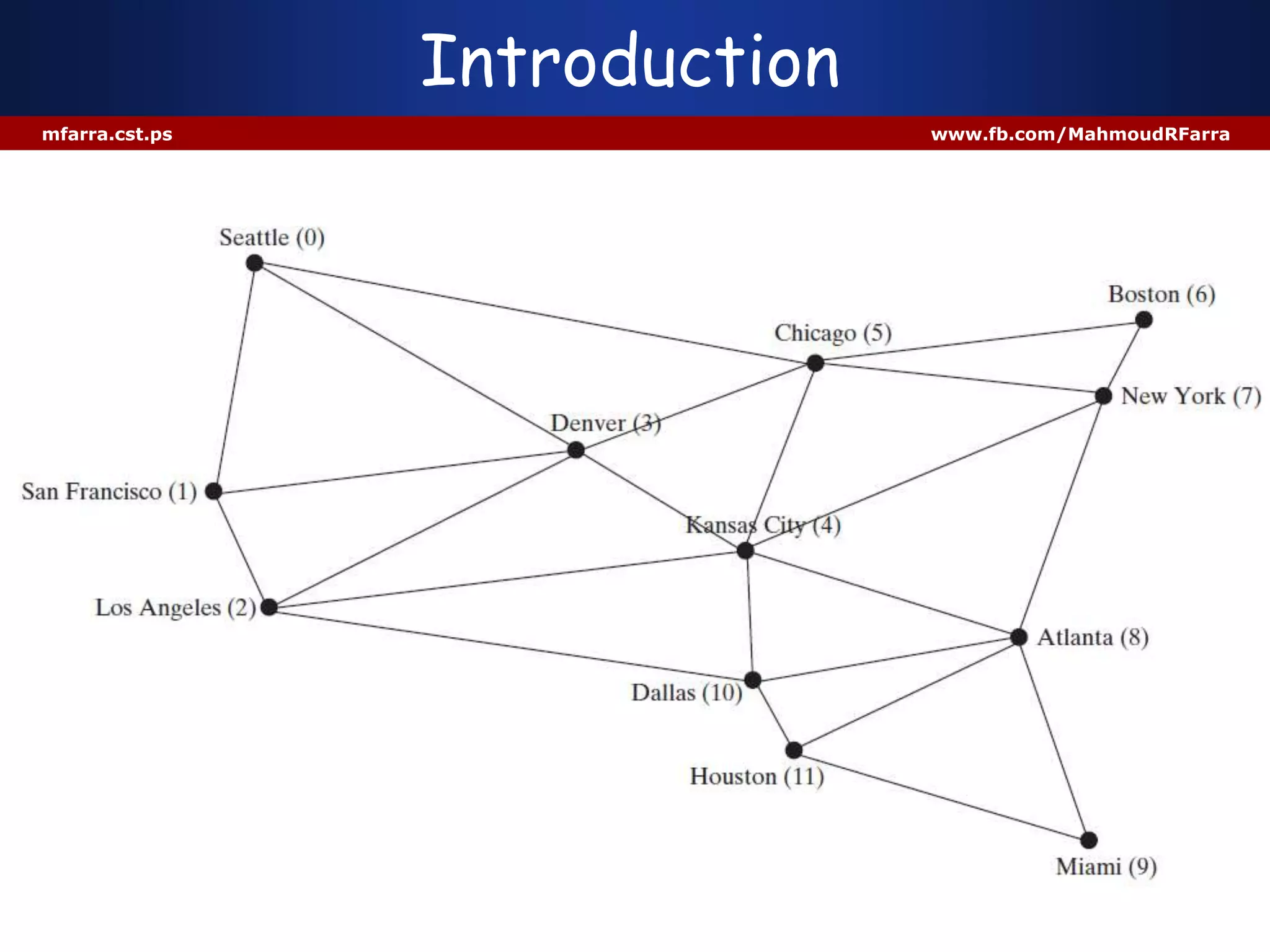
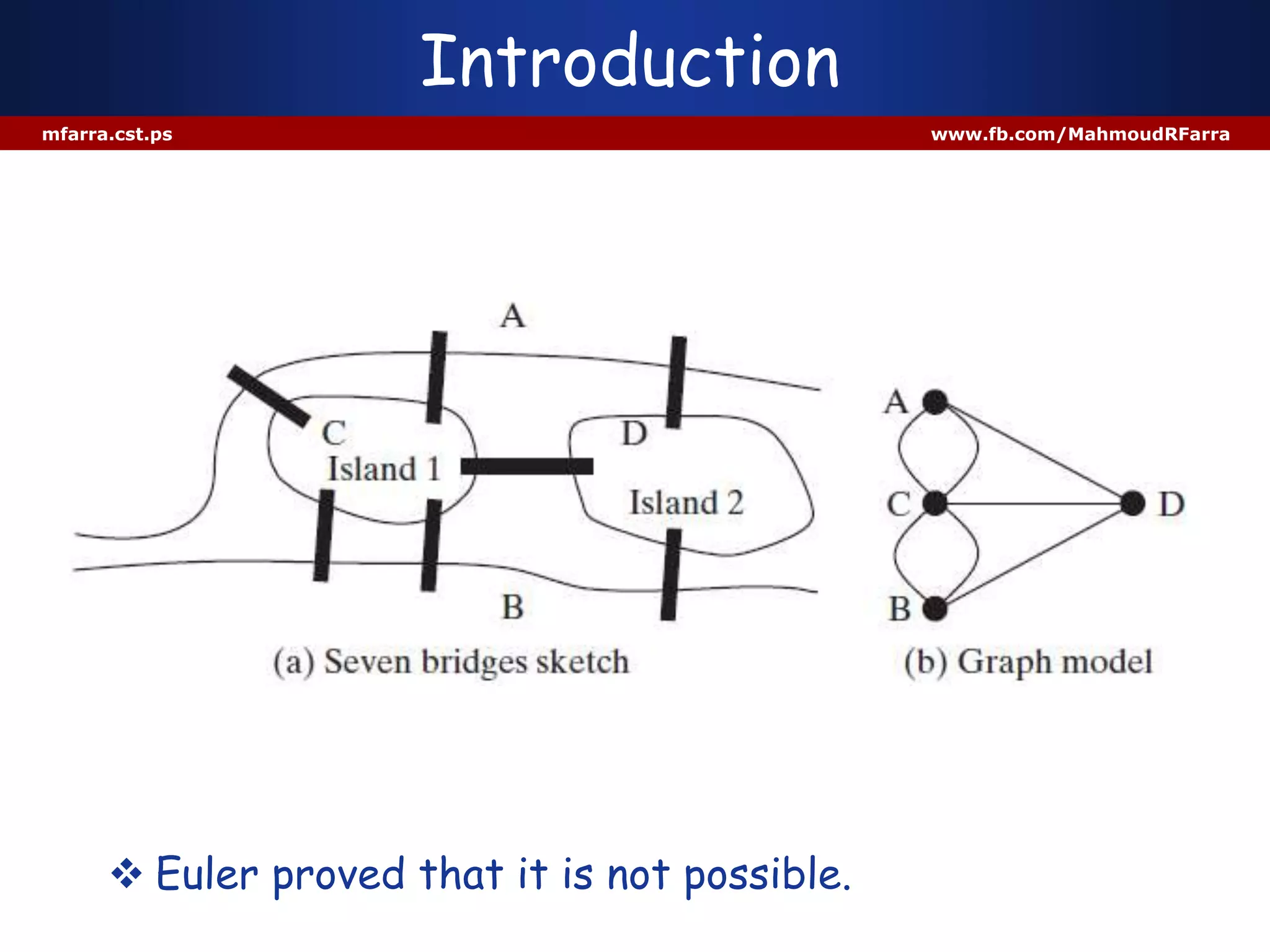
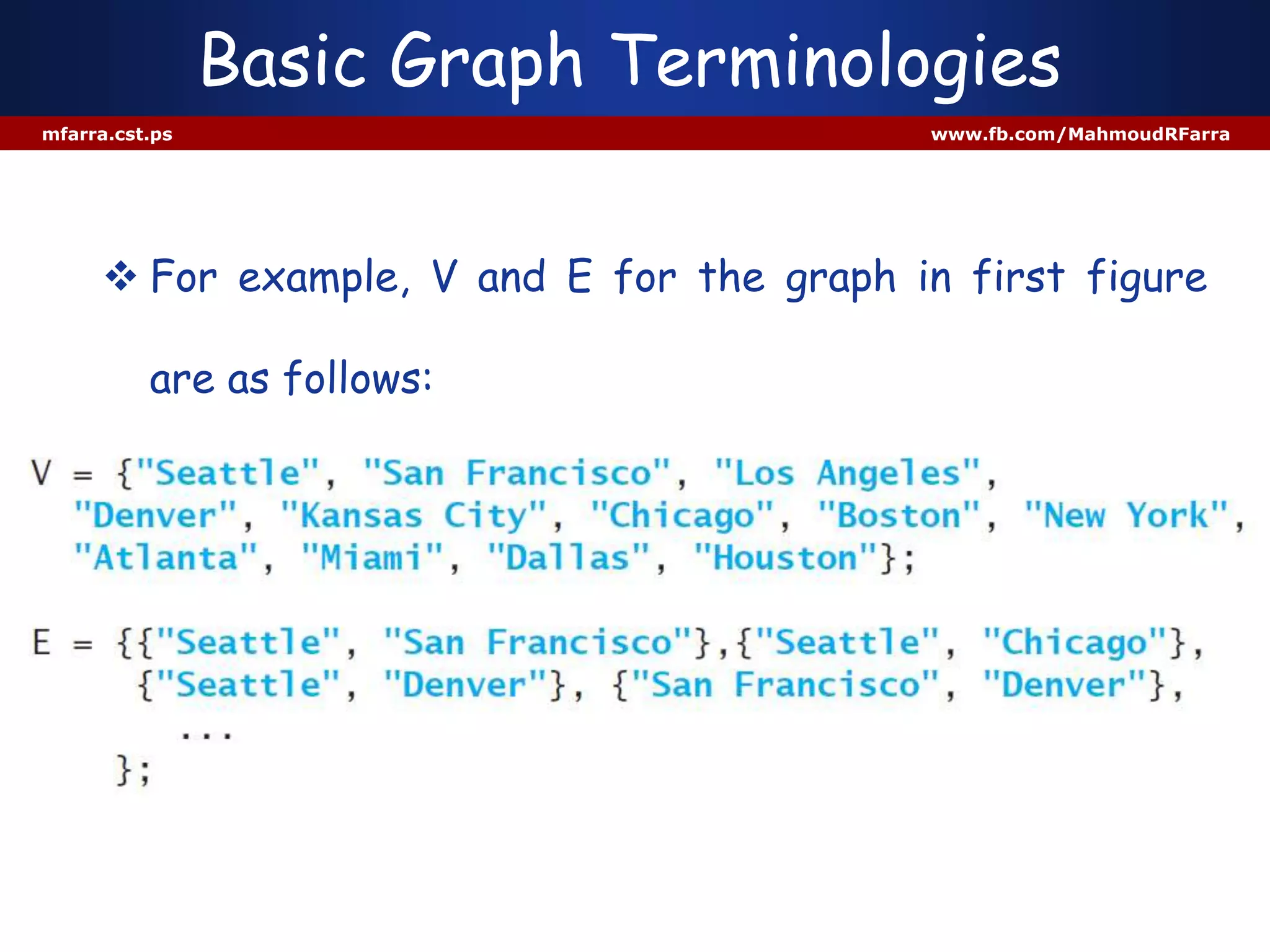
