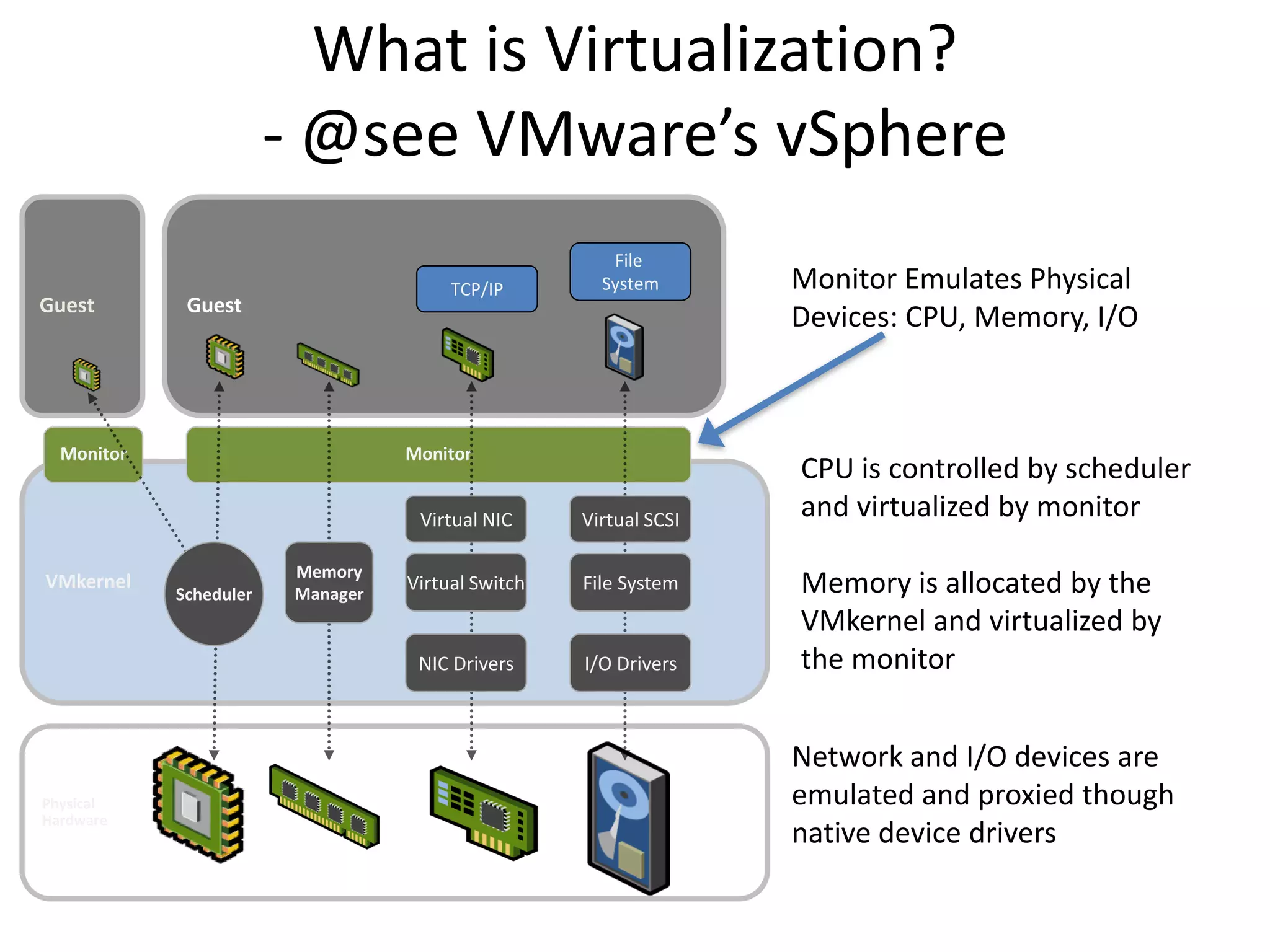
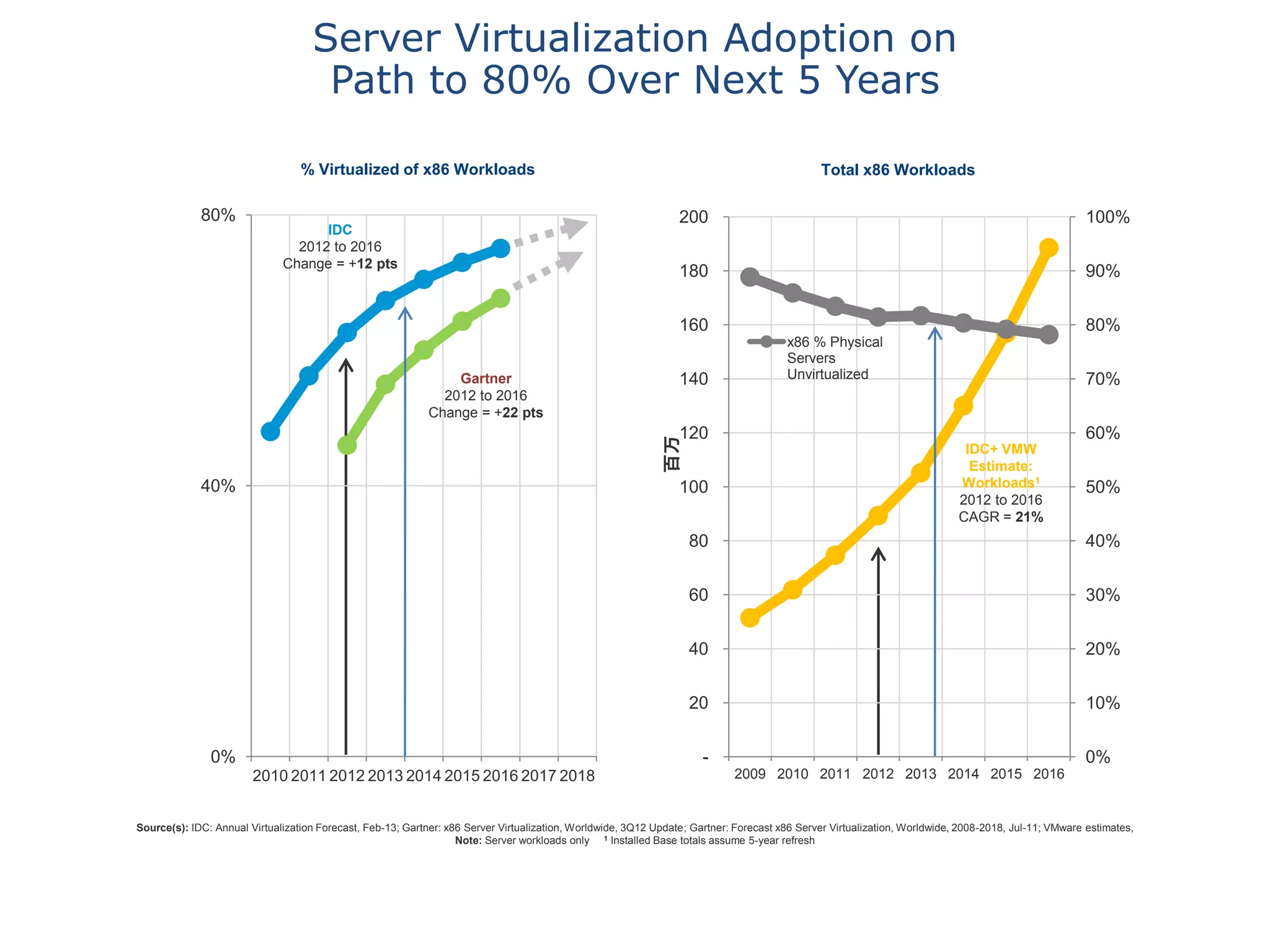
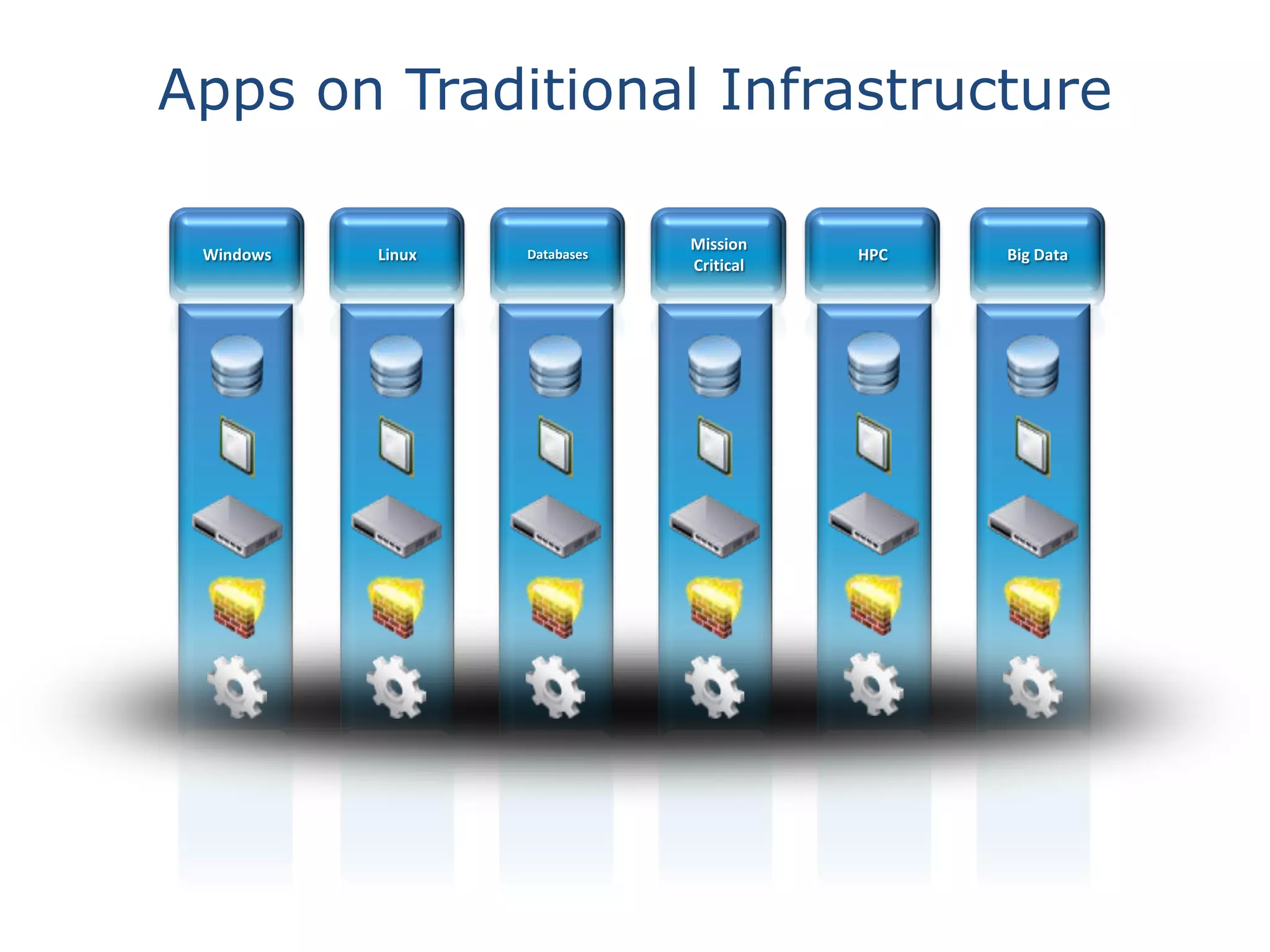
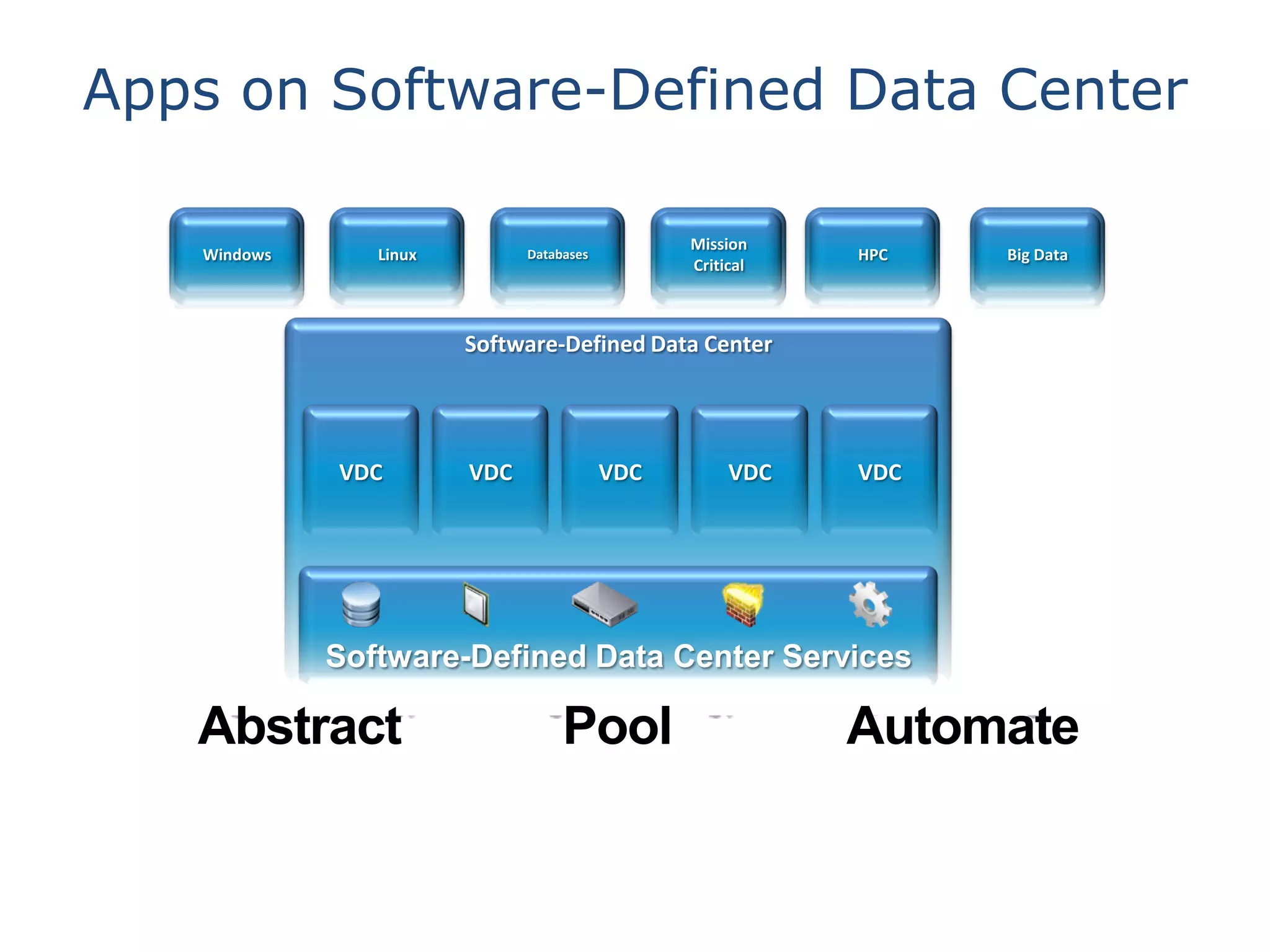
