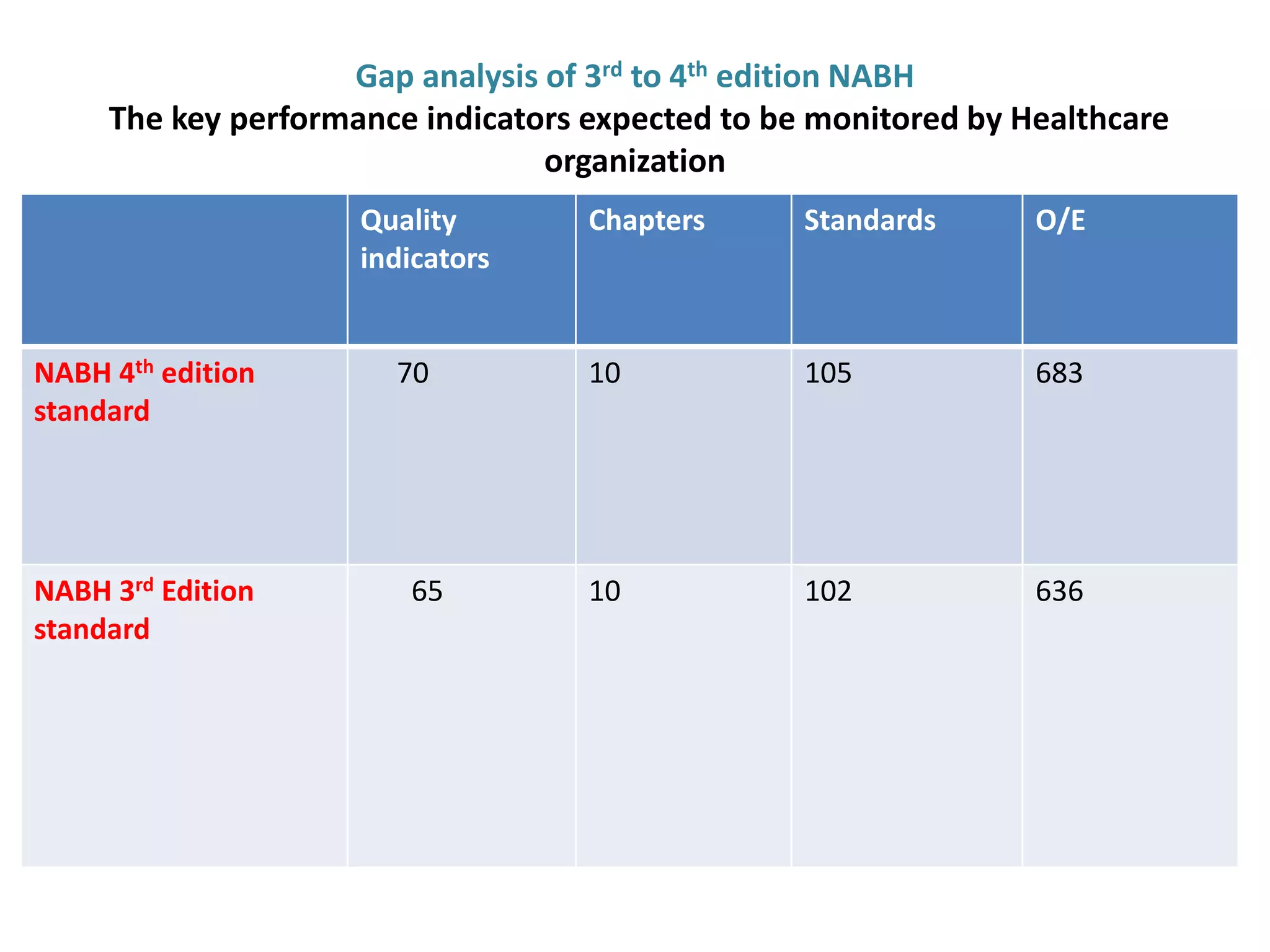
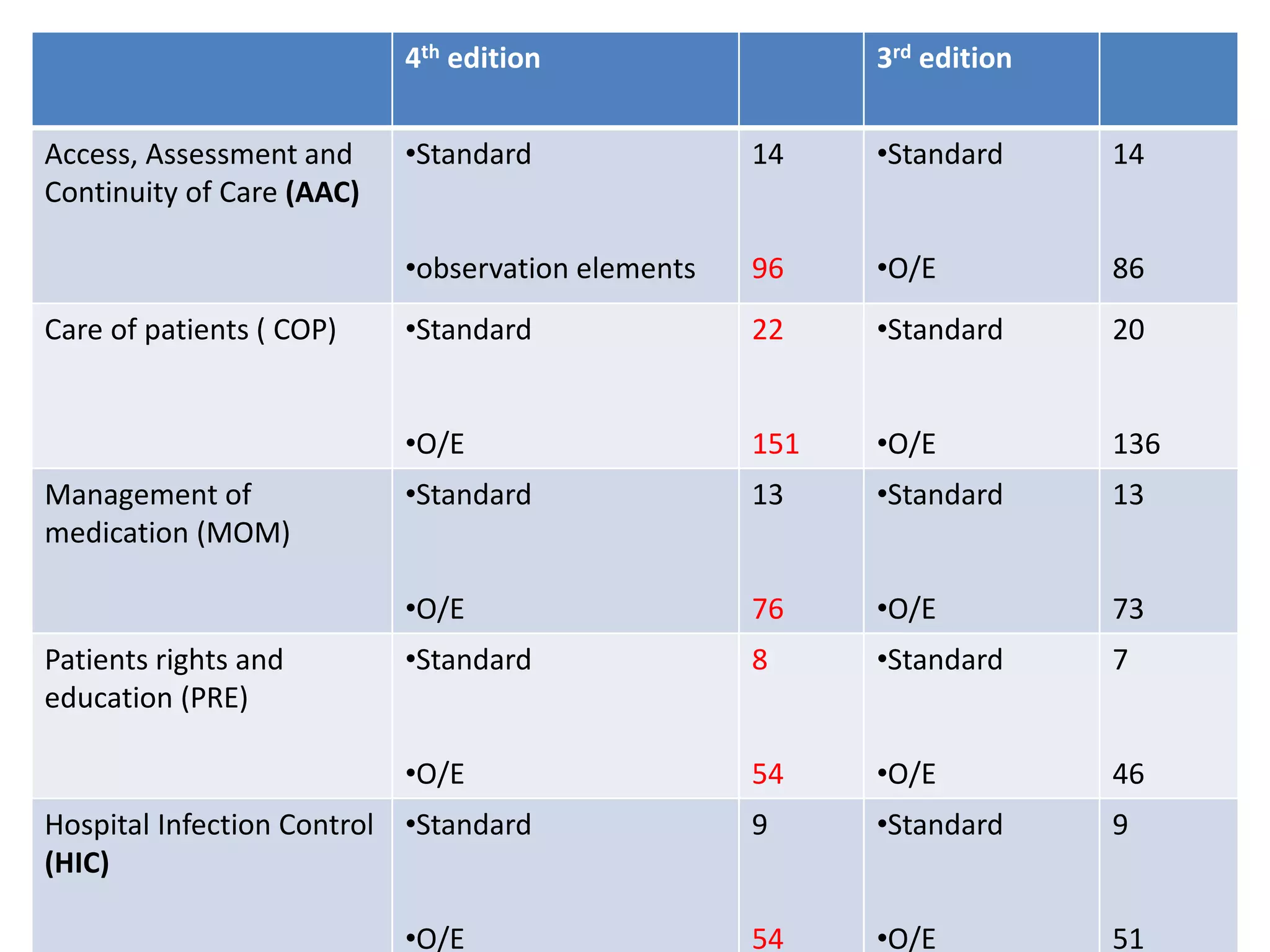
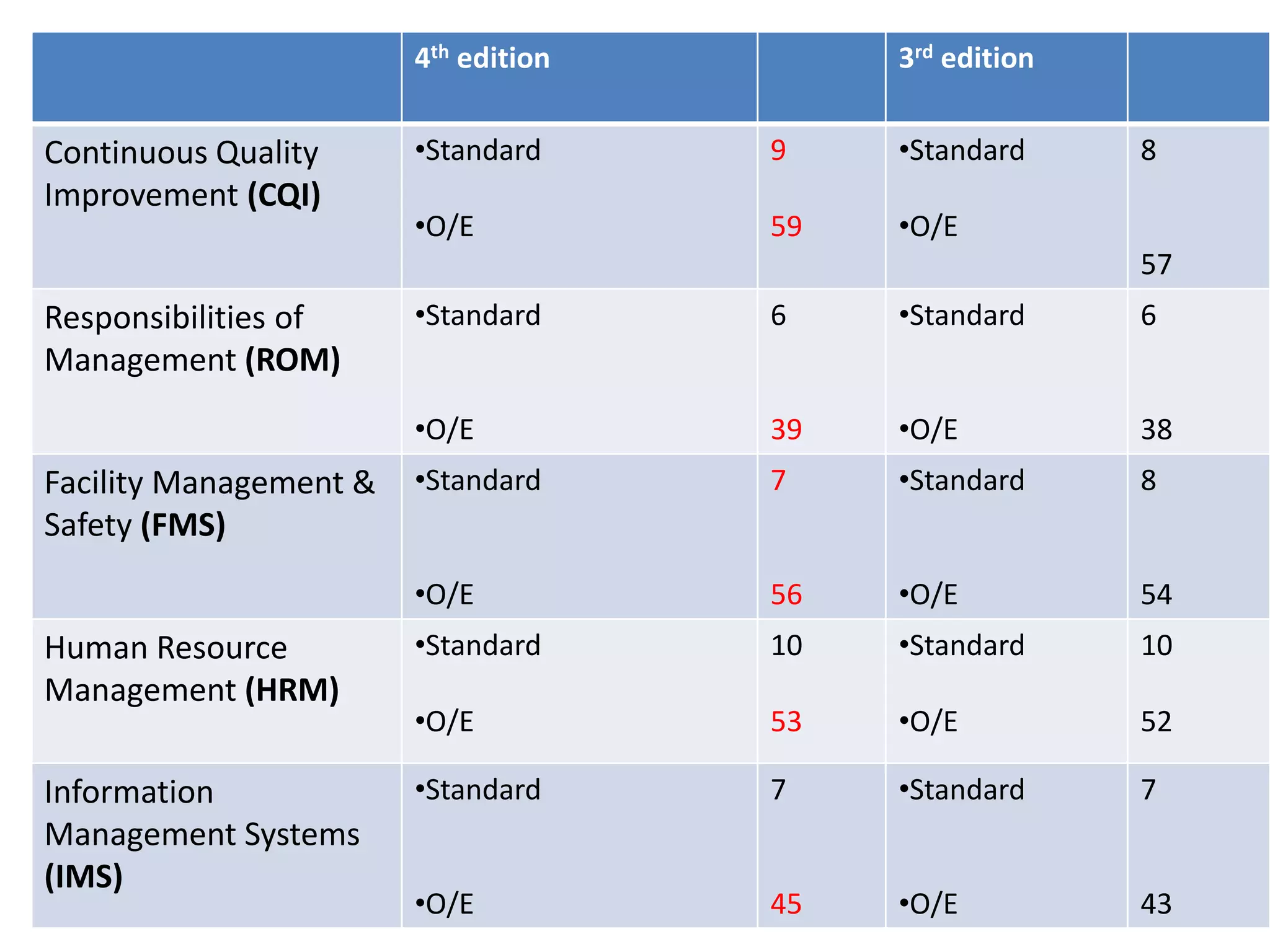
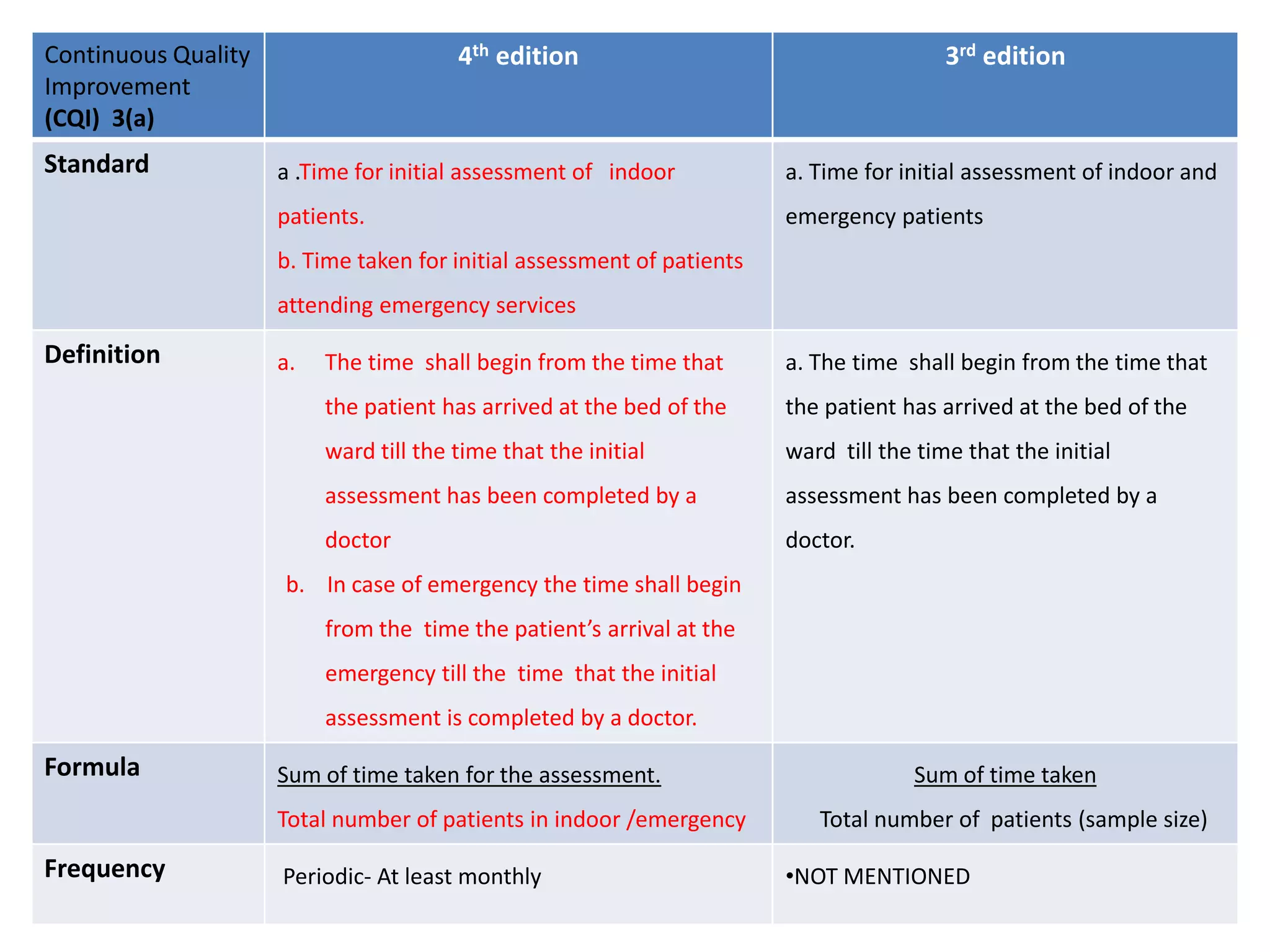
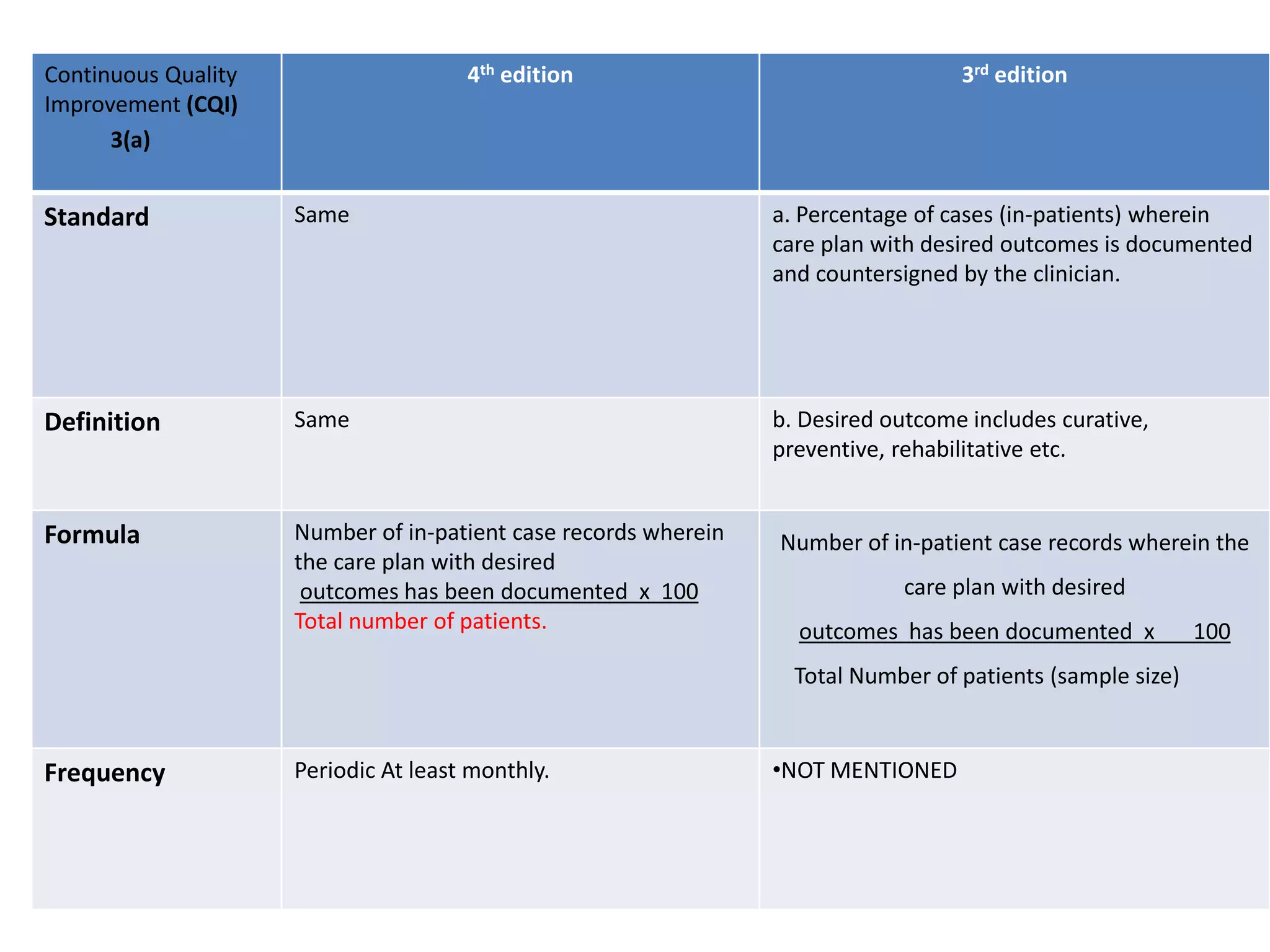
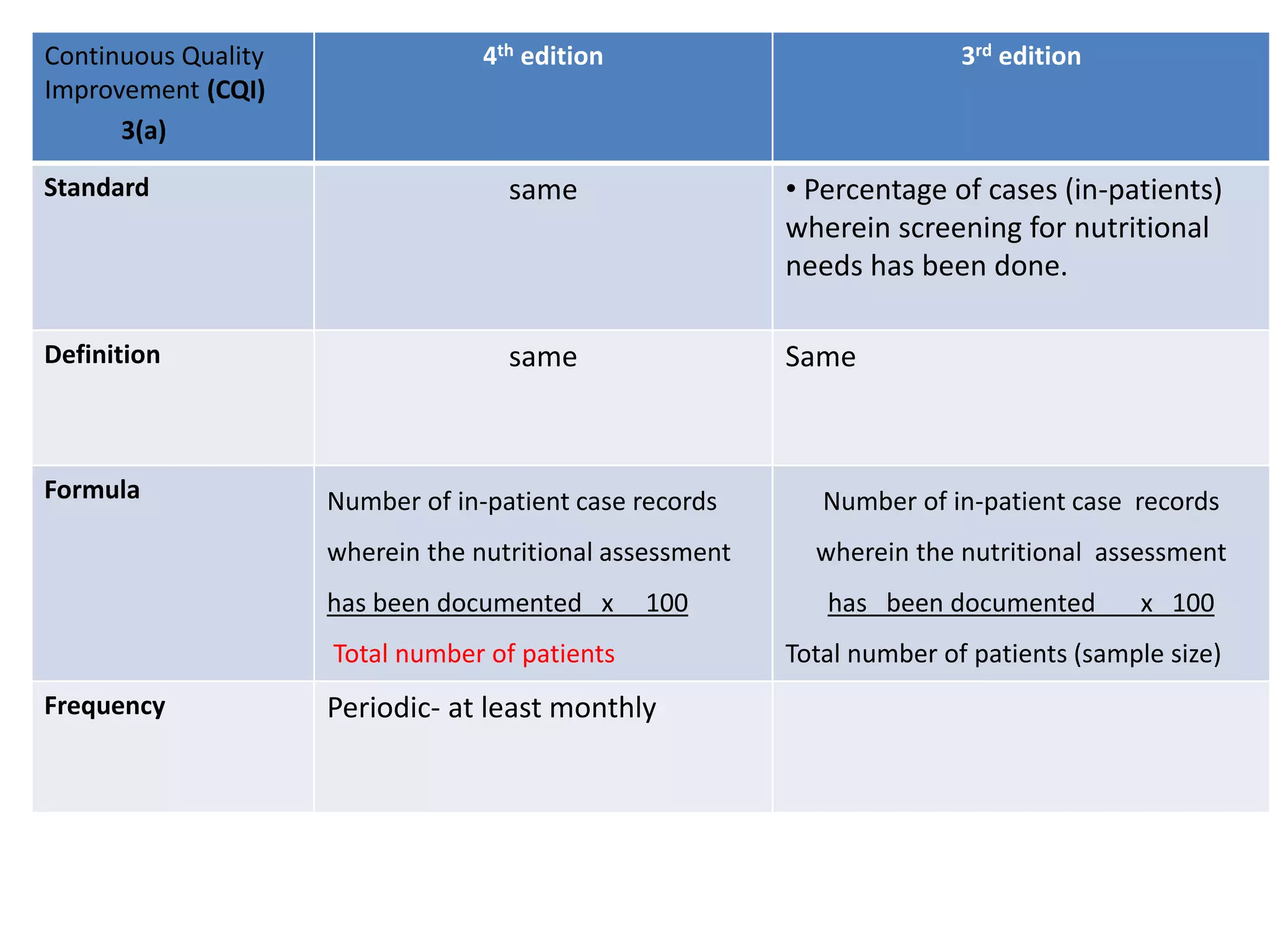
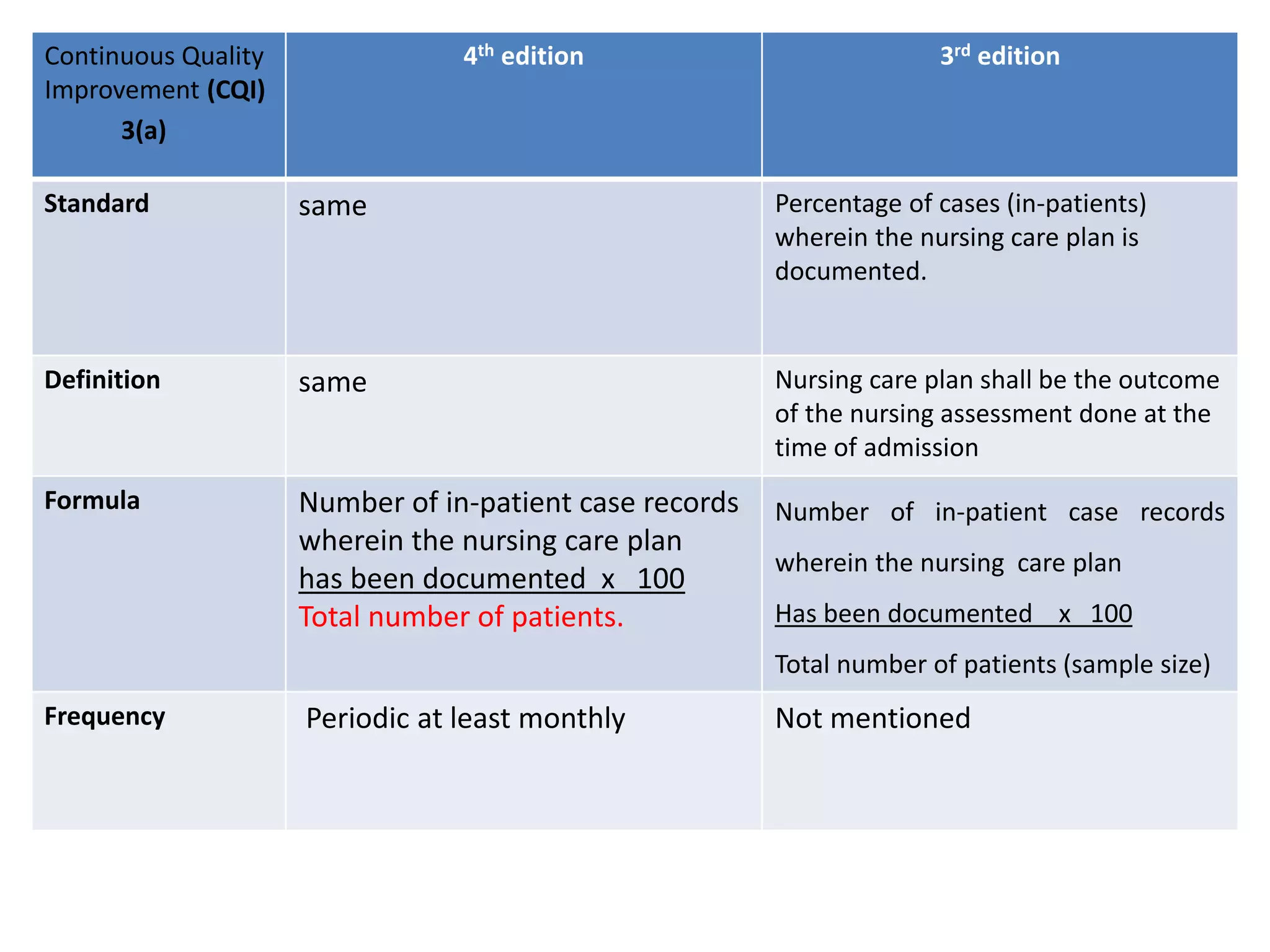
