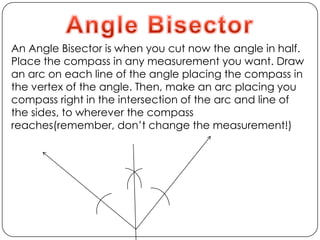
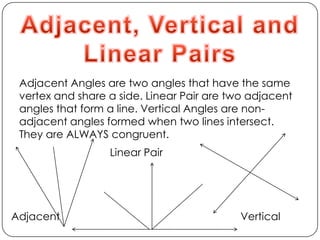
This document provides an overview of key geometry concepts including:
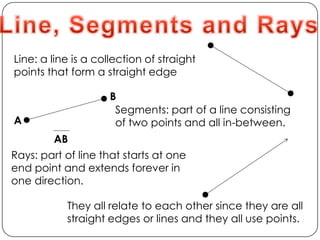
- Points, lines, and planes and their definitions
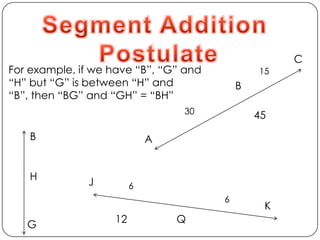
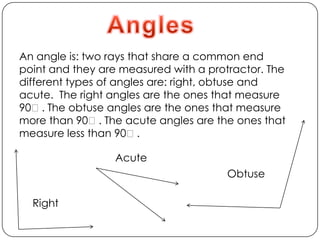
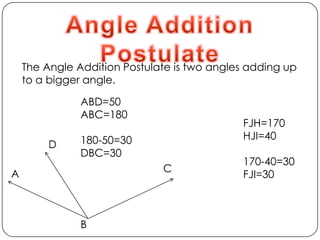
- Types of angles (acute, obtuse, right) and properties like angle addition
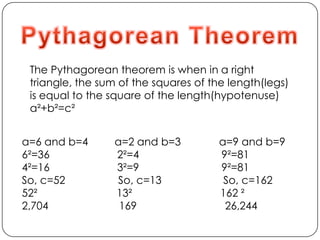
- The Pythagorean theorem and calculating distances between points
- Calculating area and circumference of circles
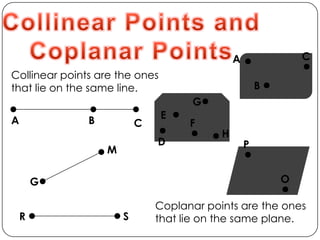
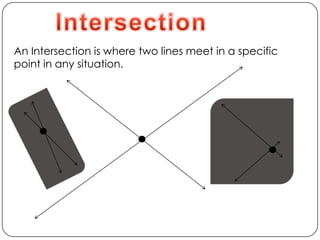
- Describes concepts like collinear points, coplanar points, segments, rays, intersections, congruence, and the five step problem solving process.