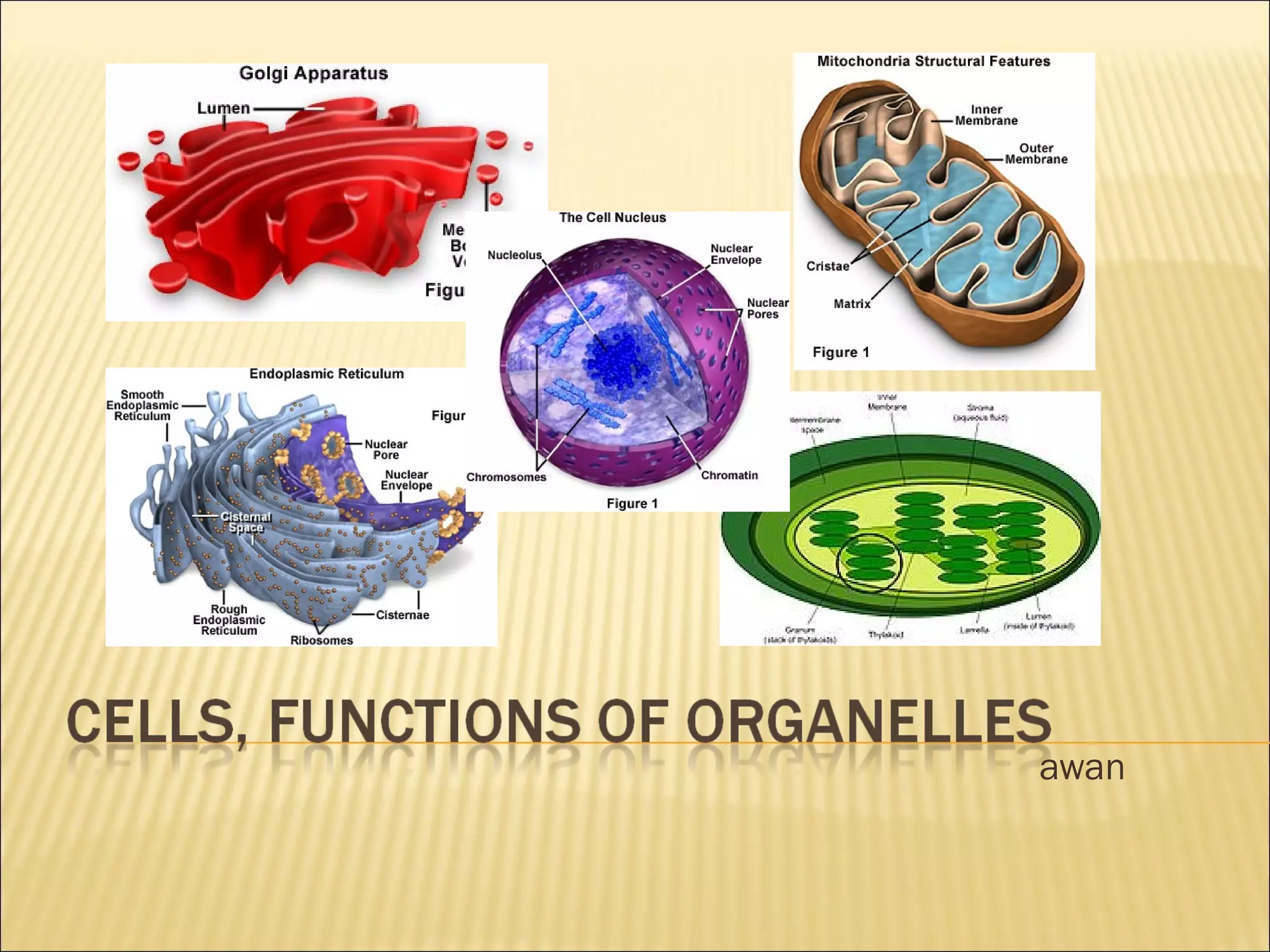
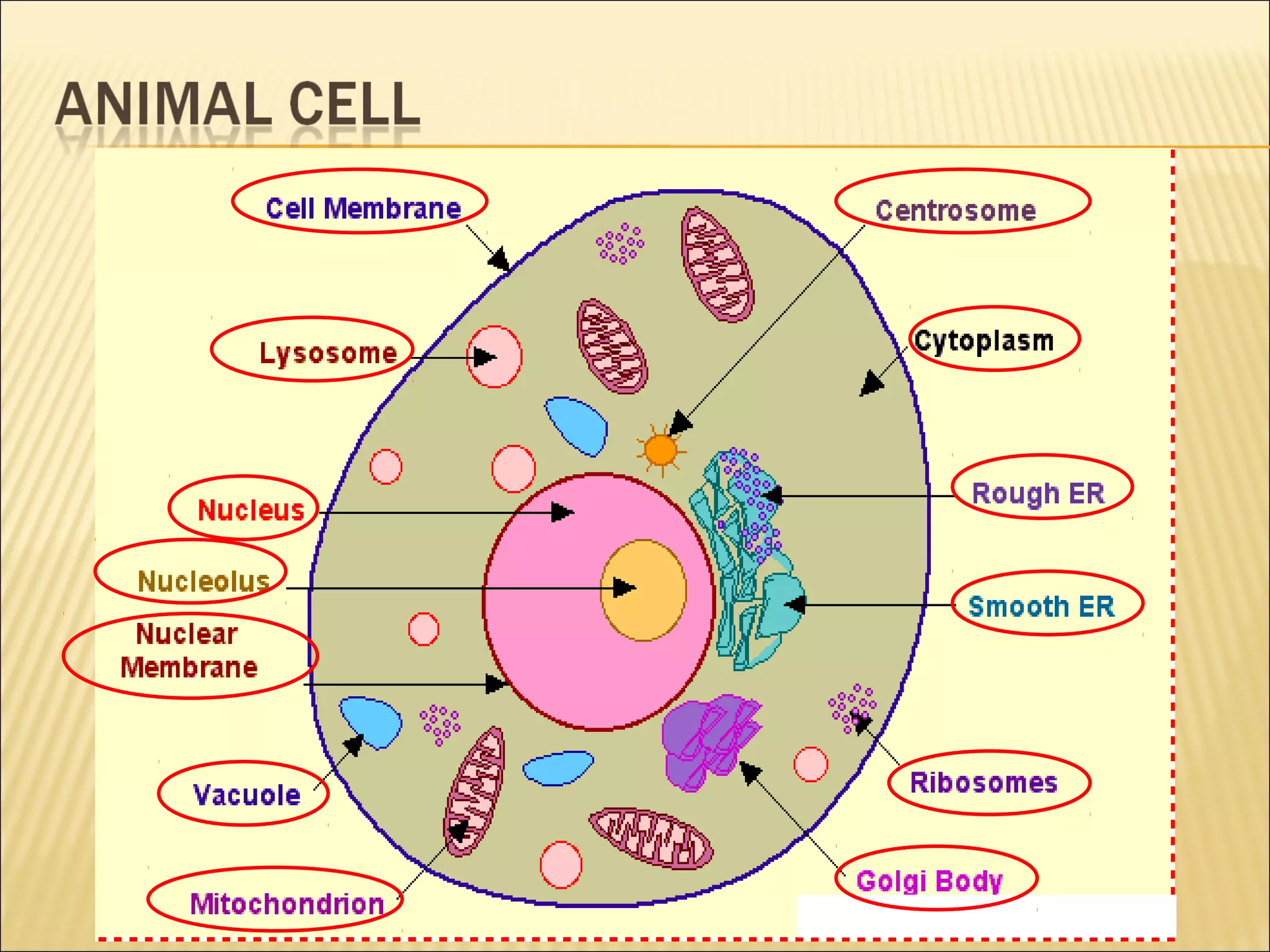
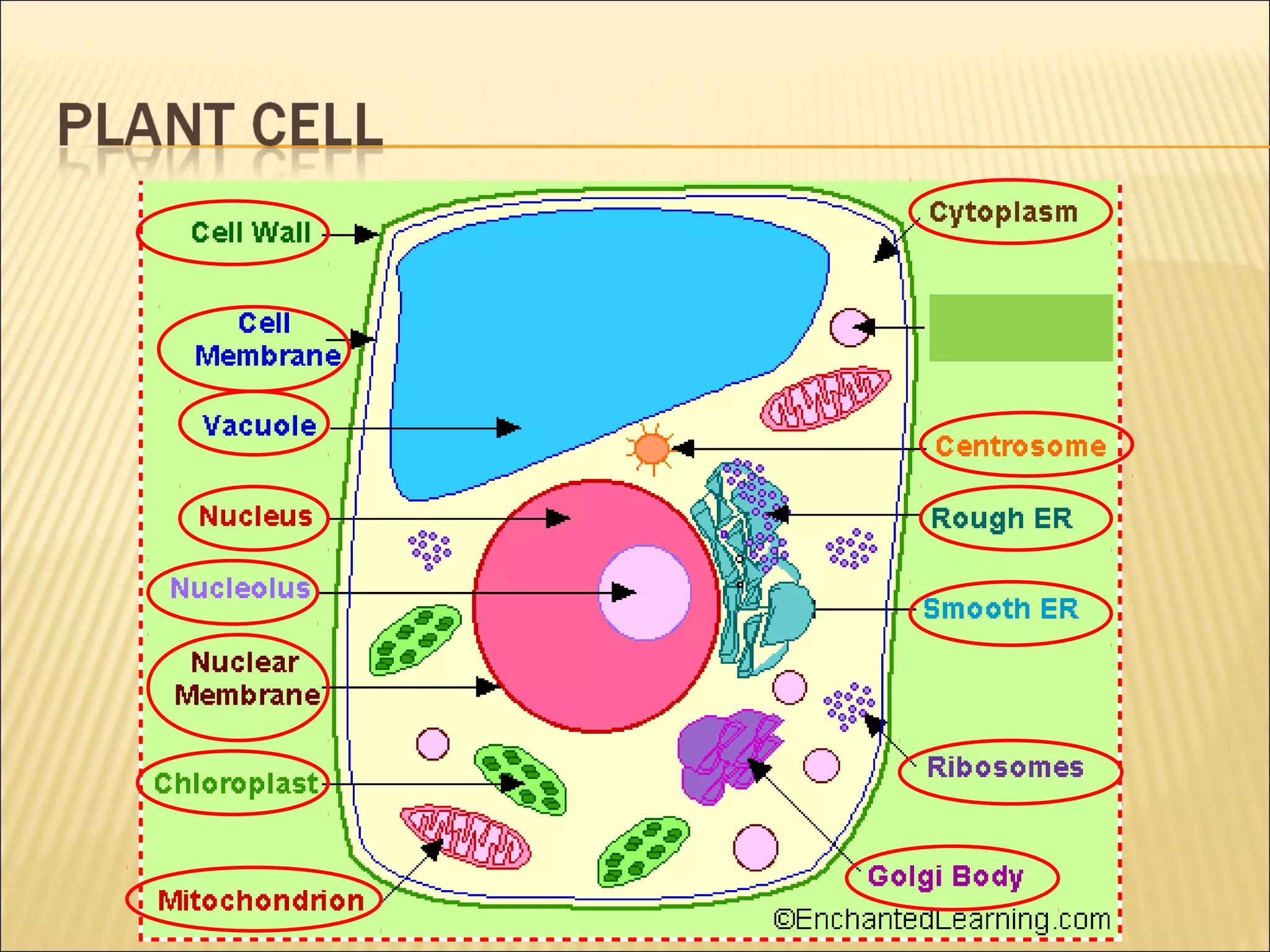
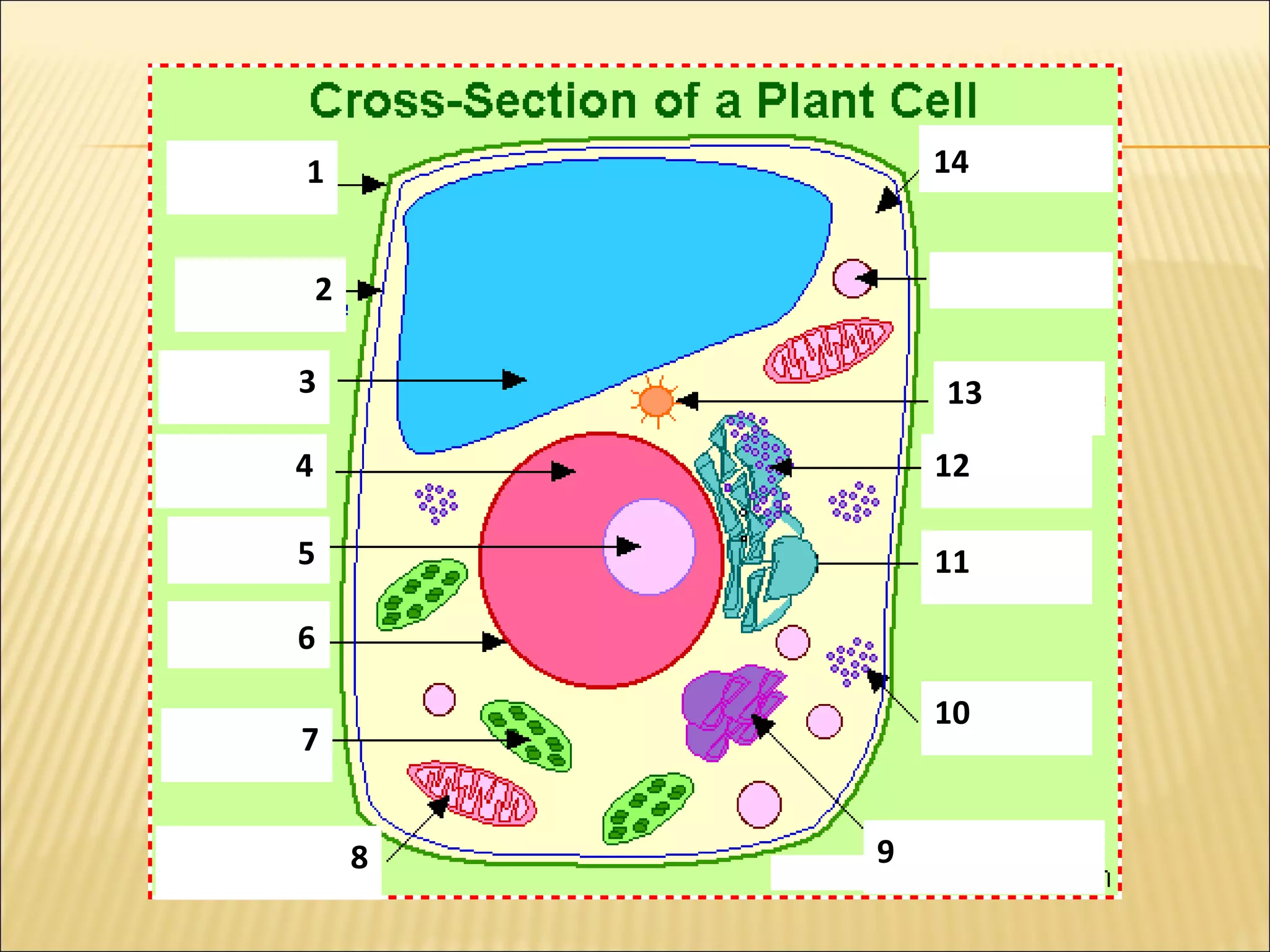
