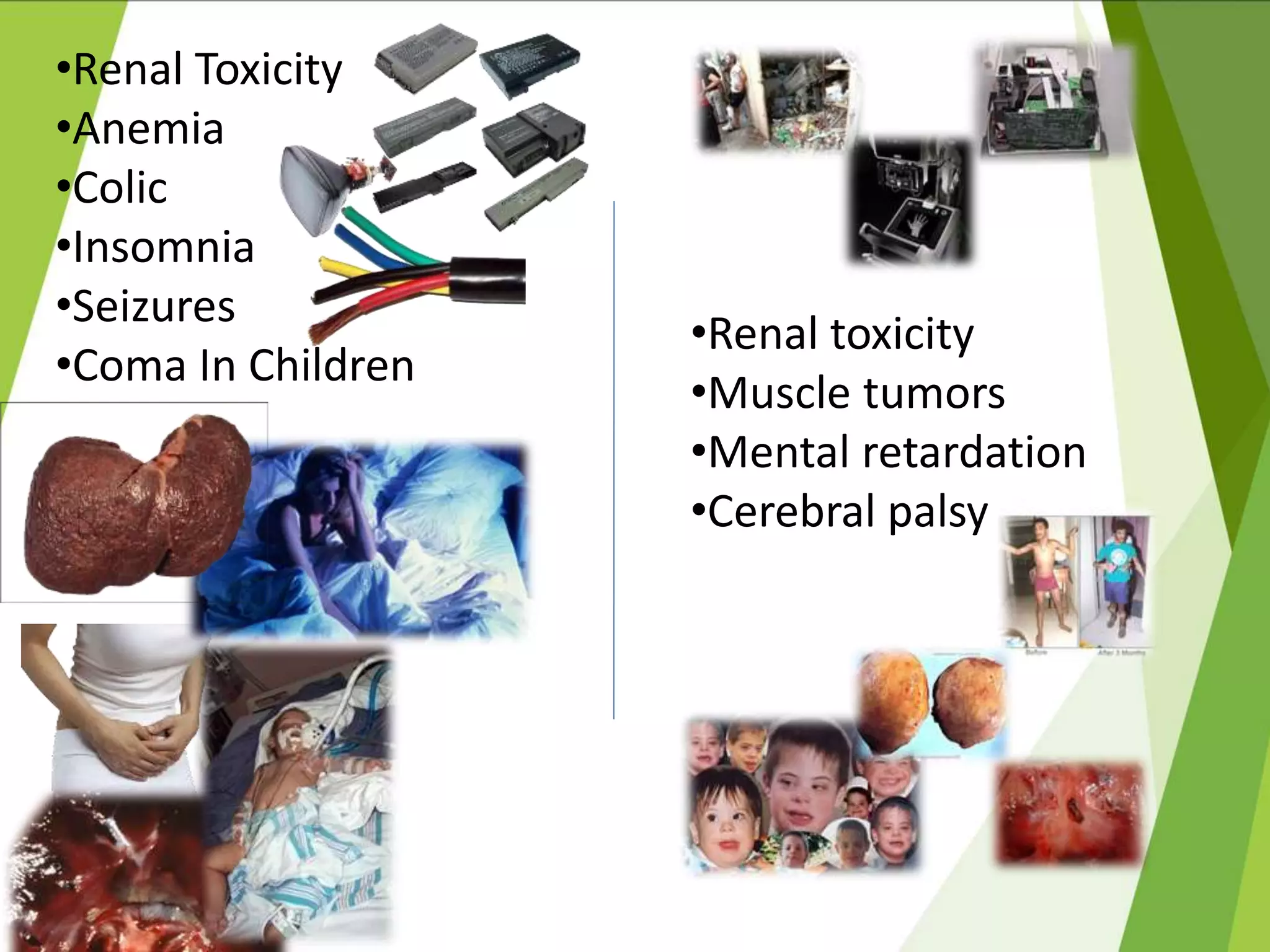
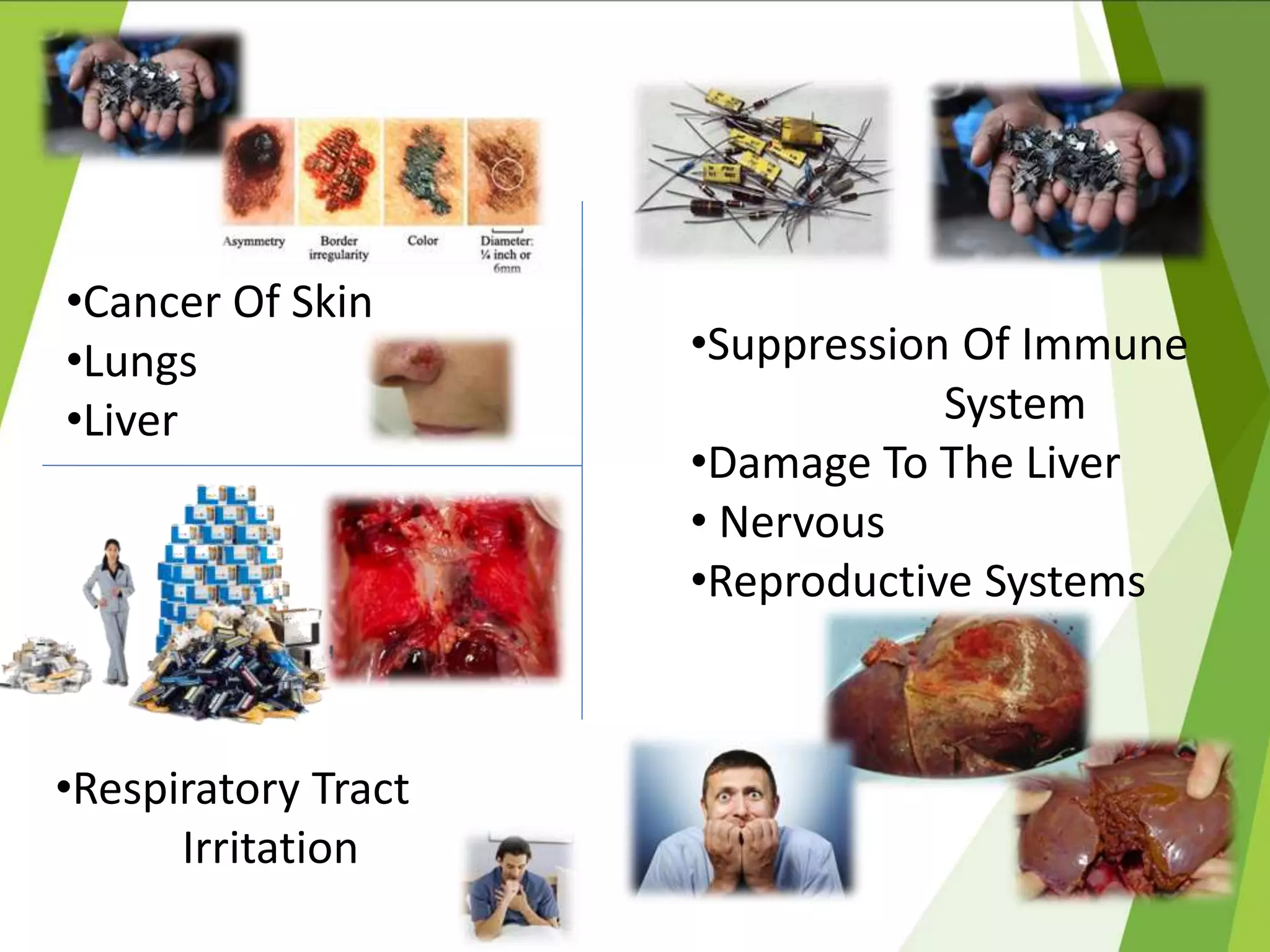
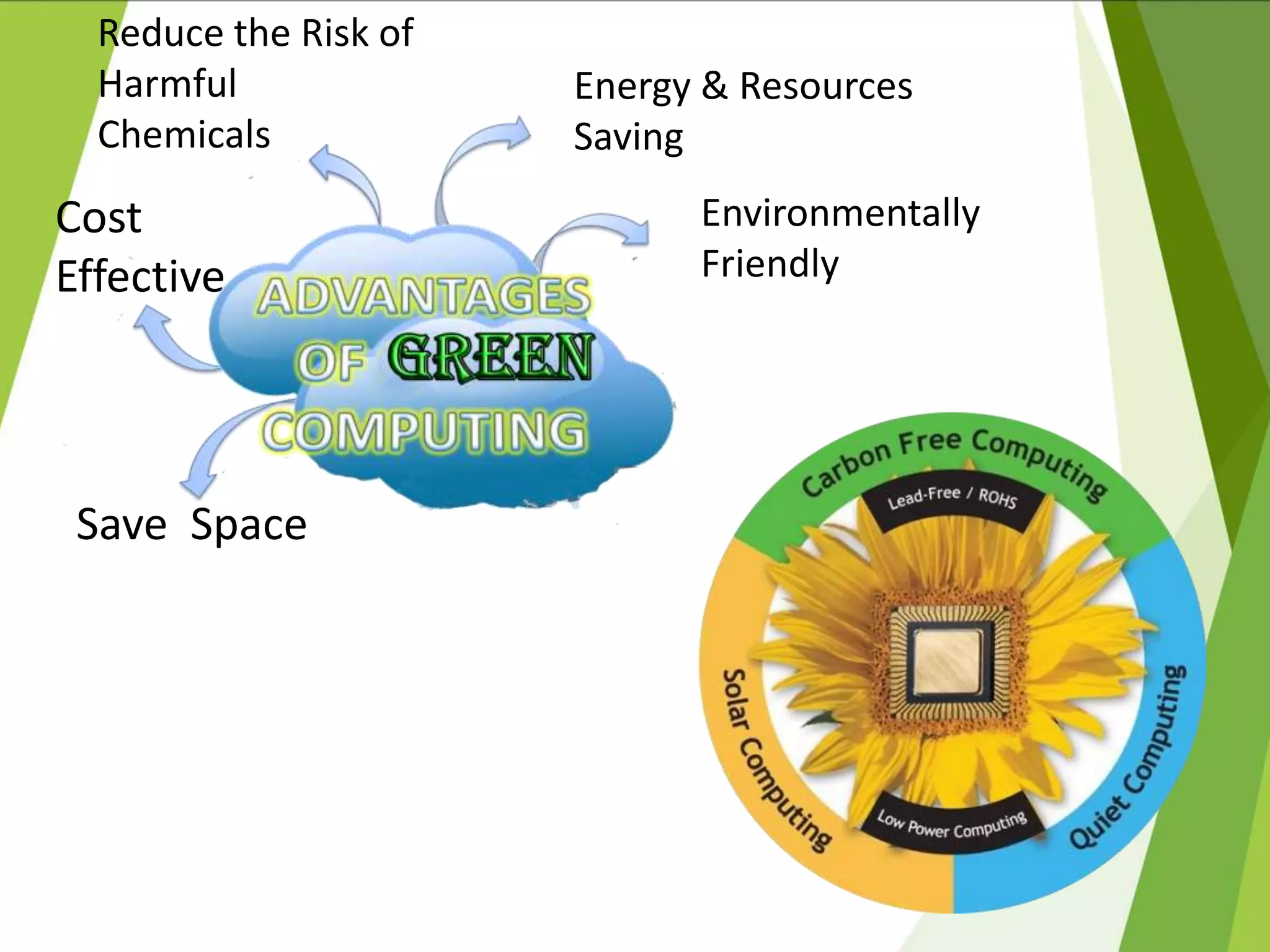
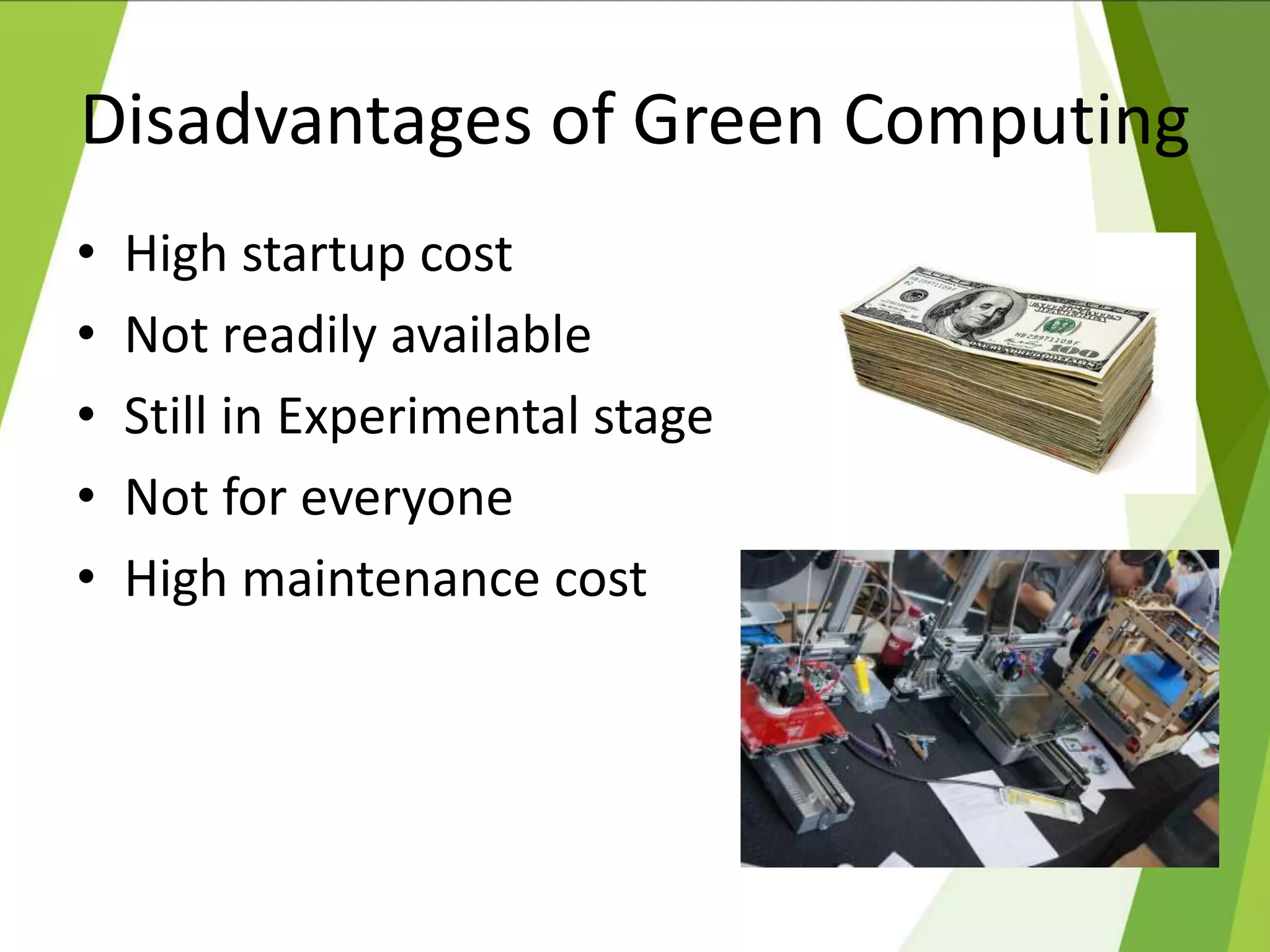
