Empiric antibiotic treatment depends on risk of multidrug-resistant pathogens.