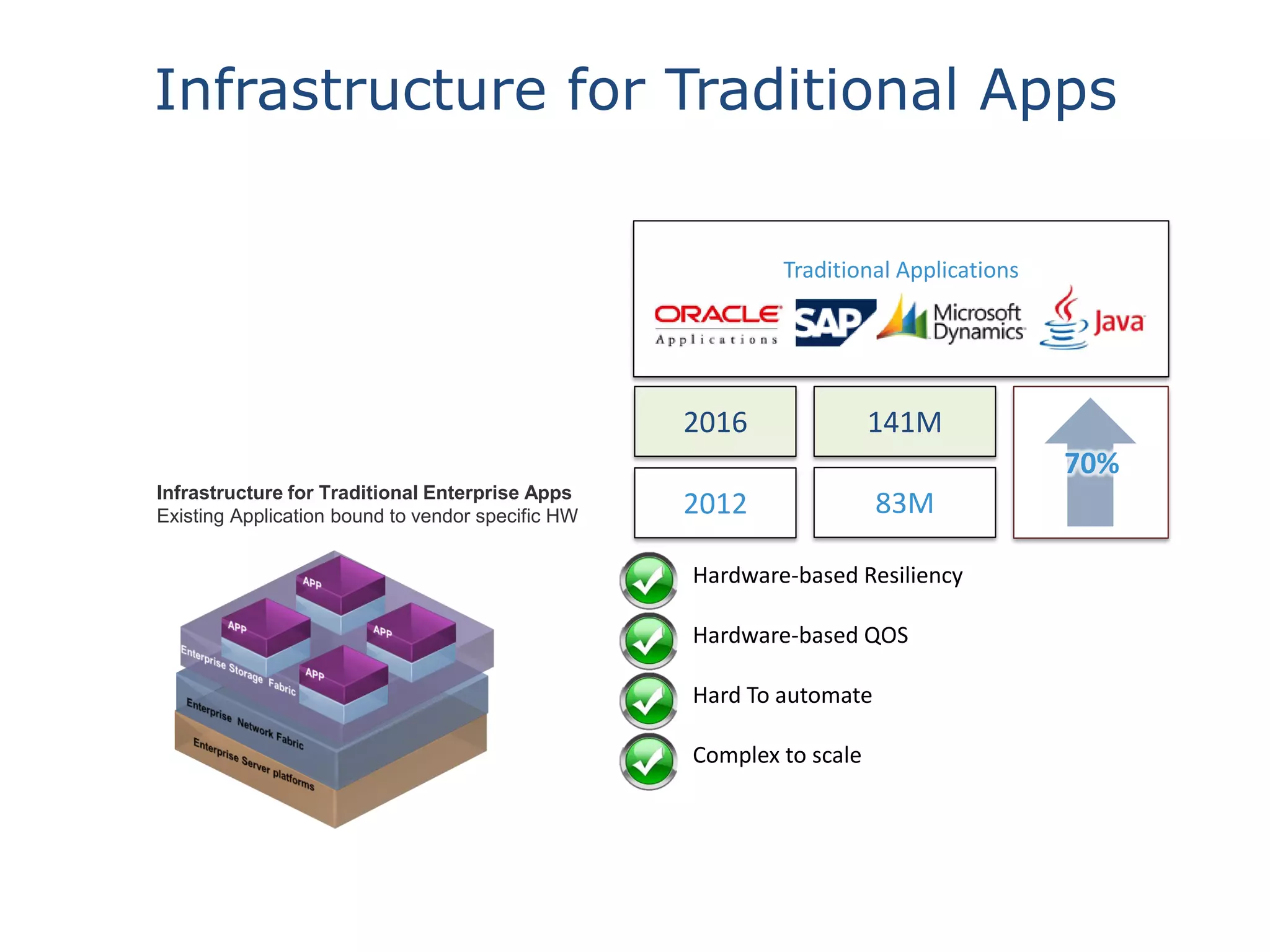
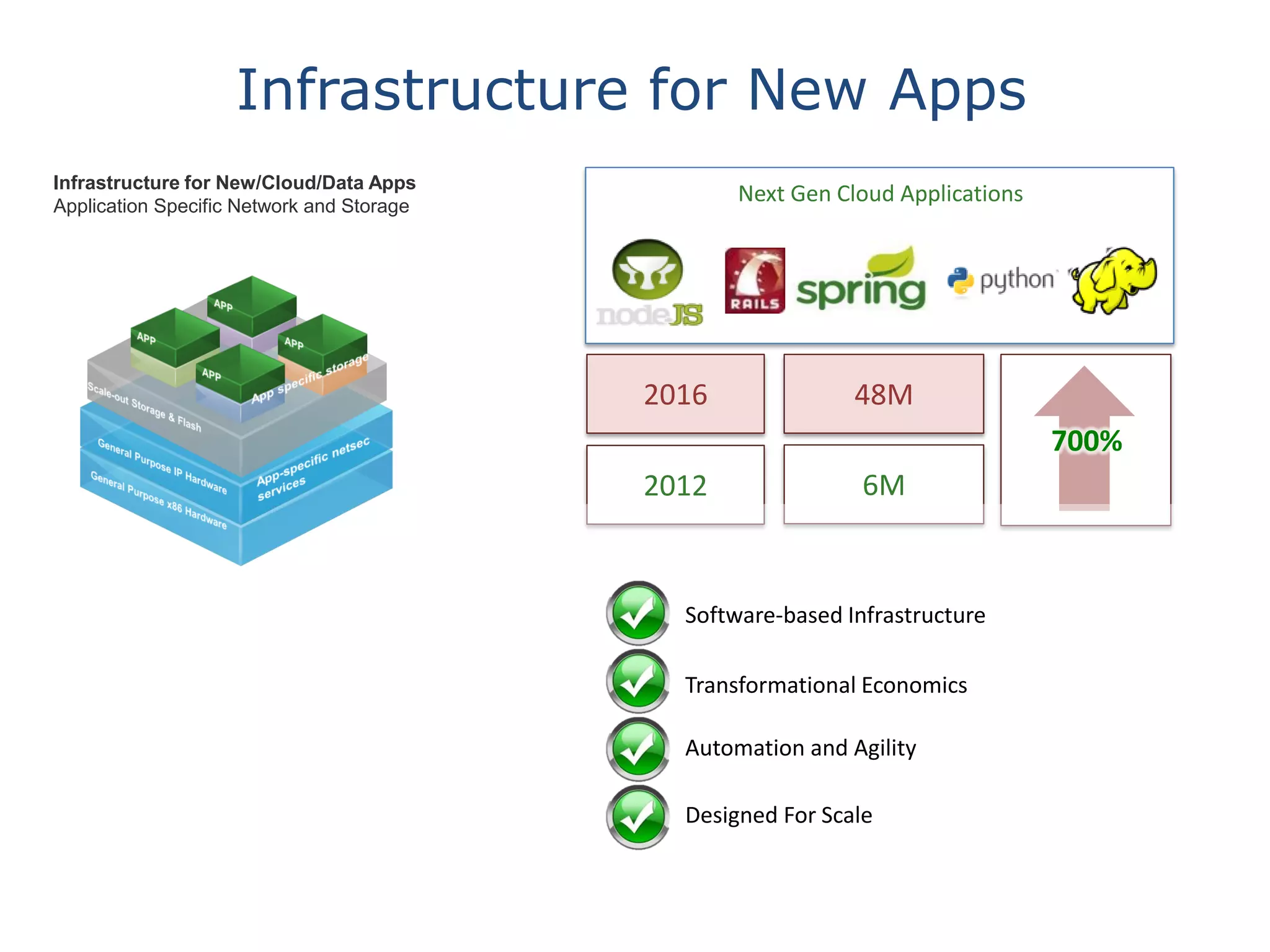
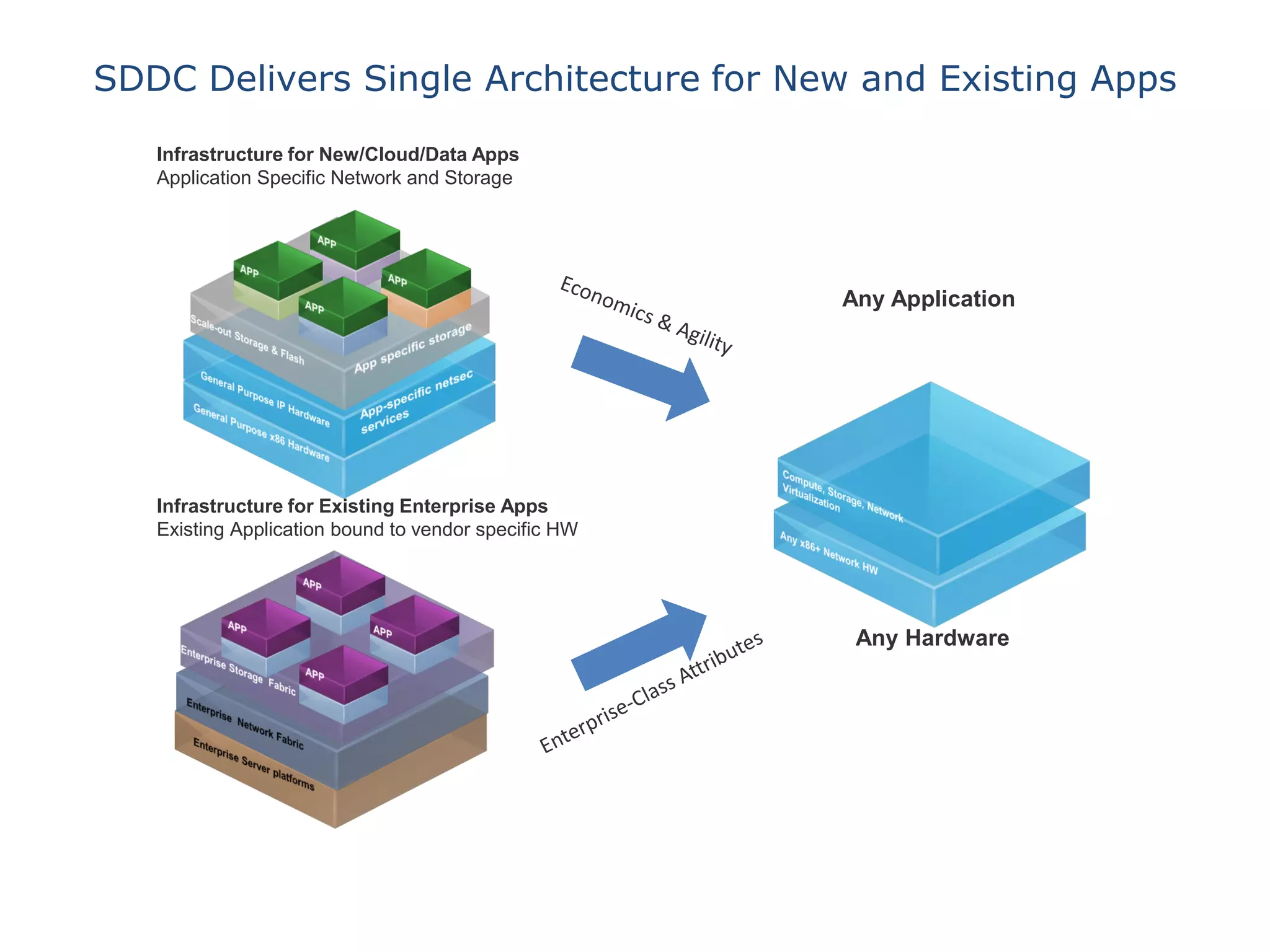
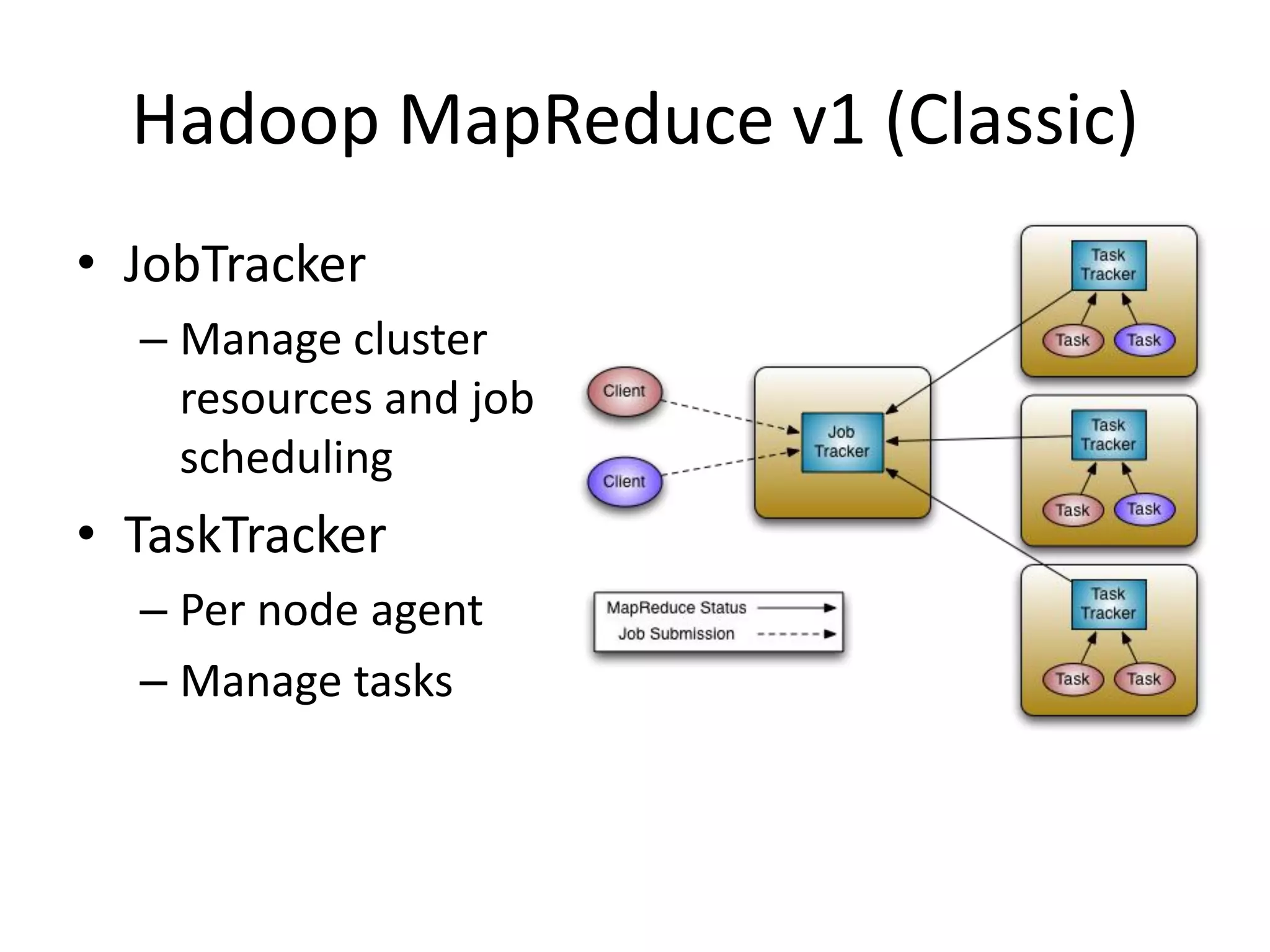
