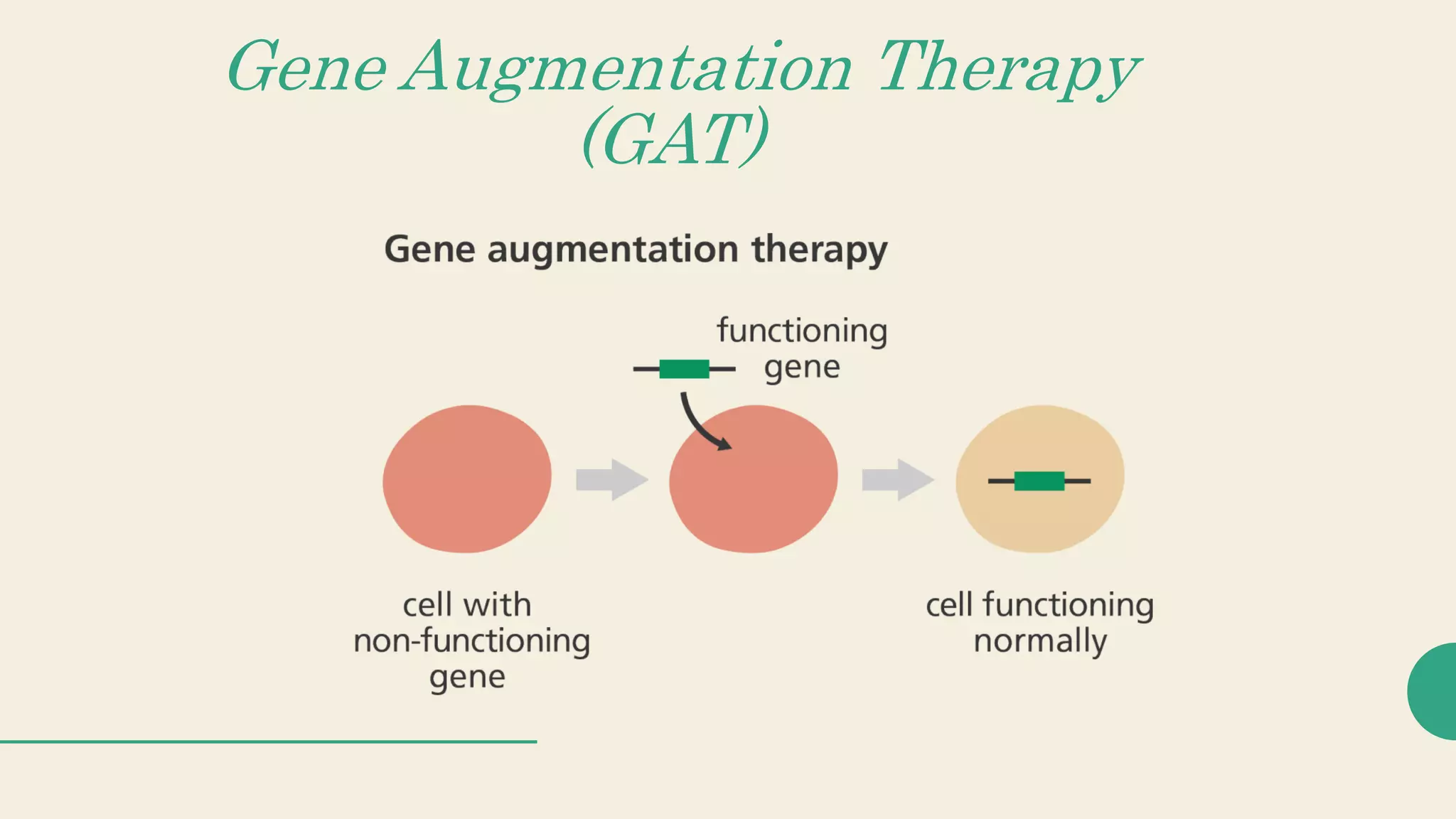
Gene therapy seeks to modify or manipulate genes to treat diseases. There are three main strategies for gene therapy: gene augmentation therapy which introduces a normal gene to compensate for an abnormal gene, targeted killing of specific cells, and targeted inhibition of gene expression. Gene therapy can be somatic, affecting most body cells, or germline, affecting eggs or sperm. Viral vectors are commonly used to deliver genes into cells, but non-viral methods also exist. Gene editing tools like ZFNs, TALENs, and CRISPR-Cas systems can also be used to precisely alter genes.