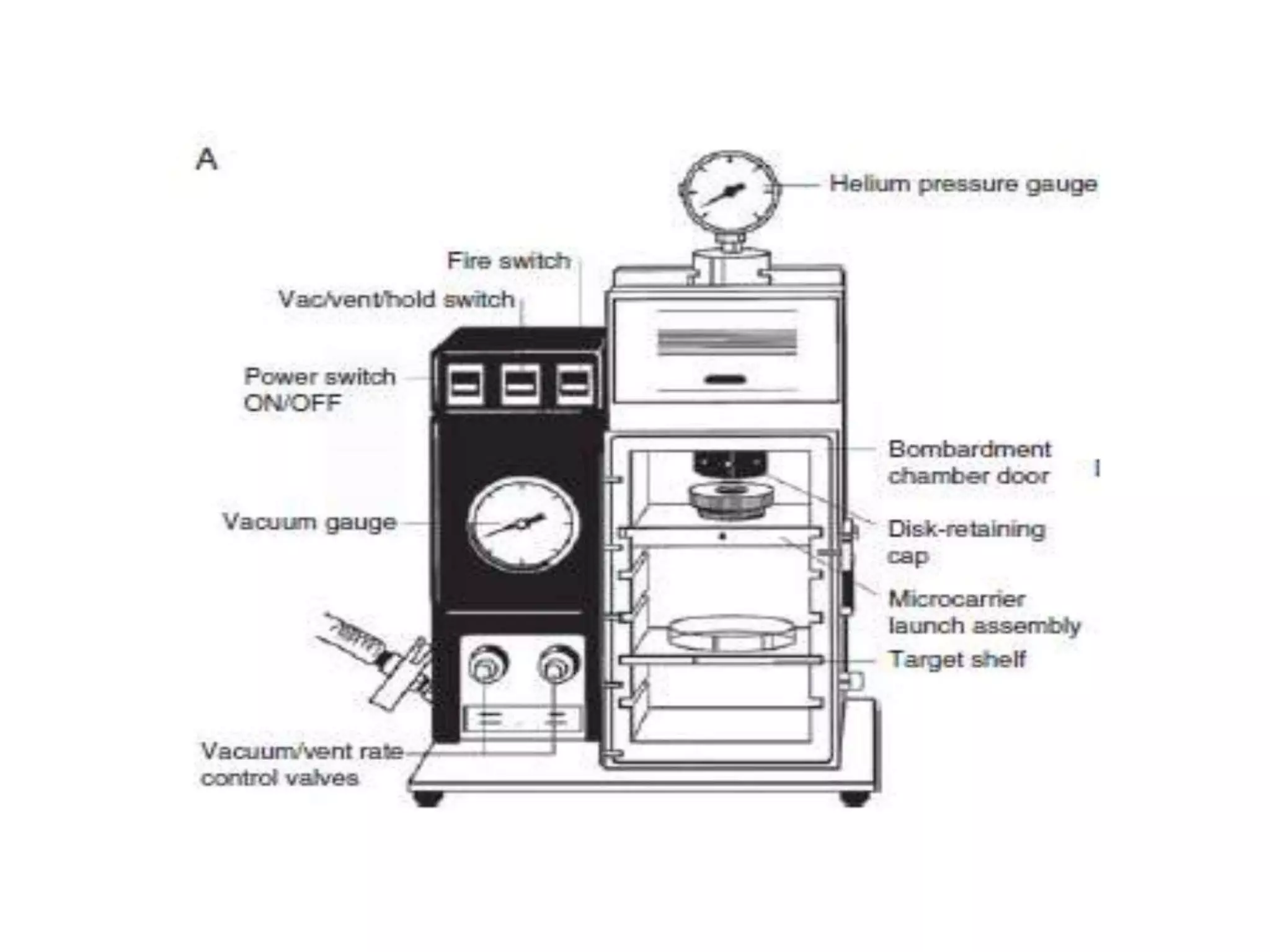
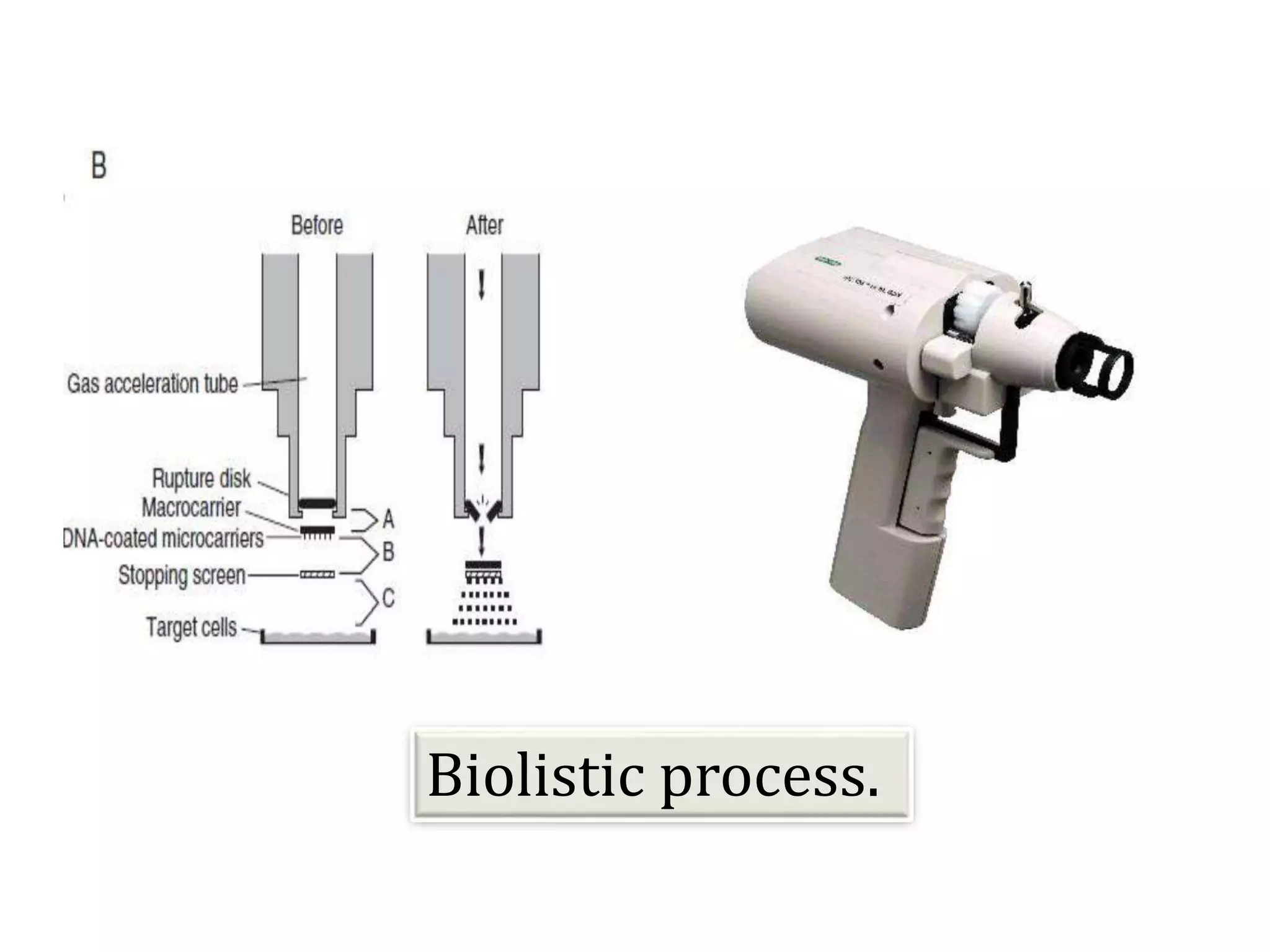
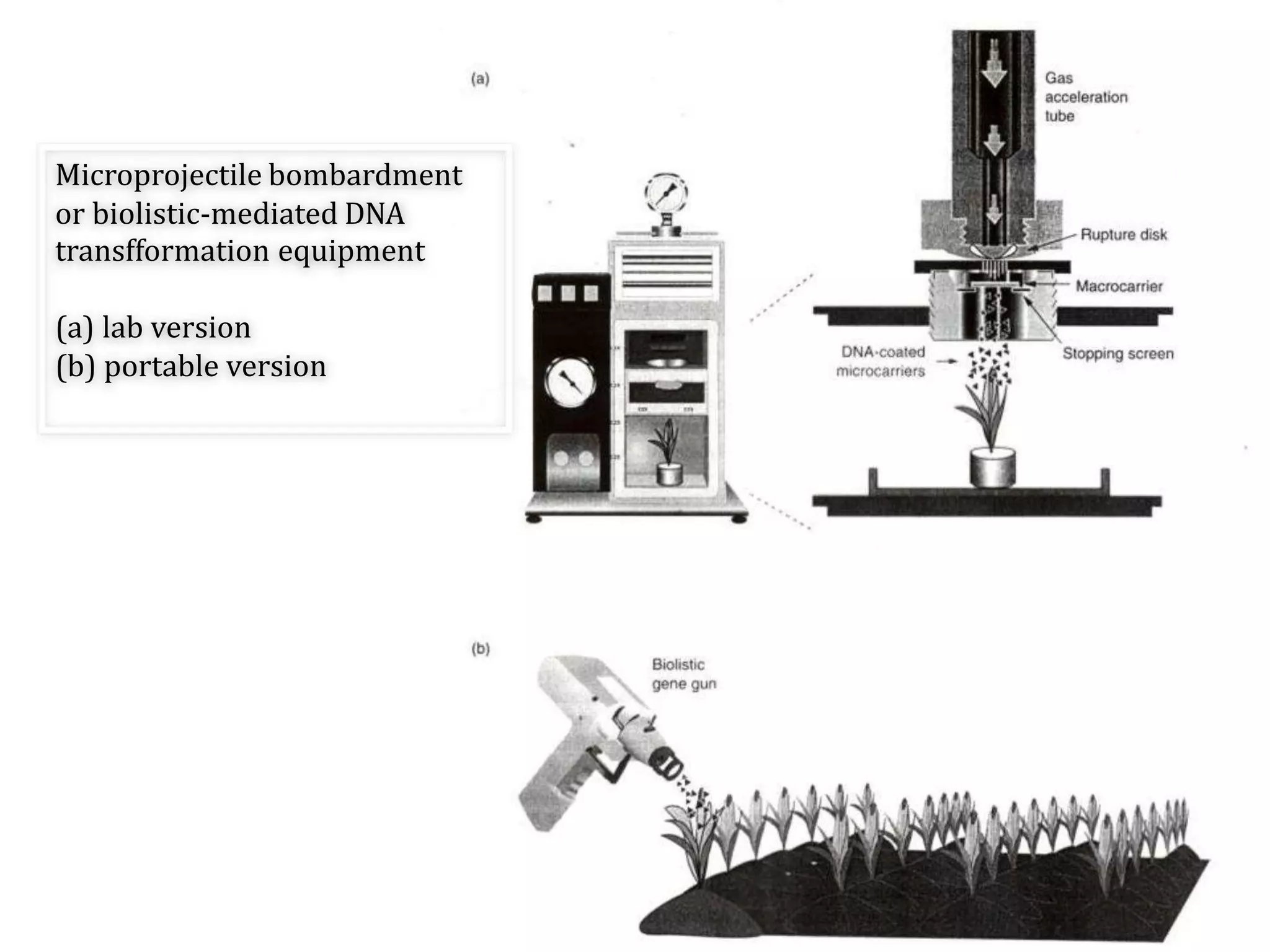
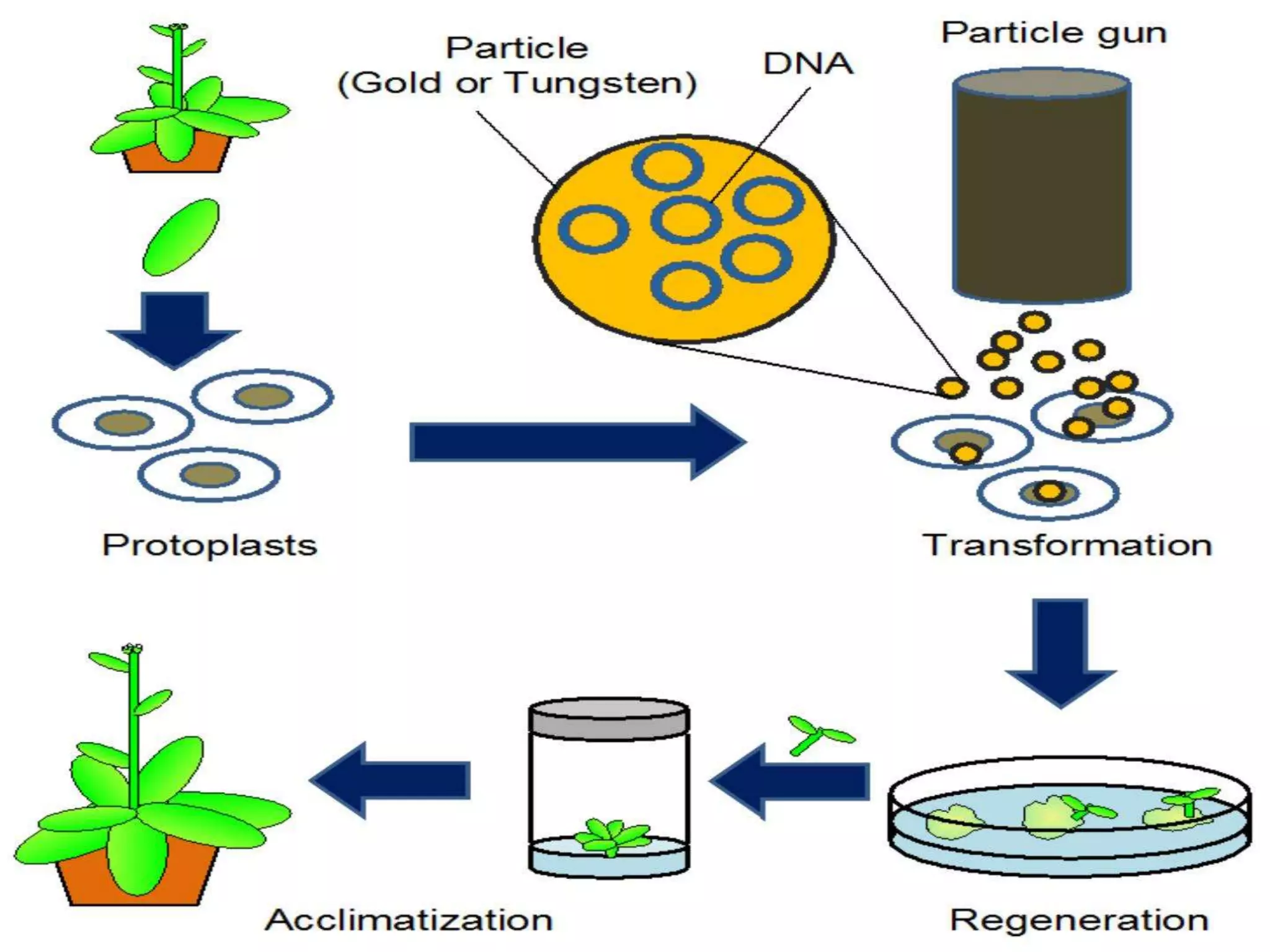
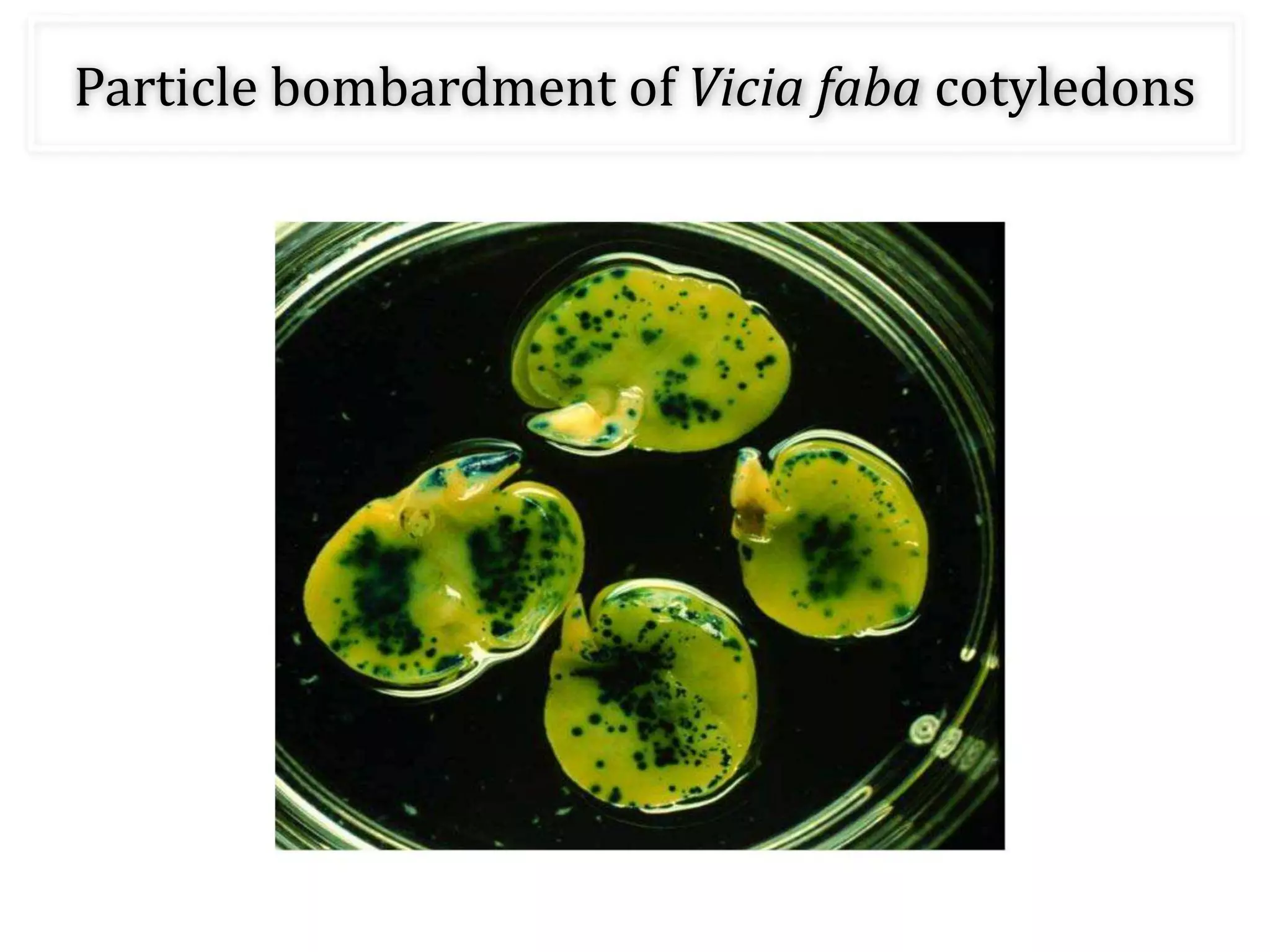
This document discusses various gene transfer techniques, including transformation, which alters an organism's genetic makeup by inserting exogenous DNA. The aims of transforming plants are to improve crop yields and make cultivated plants more resistant to pests and weather. Direct methods like particle bombardment, PEG-mediated transformation, electroporation, and microinjection are described. Particle bombardment uses a gene gun to coat microparticles with DNA and propel them into plant tissues. PEG and divalent cations render plant cell membranes permeable to naked DNA. Electroporation uses electric pulses to create pores for DNA entry. Direct methods are useful for cereals but can cause transgene rearrangement.