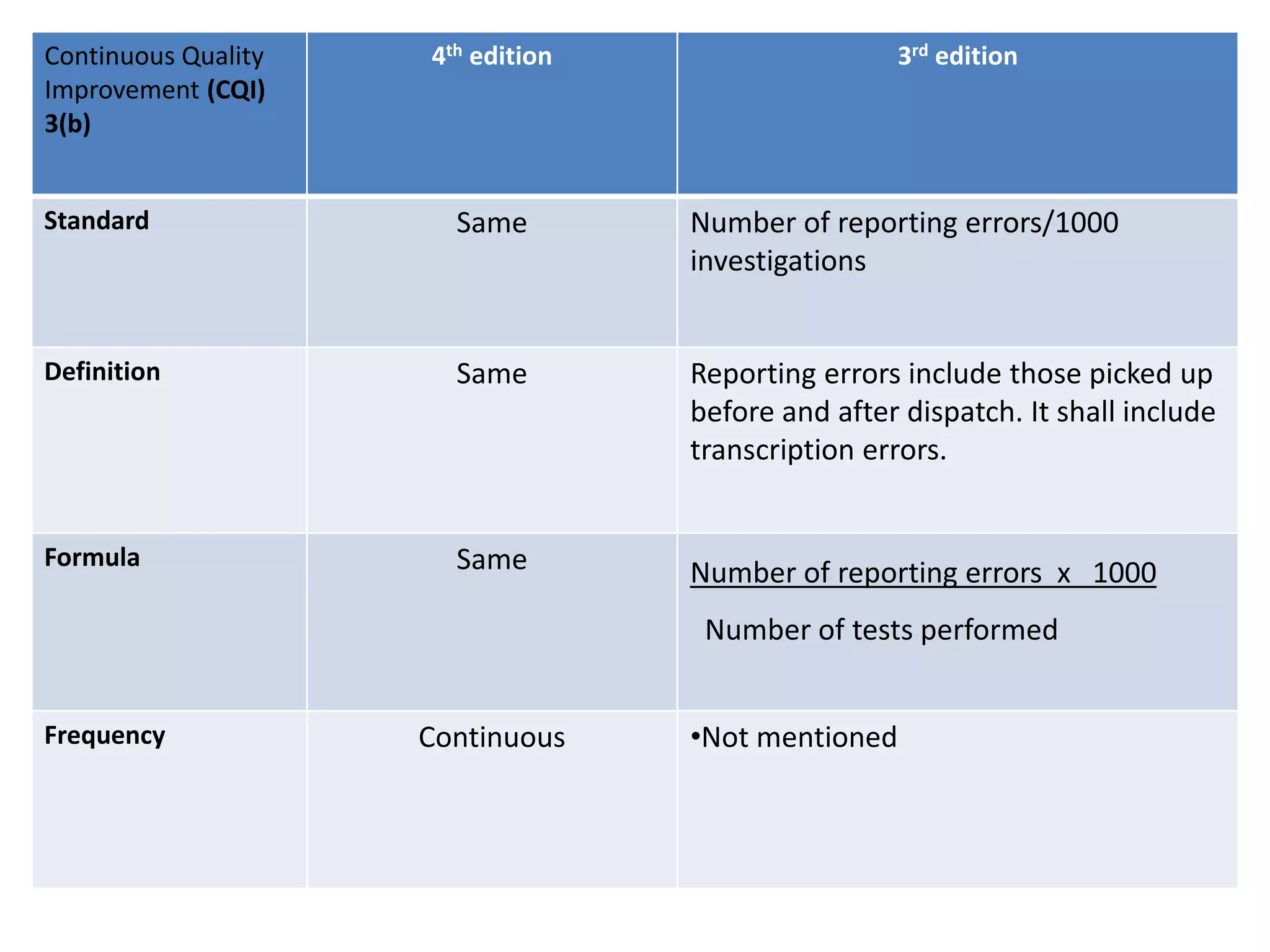
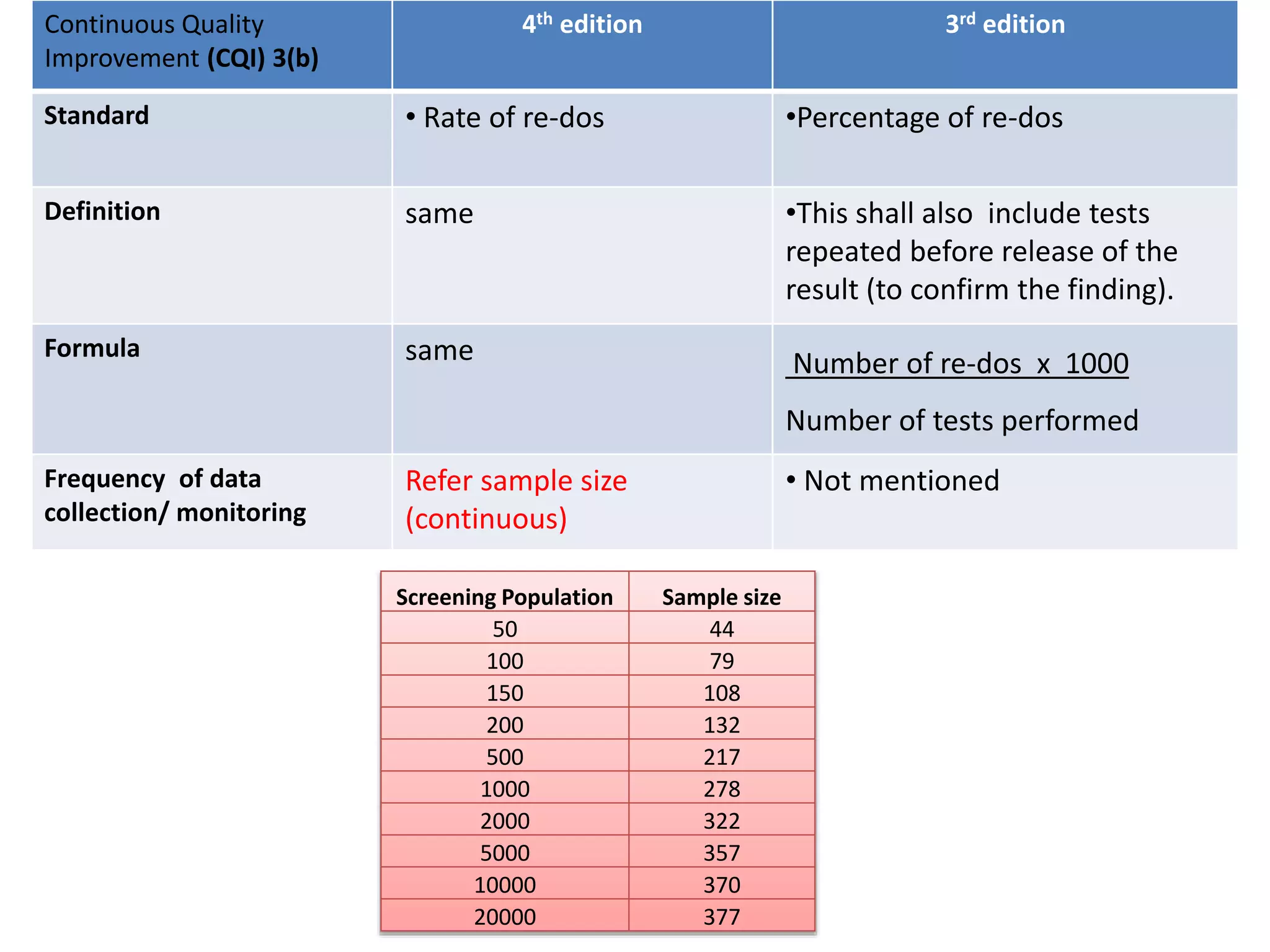
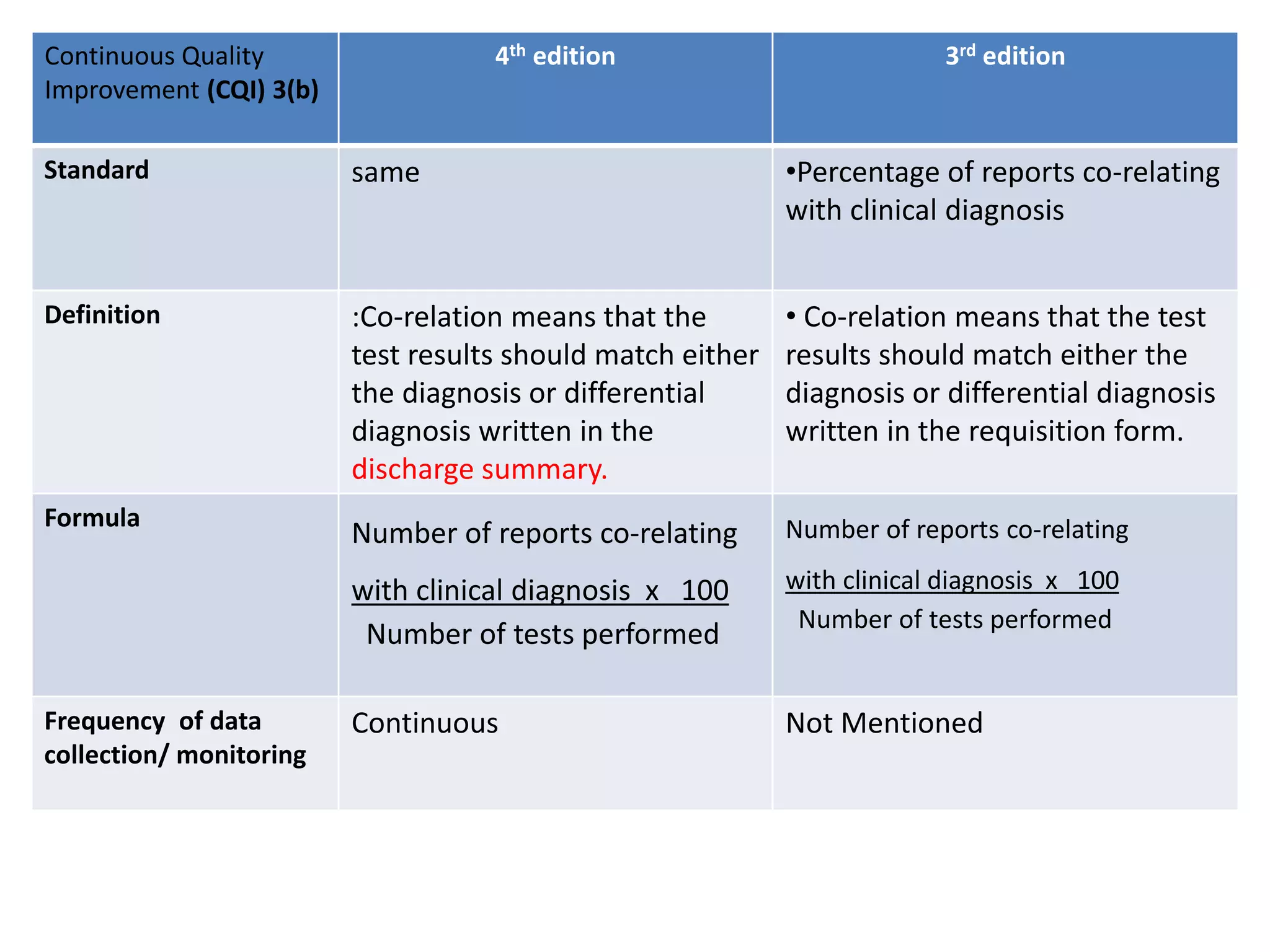
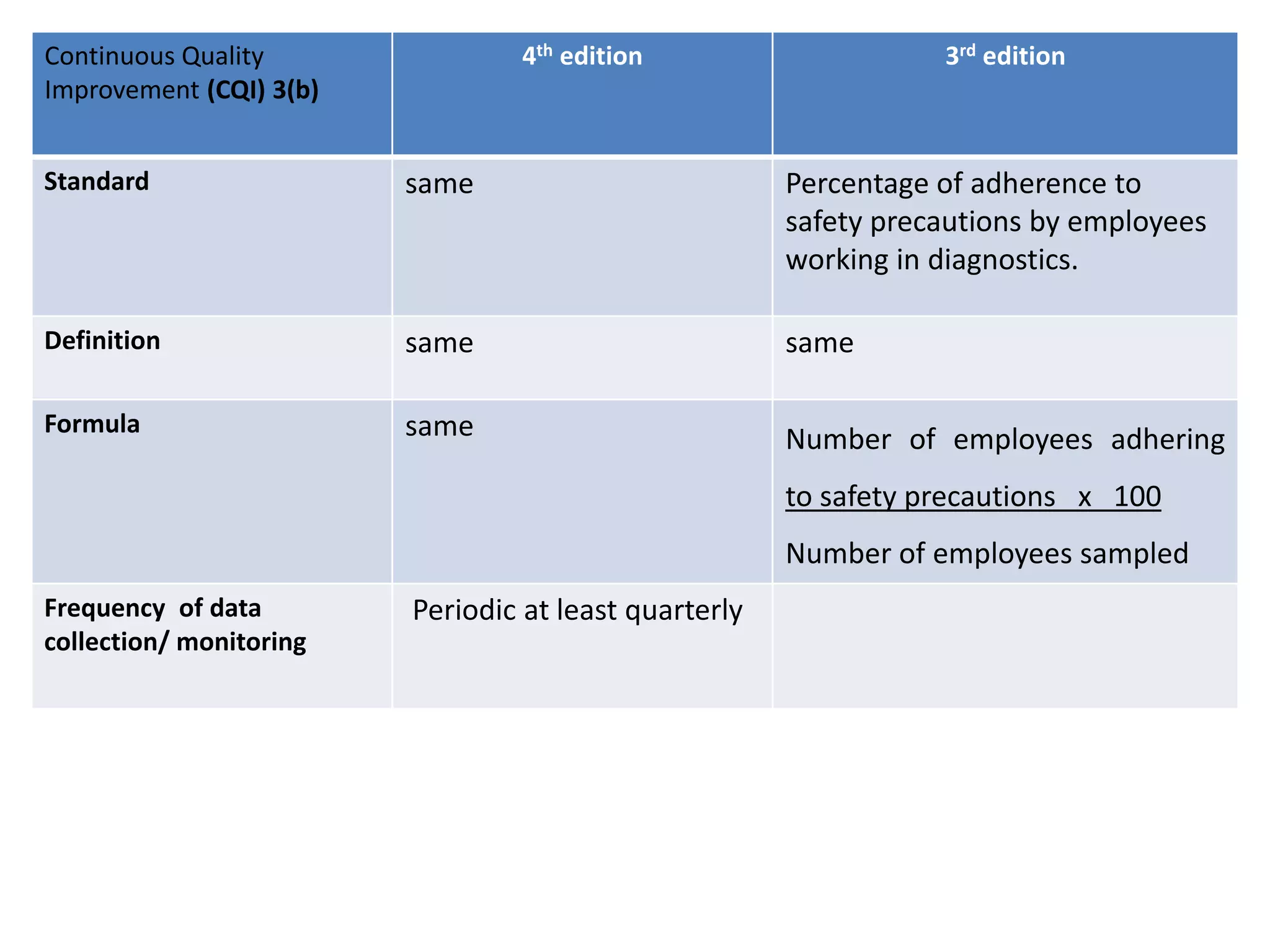
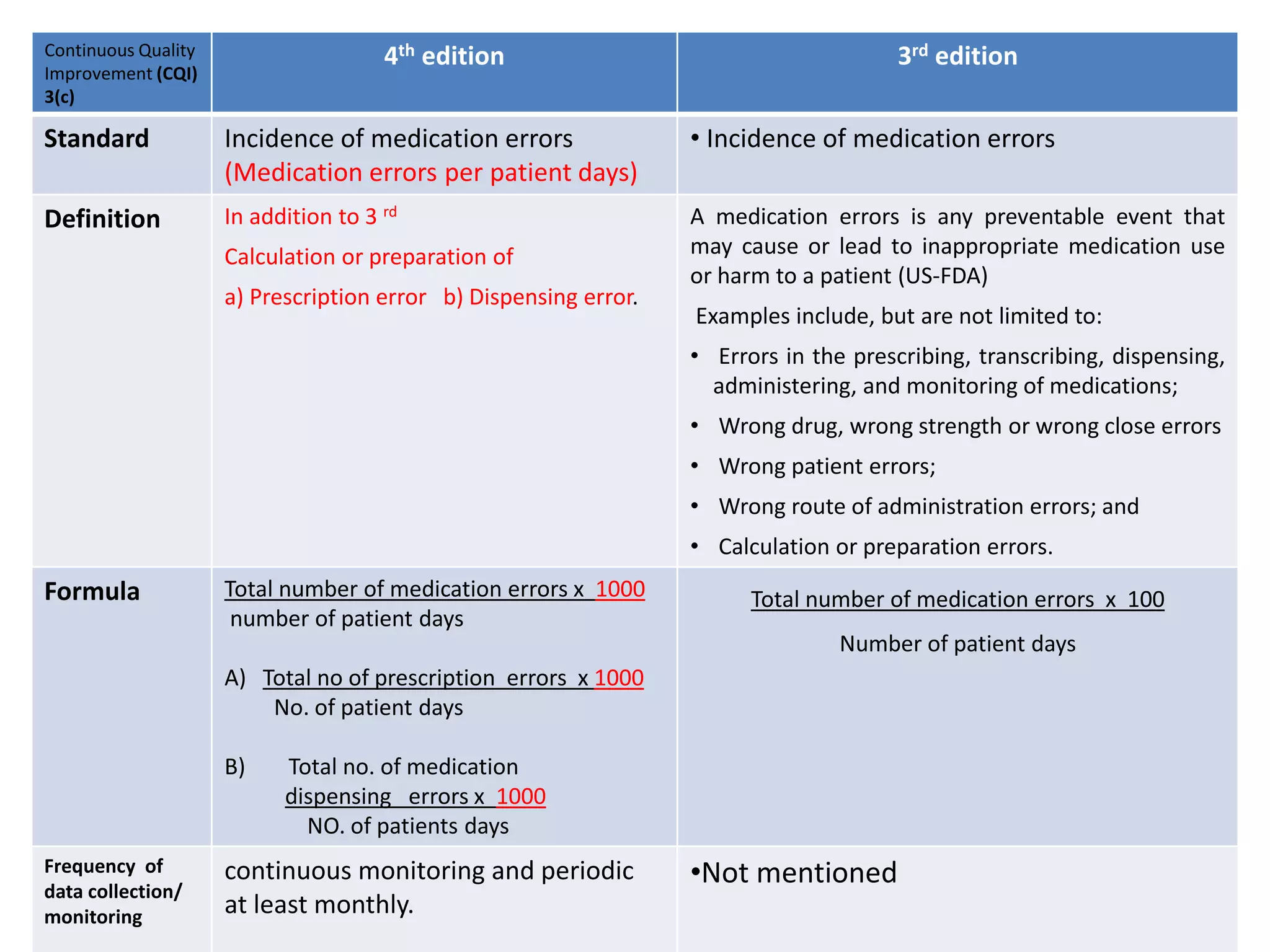
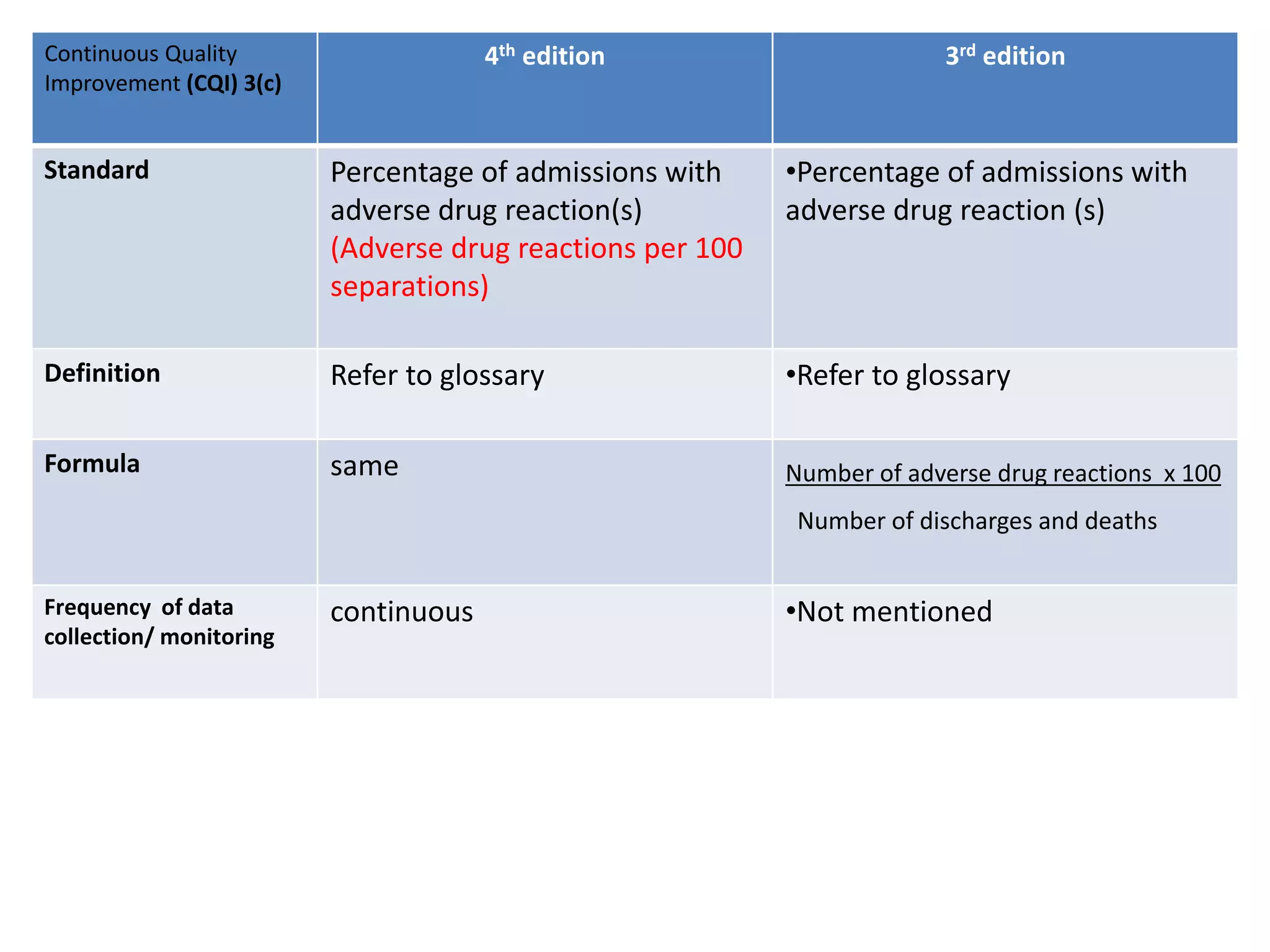
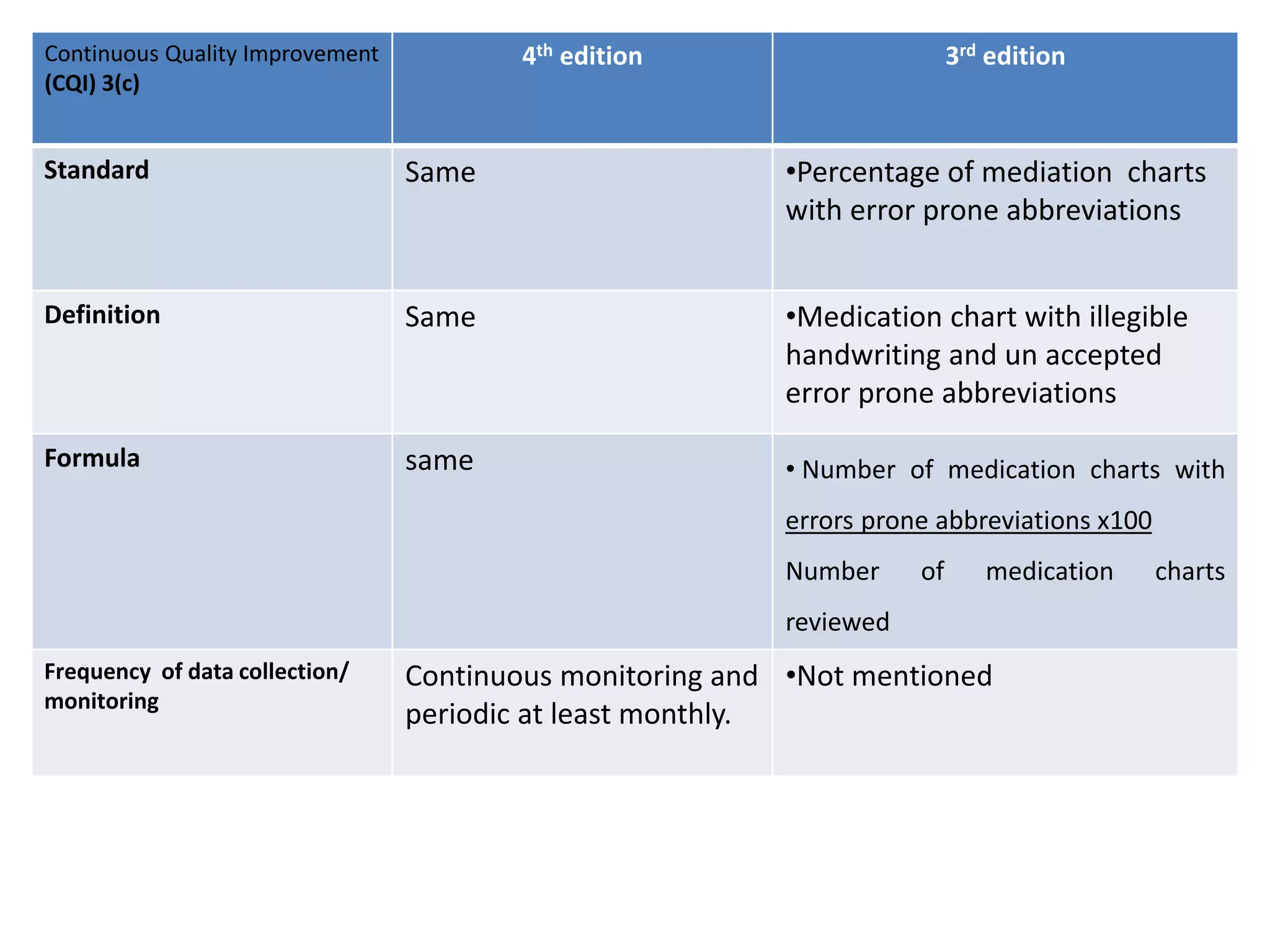
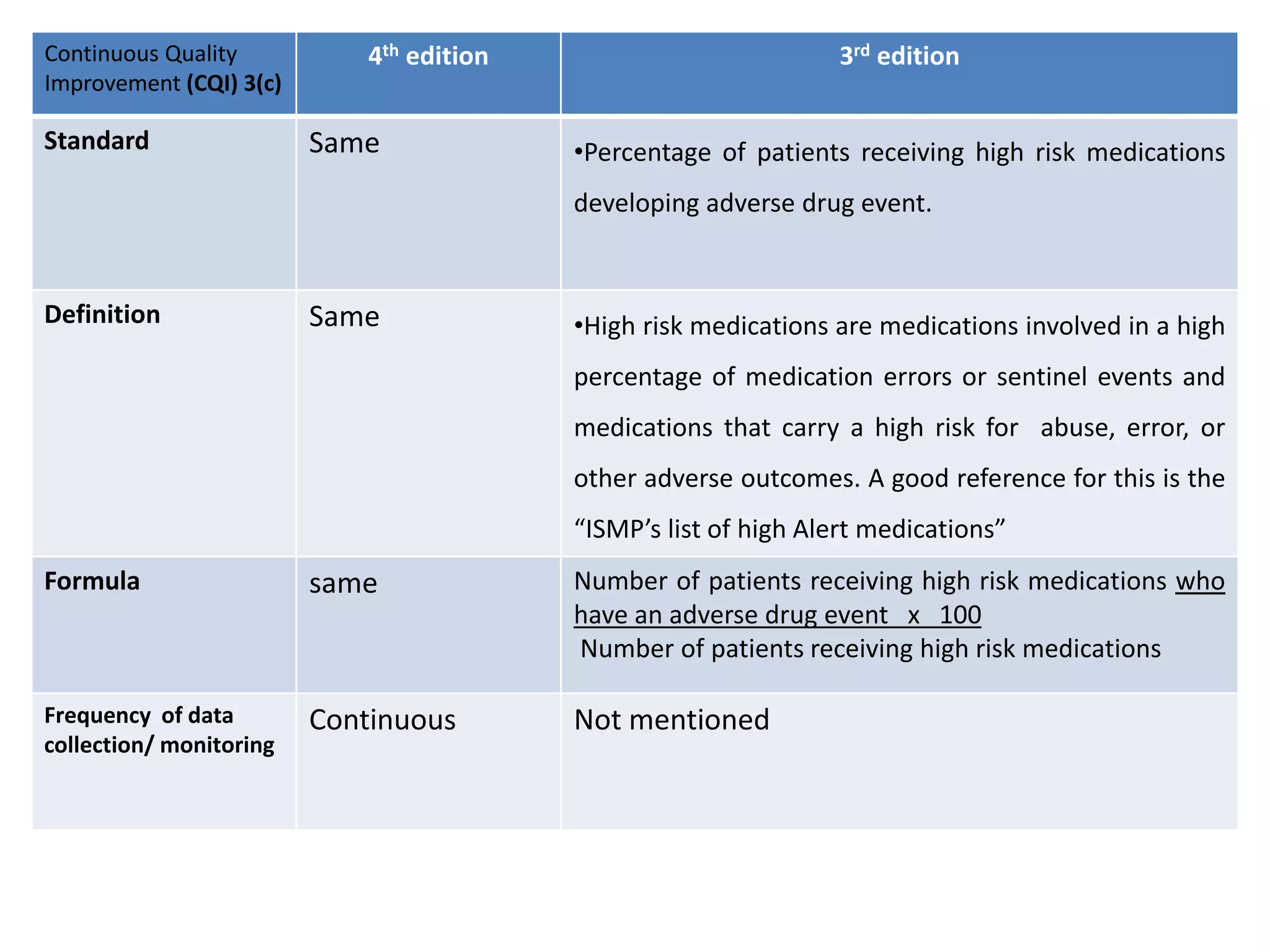
