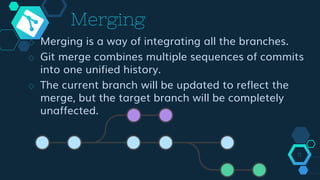
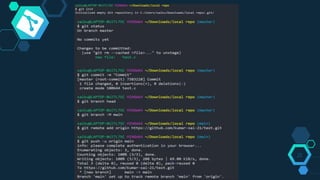
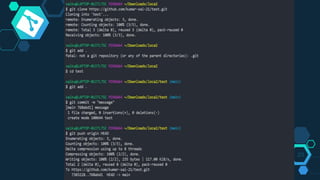
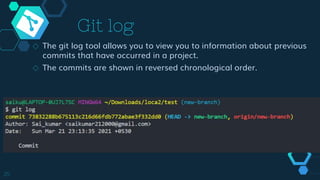
Git is a free and open source distributed version control system initially designed by Linus Torvalds for Linux kernel development. It allows multiple users to work together on projects simultaneously using the same files. Git provides benefits like enhanced collaboration and productivity, reduced errors, and traceability of changes. Key features of Git include branching, merging, and synchronizing with remote repositories. Common Git commands are used to initialize repositories, add/commit files, switch branches, clone repositories, and push/pull from remote servers.