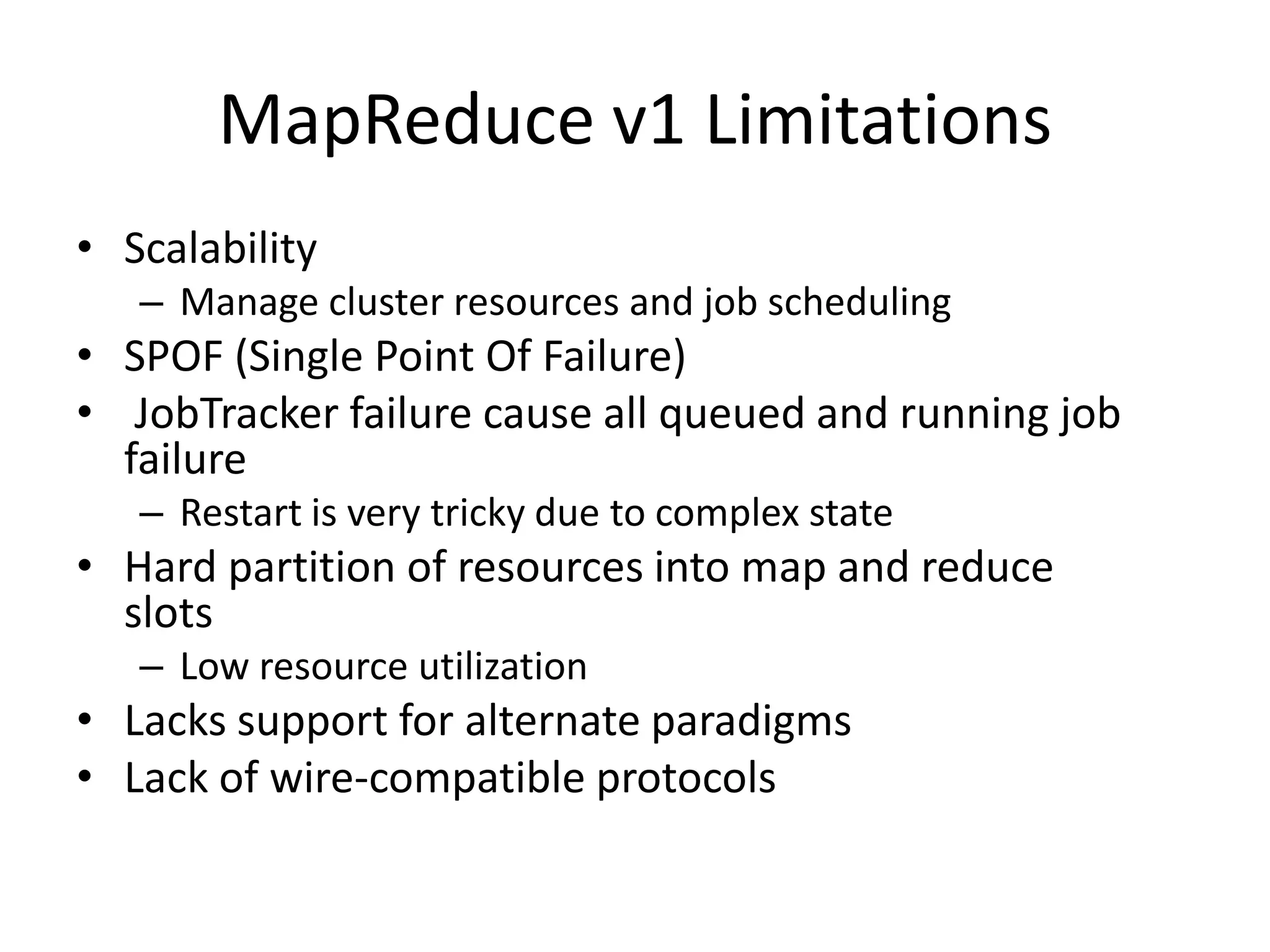
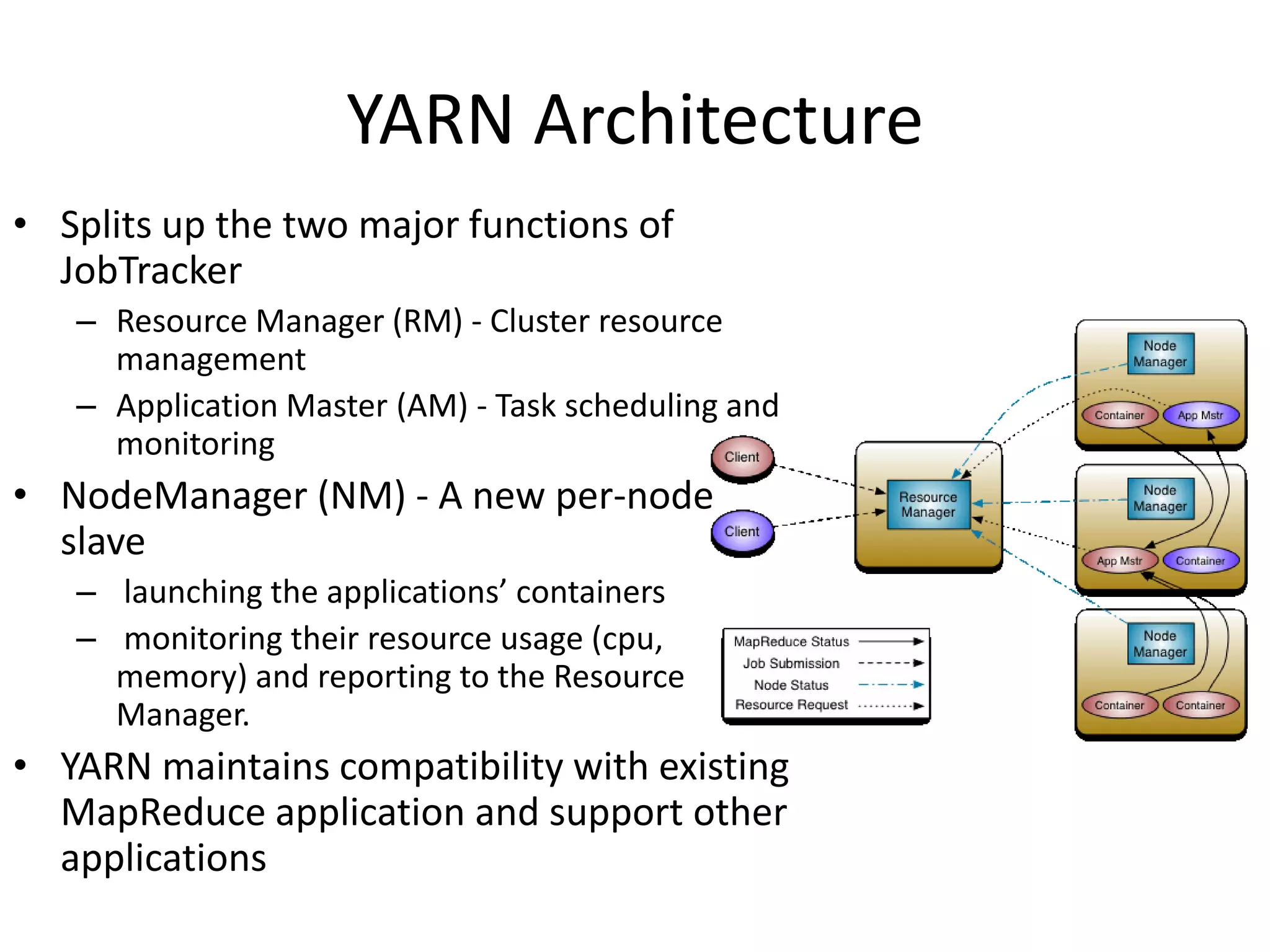
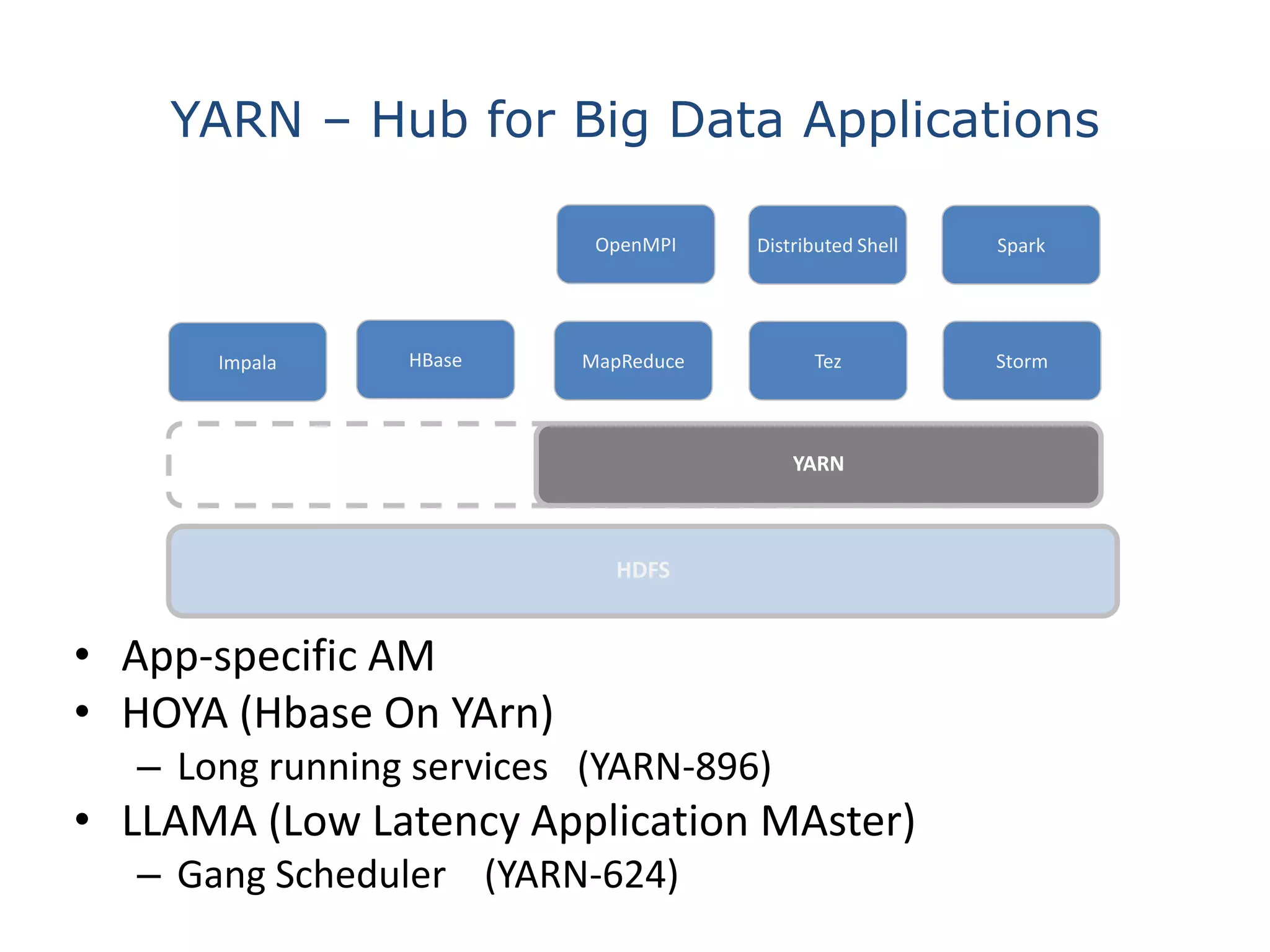
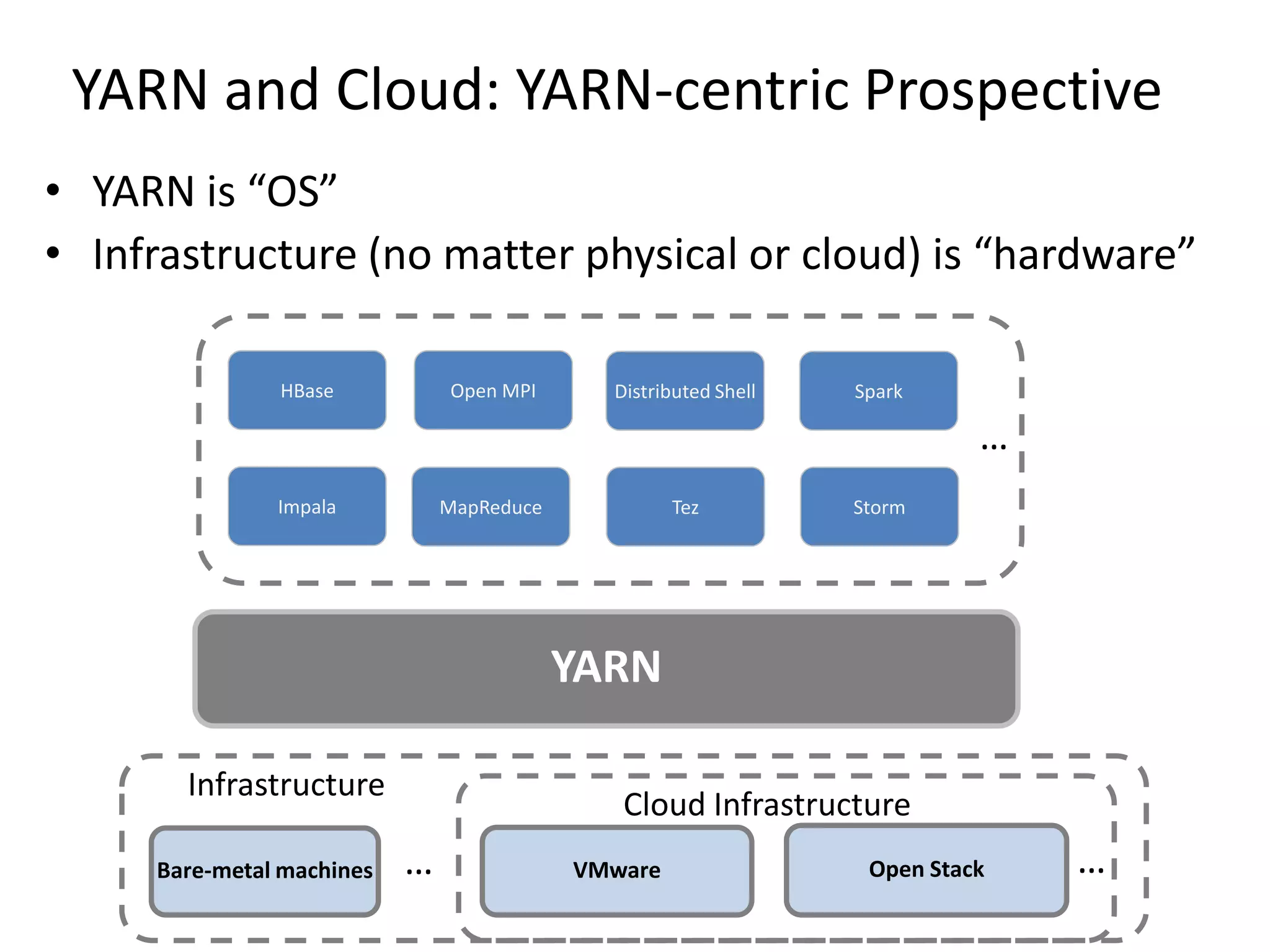