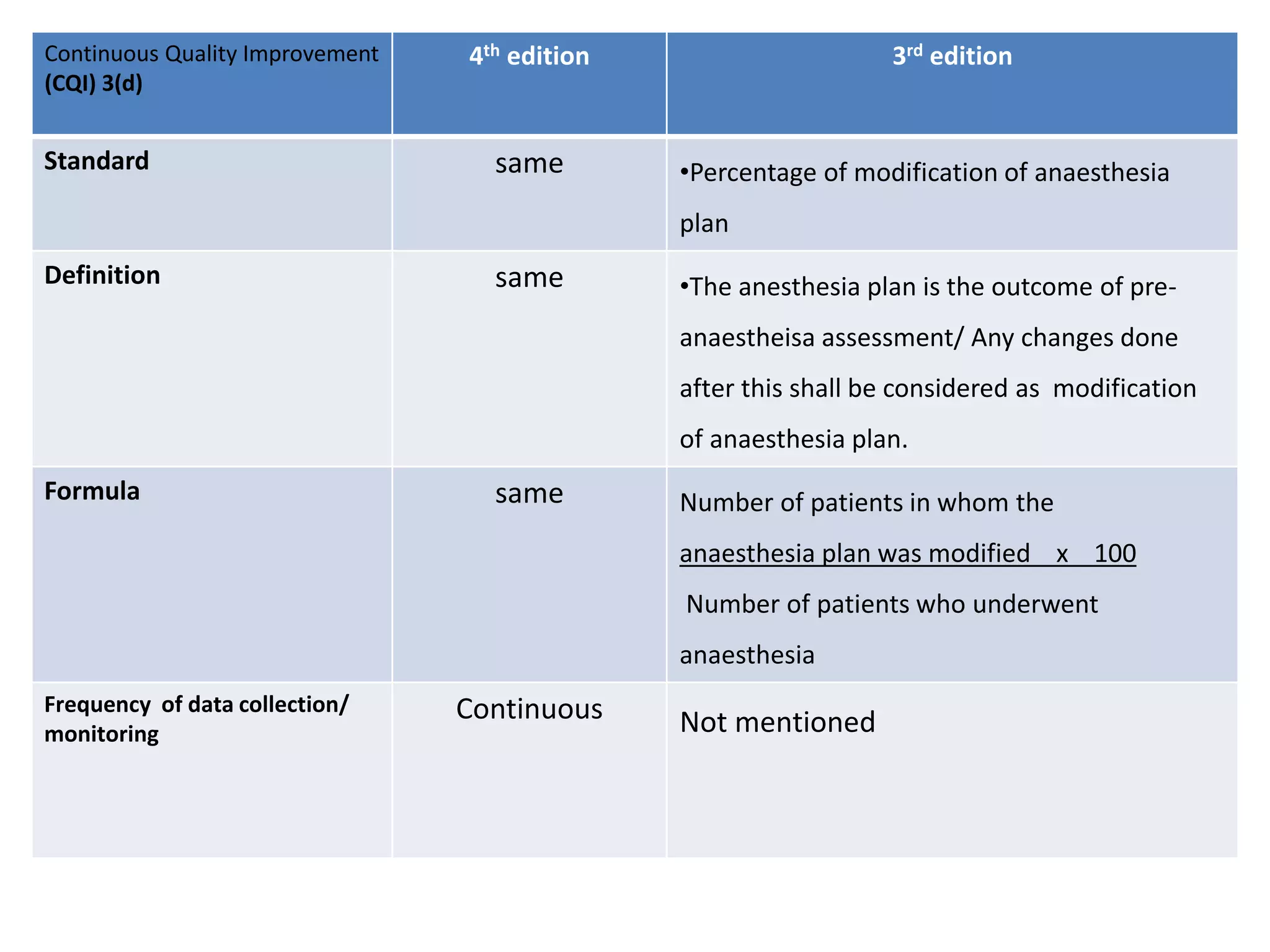
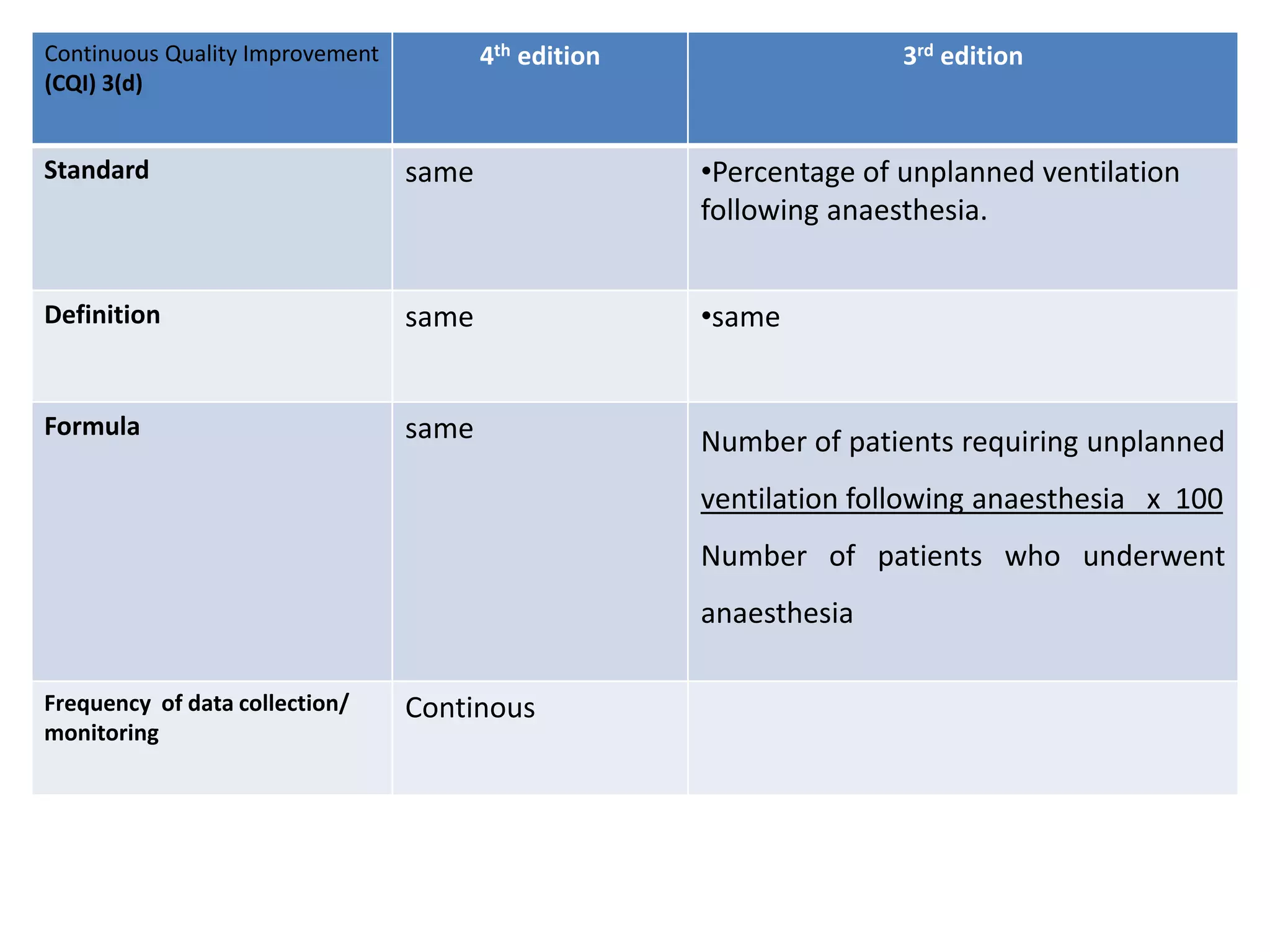
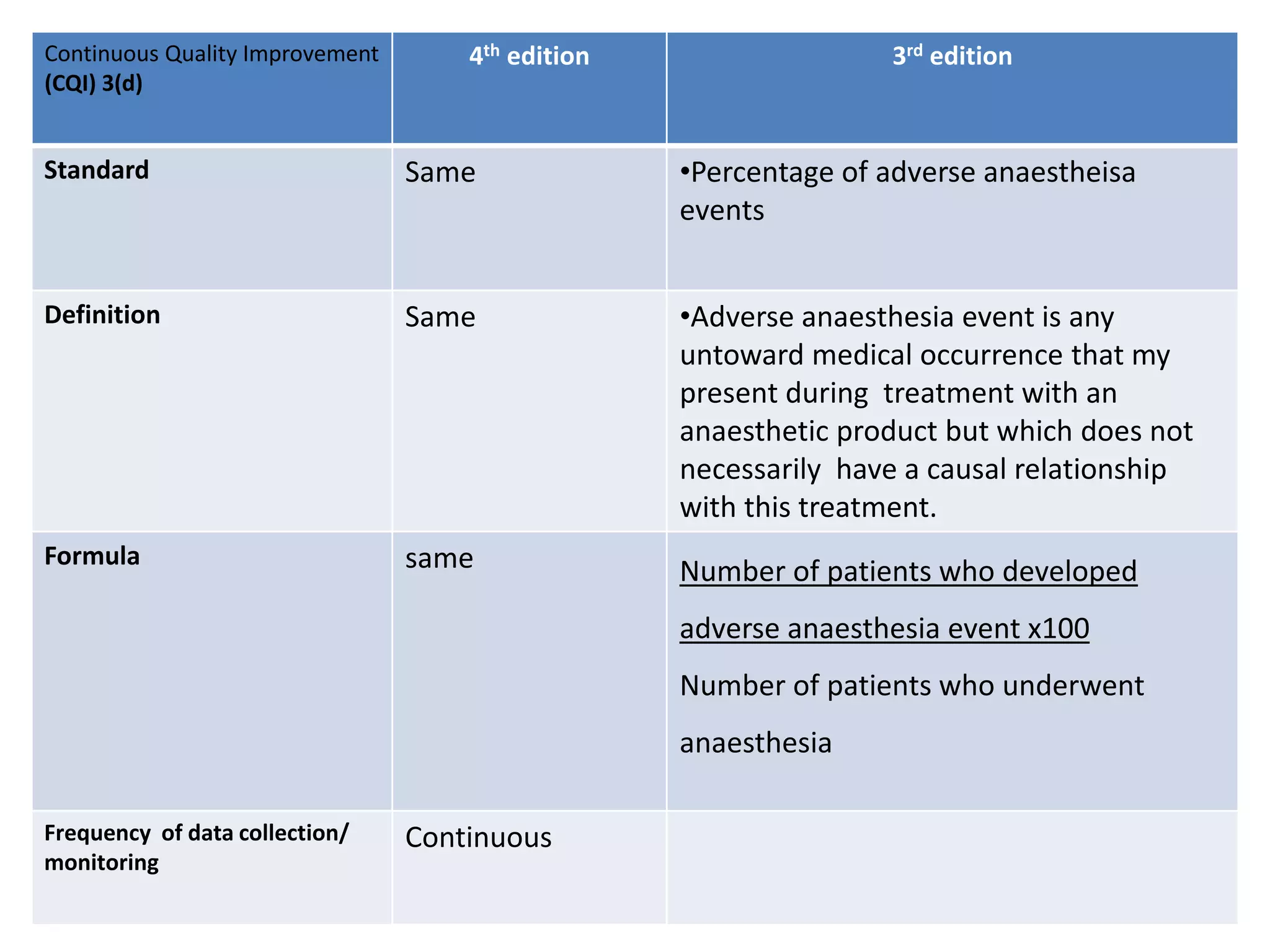
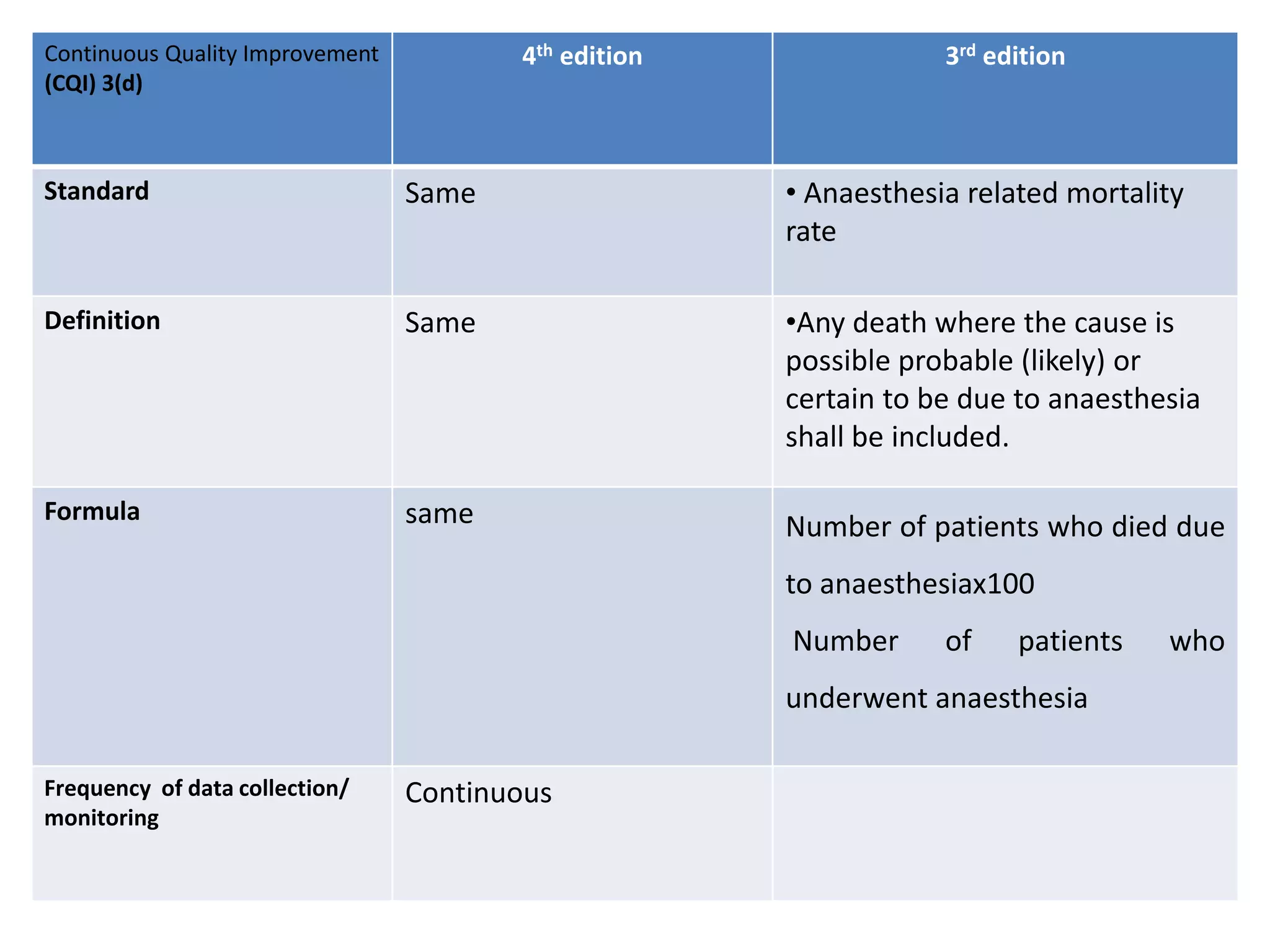
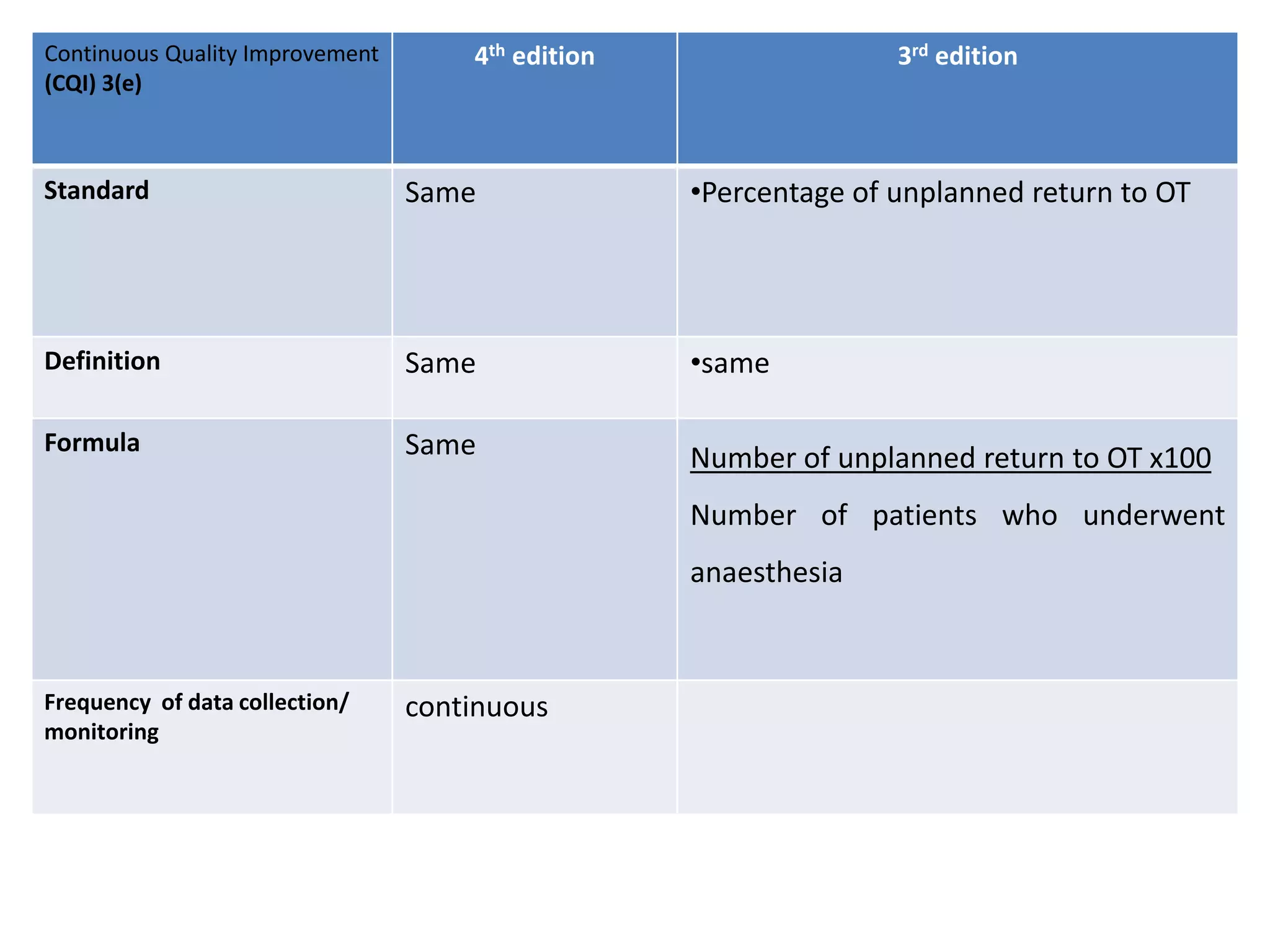
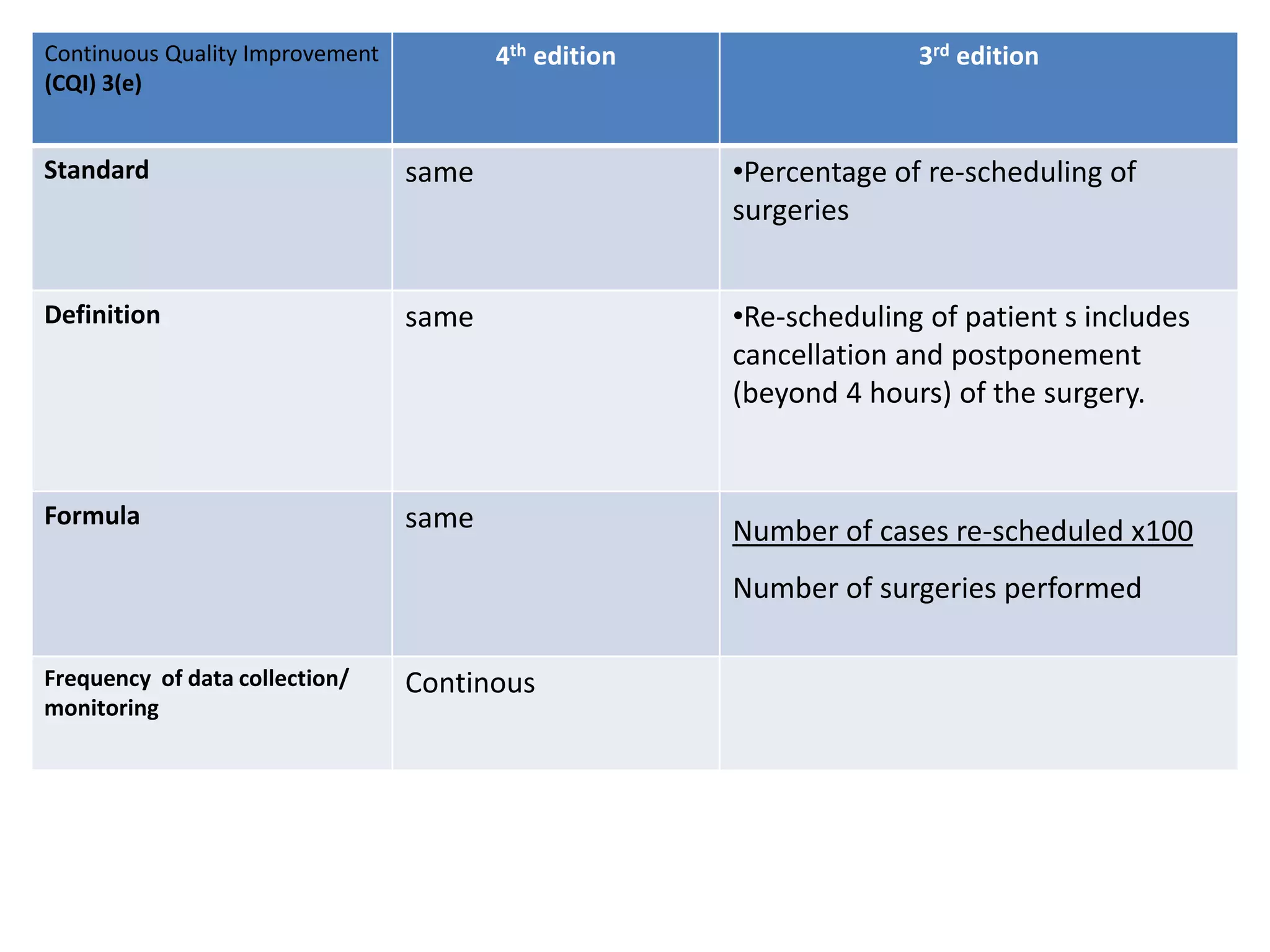
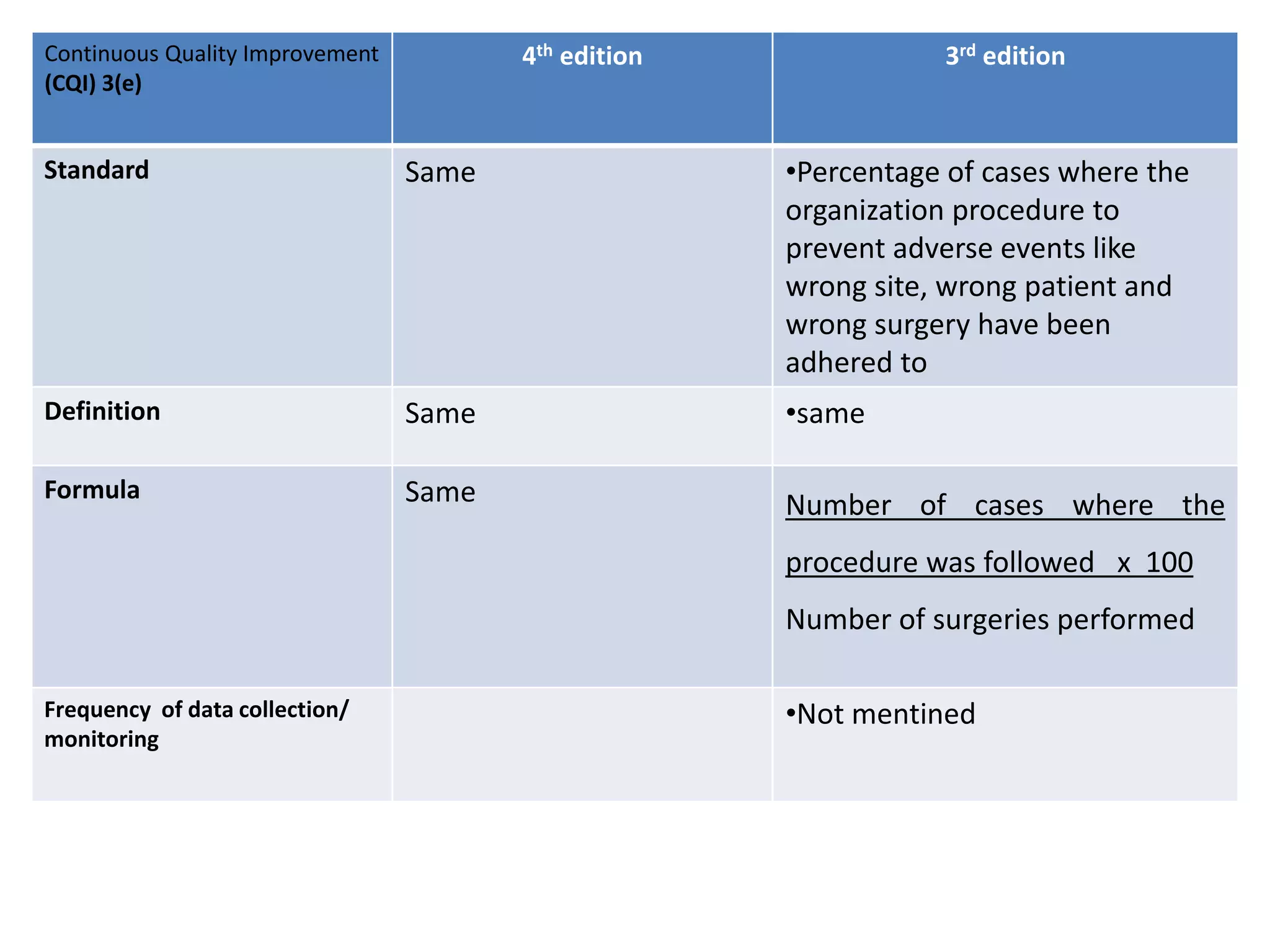