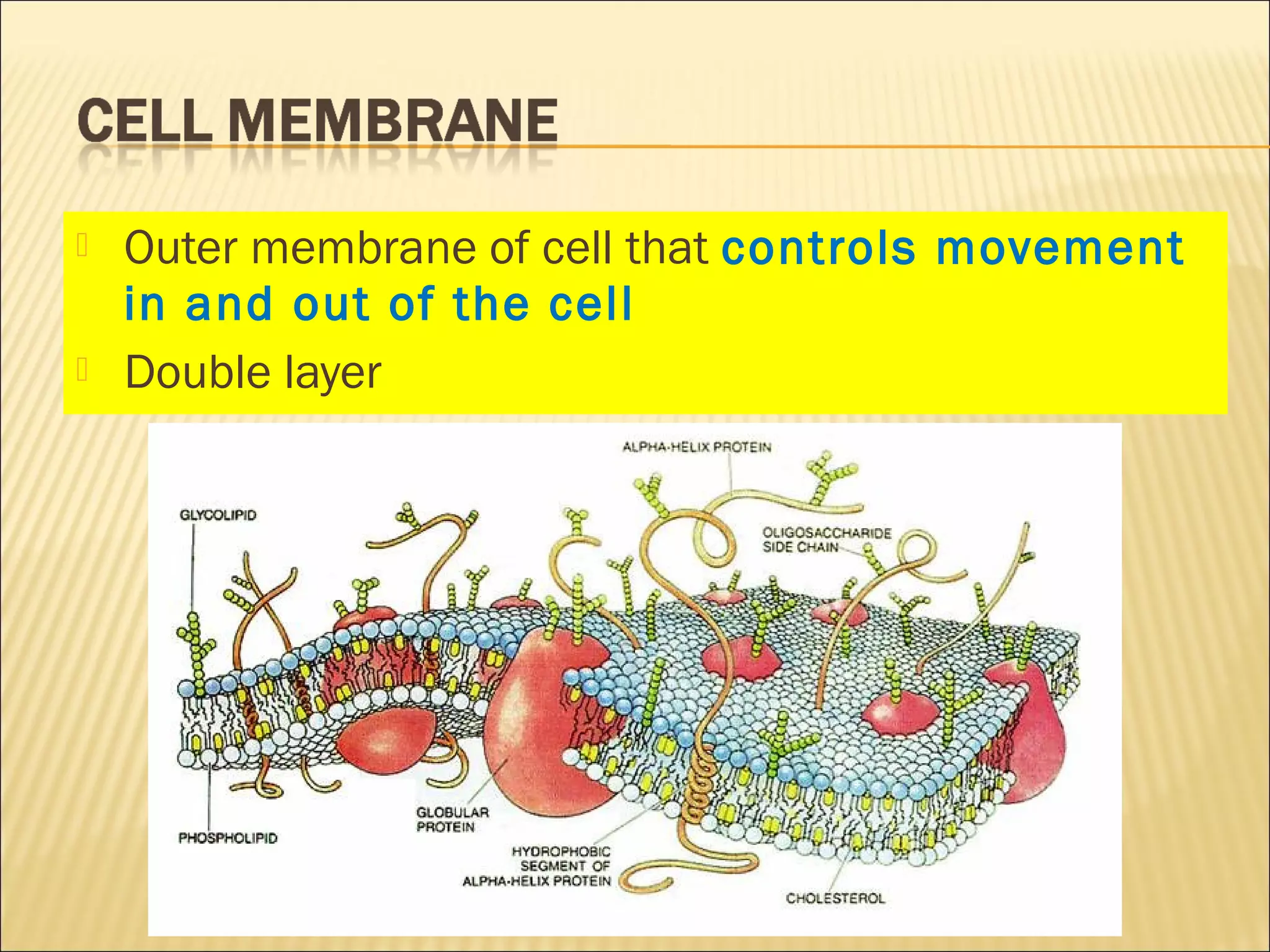
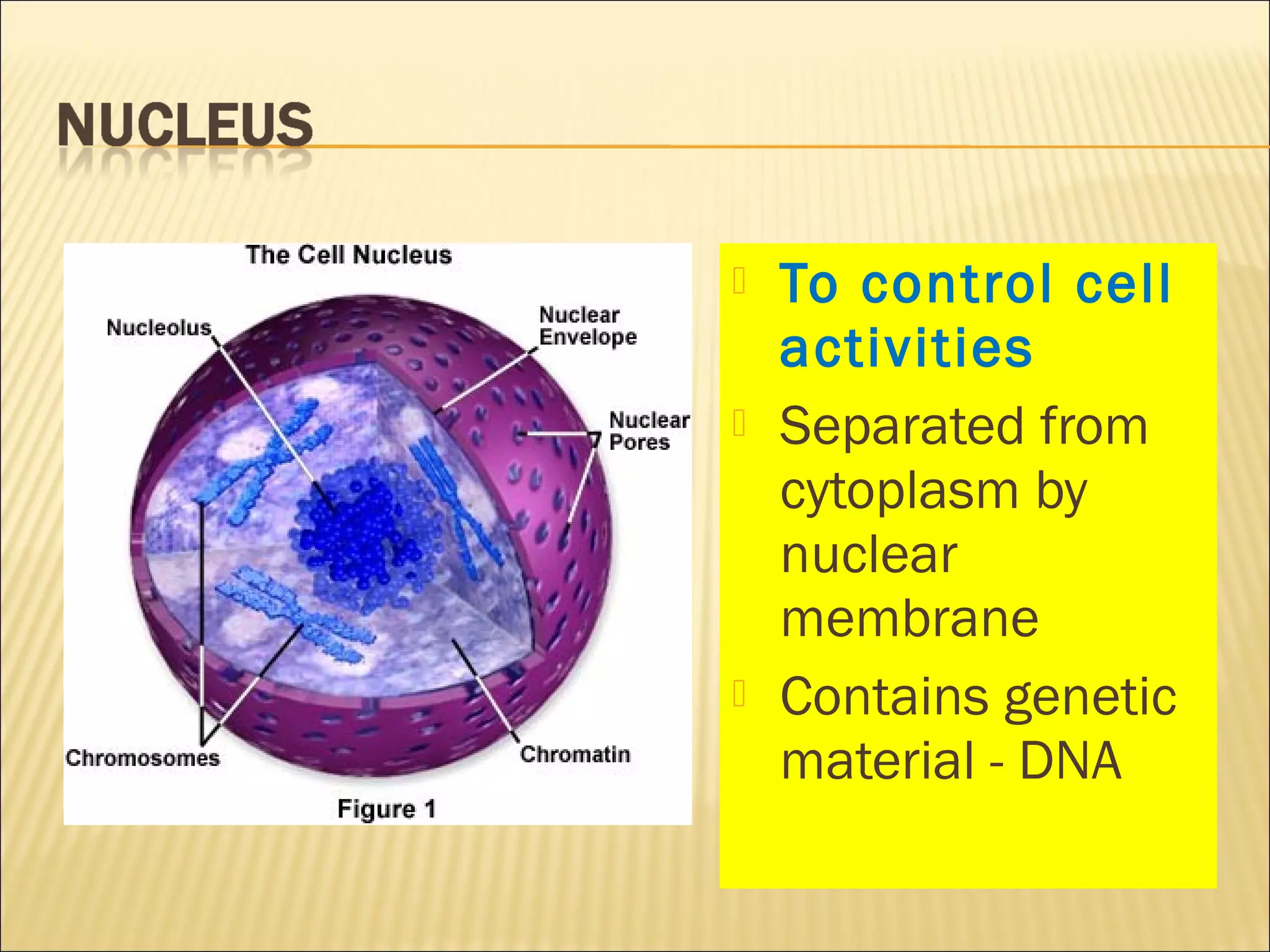
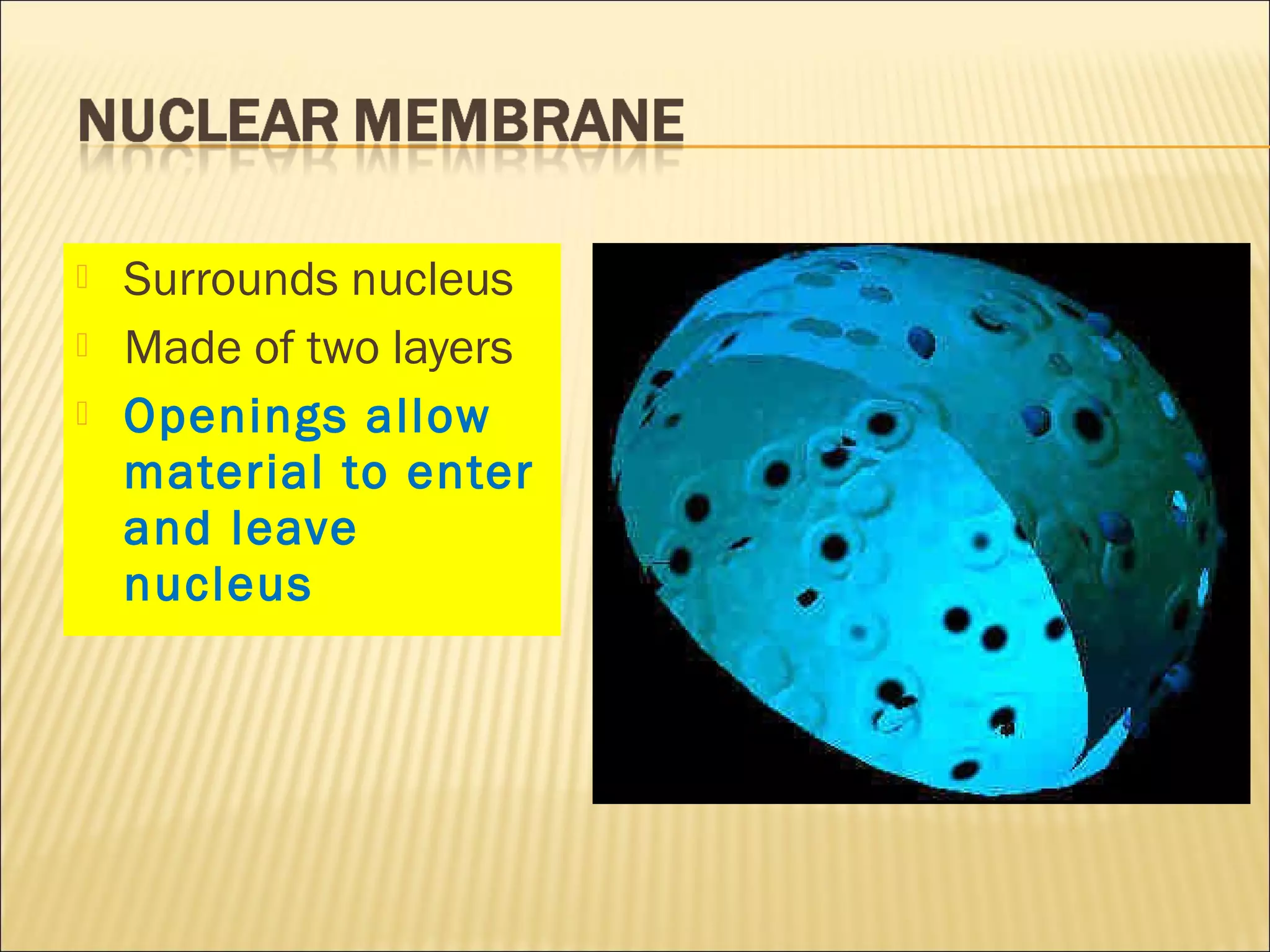
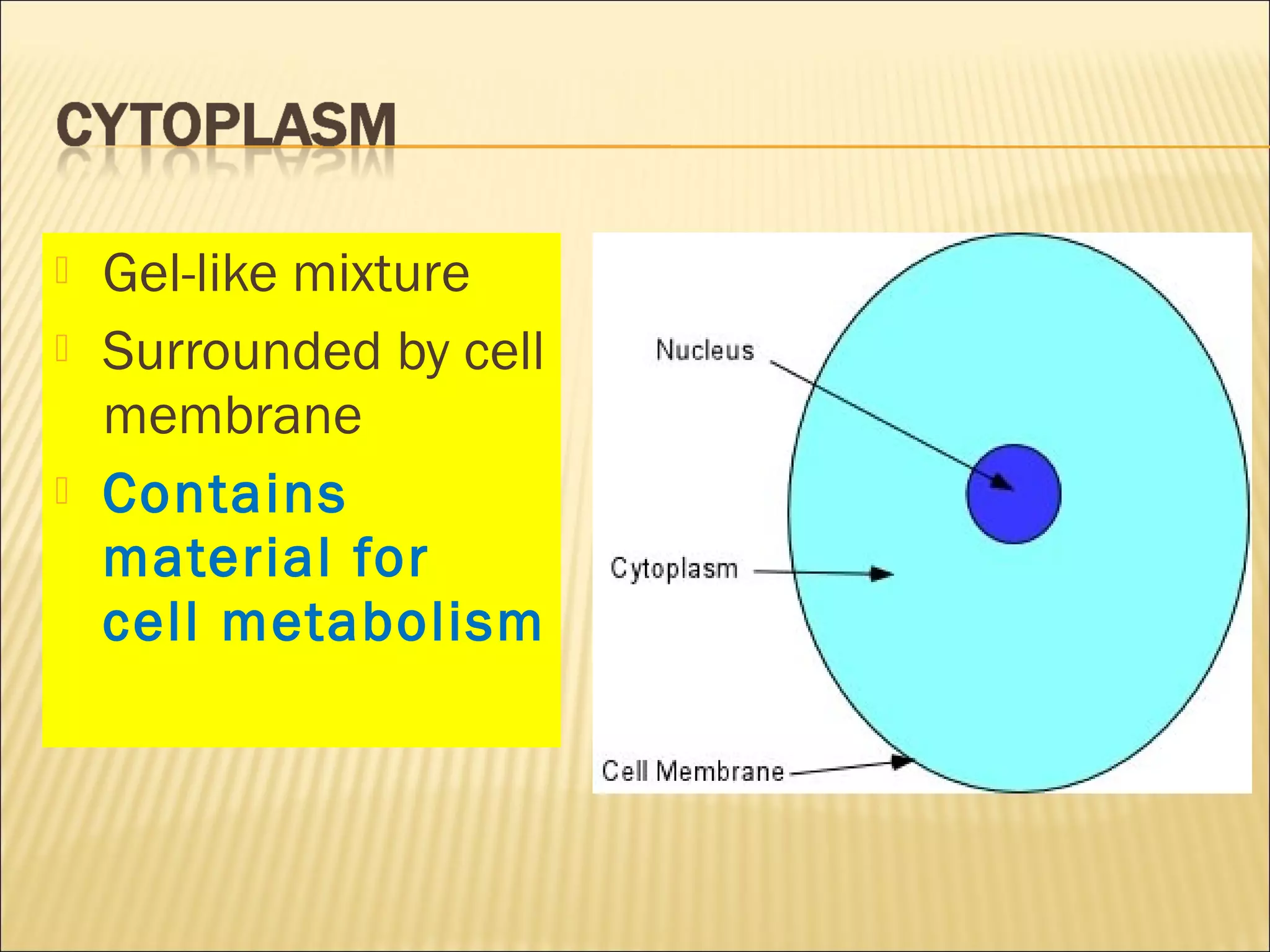