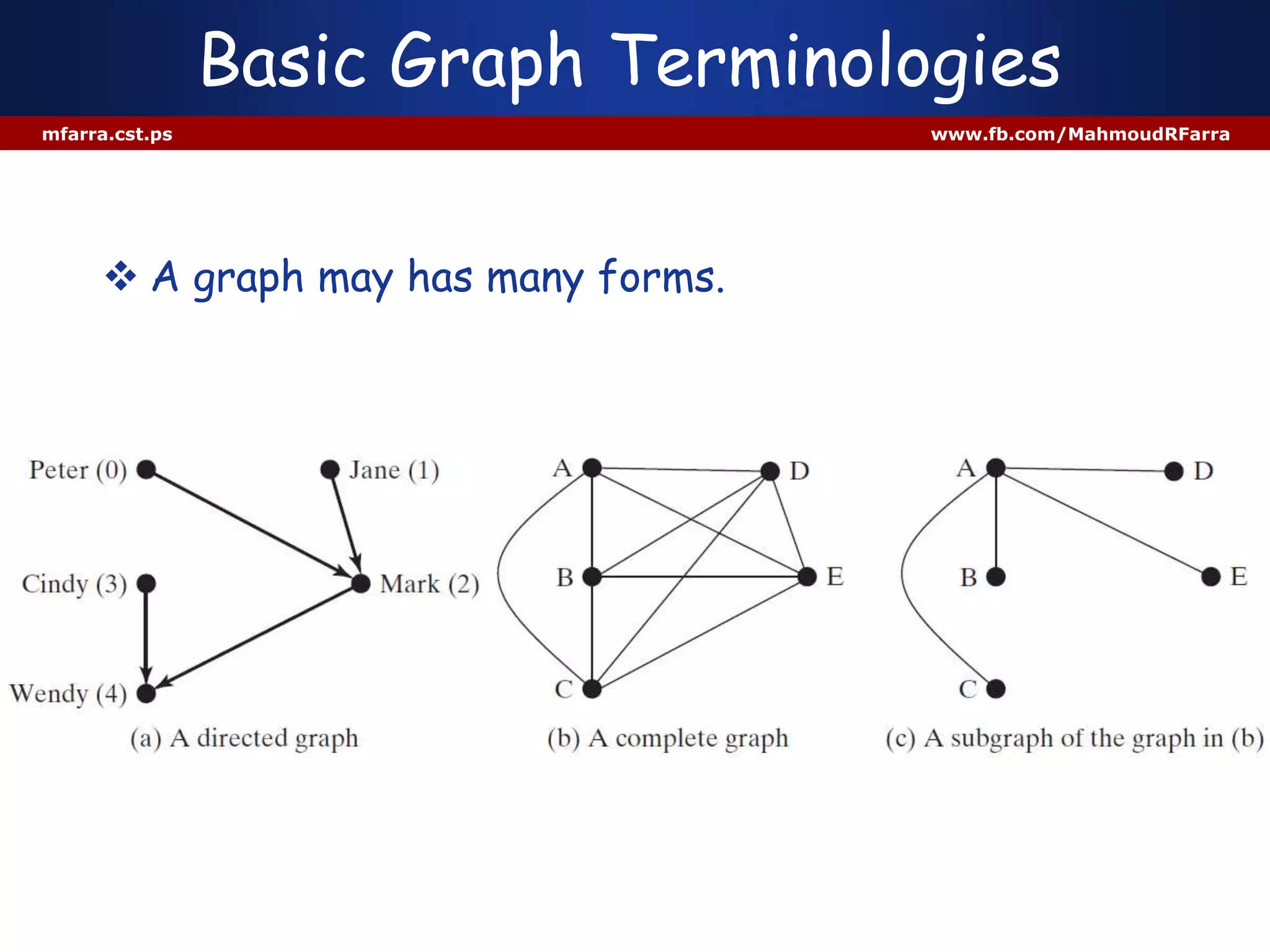
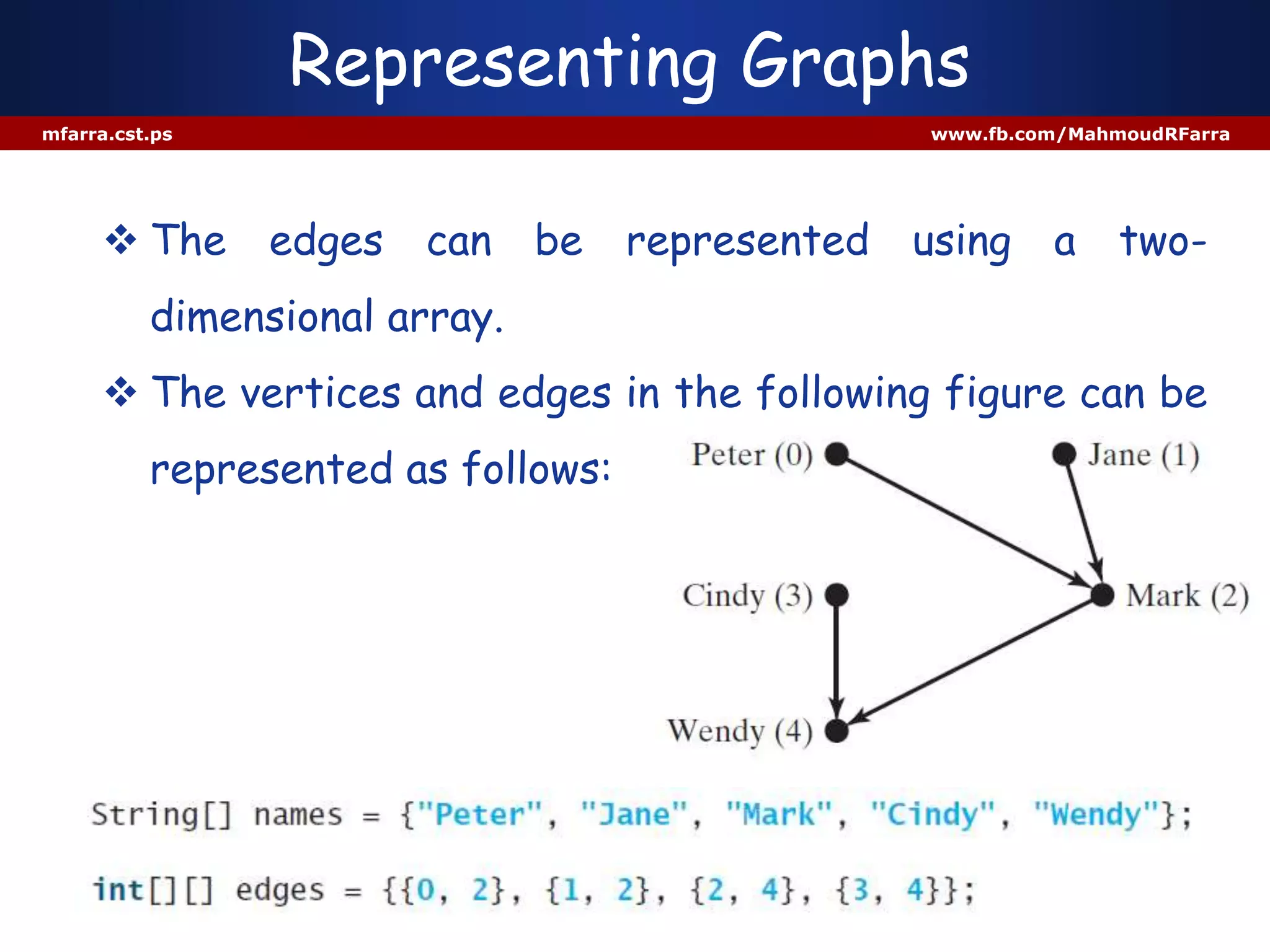
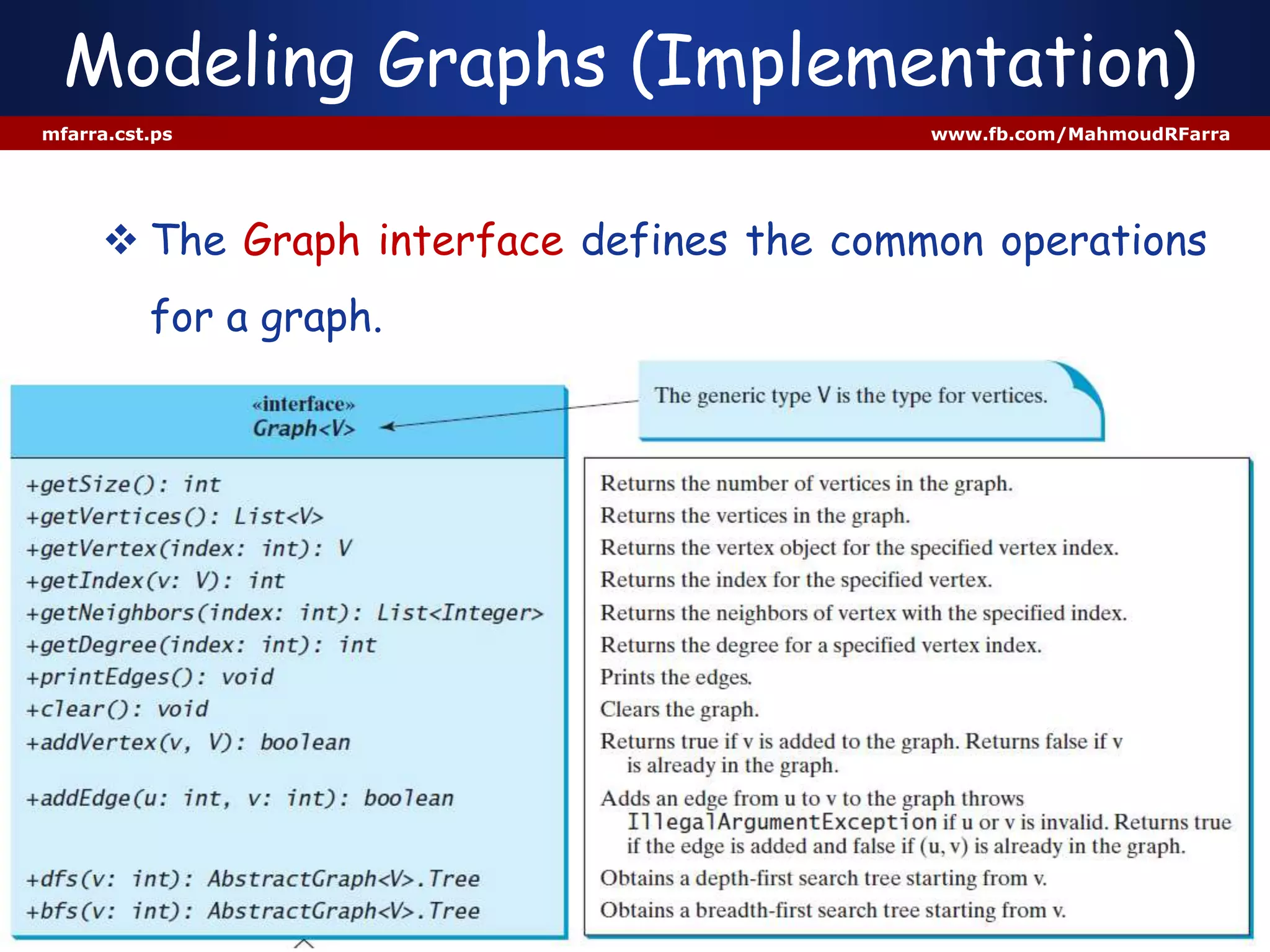
This document discusses graphs and their representation in Java. It begins with basic graph terminology like vertices, edges, directed/undirected graphs. It then discusses modeling graphs in Java using interfaces and data structures like arrays and lists to store vertices and edges. Specific implementations are shown to represent sample graphs. The document is intended to introduce basic graph concepts and their modeling in Java.