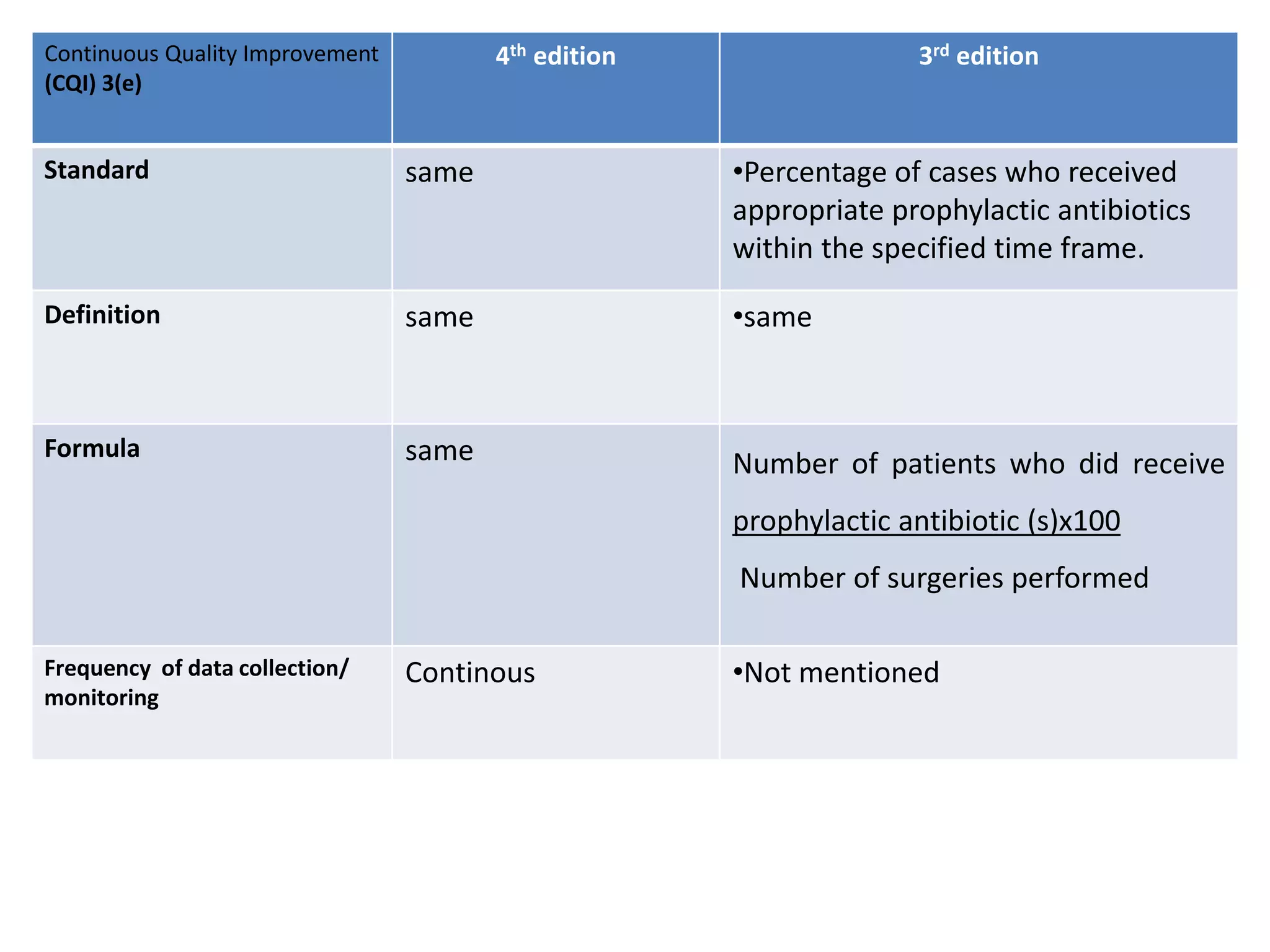
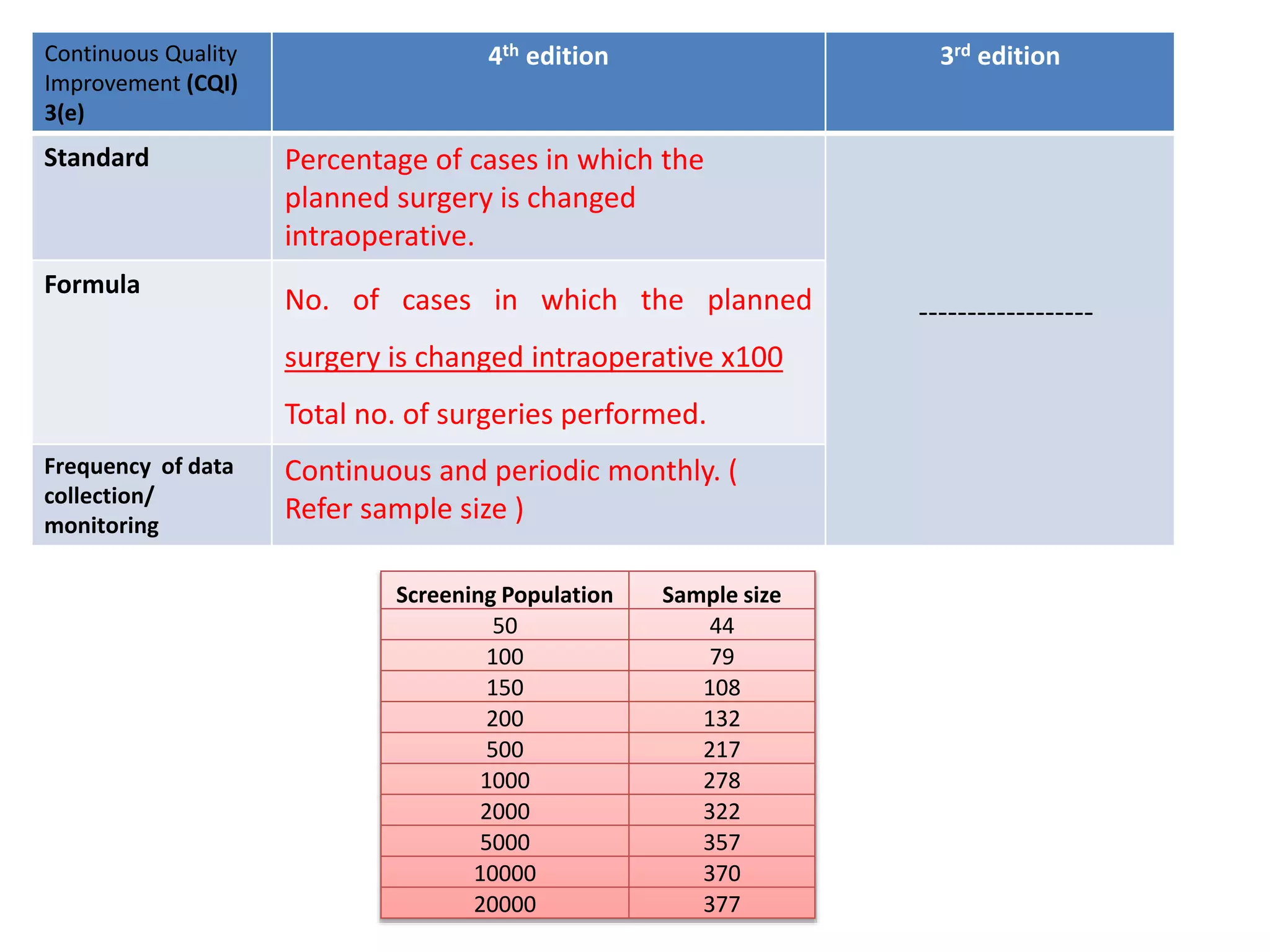
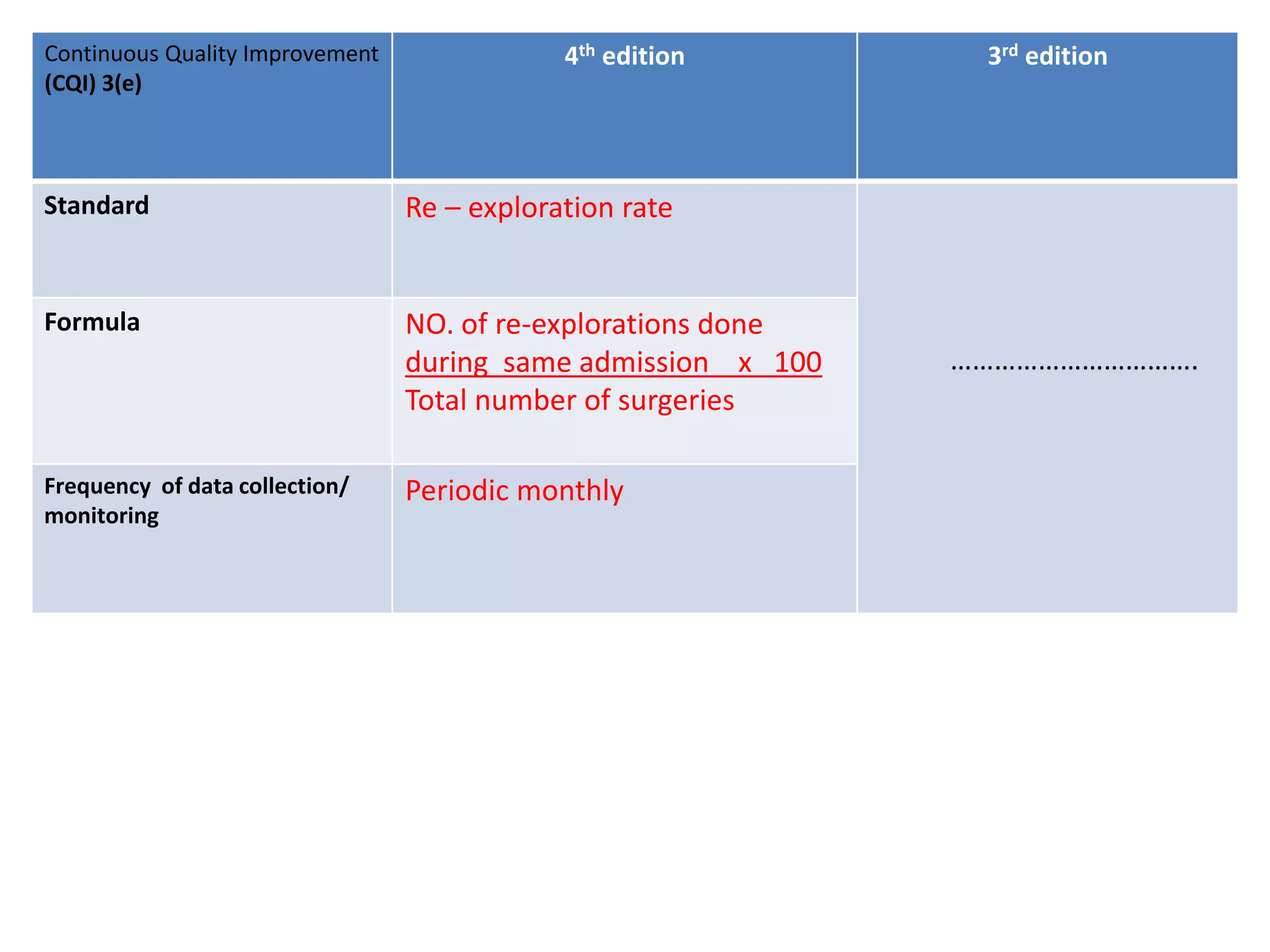
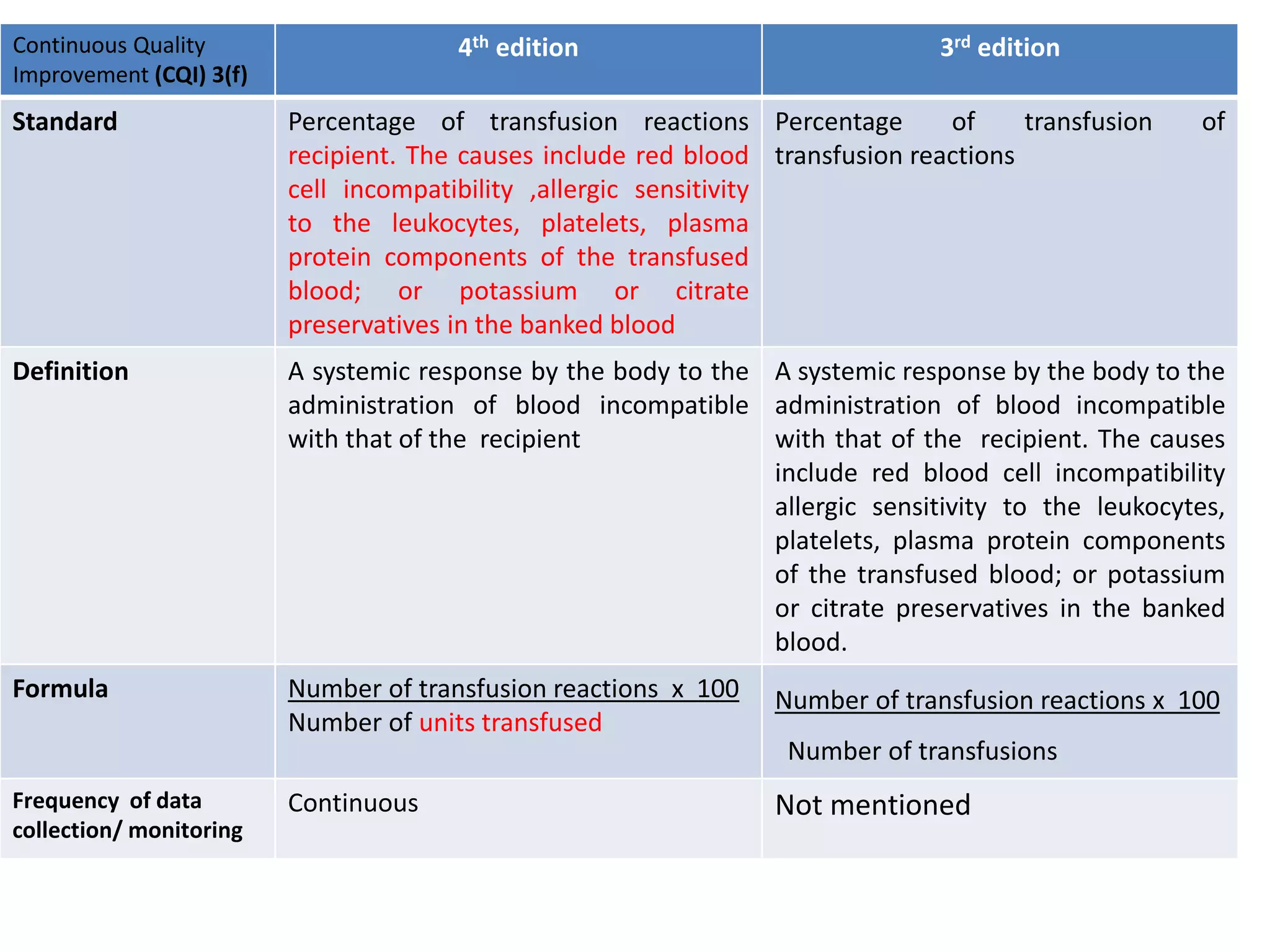
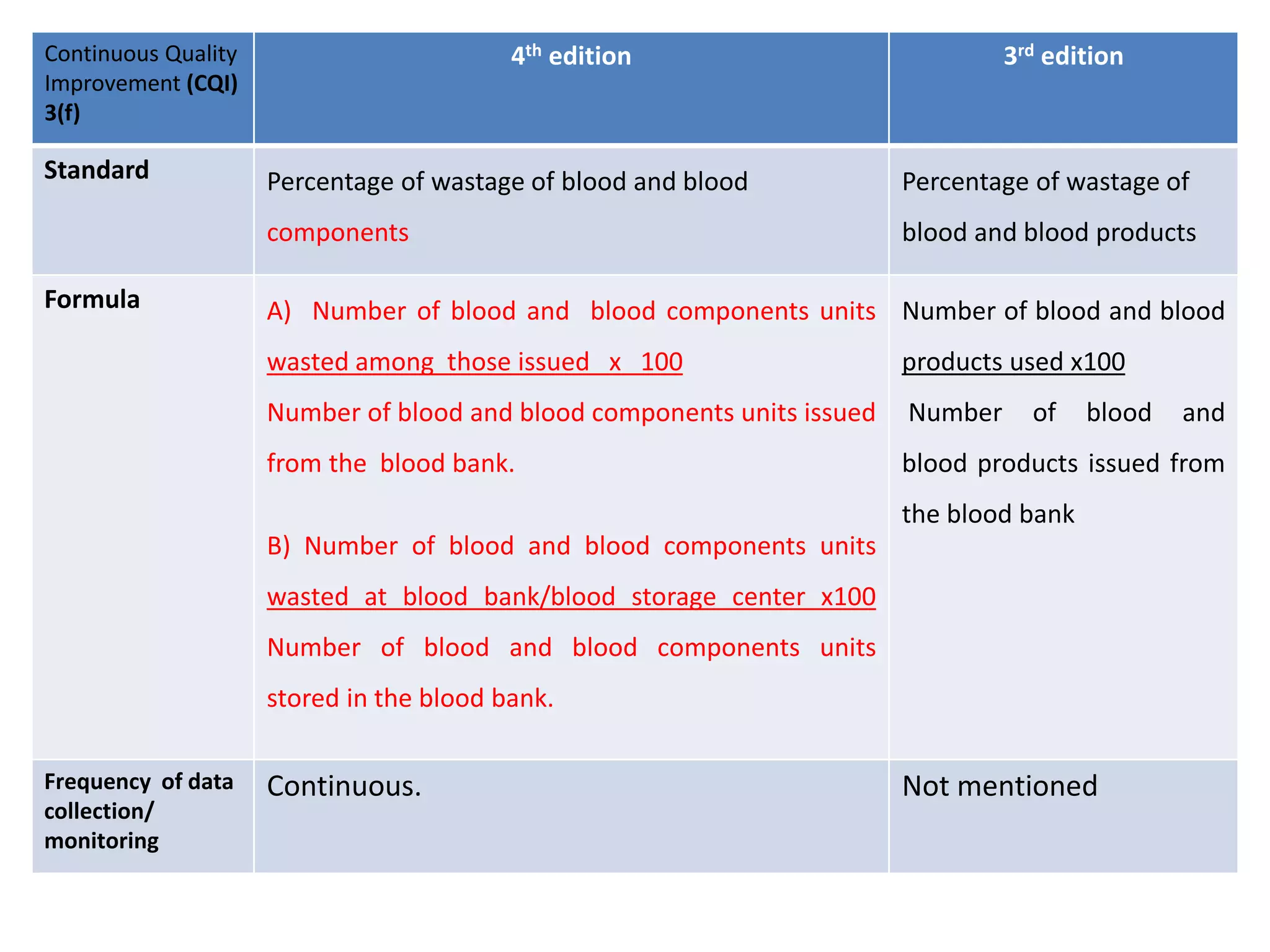
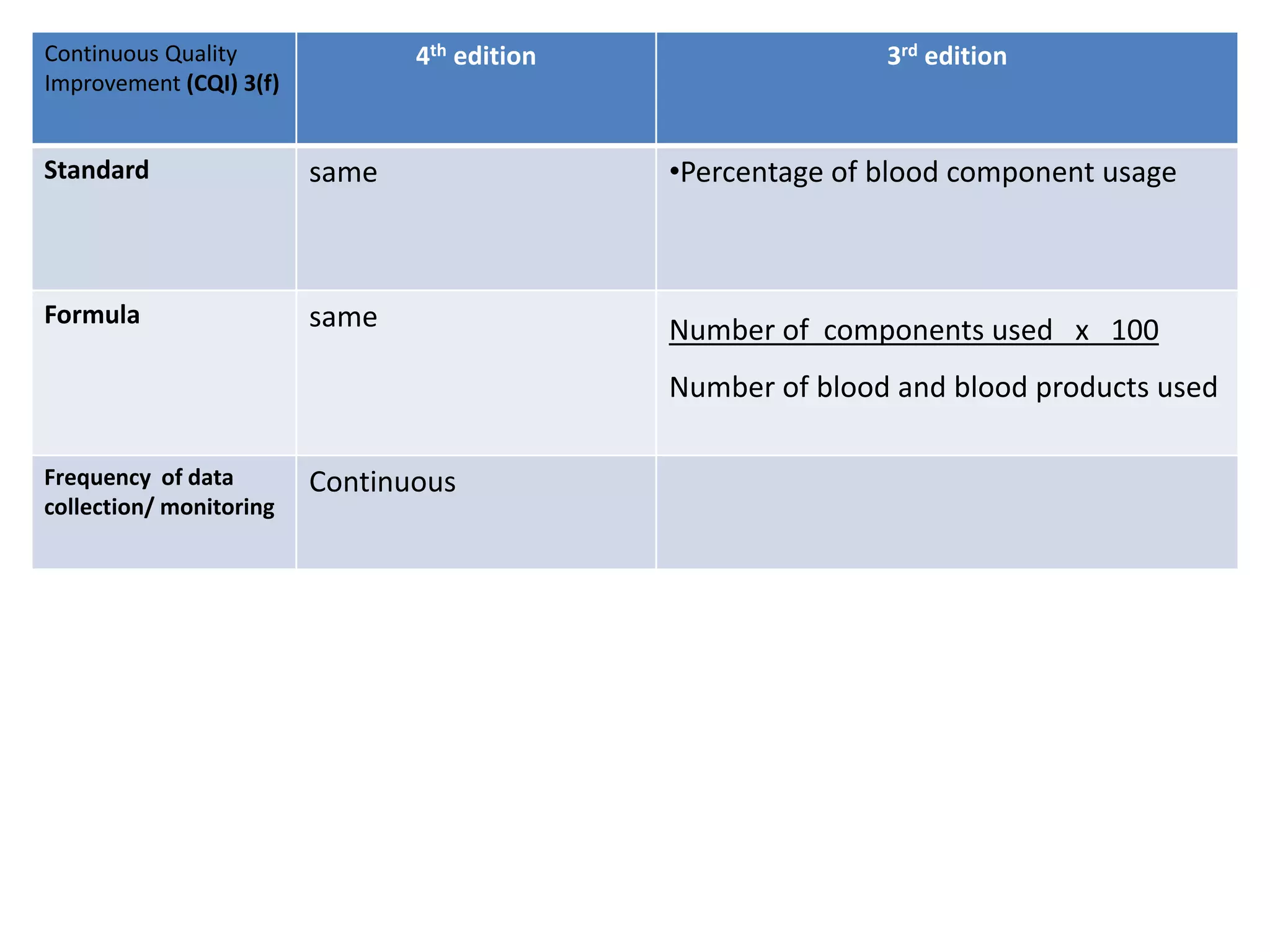
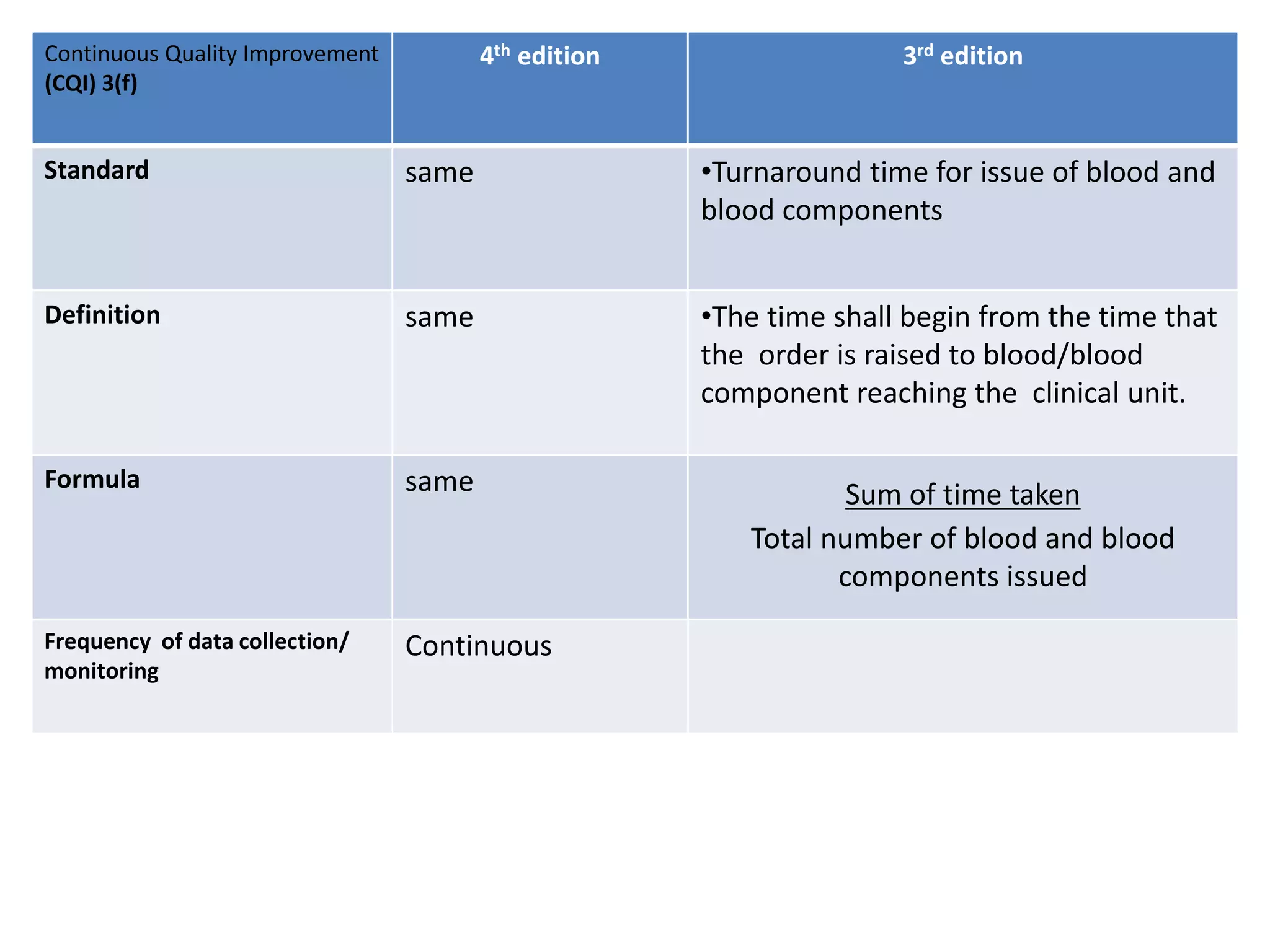
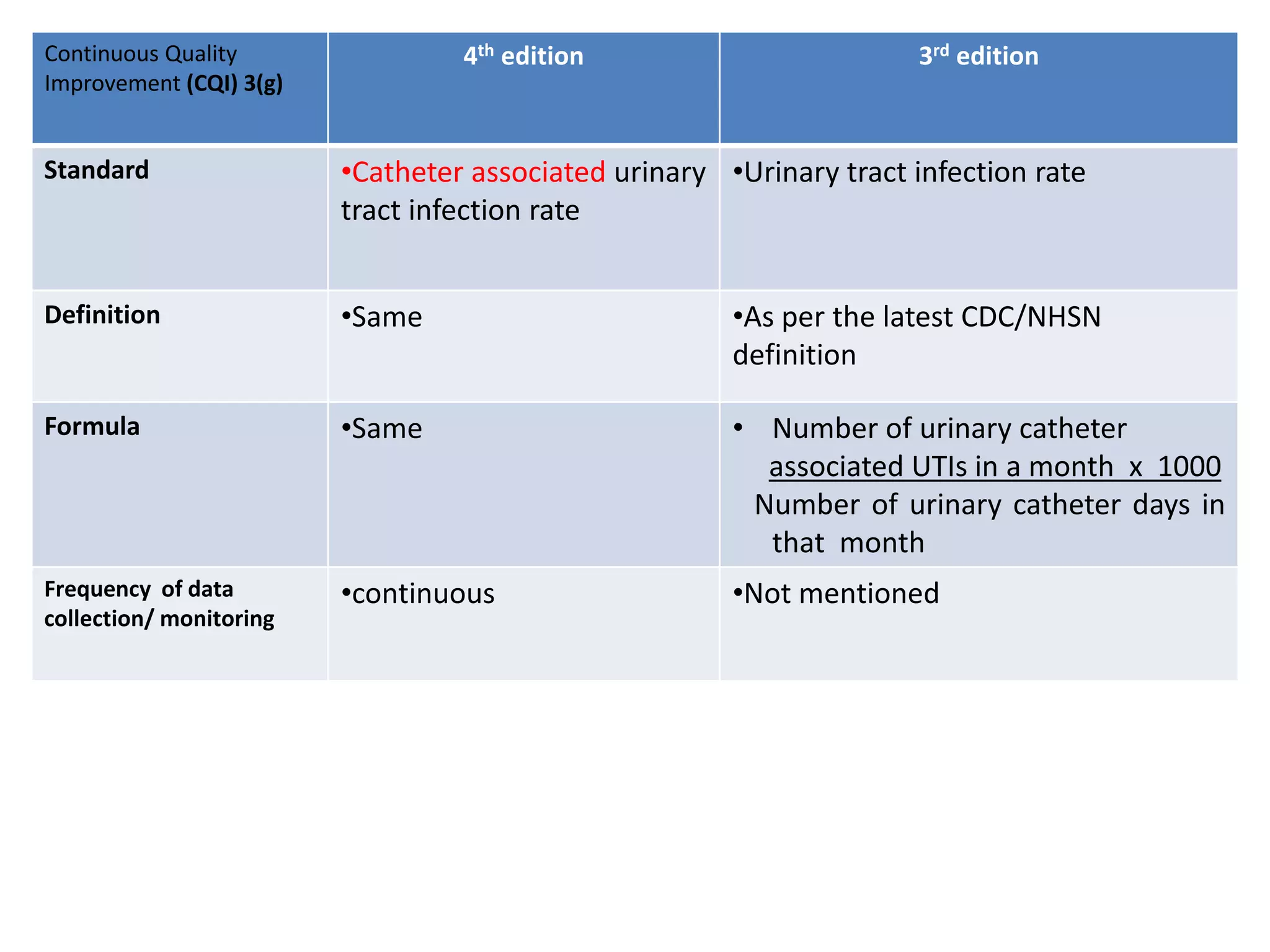
