The Visitor design pattern is a classic solution for operating on complex object hierarchies- but in traditional Java, it often comes with a significant drawback: verbose, repetitive, and hard-to-maintain boilerplate code.
In this XtremeJ 2025 session, Haim Michael revisits the Visitor pattern through the lens of modern Java, demonstrating how recent language features fundamentally change how the pattern can be implemented.
By combining sealed classes, record classes, and pattern matching with switch expressions, this talk shows how the Visitor pattern can be expressed in a way that is:
+ More concise
+ Easier to reason about
+ Safer and more explicit
+ Significantly easier to maintain over time
+ The slides walk step by step through:
+ The original problem the Visitor pattern is designed to solve
+ A traditional, textbook Visitor implementation in Java
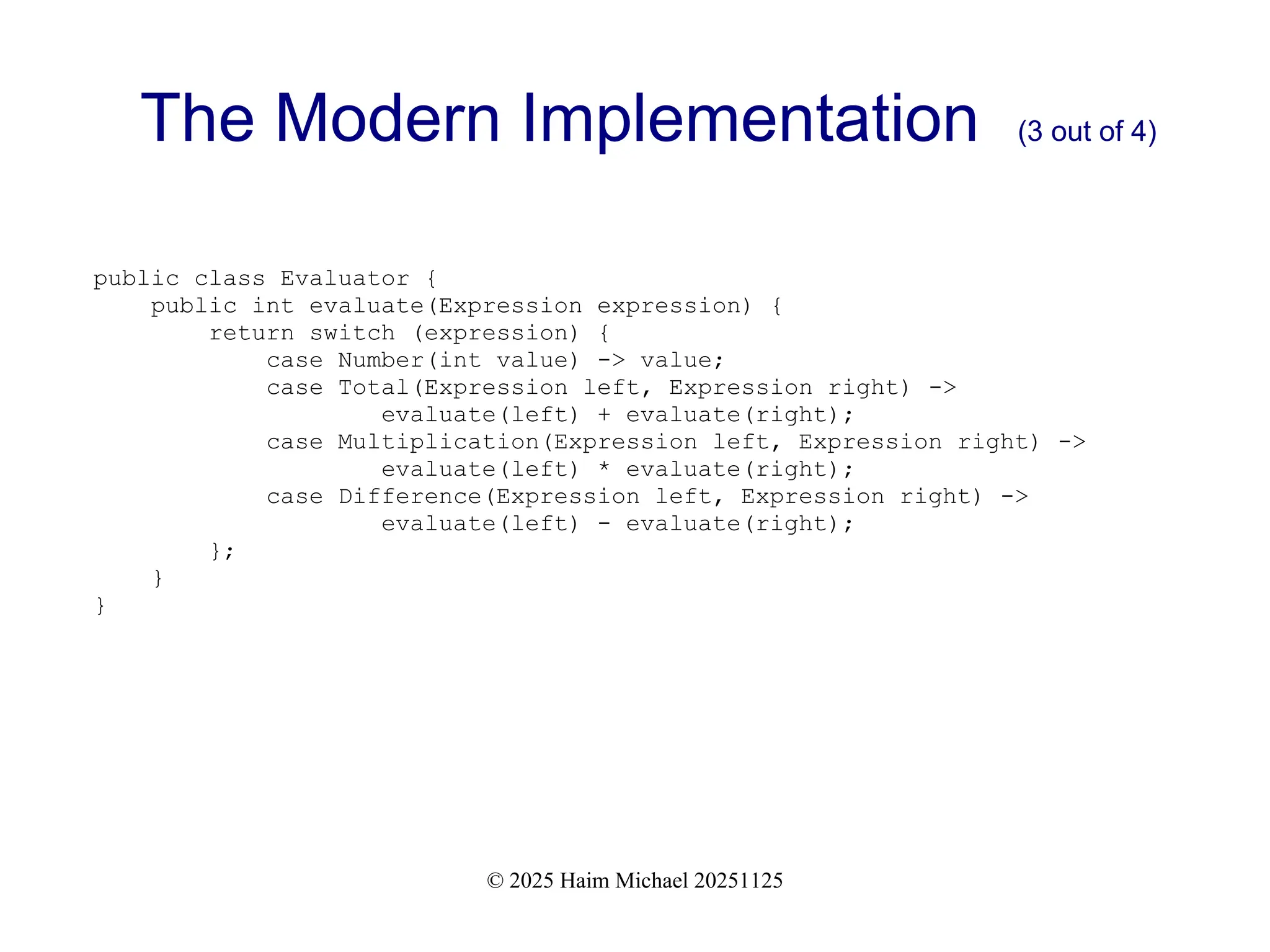
+ A modern alternative using sealed interfaces and records
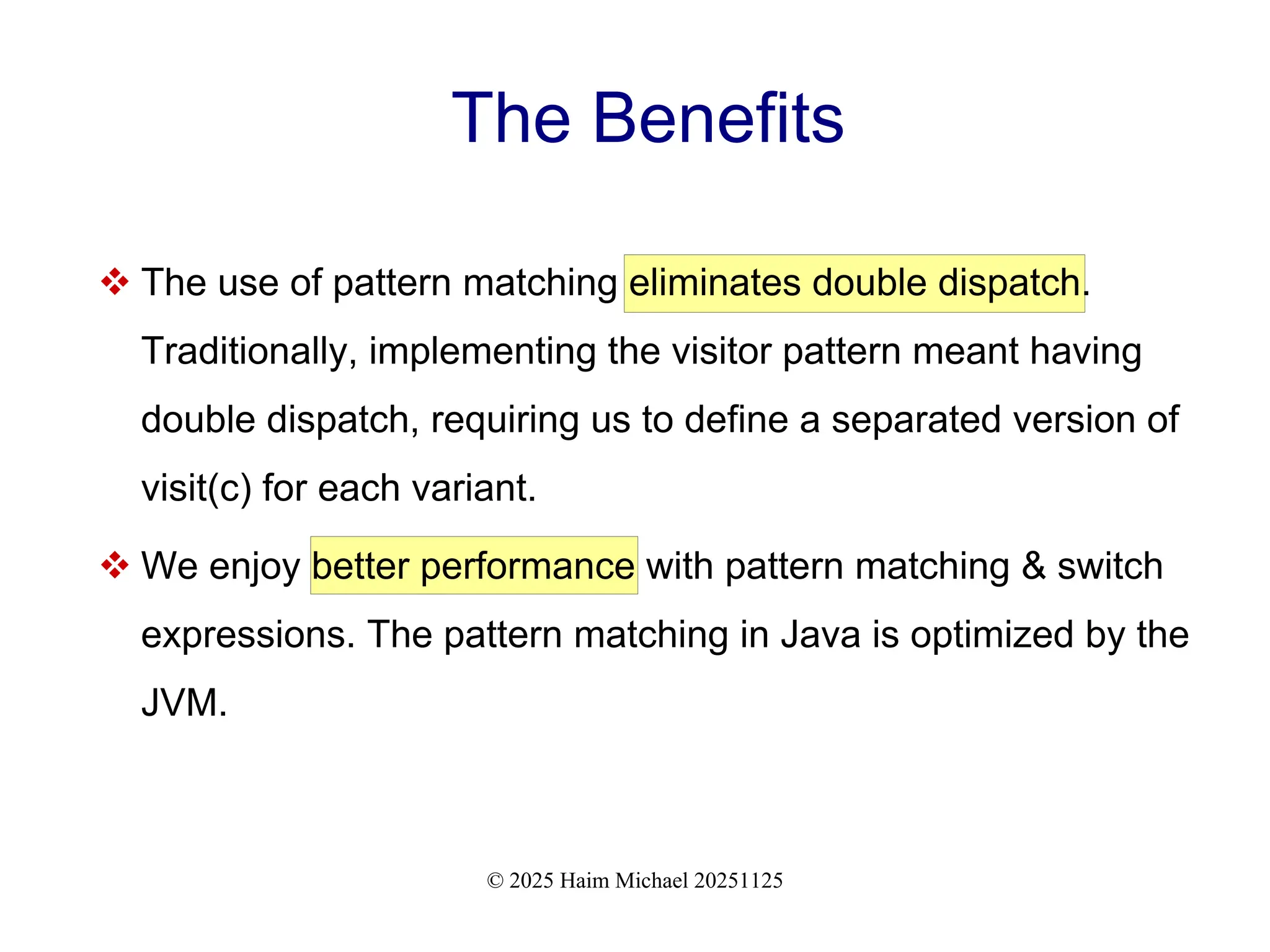
+ How pattern matching removes the need for double dispatch
+ Why modern Java enables cleaner, centralized, and more expressive logic
Key takeaways include:
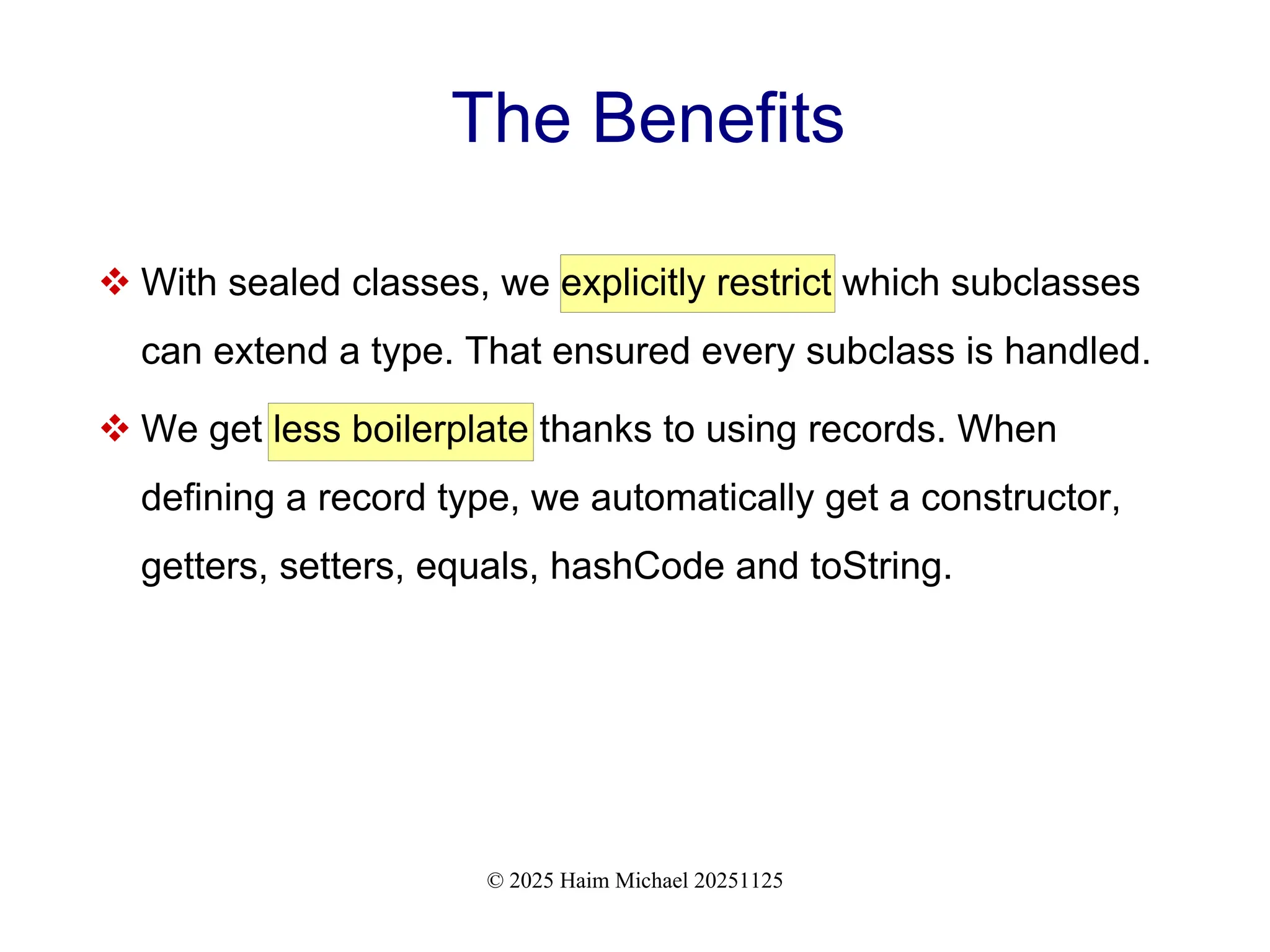
+ How sealed classes enforce complete and controlled hierarchies
+ How records drastically reduce structural boilerplate
+ How pattern matching ensures exhaustiveness and clarity
+ Why modern implementations improve readability, performance, and maintainability
+ When this approach is a better fit than the classic Visitor pattern
This session offers a fresh, practical perspective on a well-known design pattern, showing how Java’s evolution empowers developers to modernize legacy designs without sacrificing architectural intent.
These slides were presented at XtremeJ 2025, the online Java conference for professional developers.
About the Conference:
More information about the XtremeJ 2025 online conference is available at:
https://xtremej.dev














![© 2025 Haim Michael 20251125
The Modern Implementation (4 out of 4)
public class Program {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Expression expression = new Multiplication(
new Total(new Number(3),new Number(2)),
new Total(new Number(6),new Number(4)));
System.out.println(new Evaluator().evaluate(expression));
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/visitor-251213172208-a29853c8/75/Goodbye-Boilerplate-The-Visitor-Pattern-Reimagined-in-Modern-Java-Haim-Michael-18-2048.jpg)