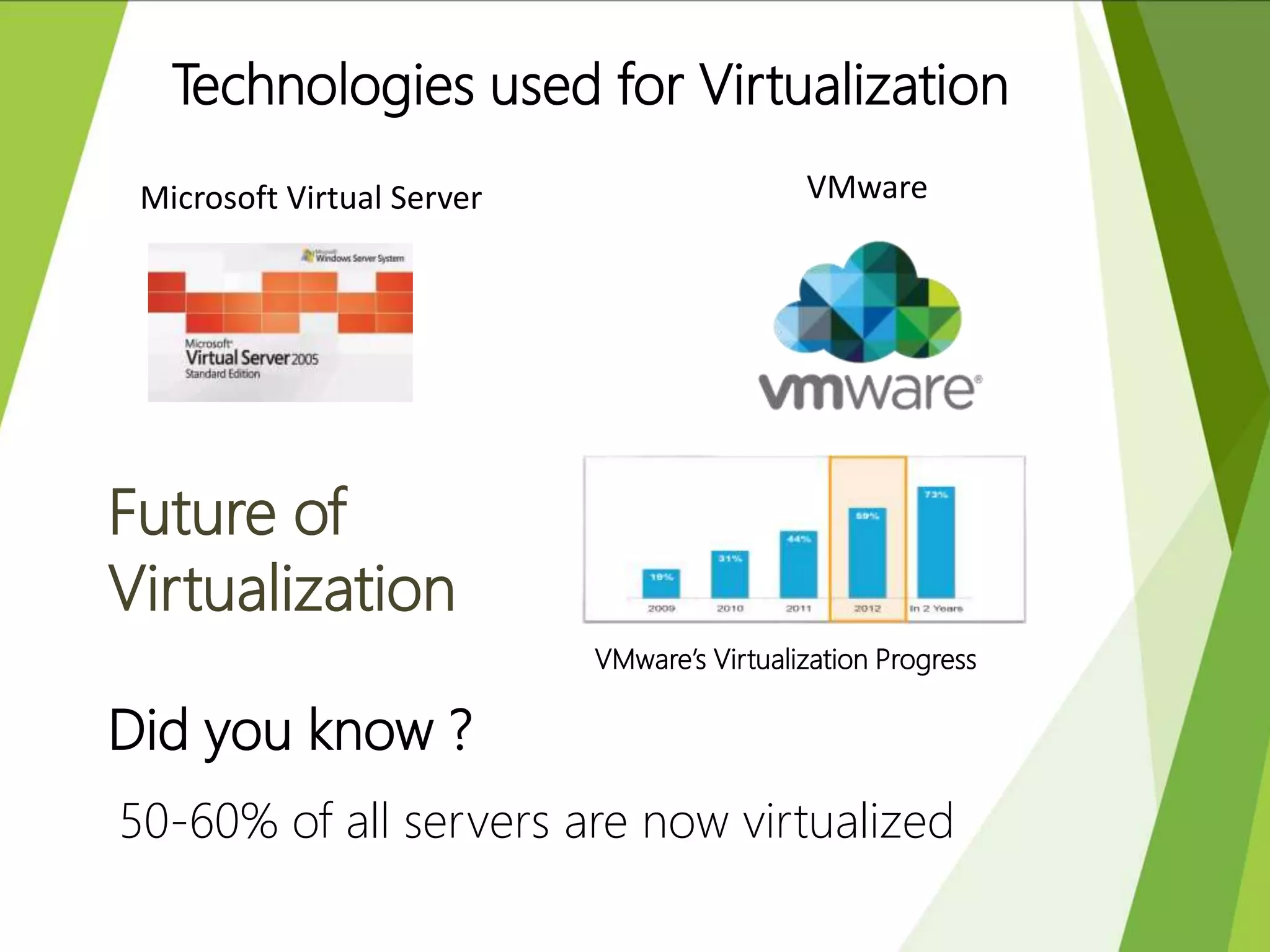
This document discusses green computing, including its origins, advantages, and pathways. It began in 1992 with Energy Star, which promoted energy efficiency. Green computing aims to reduce environmental impacts and costs through energy efficiency, reducing waste, and recycling electronics. It allows cost savings, uses less resources, and lessens health risks from toxic materials. Sri Lanka has e-waste collection centers and standards to minimize impacts. The future of green computing involves virtualization, more energy savings, eco-friendly materials, and increased recycling.