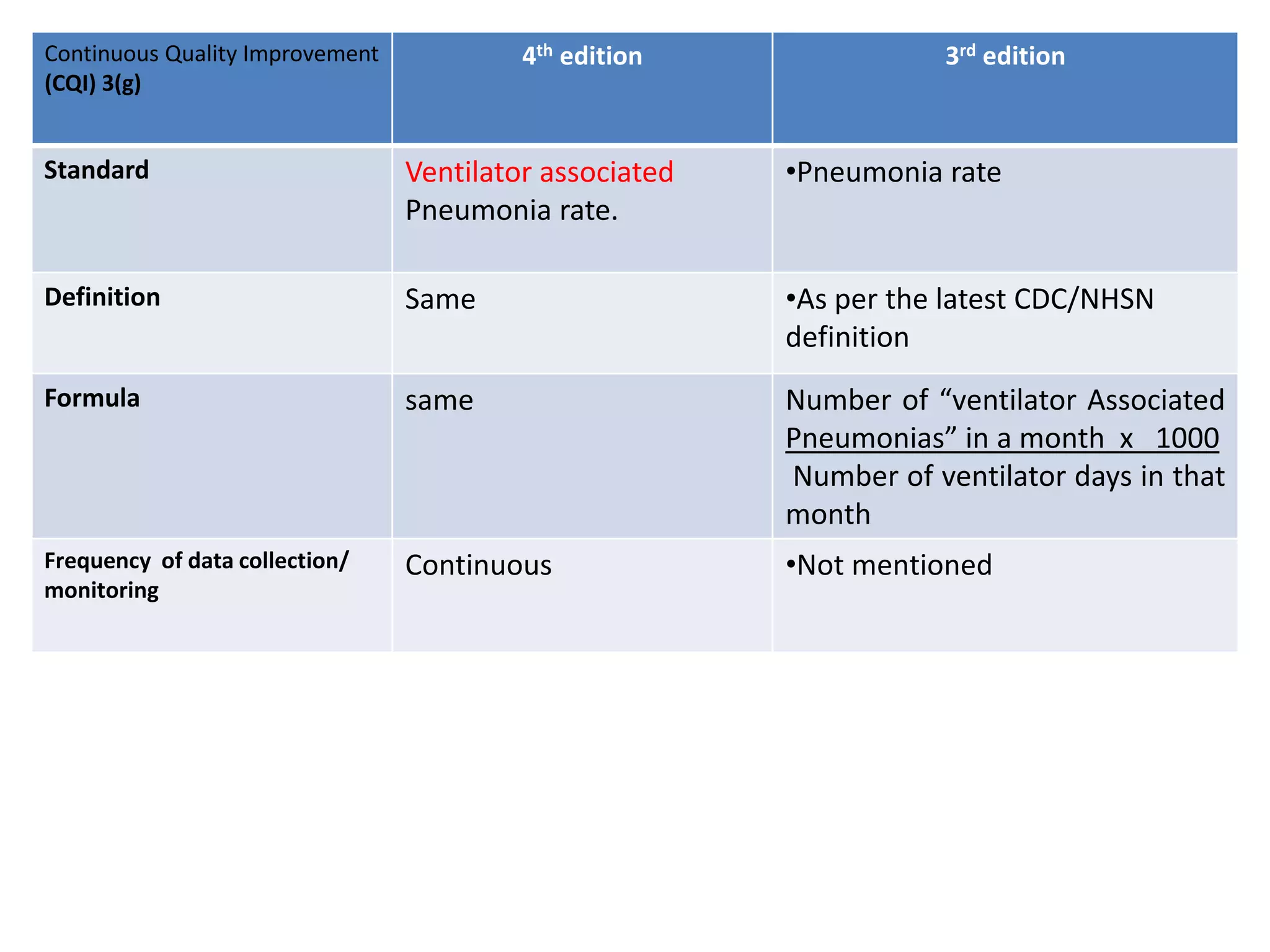
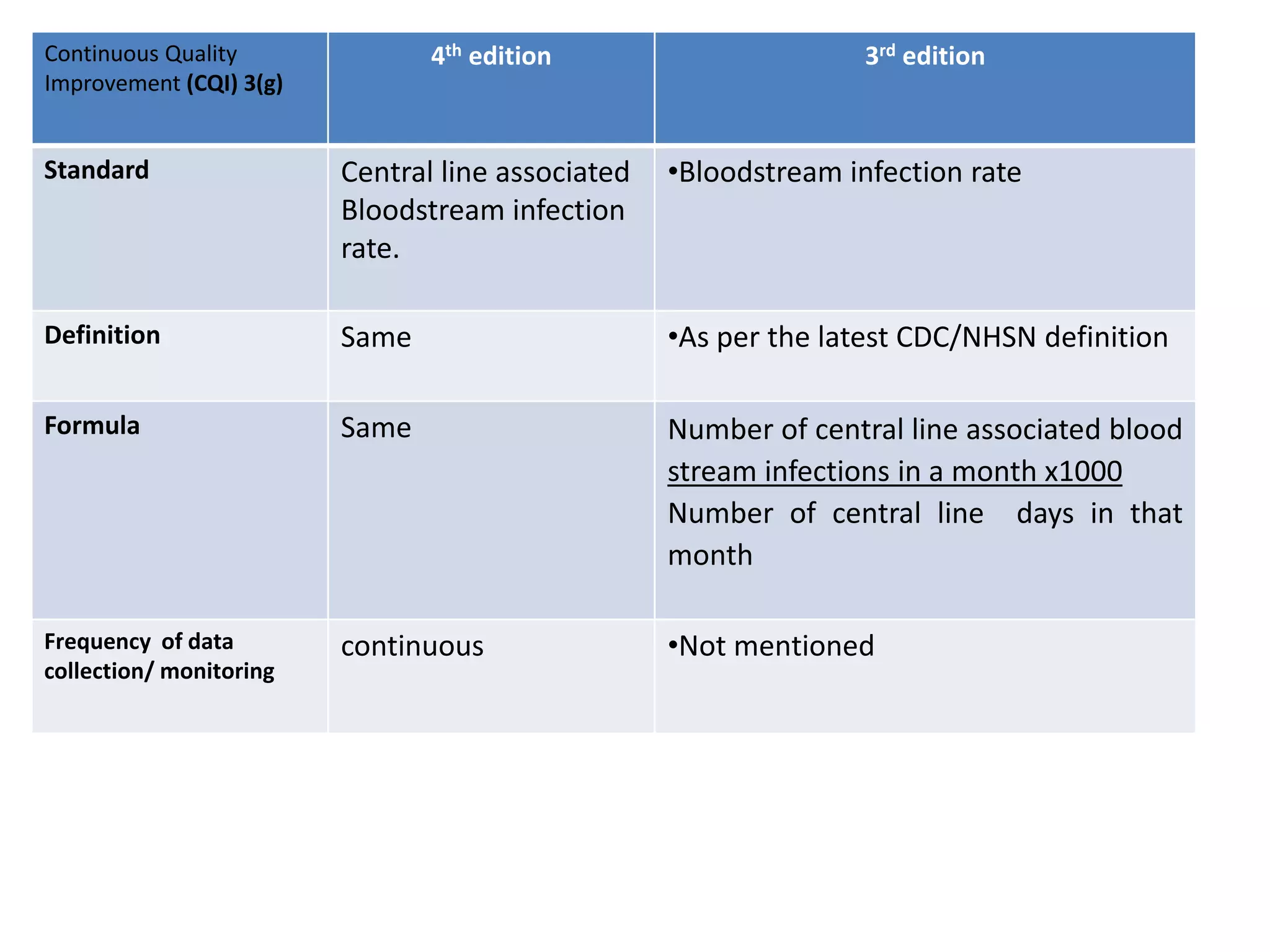
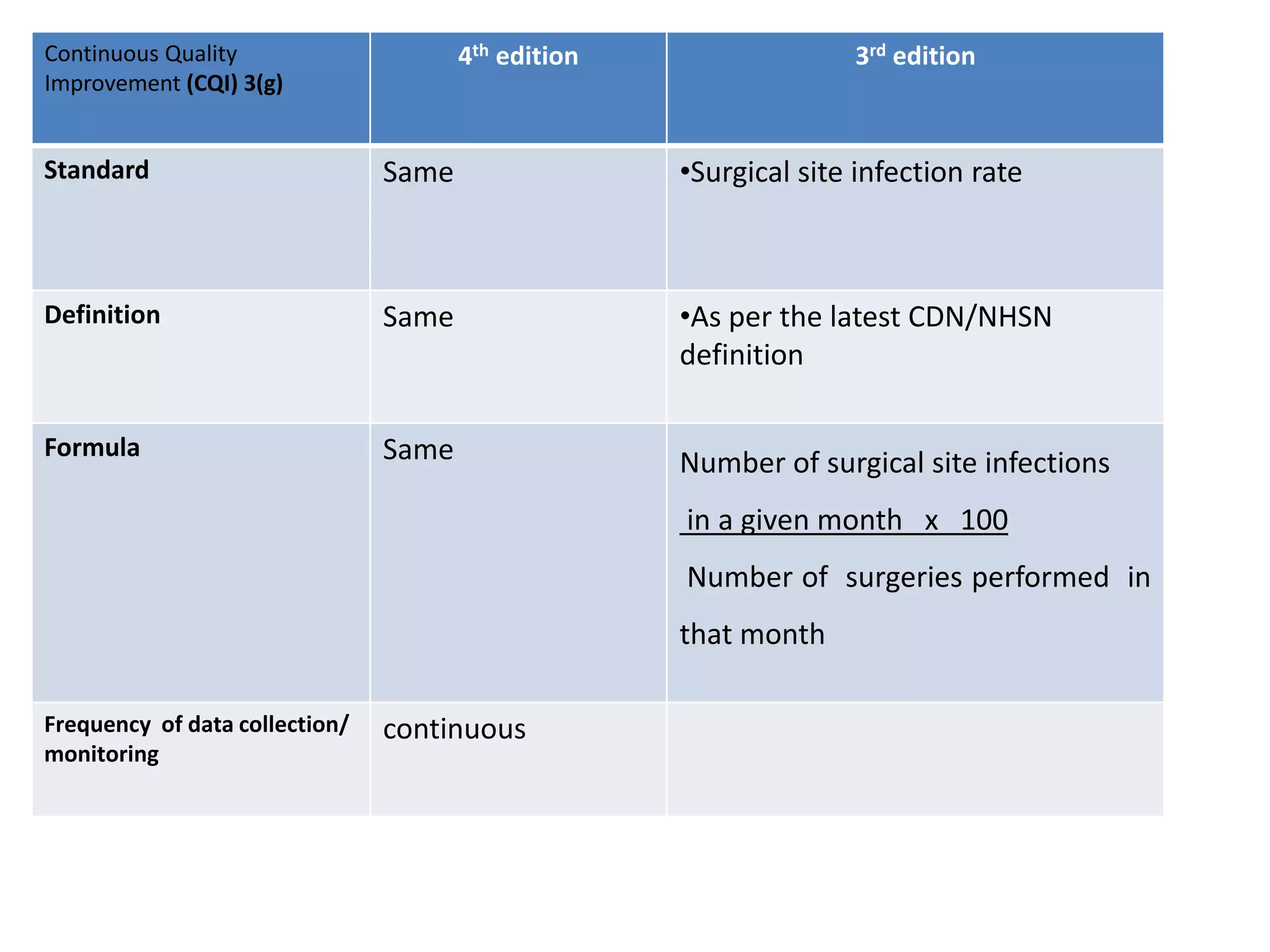
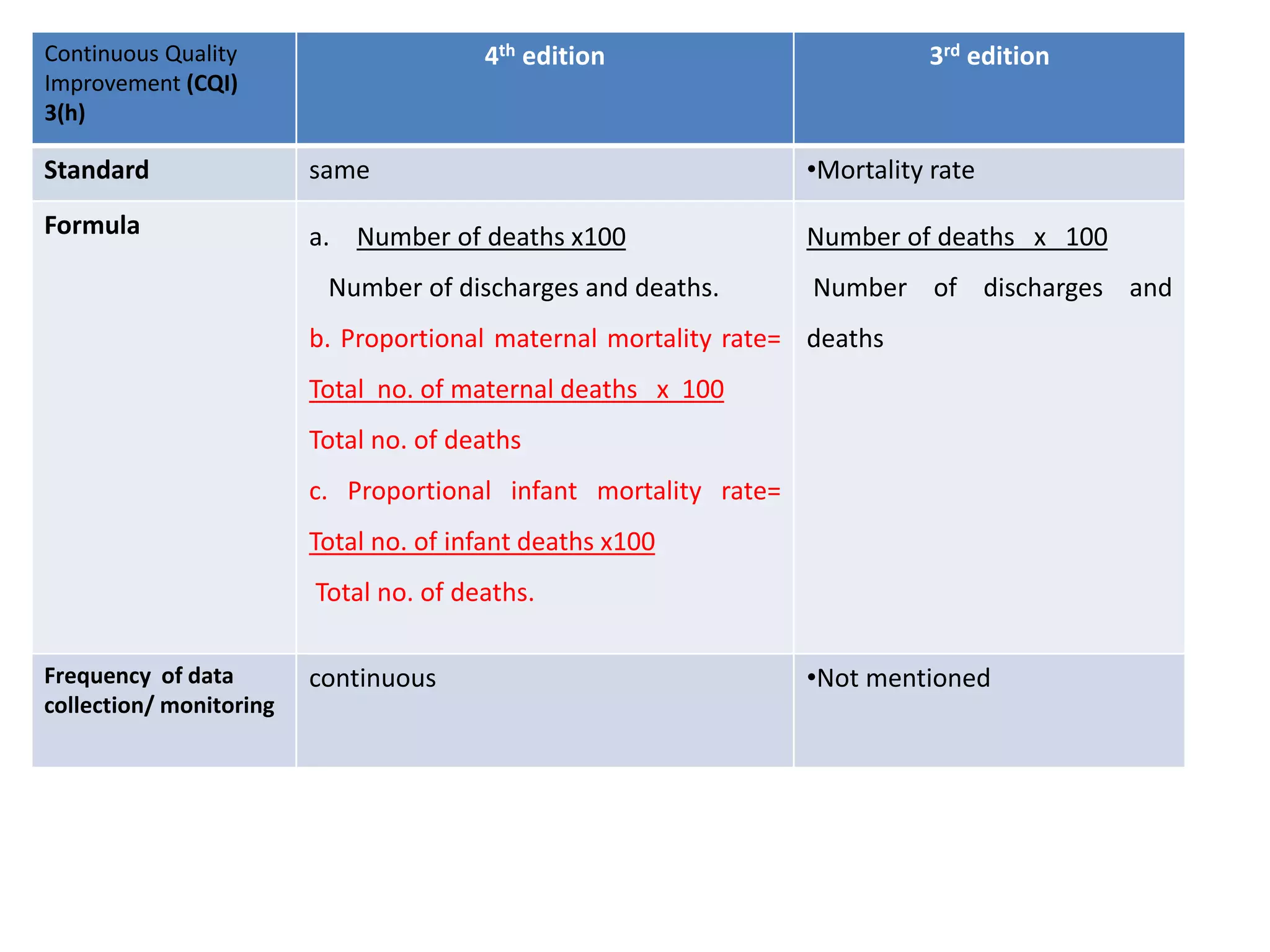
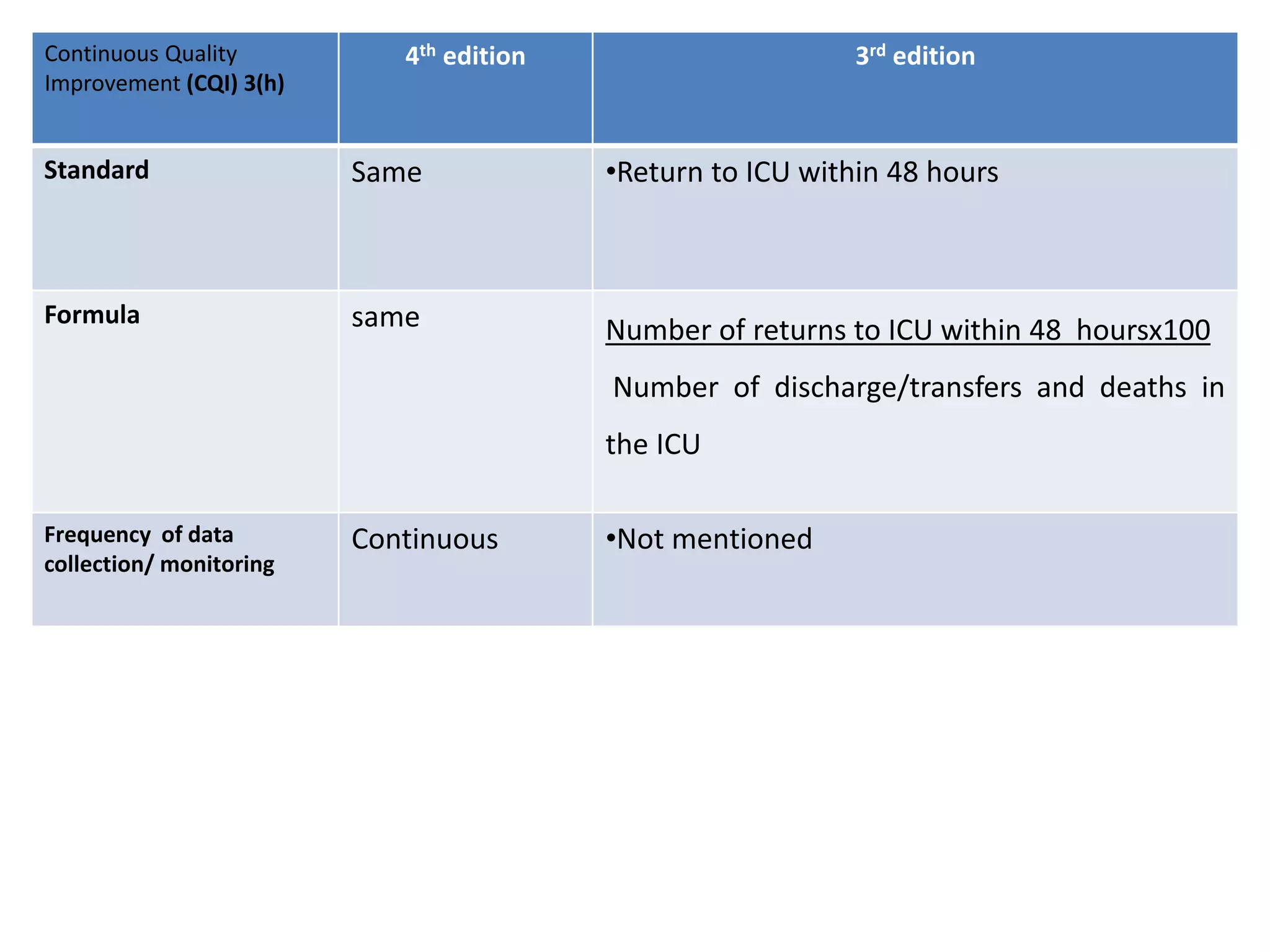
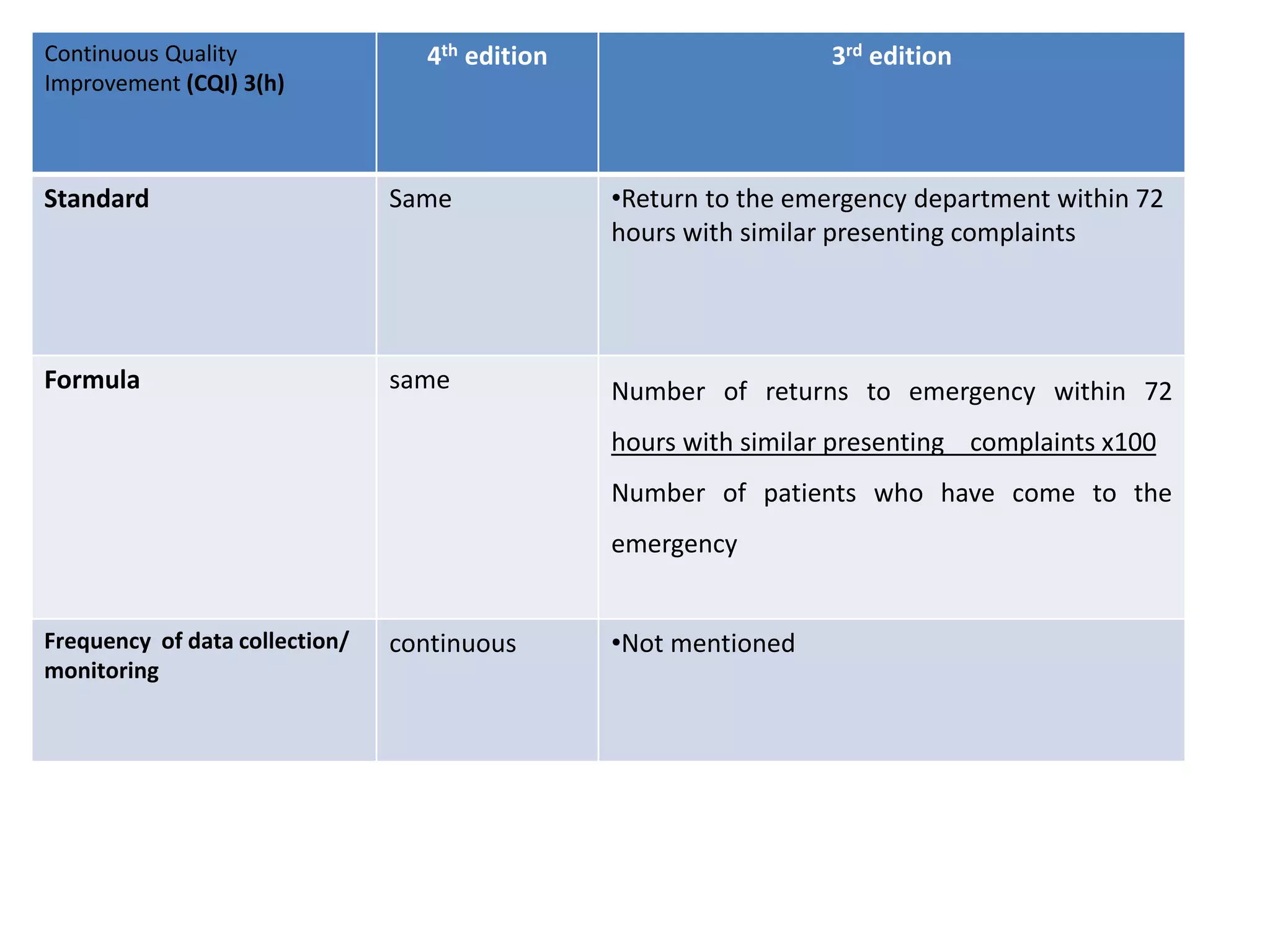
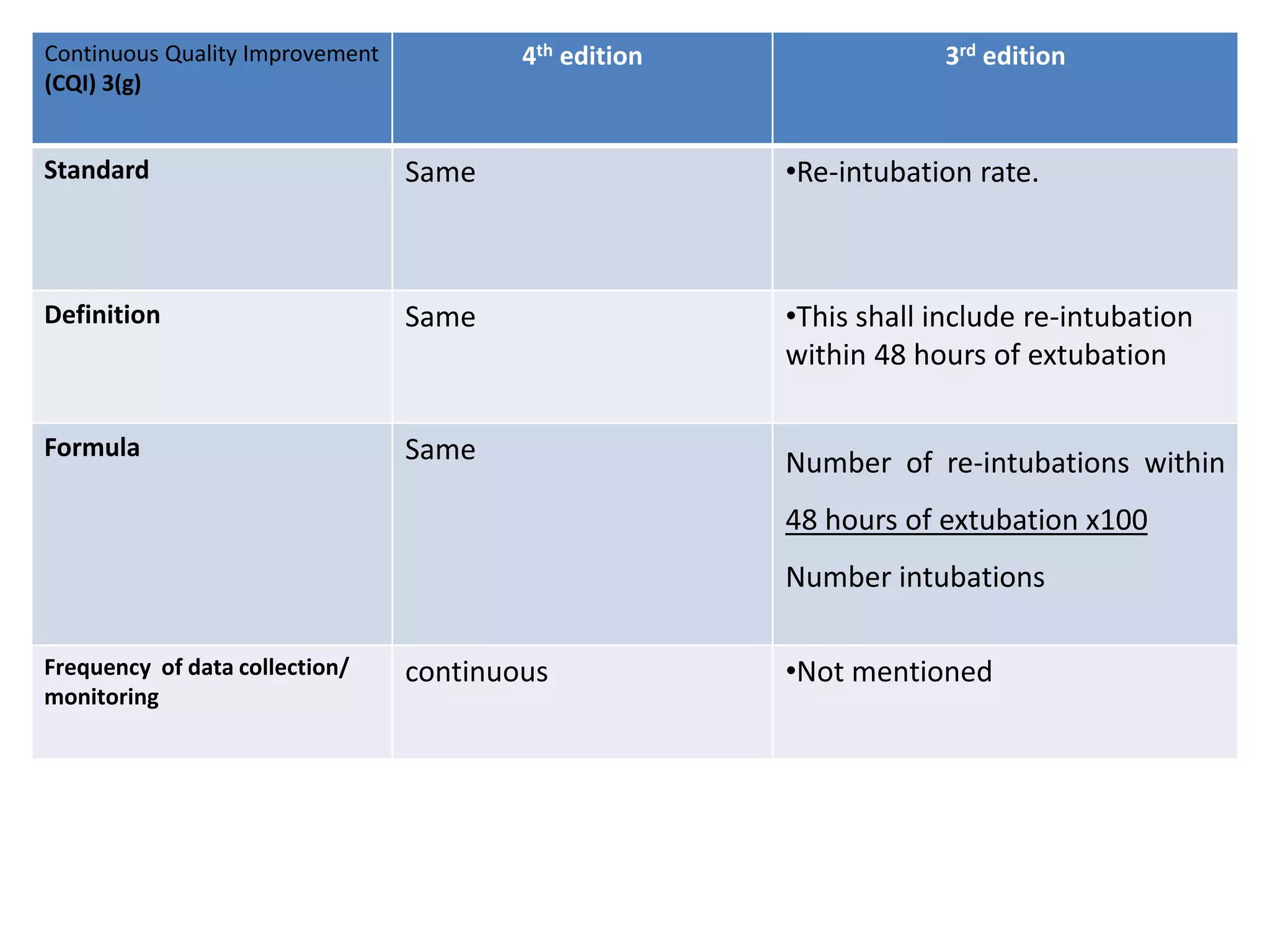