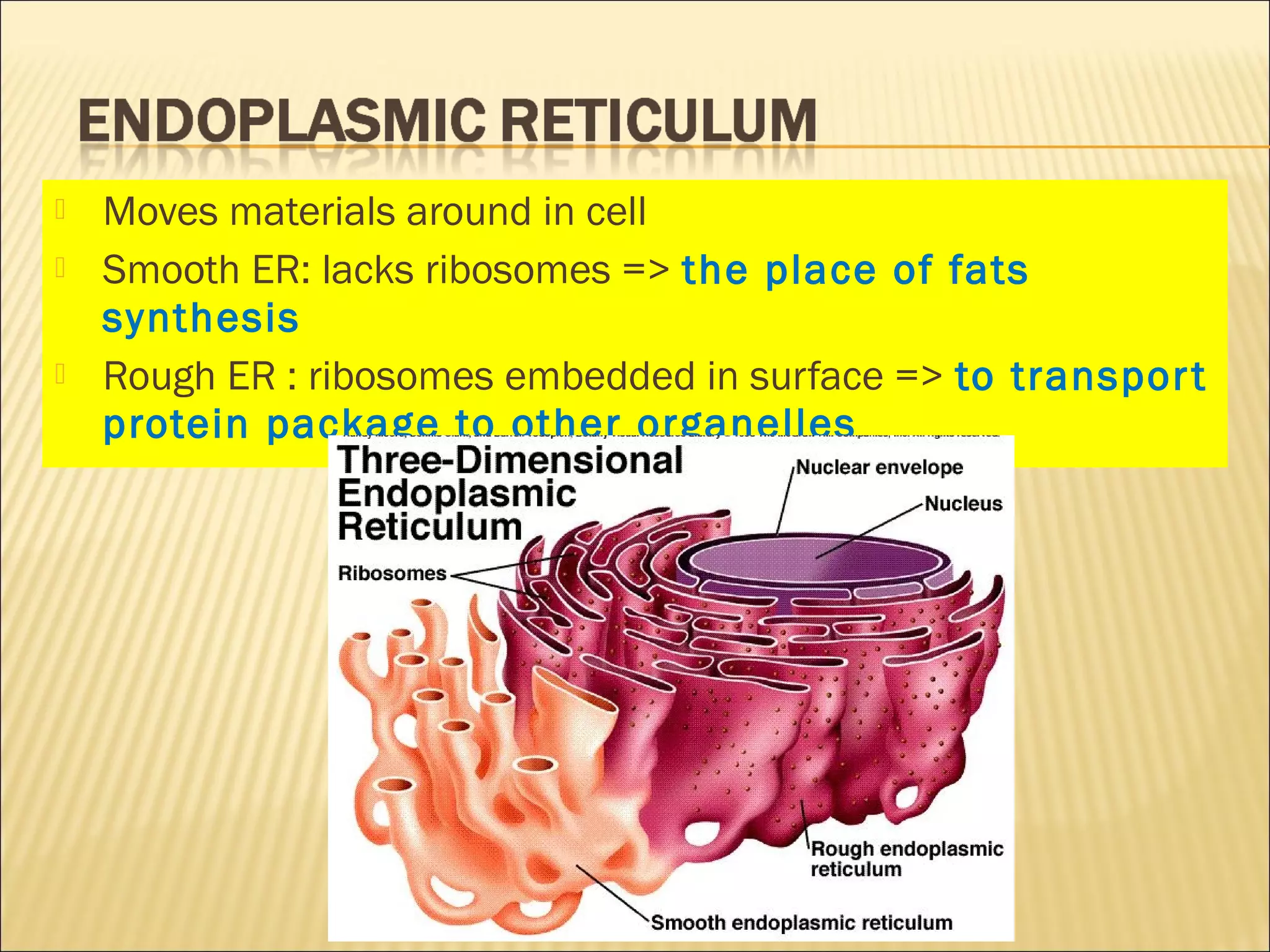
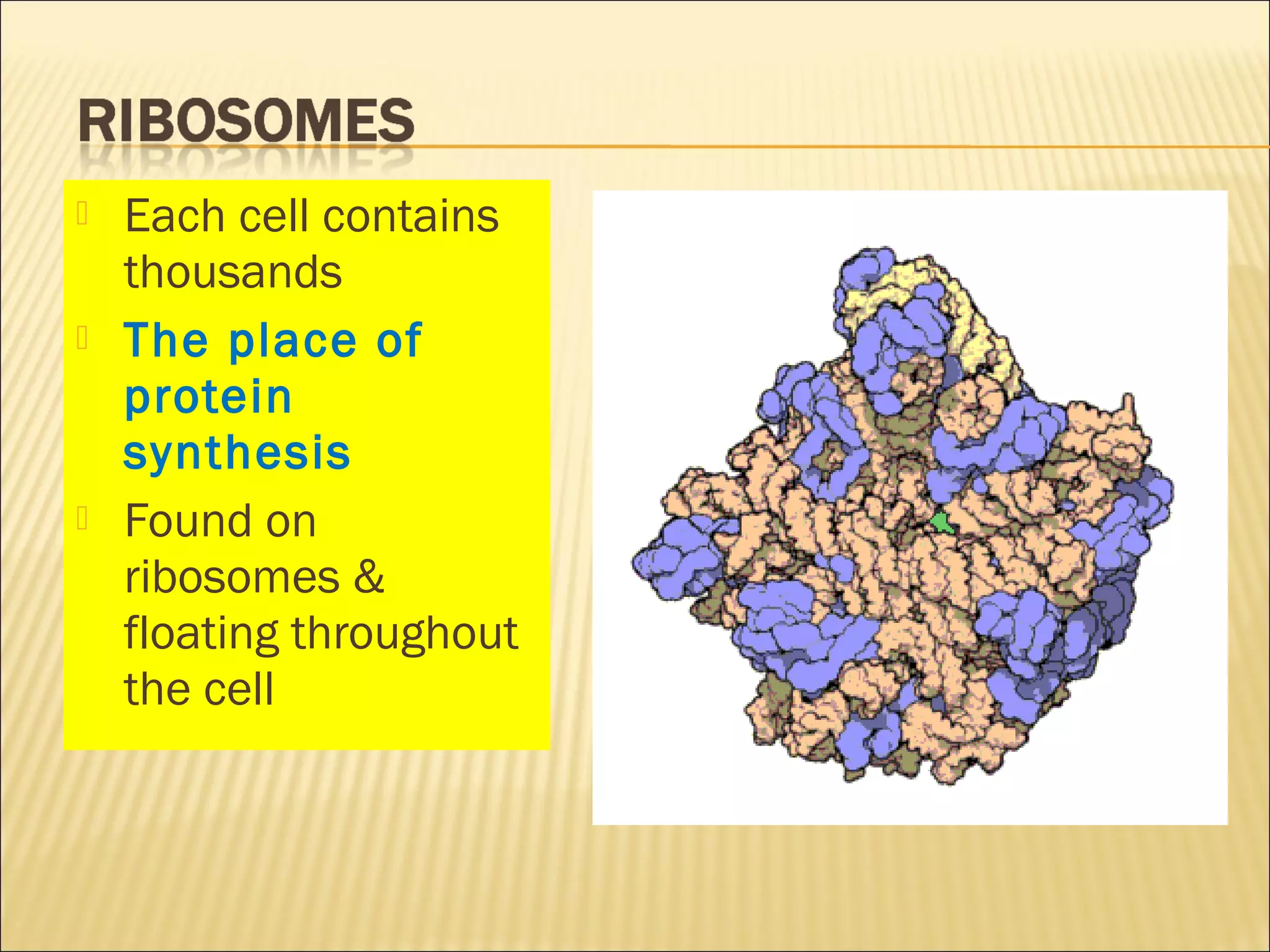
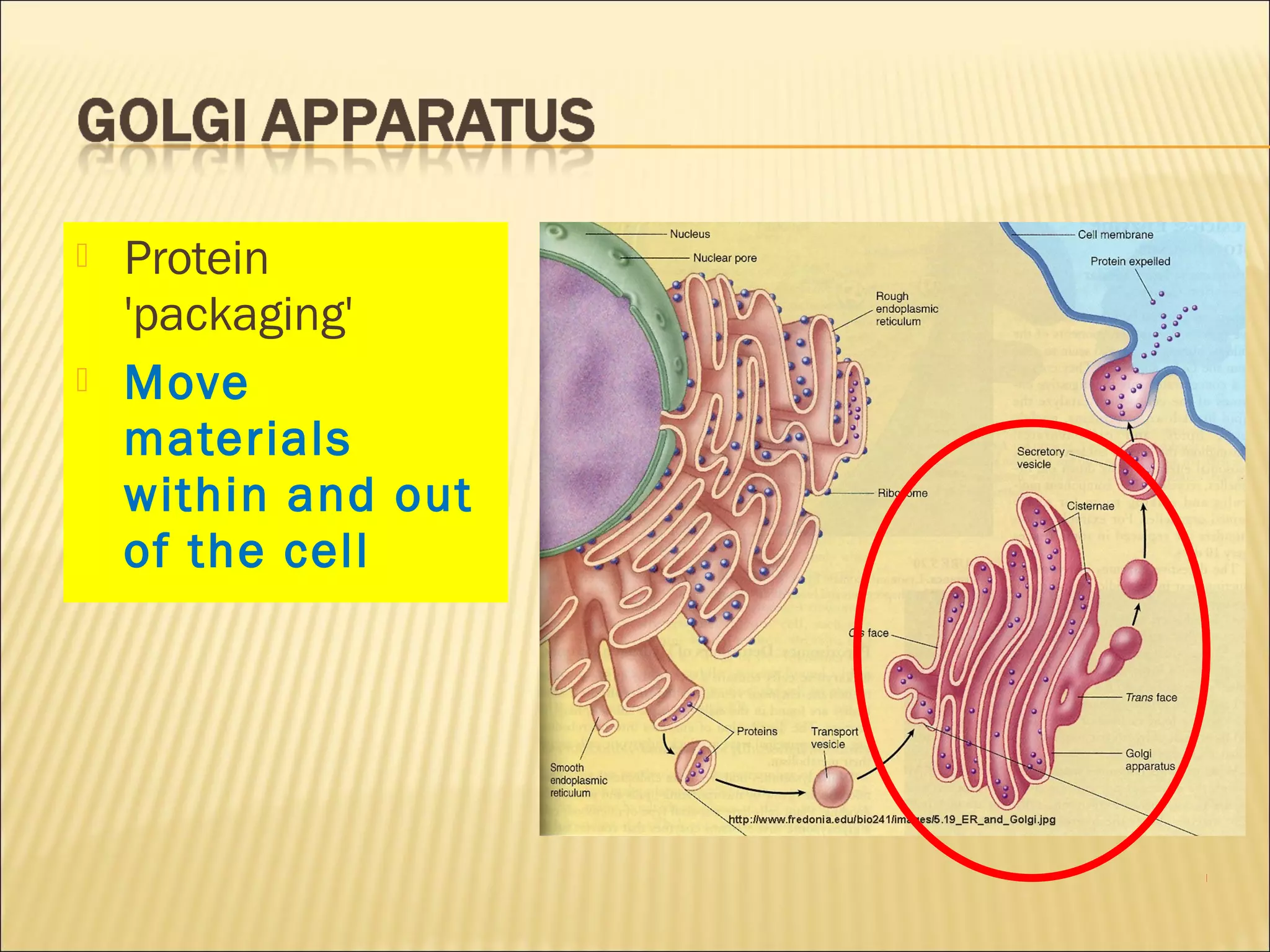
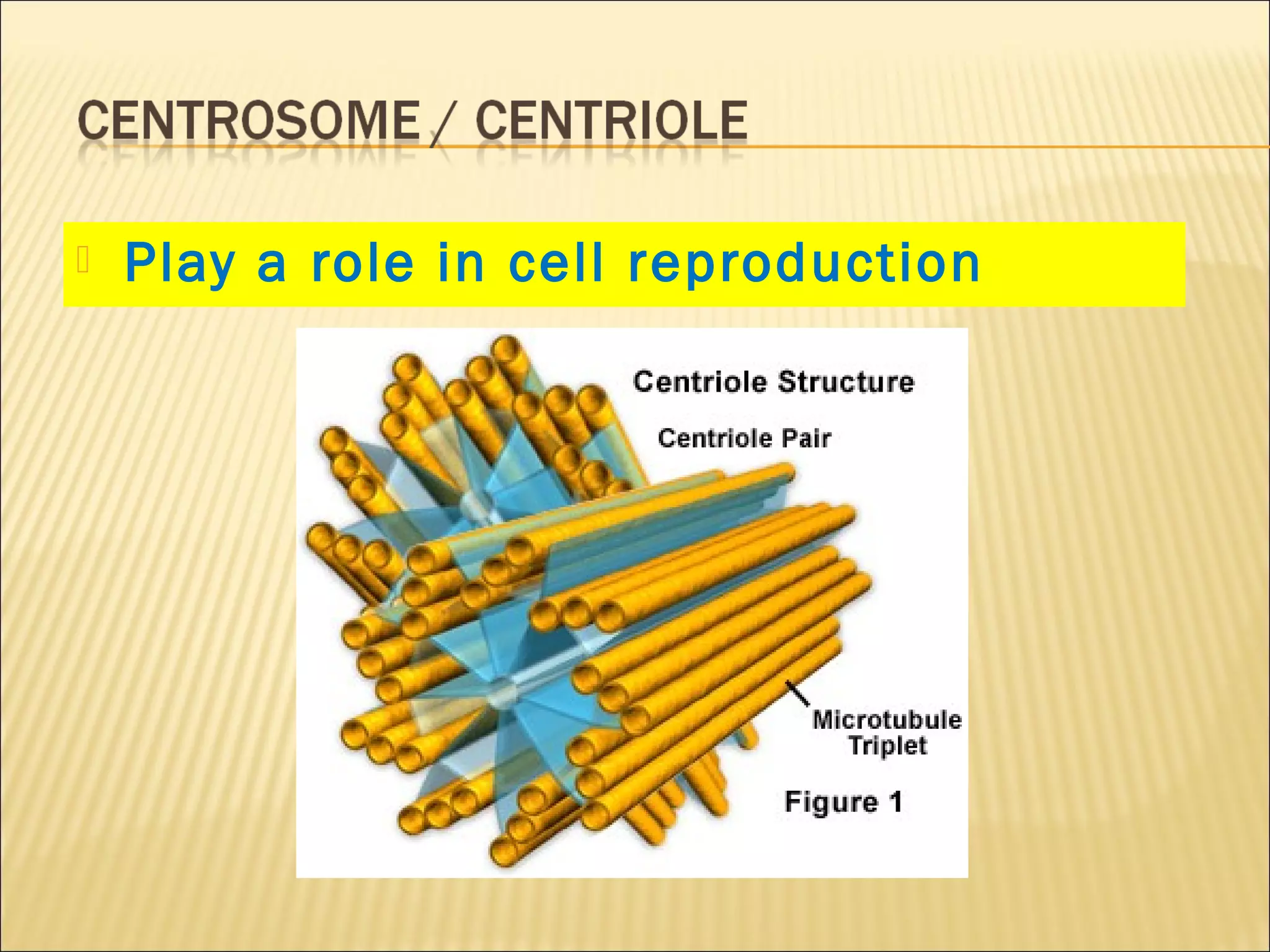