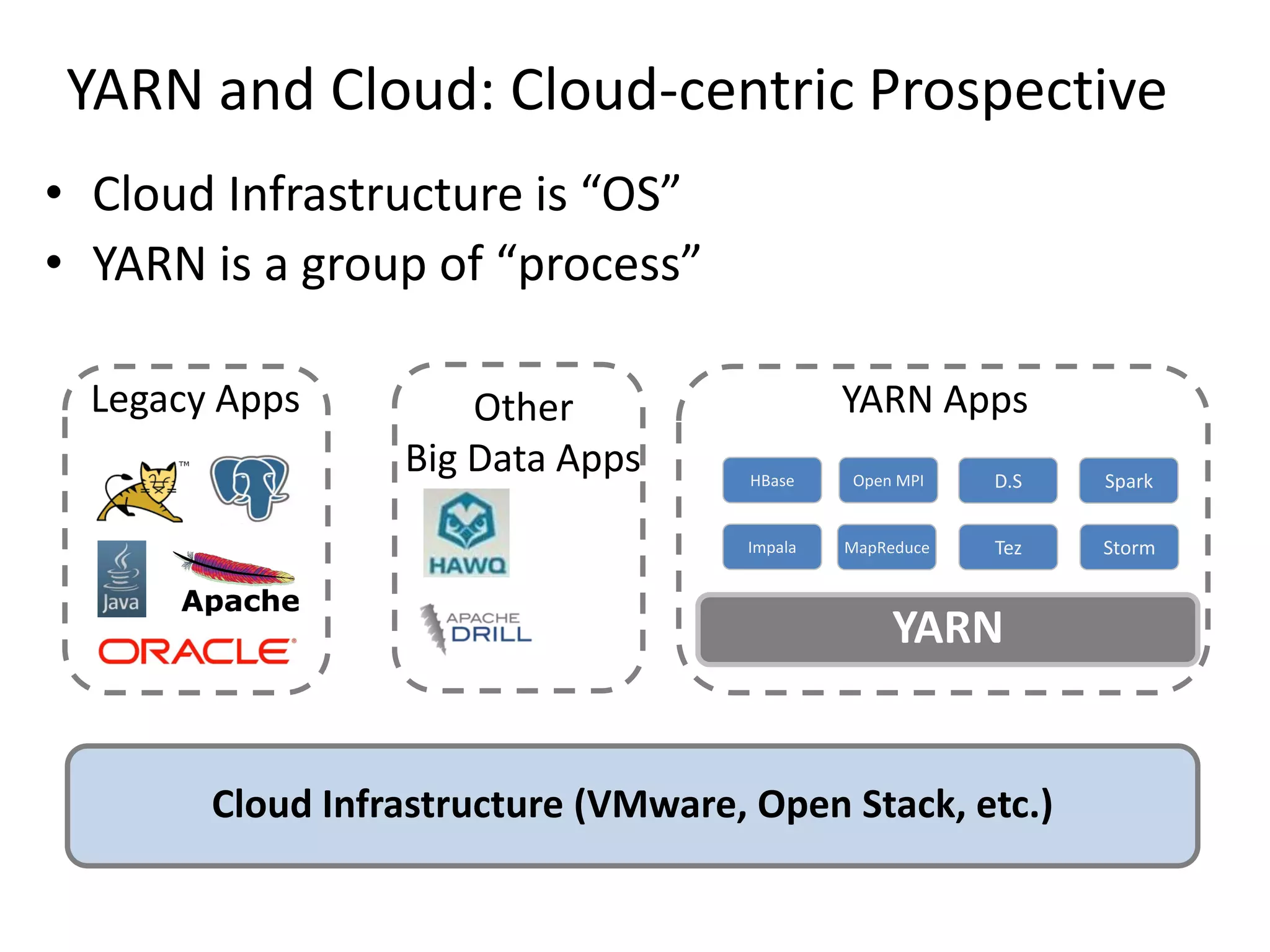
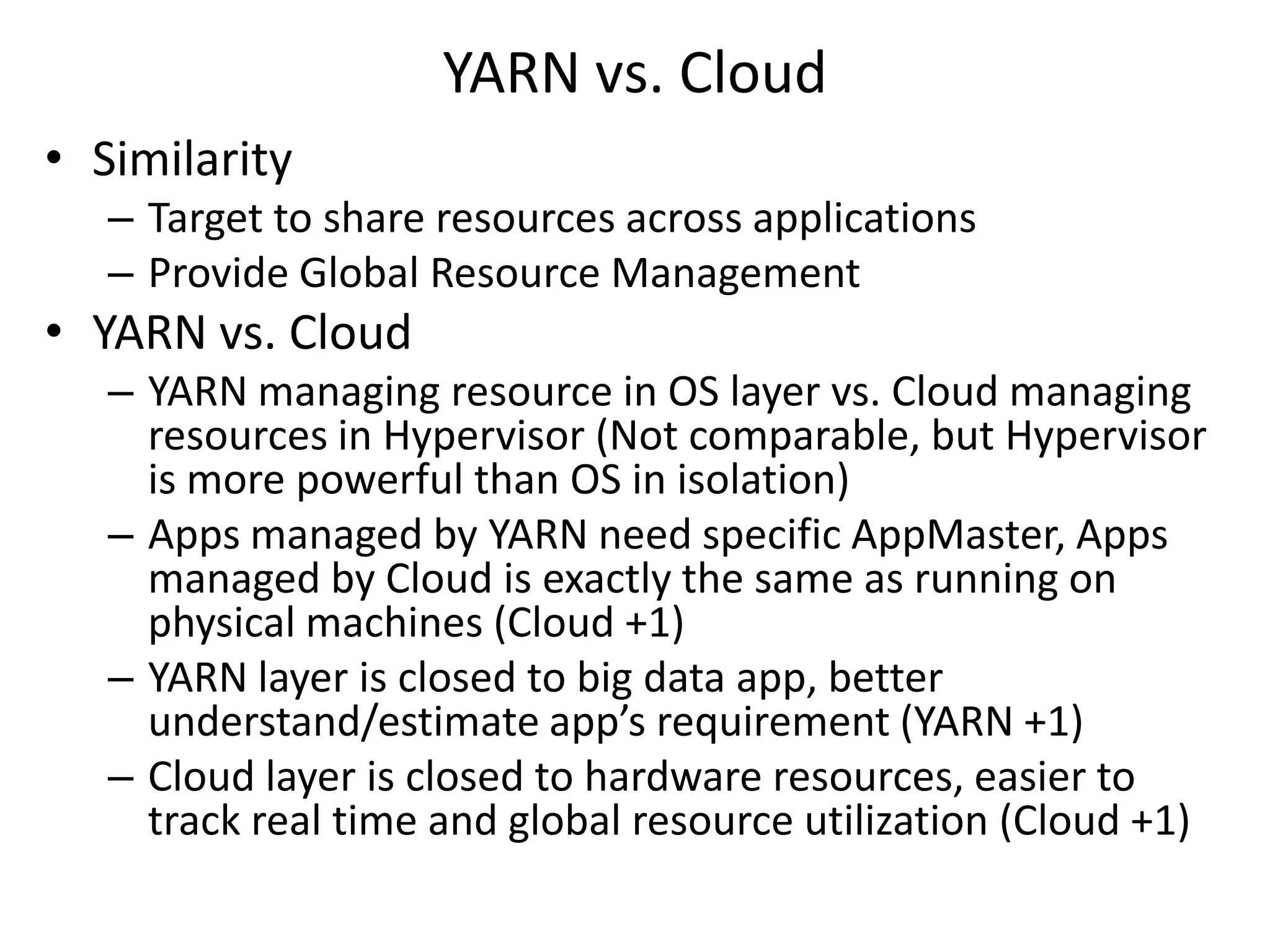
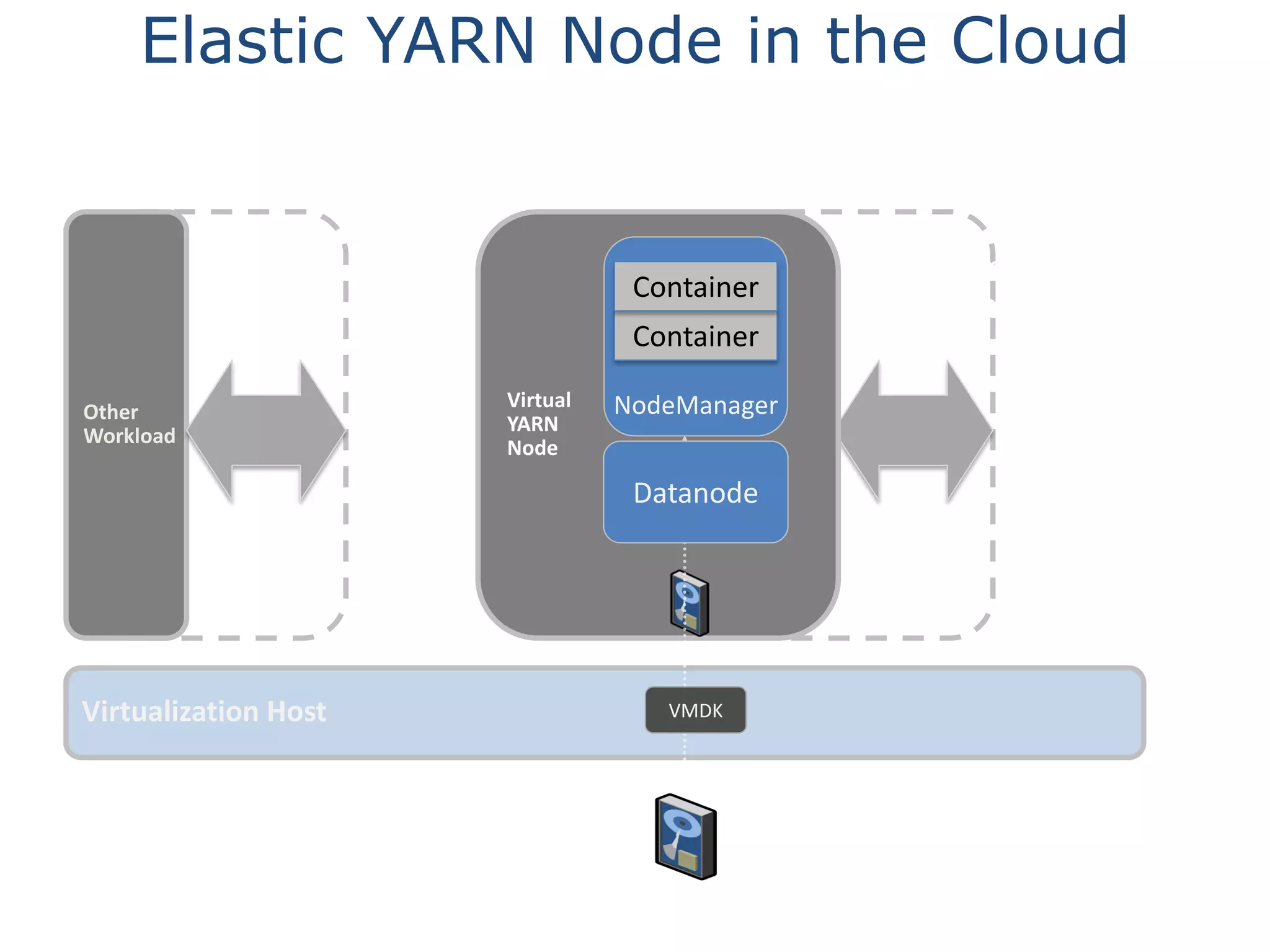
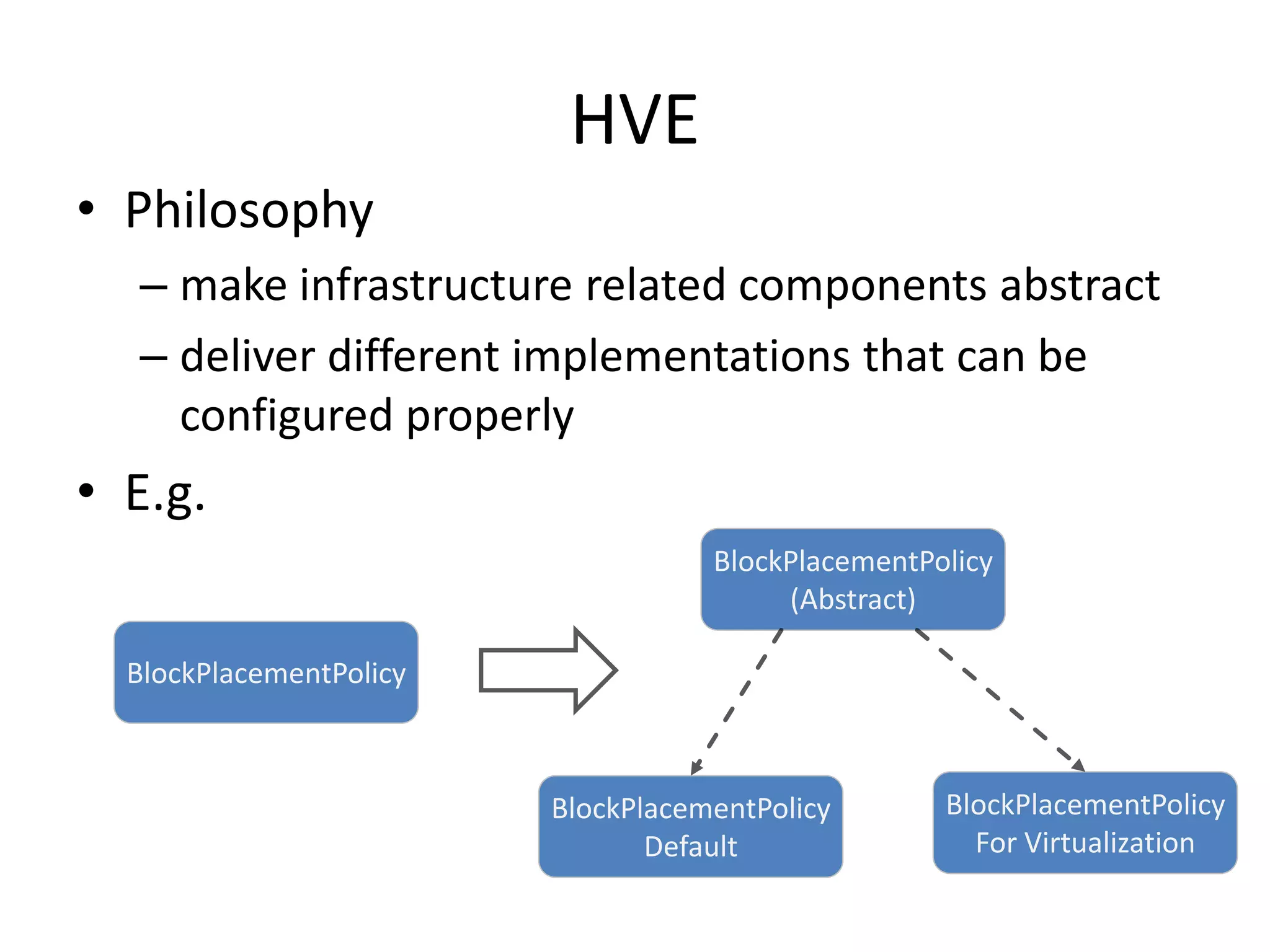