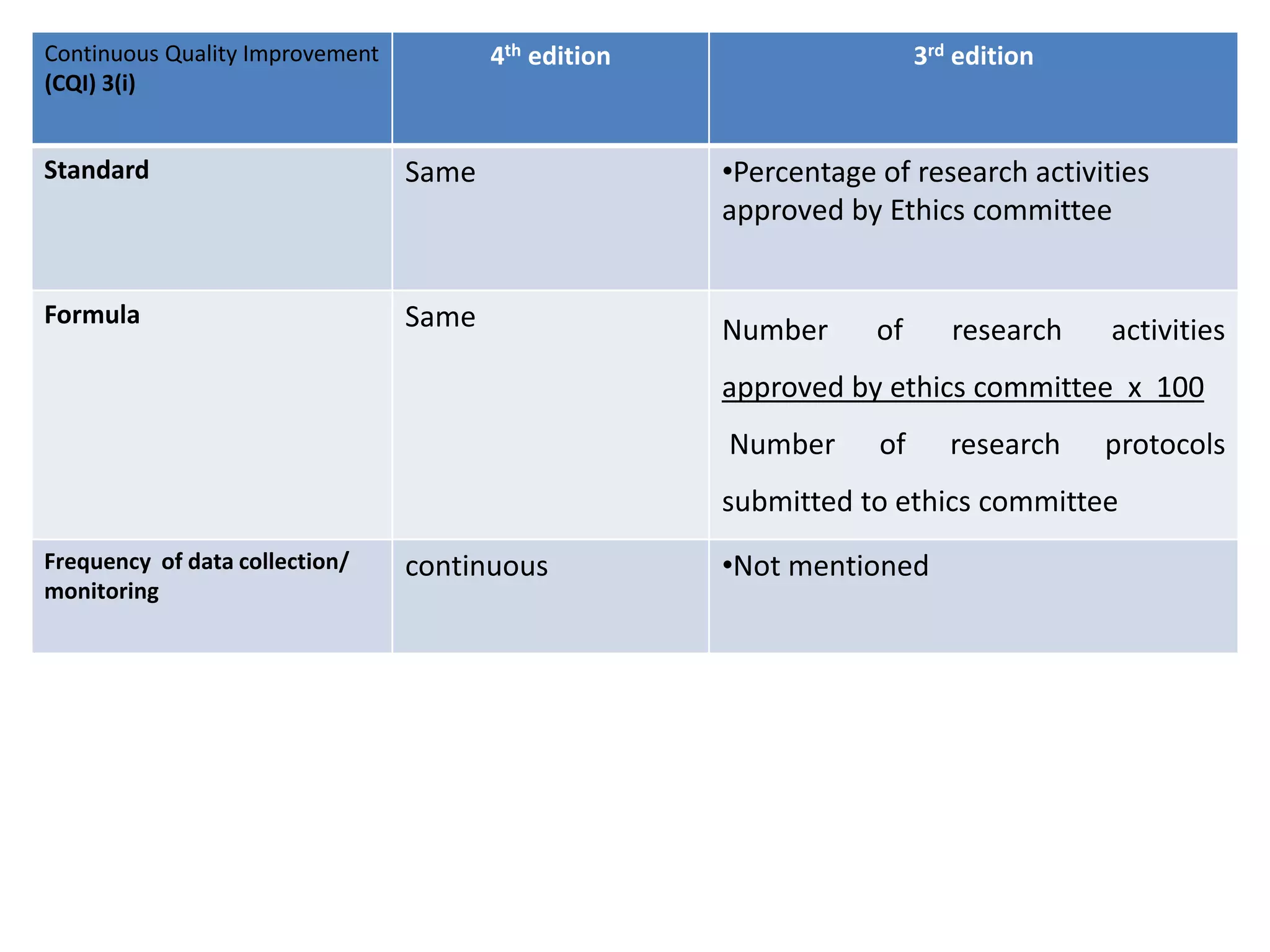
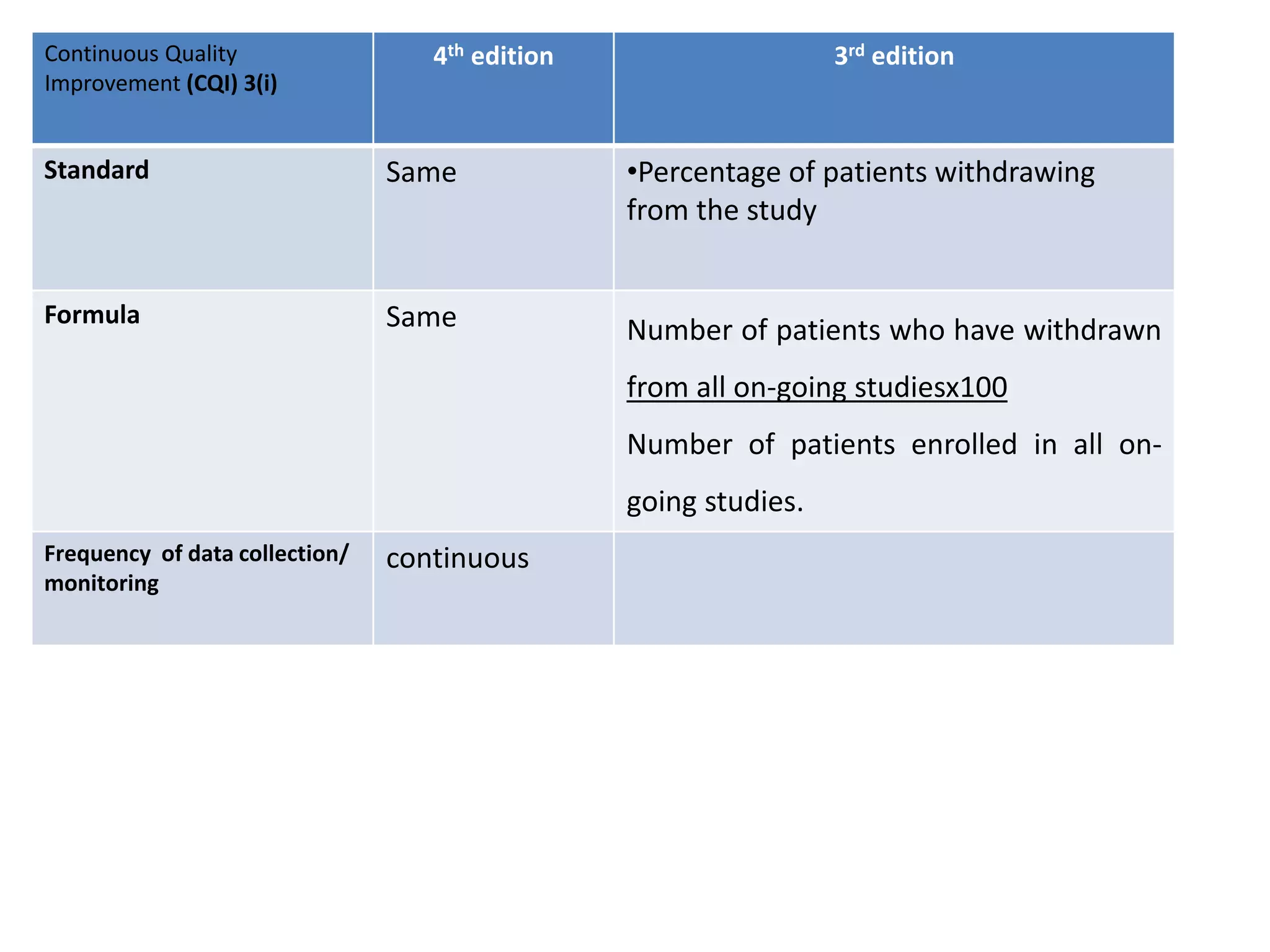
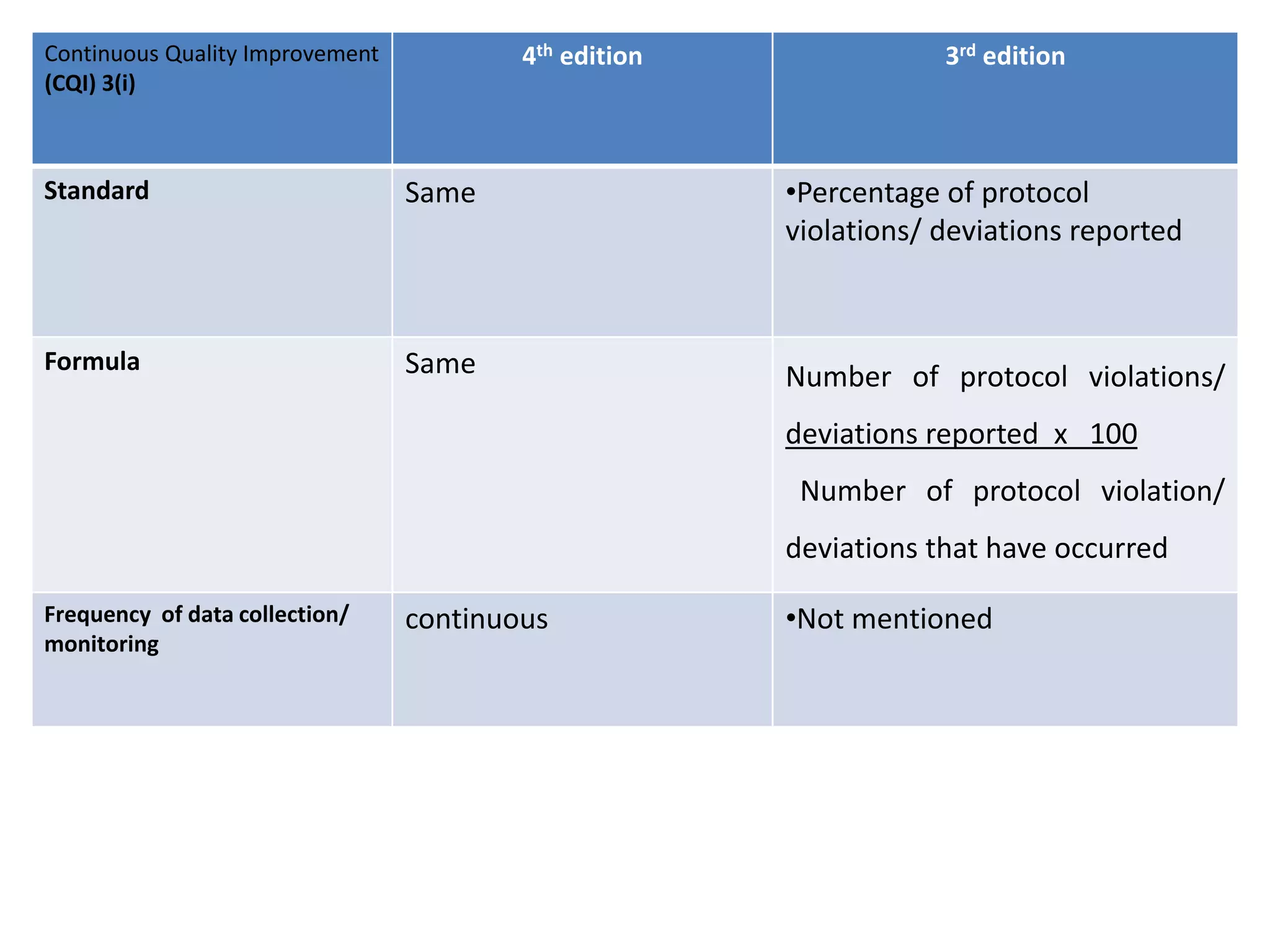
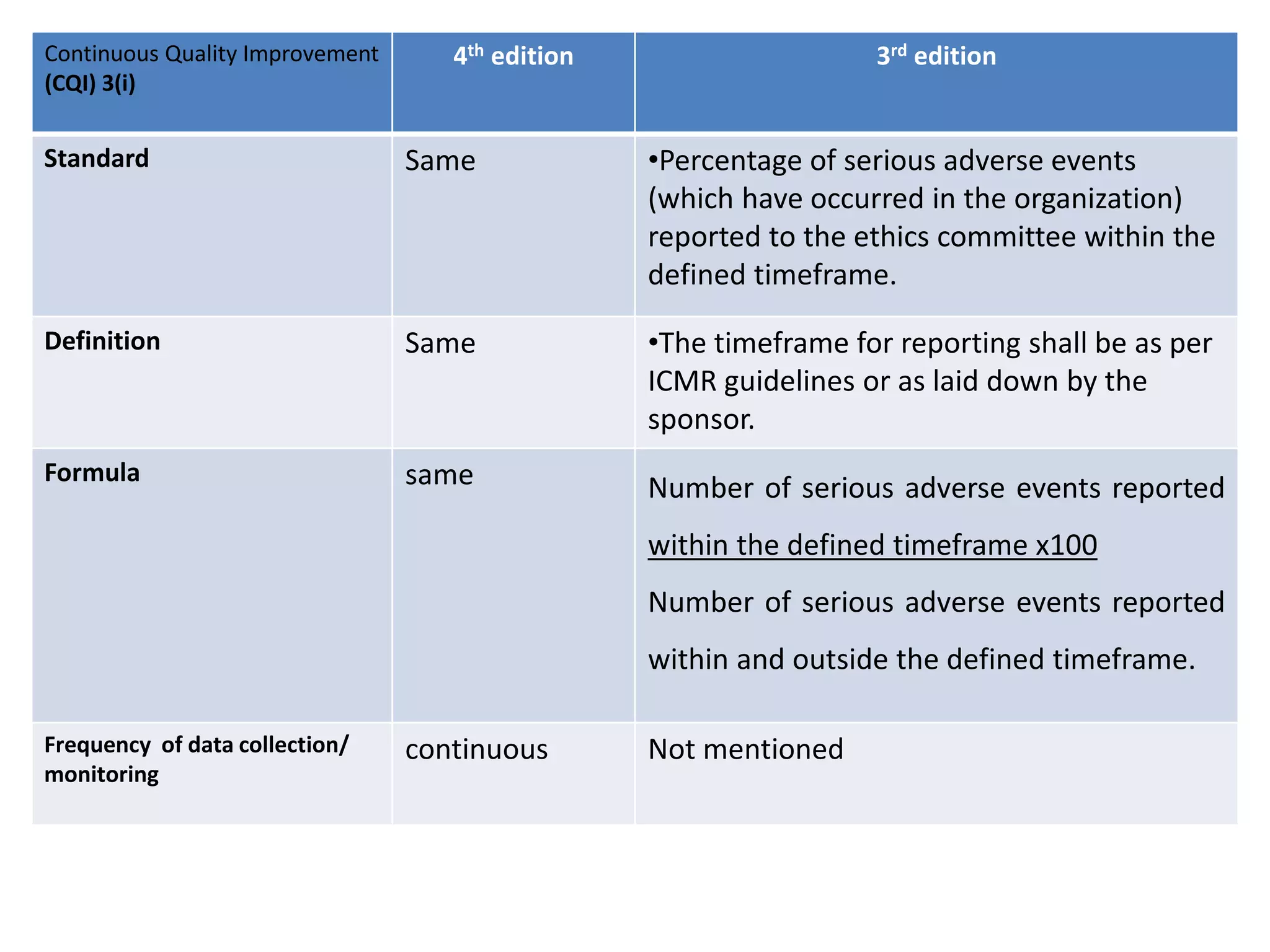
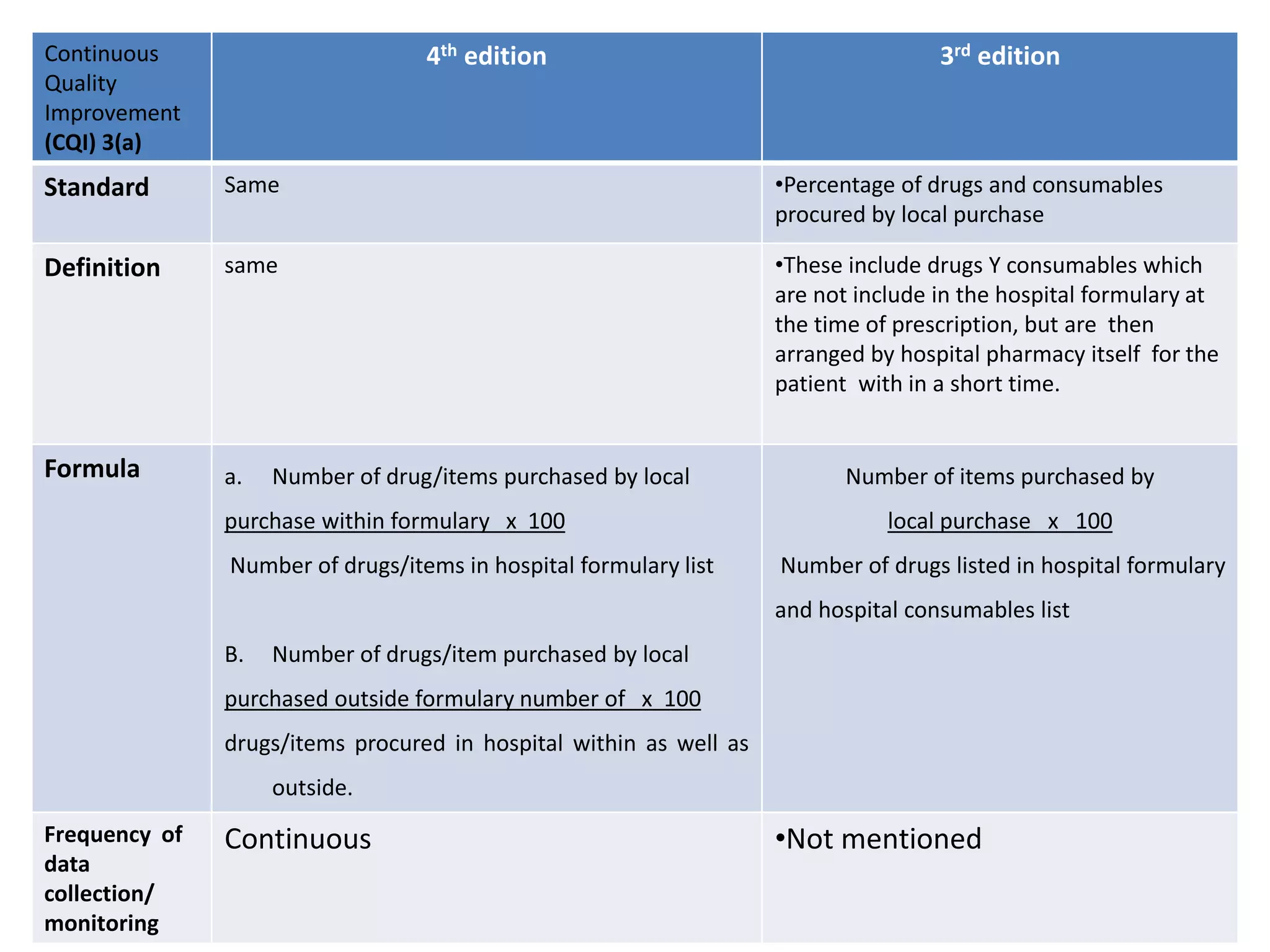
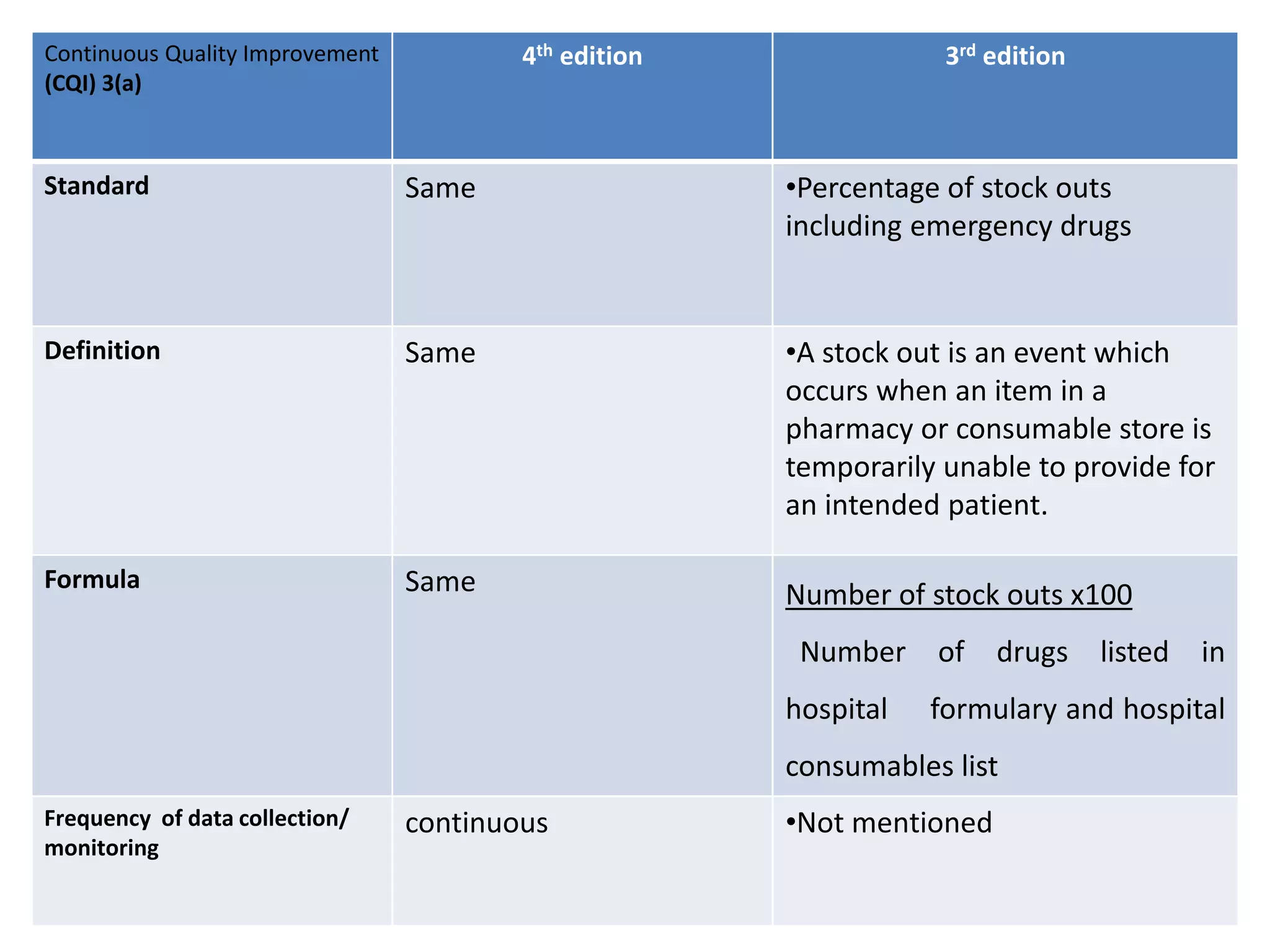
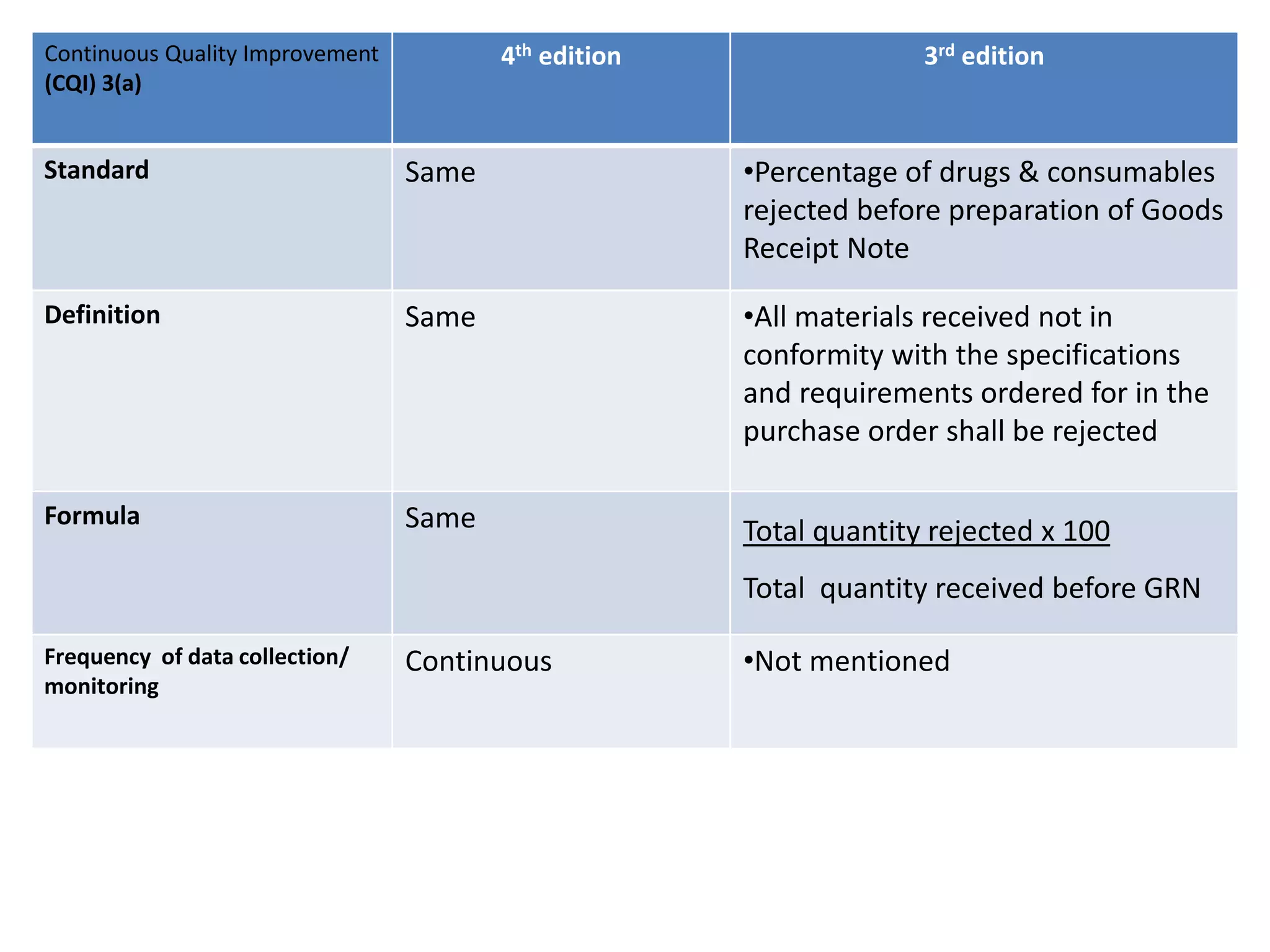
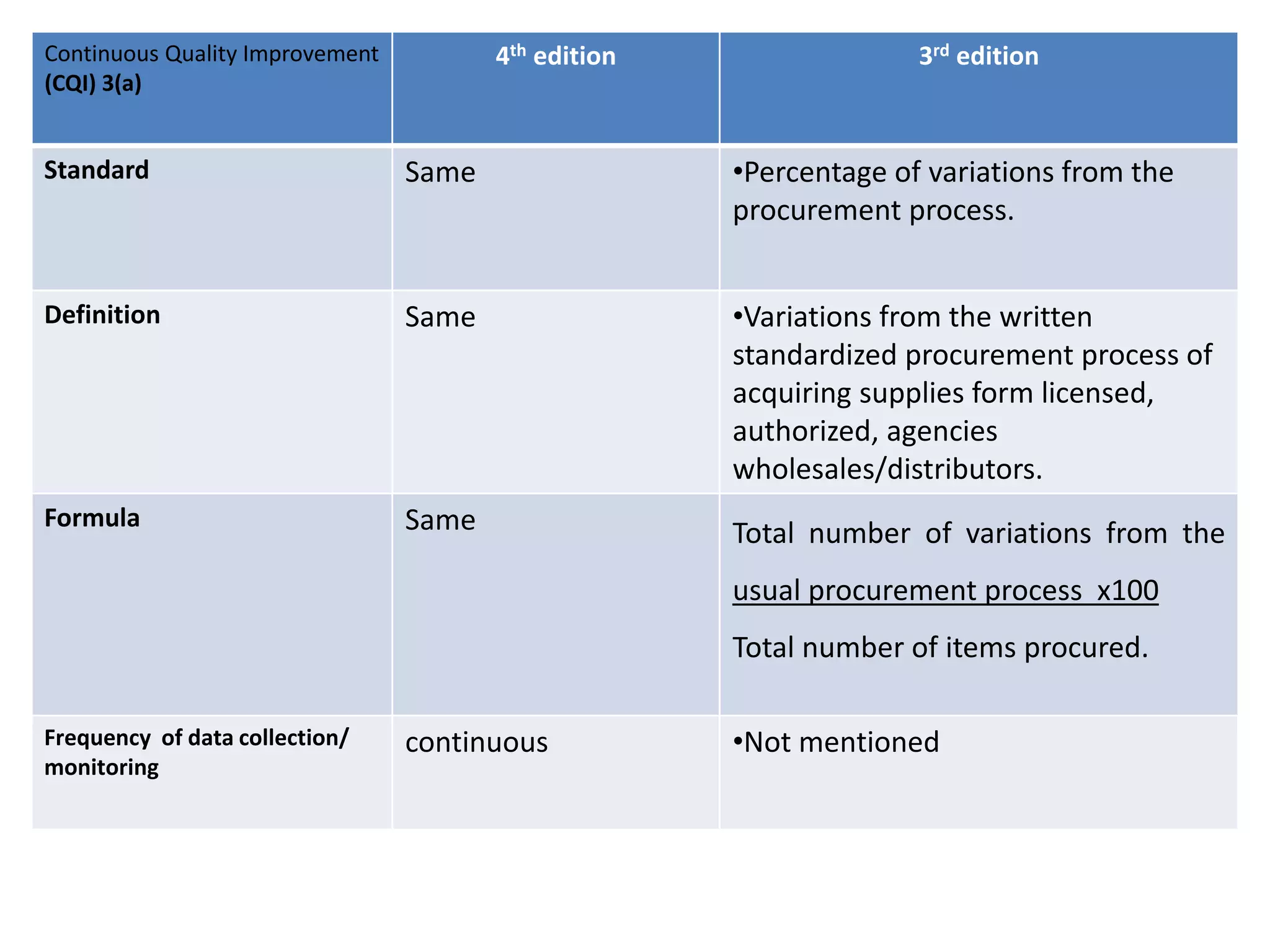
