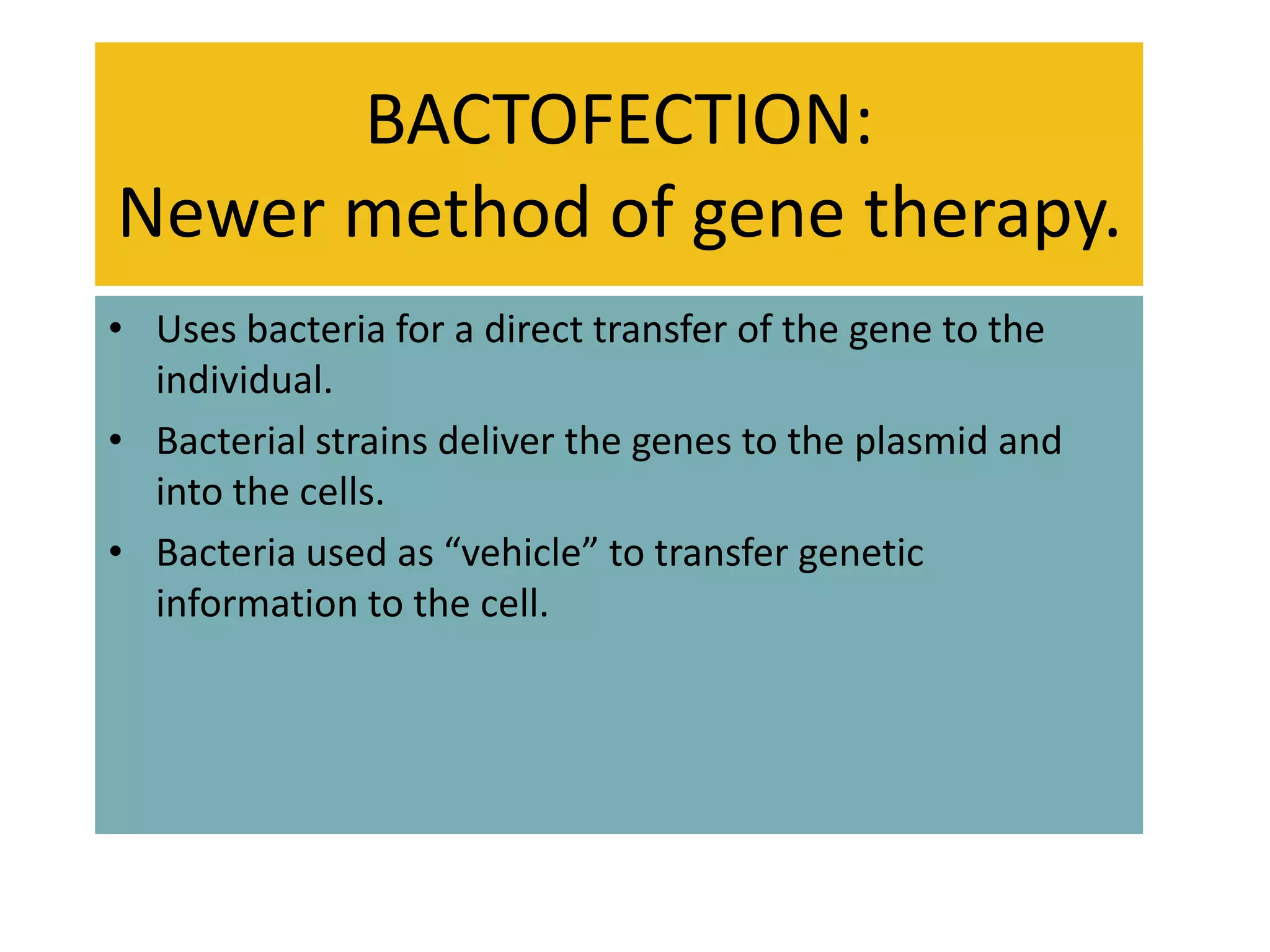
Gene therapy is a technique used to substitute defective genes that cause diseases with functional genes. It involves identifying the defective gene, extracting DNA, inserting a functional gene, and reinserting the modified DNA. There are two main types of gene therapy - somatic cell gene therapy, which treats only the individual and is not hereditary, and germline cell gene therapy, which could affect future generations but may be most effective. Gene therapy delivers the new genes via viral or bacterial vectors and holds promise to cure genetic diseases but also poses risks such as immune reactions or unintended effects.