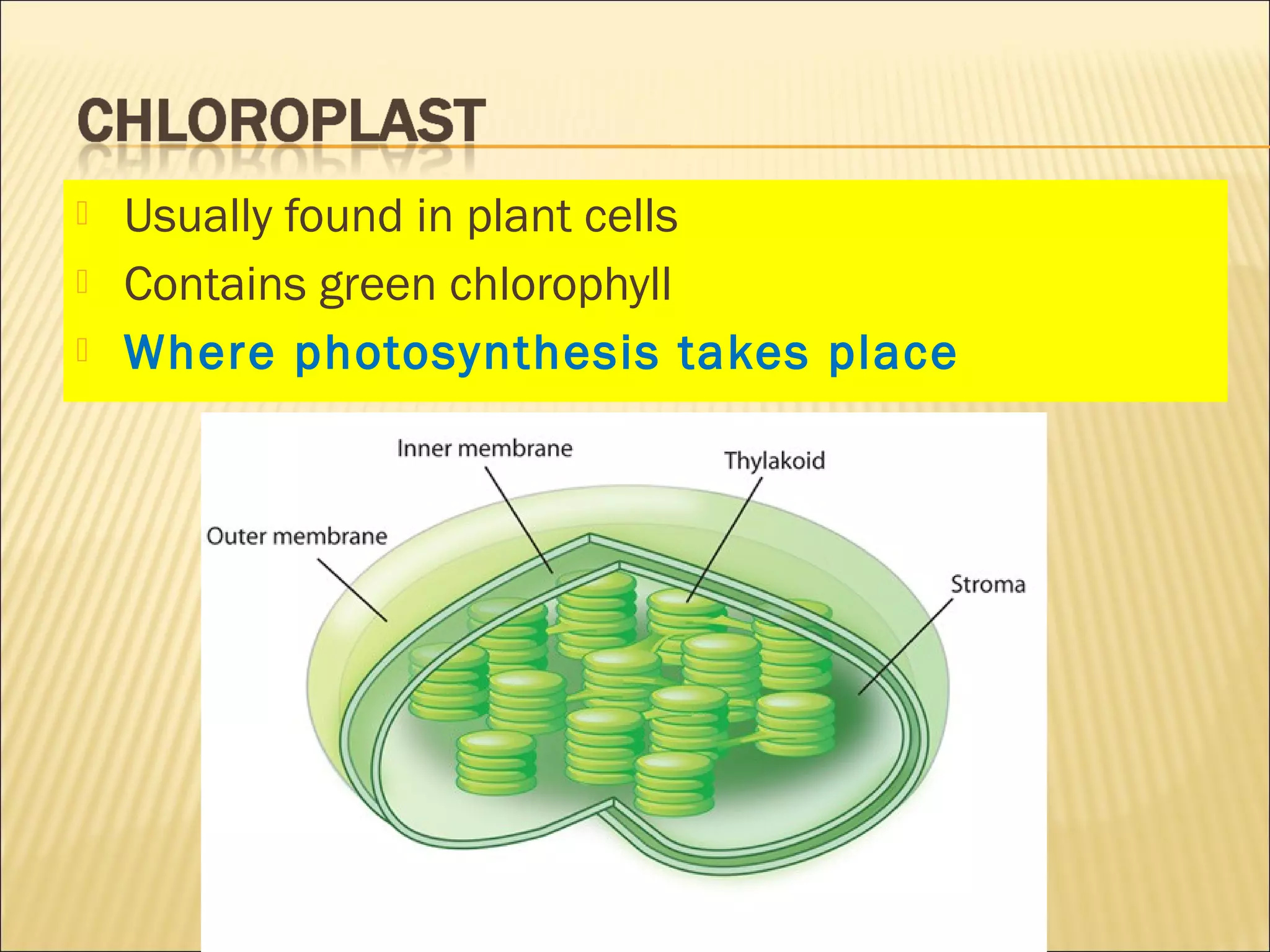
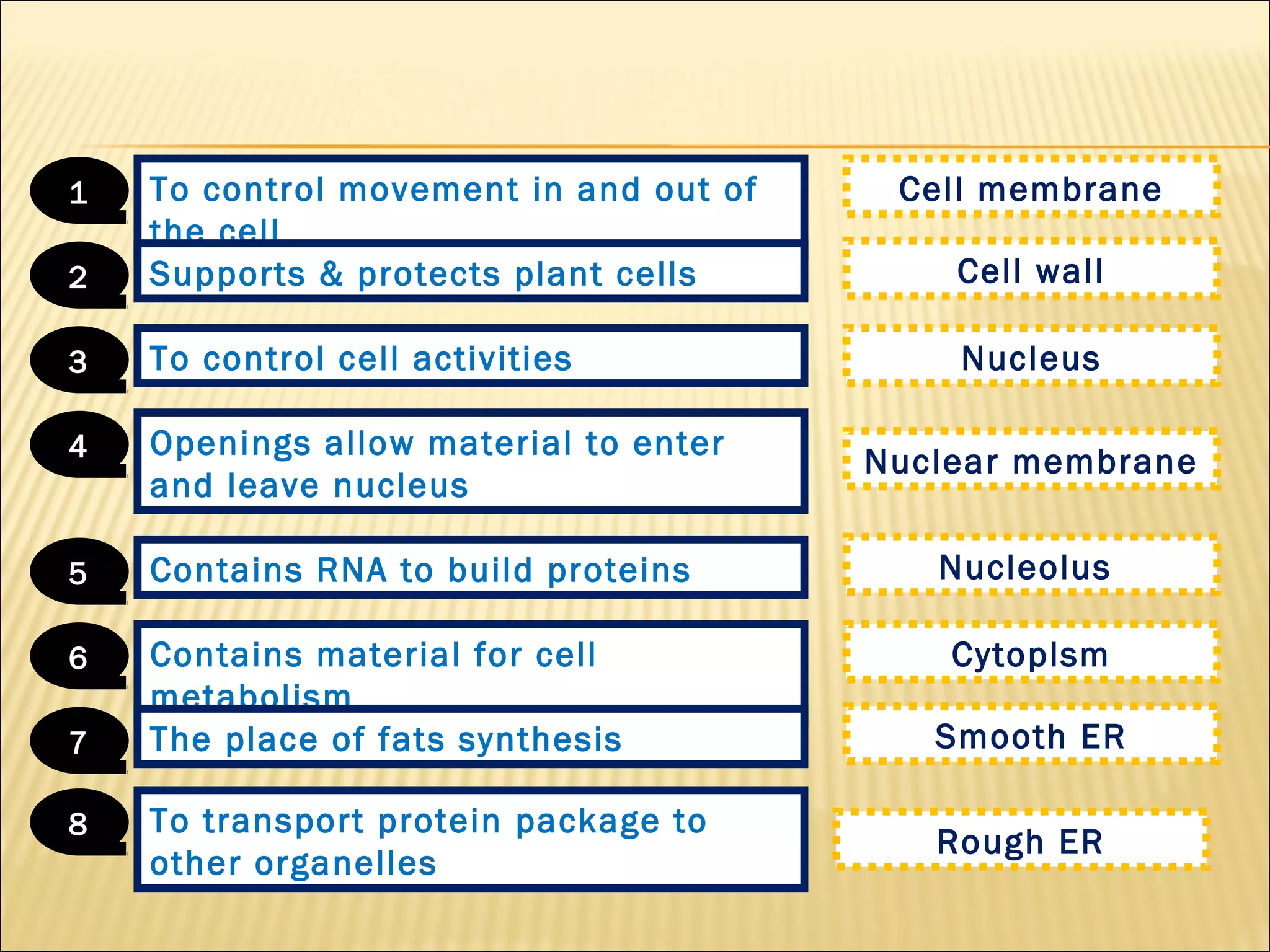
This document describes the structure and functions of various organelles found within cells. It explains that the cell membrane controls movement in and out of the cell, and that the cell wall supports and protects plant cells. The nucleus contains genetic material and is surrounded by the nuclear membrane. The endoplasmic reticulum helps transport proteins, with the smooth ER involved in fat synthesis and the rough ER containing ribosomes. Mitochondria produce energy and the Golgi apparatus packages proteins for transport. Lysosomes digest materials and vacuoles store reserves and control water levels. Chloroplasts are found in plant cells and are the site of photosynthesis.