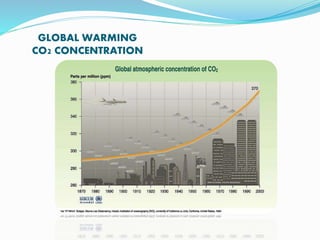
Global warming is the increase of Earth's average surface temperature due to greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide trapping heat that would otherwise escape. Earth's climate is influenced by the thin atmosphere layer containing most air. While thin, human emissions make it plausible we can impact climate. Significant greenhouse gases include water vapor and carbon dioxide, which has internal vibrational modes that absorb and re-emit infrared radiation. Carbon dioxide remains in the atmosphere for hundreds of years, acting as a controlling factor rather than reacting one. Human emissions have increased atmospheric carbon dioxide by 30% correlating with fossil fuel use, with future projections showing levels not seen in 50 million years posing serious negative effects.