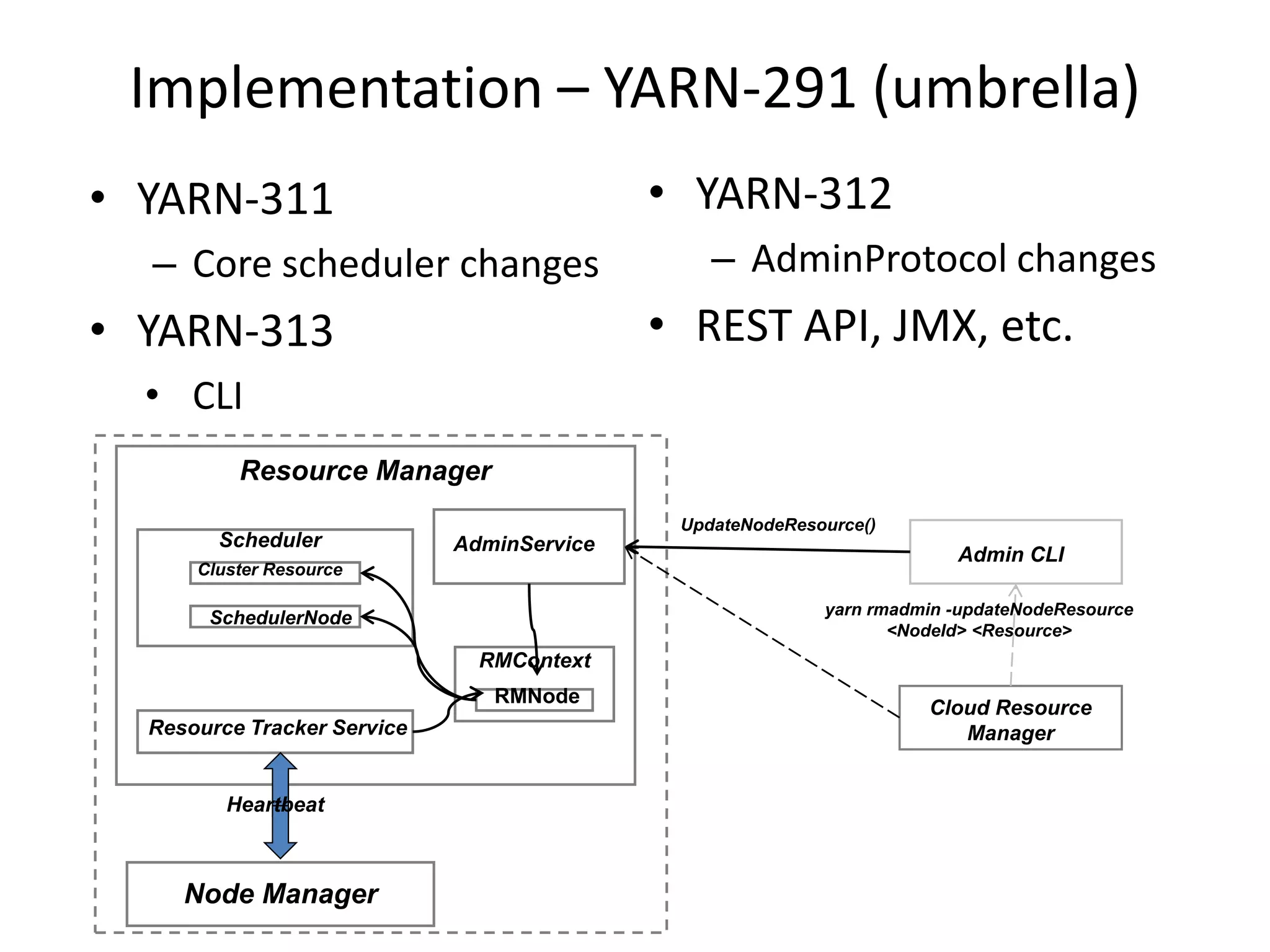
This document discusses big data in the cloud and provides an overview of YARN. It begins with introducing the speaker and their experience with VMware and Apache Hadoop. The rest of the document covers: 1) trends in big data like the rise of YARN, faster query engines, and focus on enterprise capabilities, 2) how YARN addresses limitations of MapReduce by splitting responsibilities, 3) how YARN serves as a hub for various big data applications, and 4) how YARN can integrate with cloud infrastructure for elastic resource management between the two frameworks. The document advocates for open source contribution to help advance big data technologies.