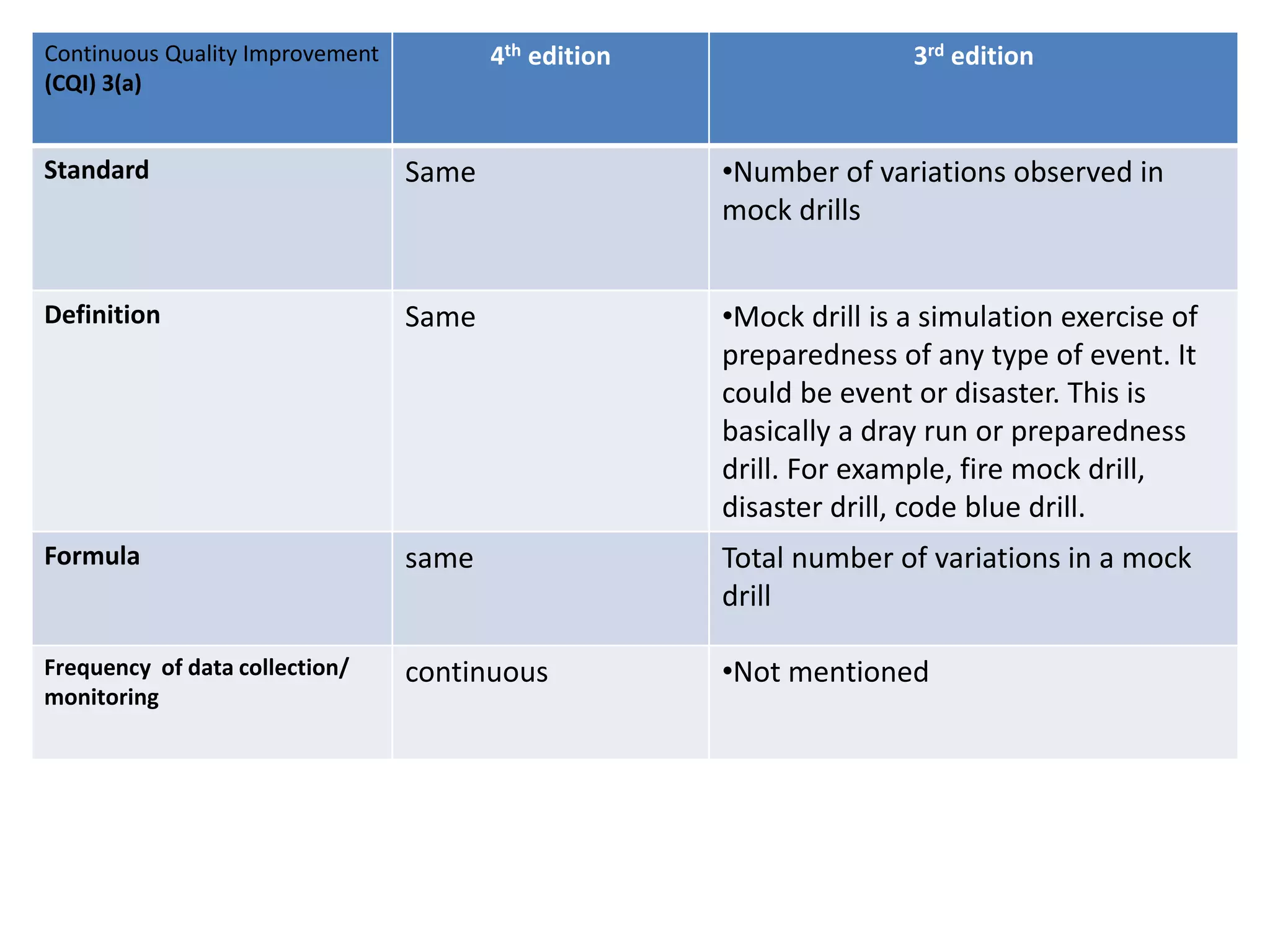
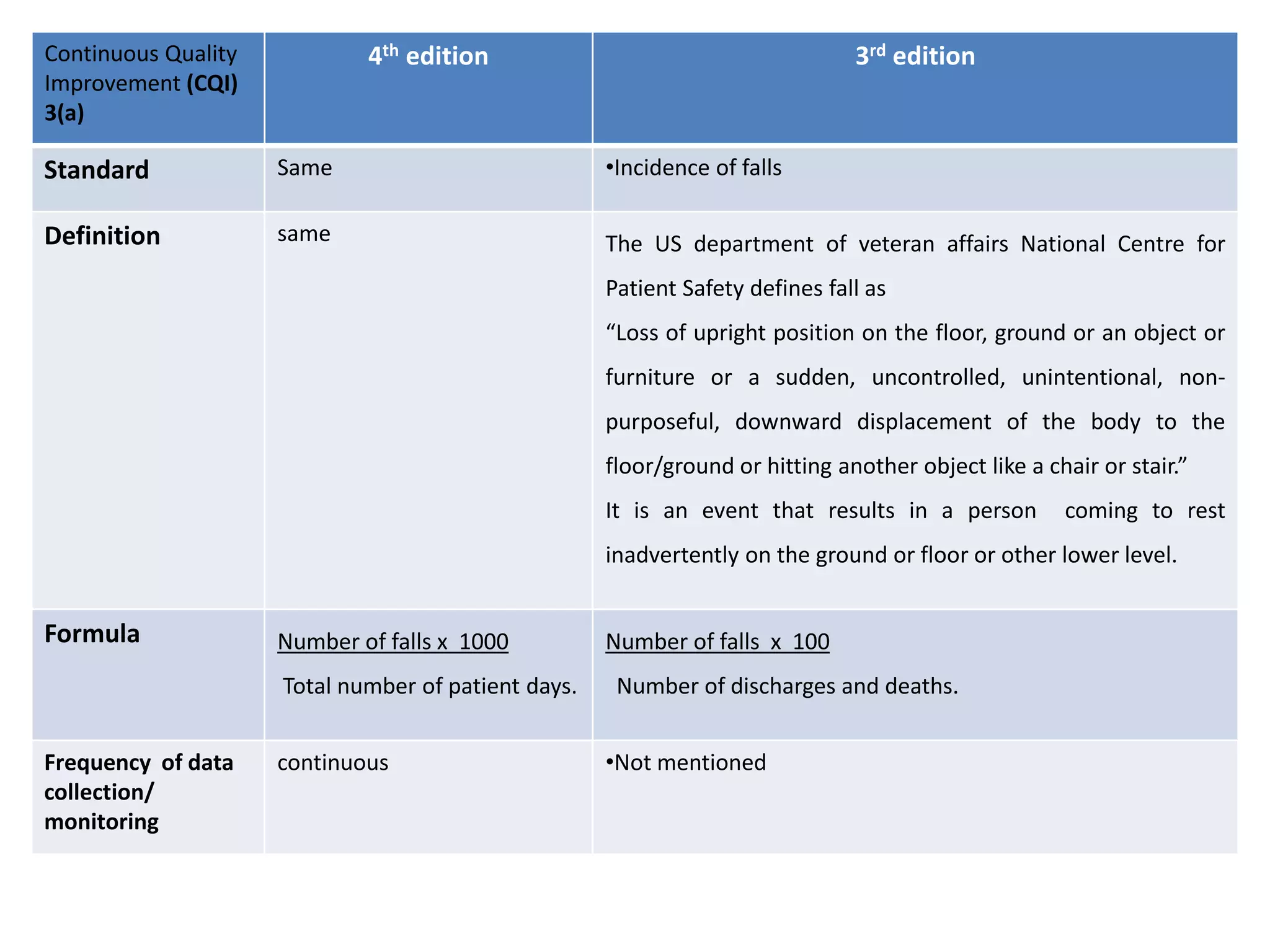
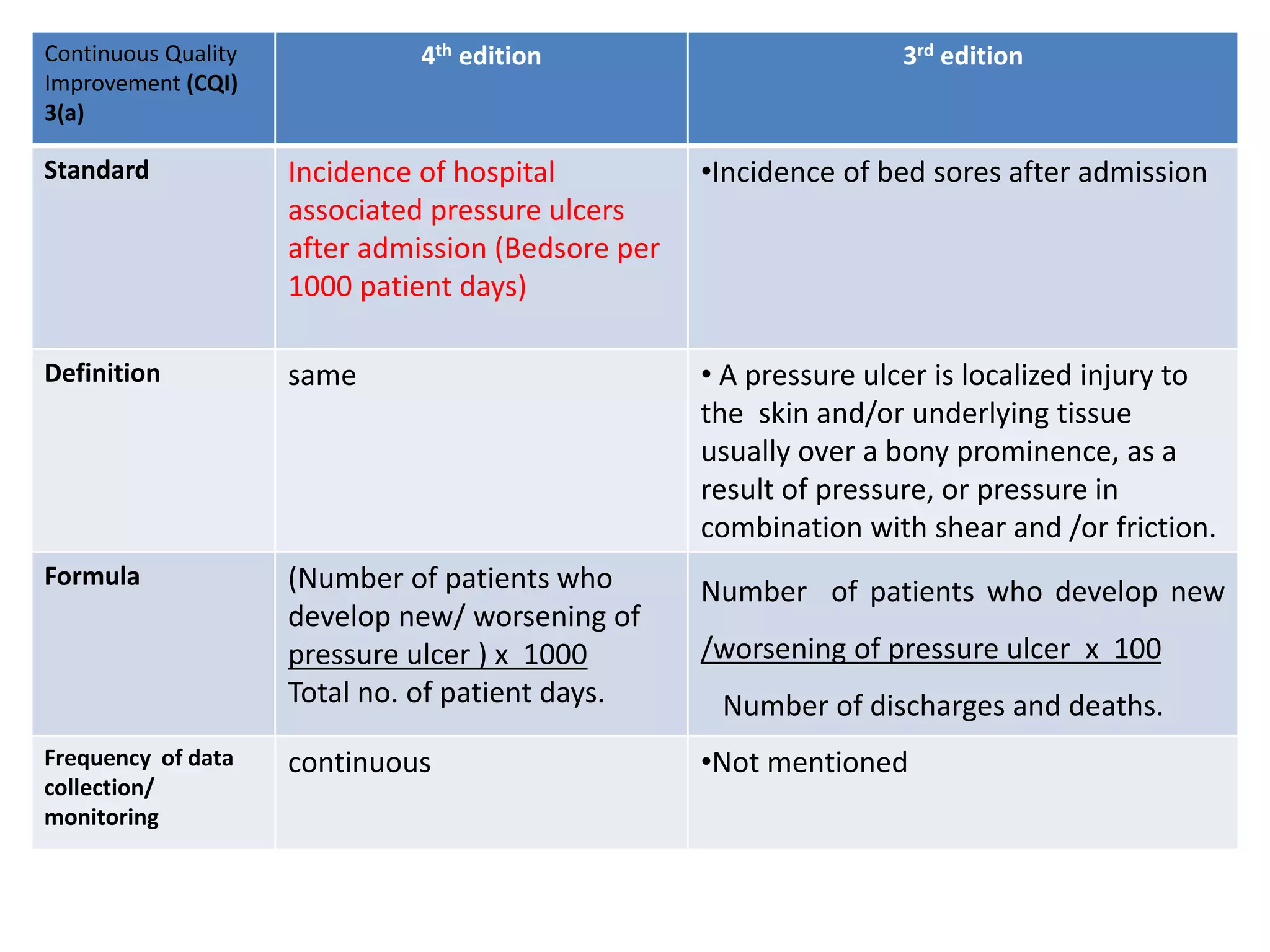
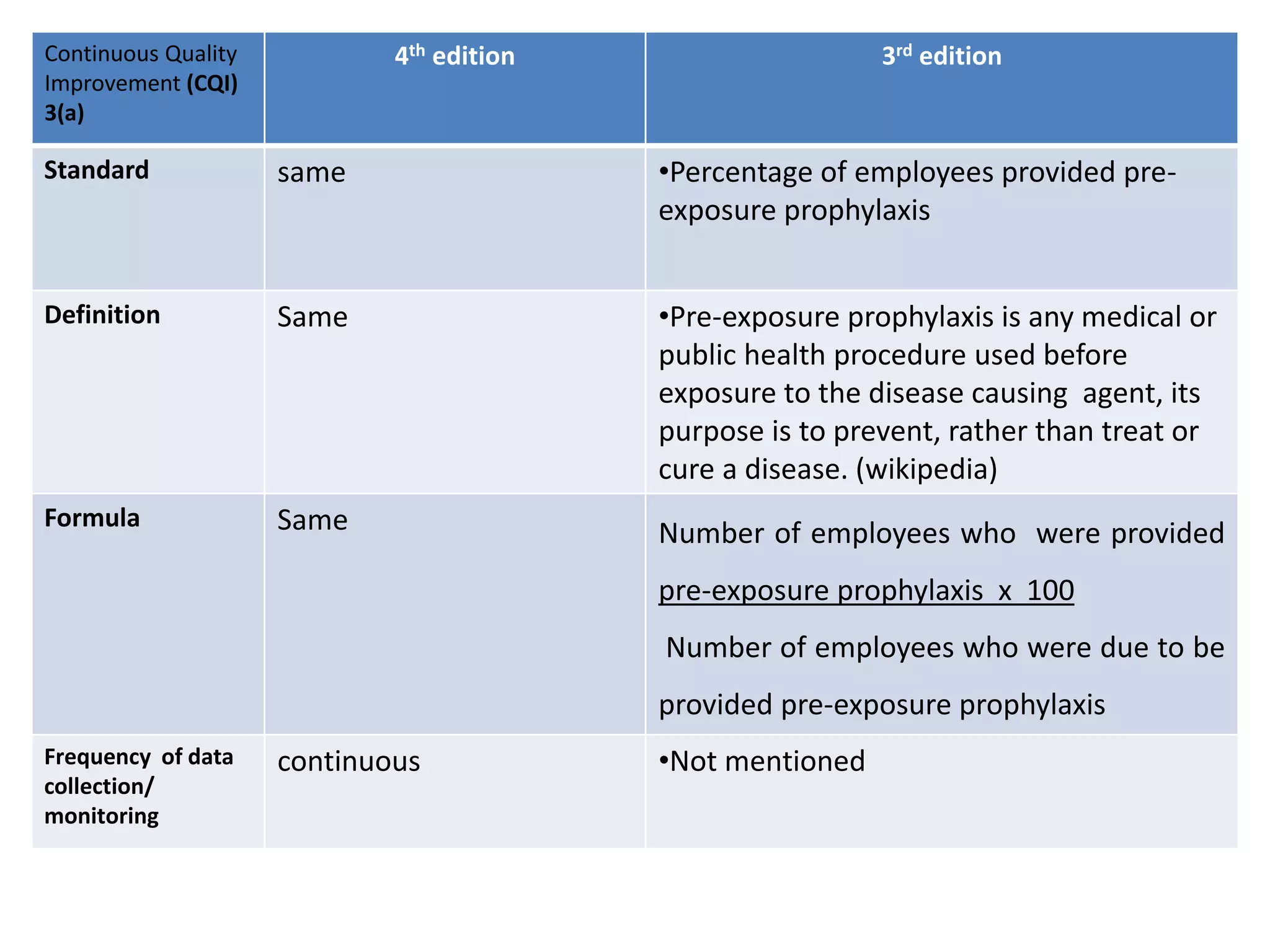
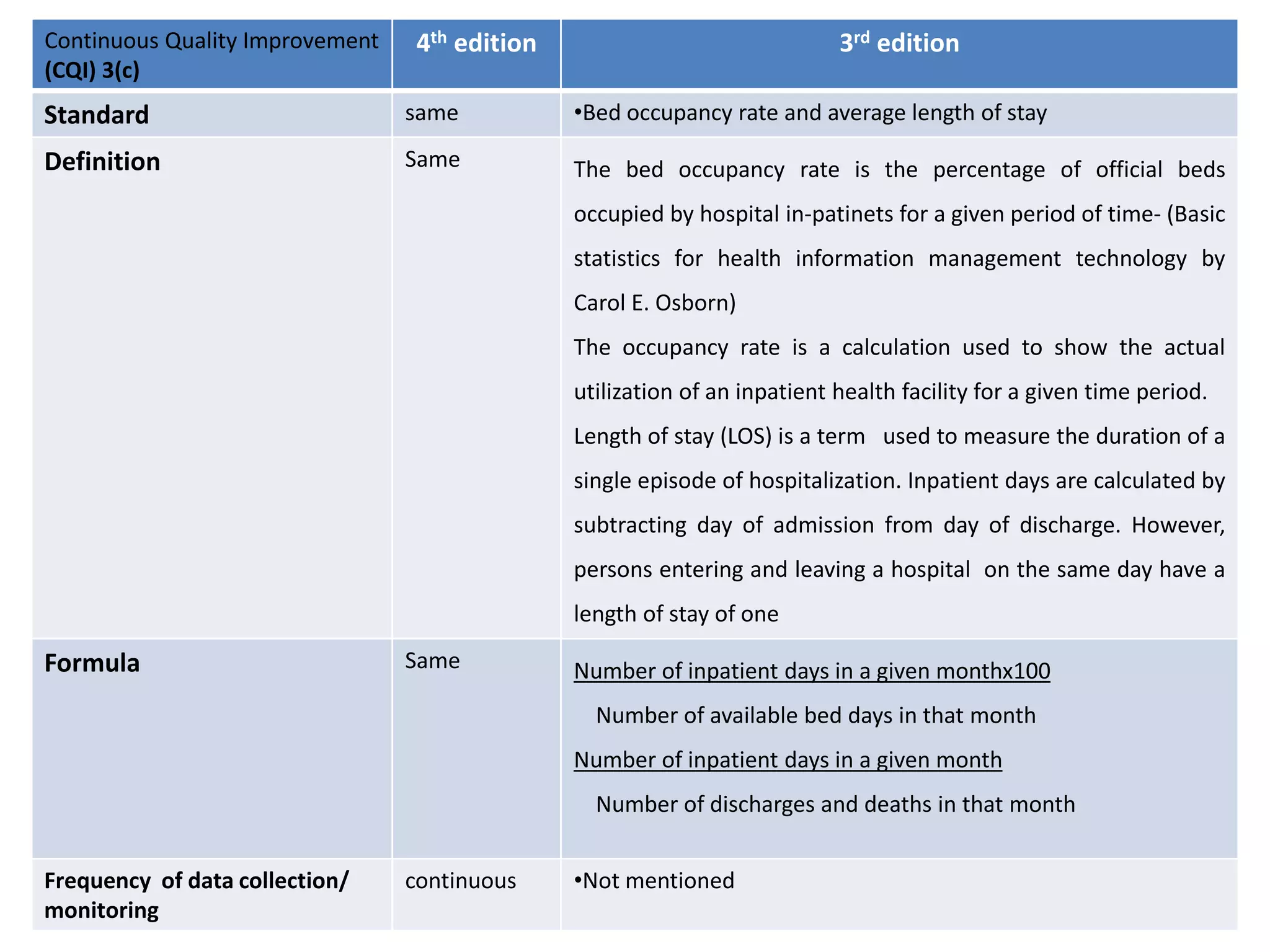
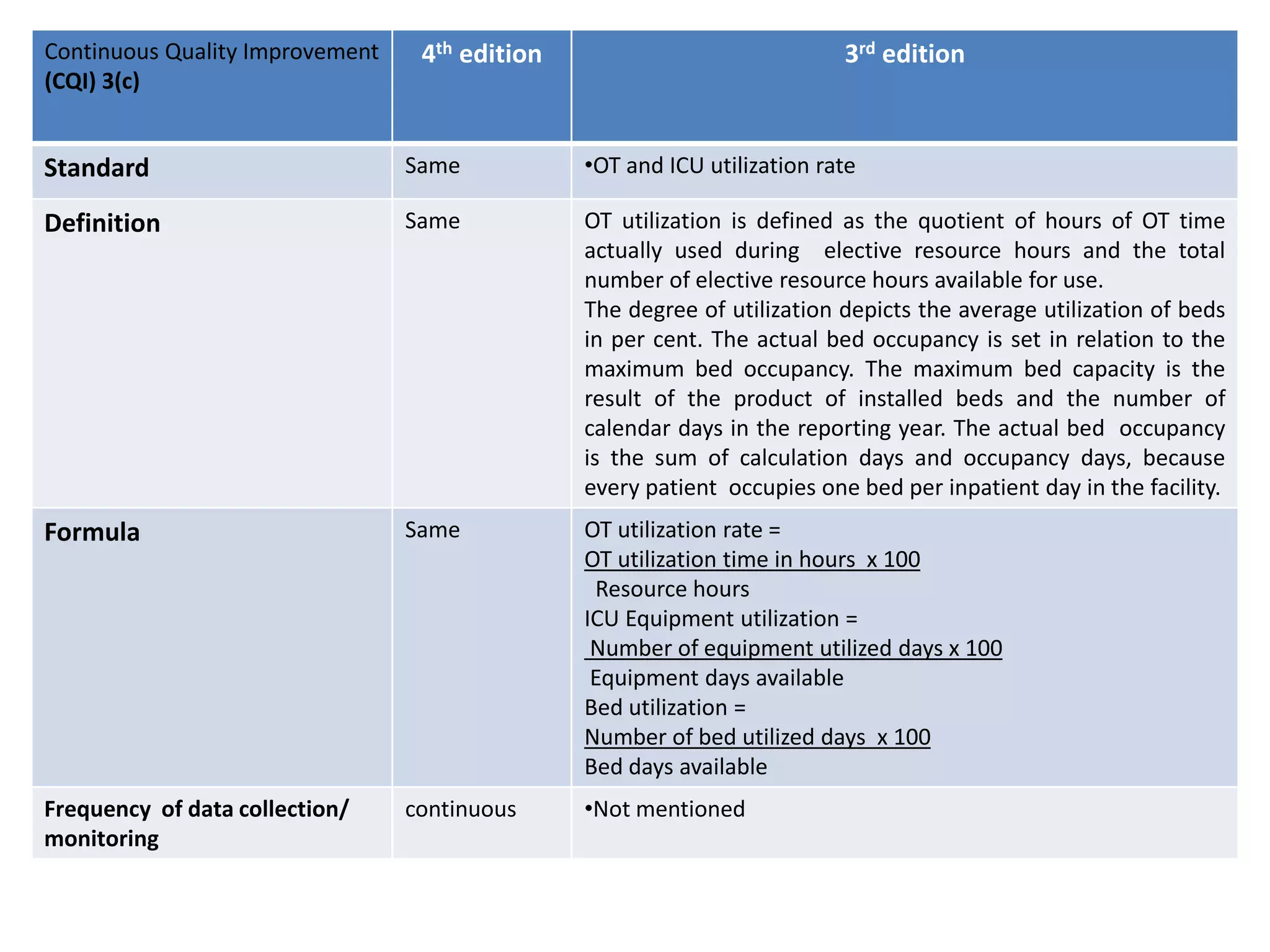
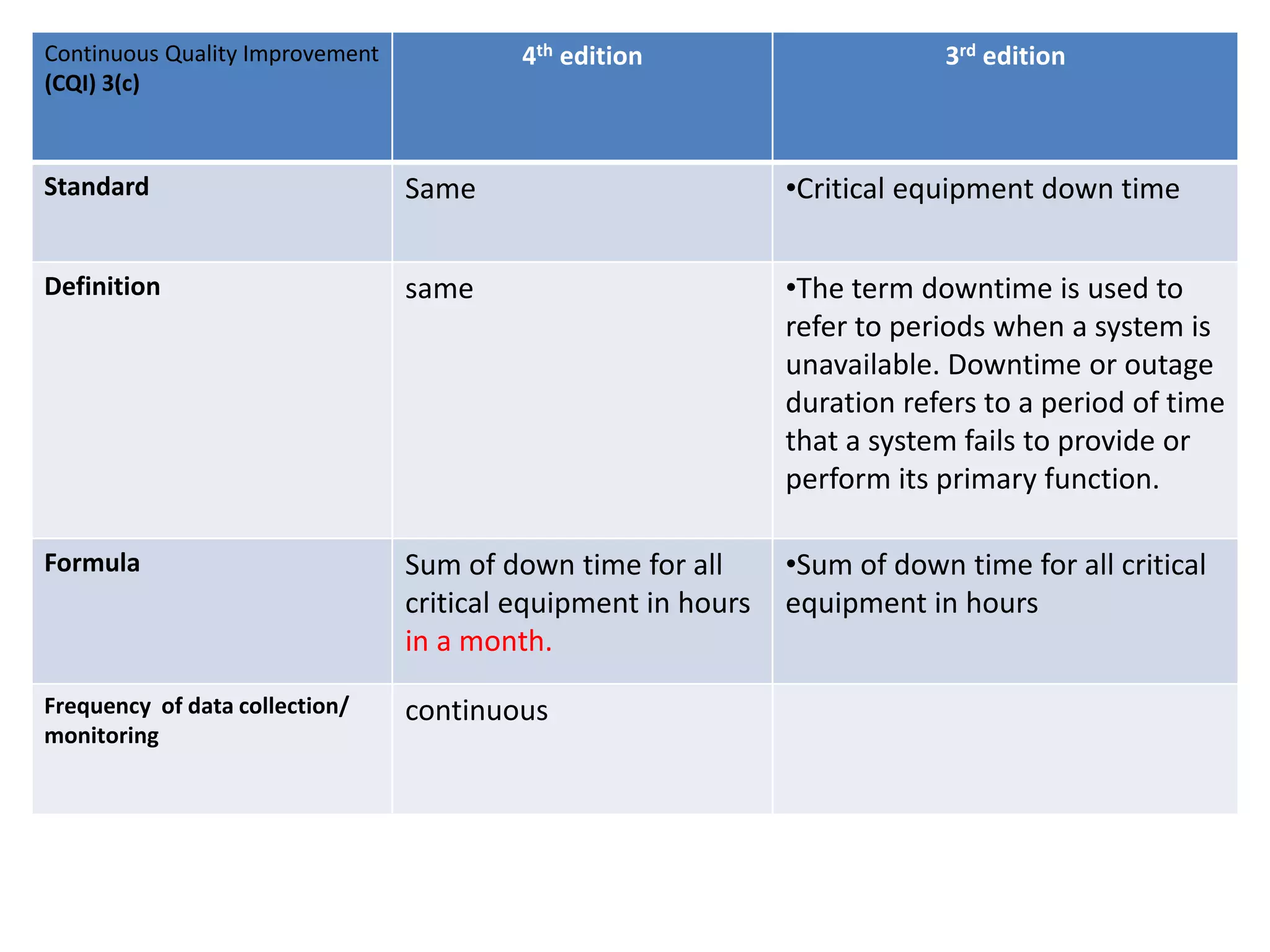
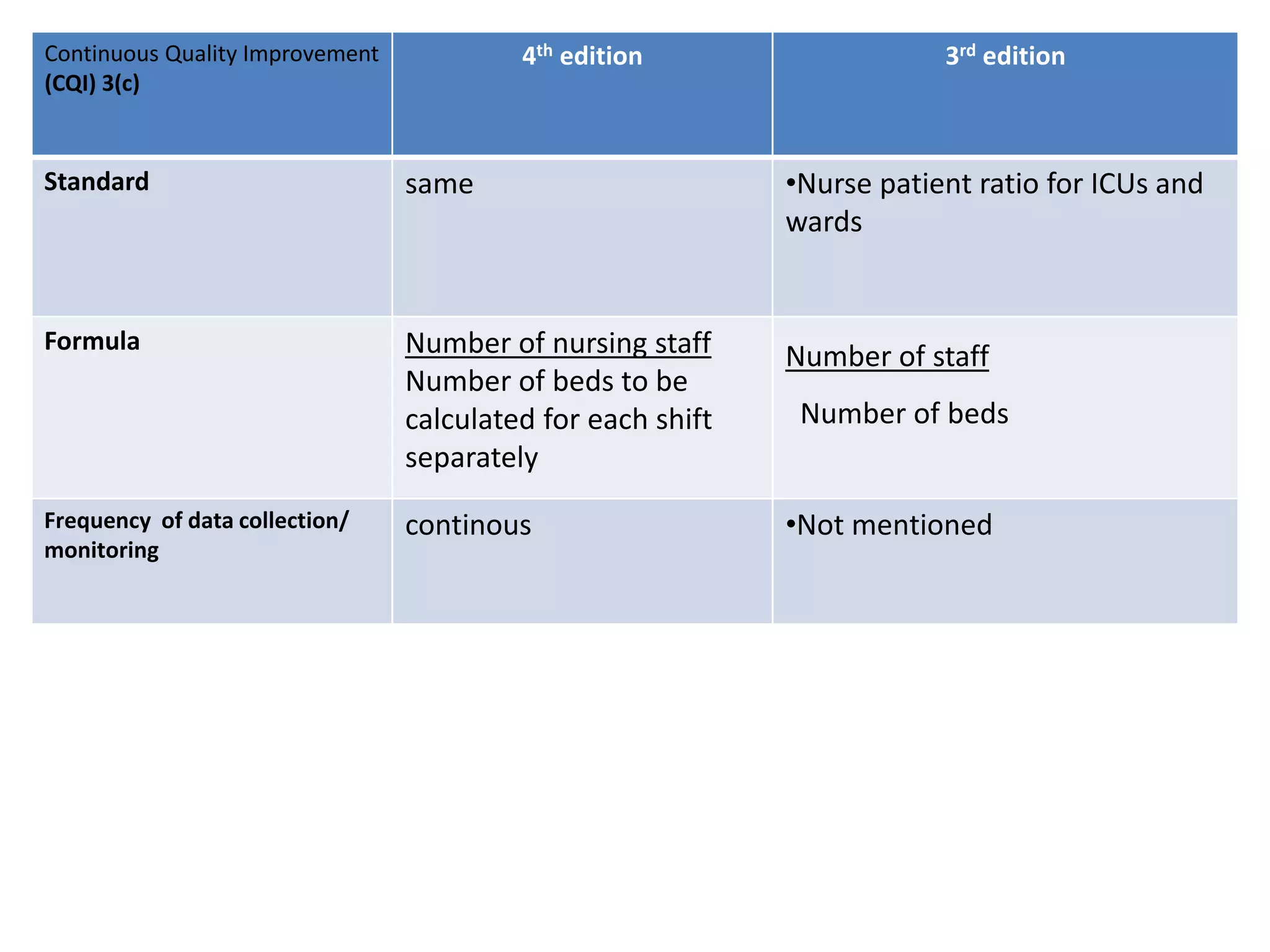
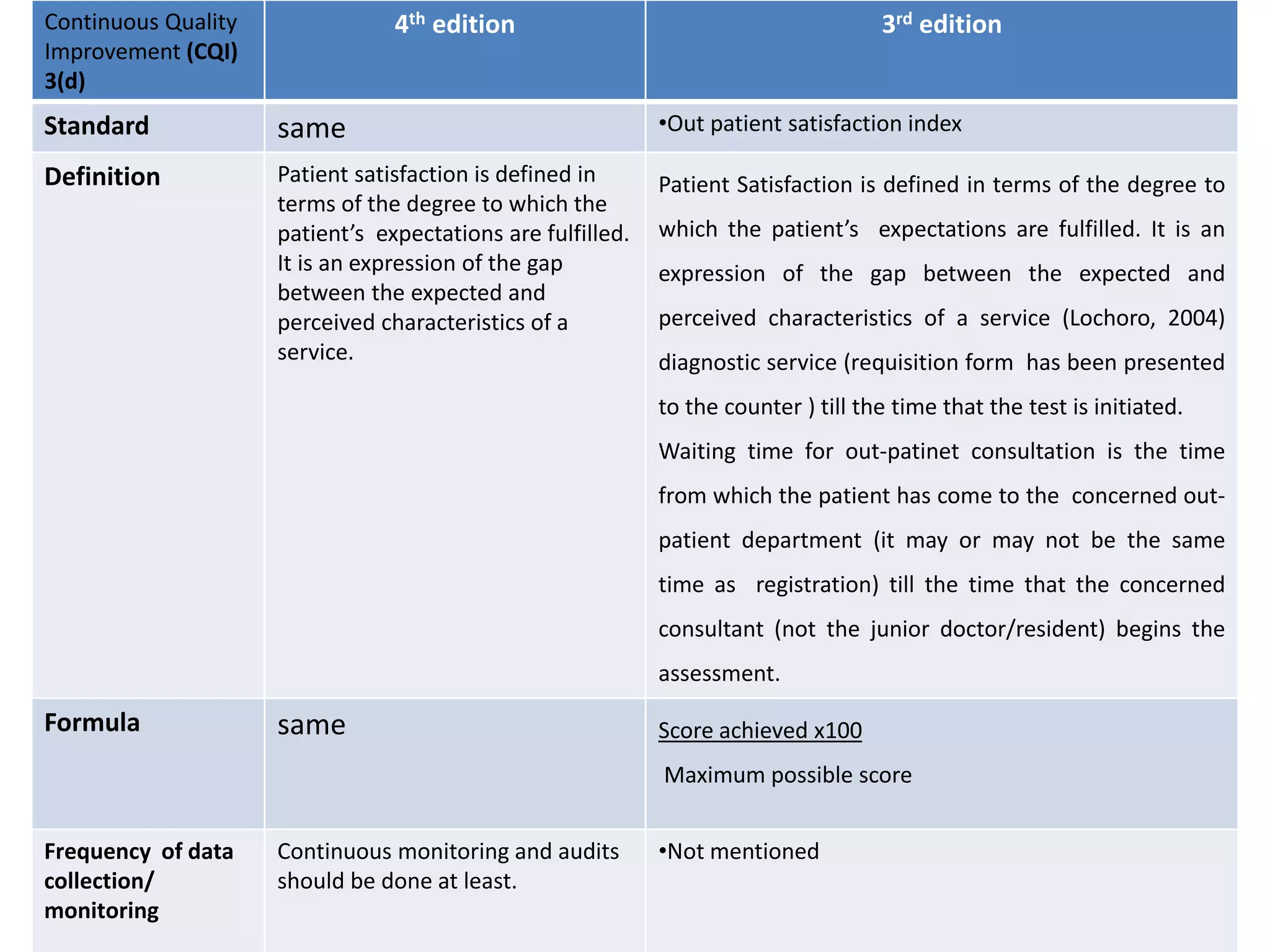
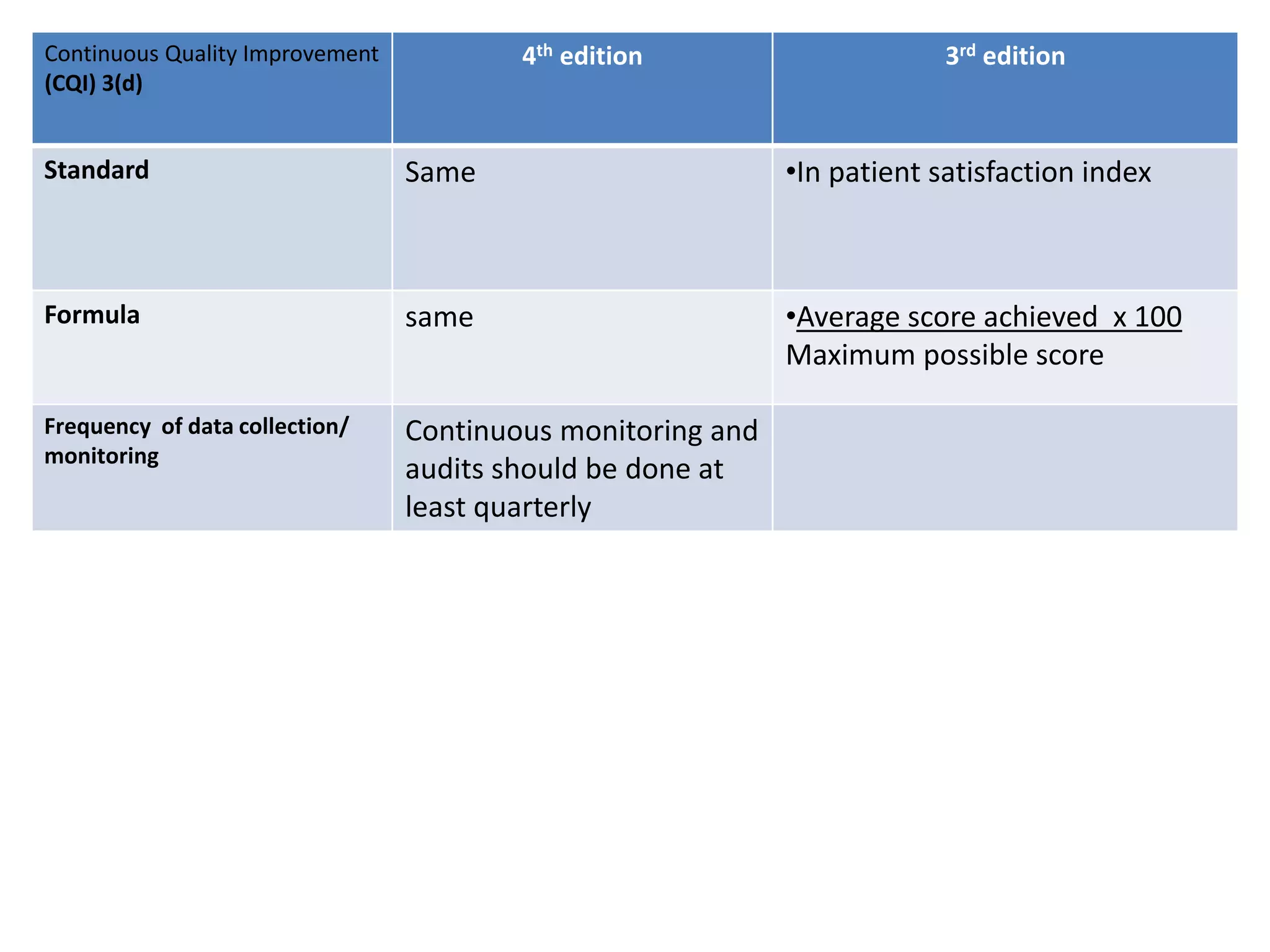
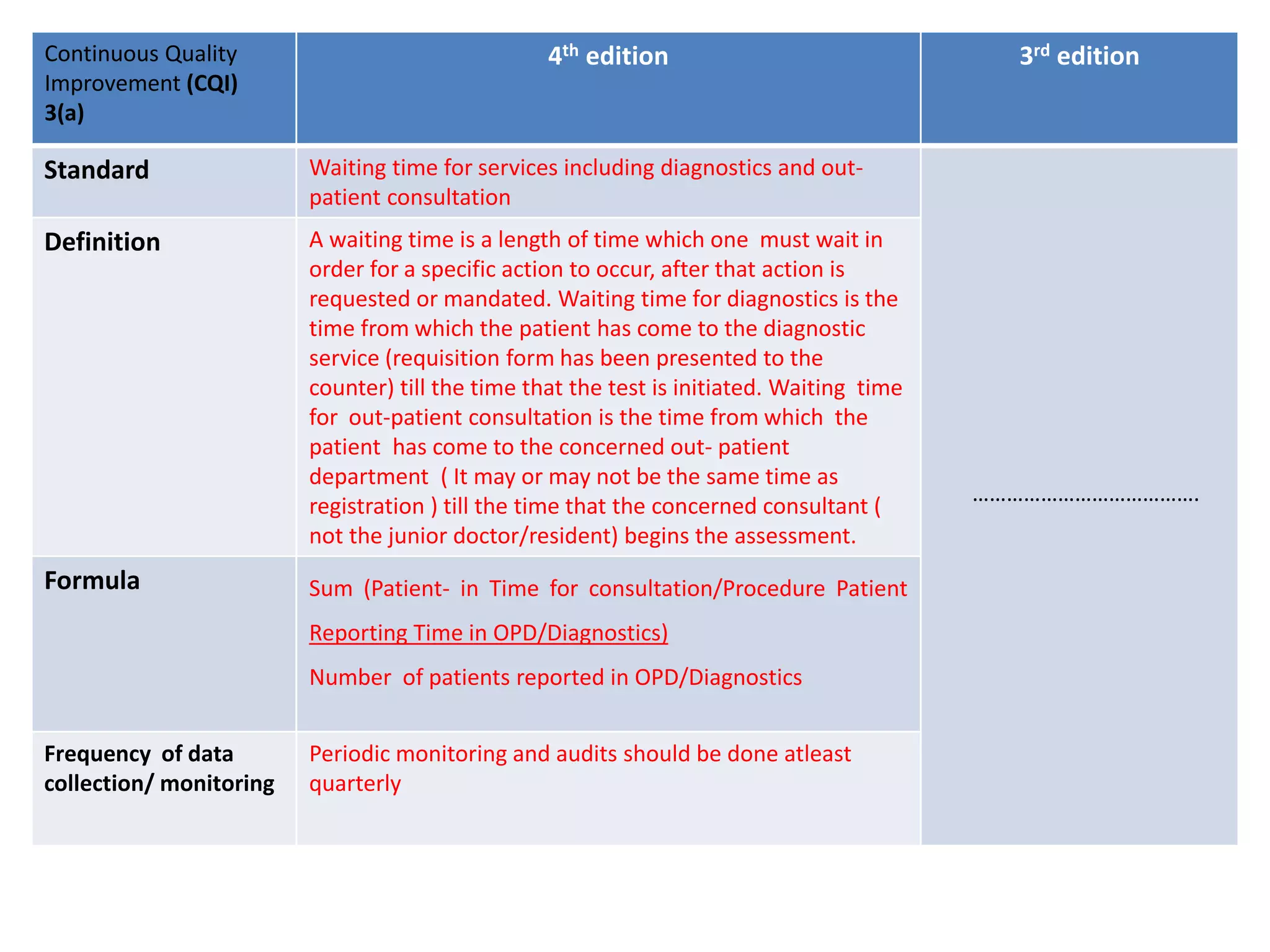
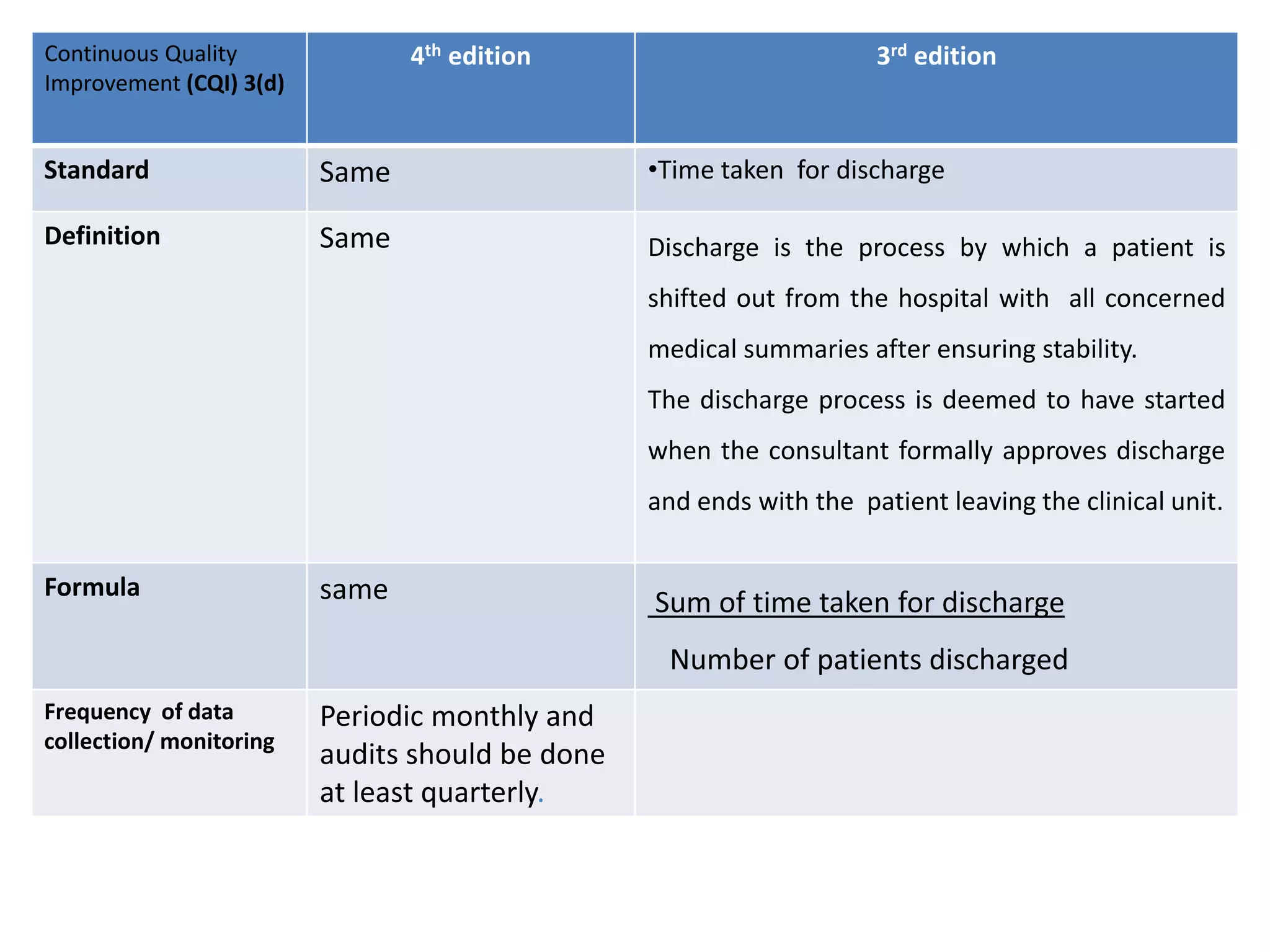
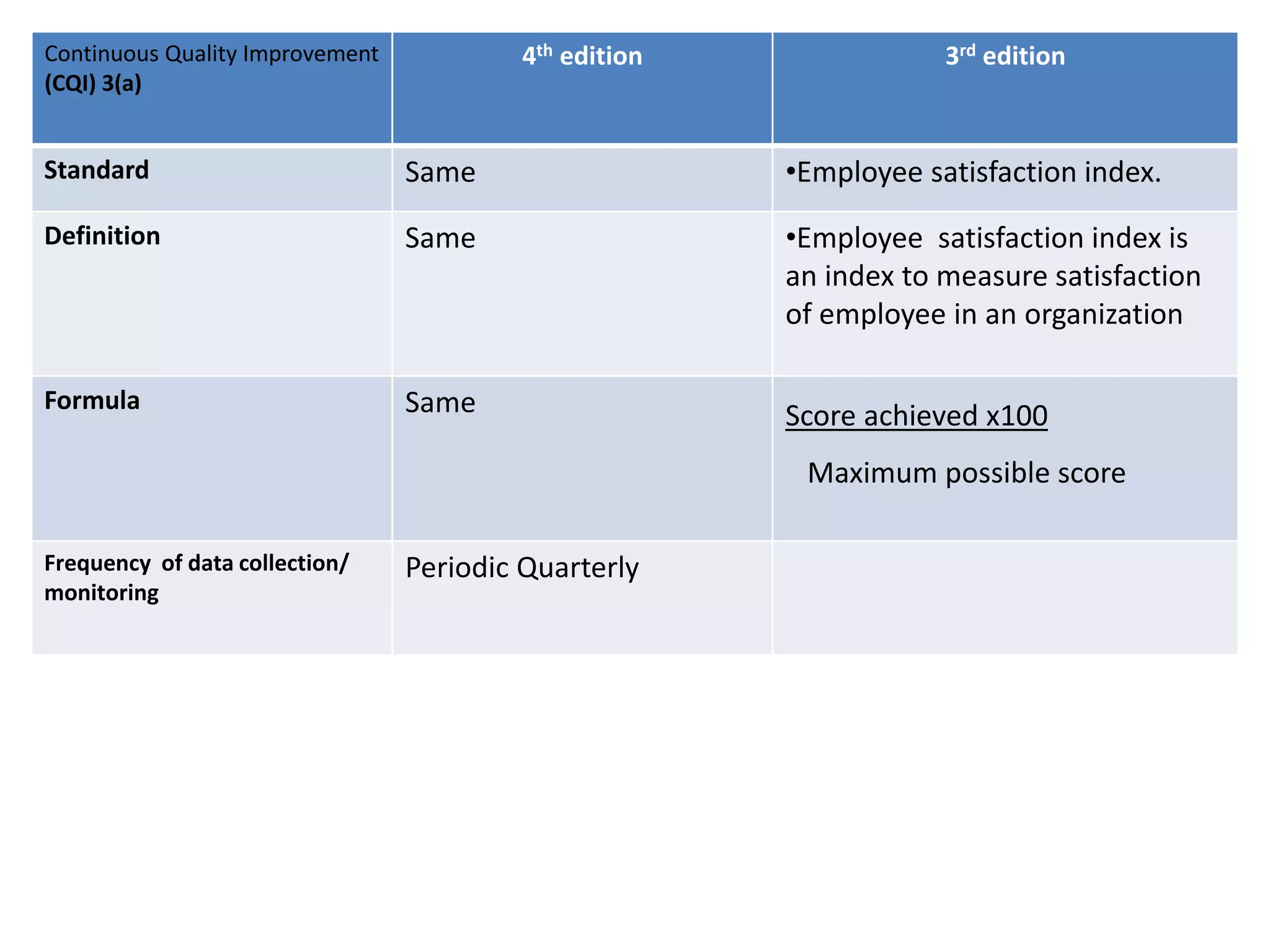
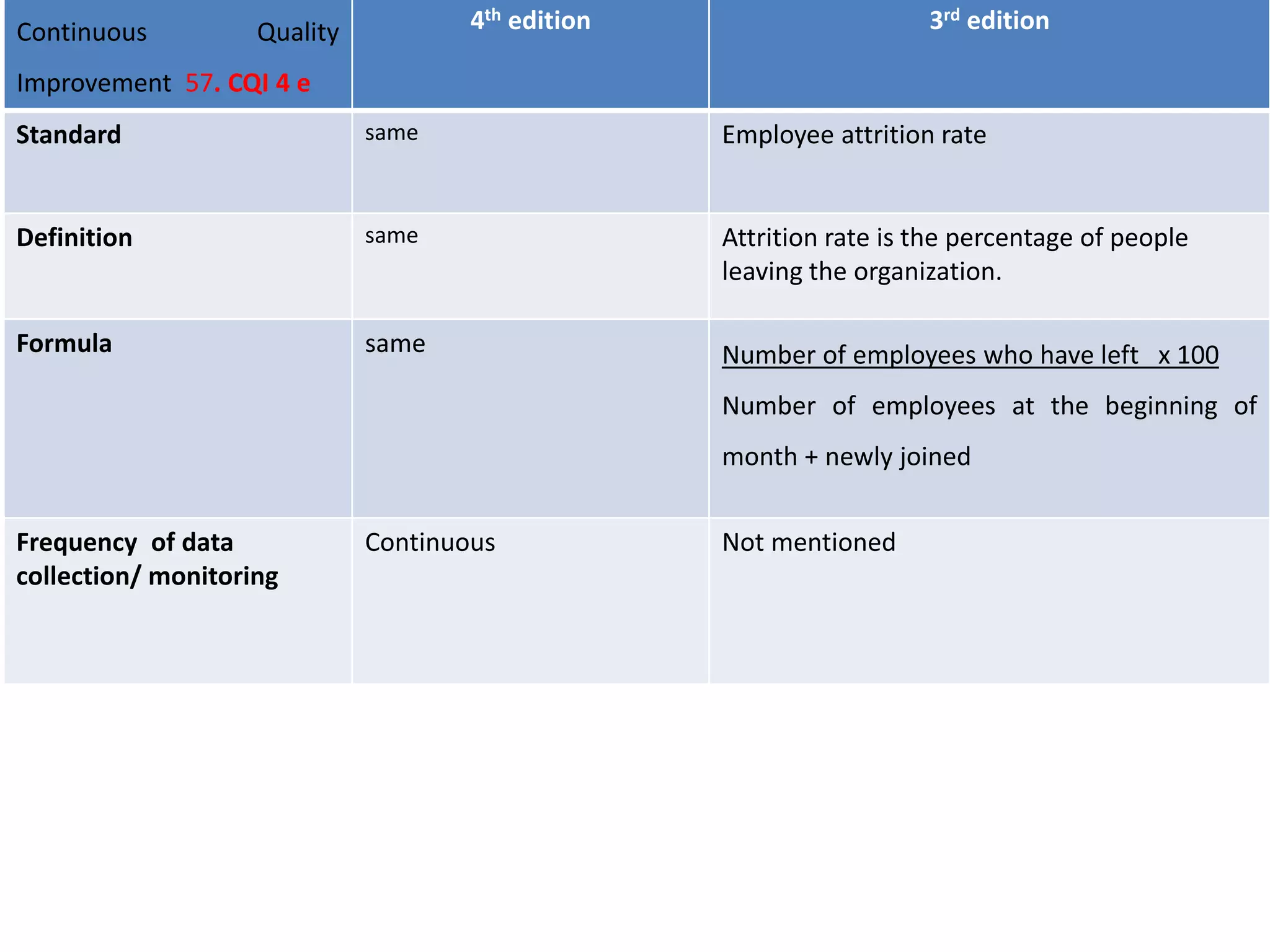
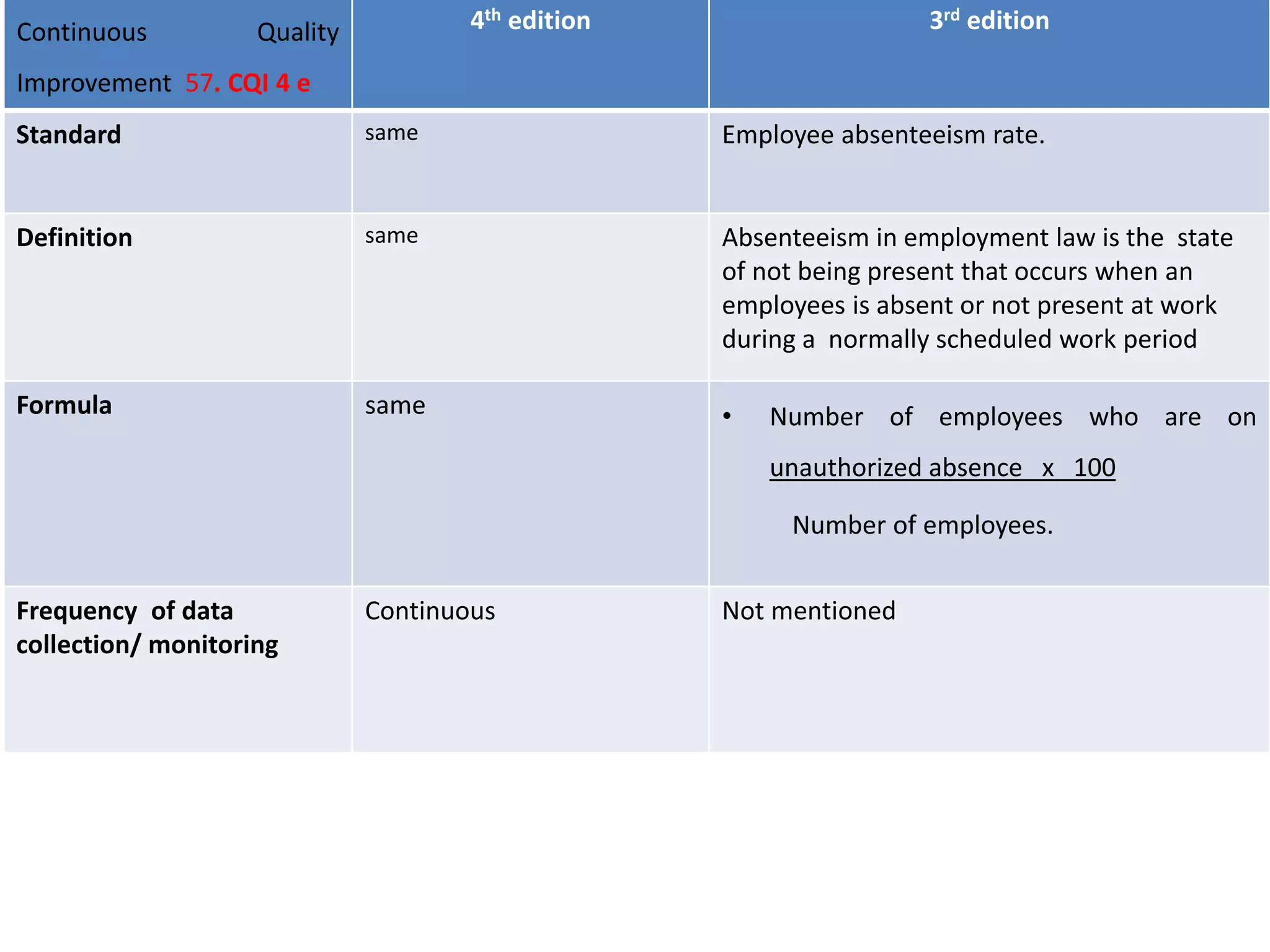
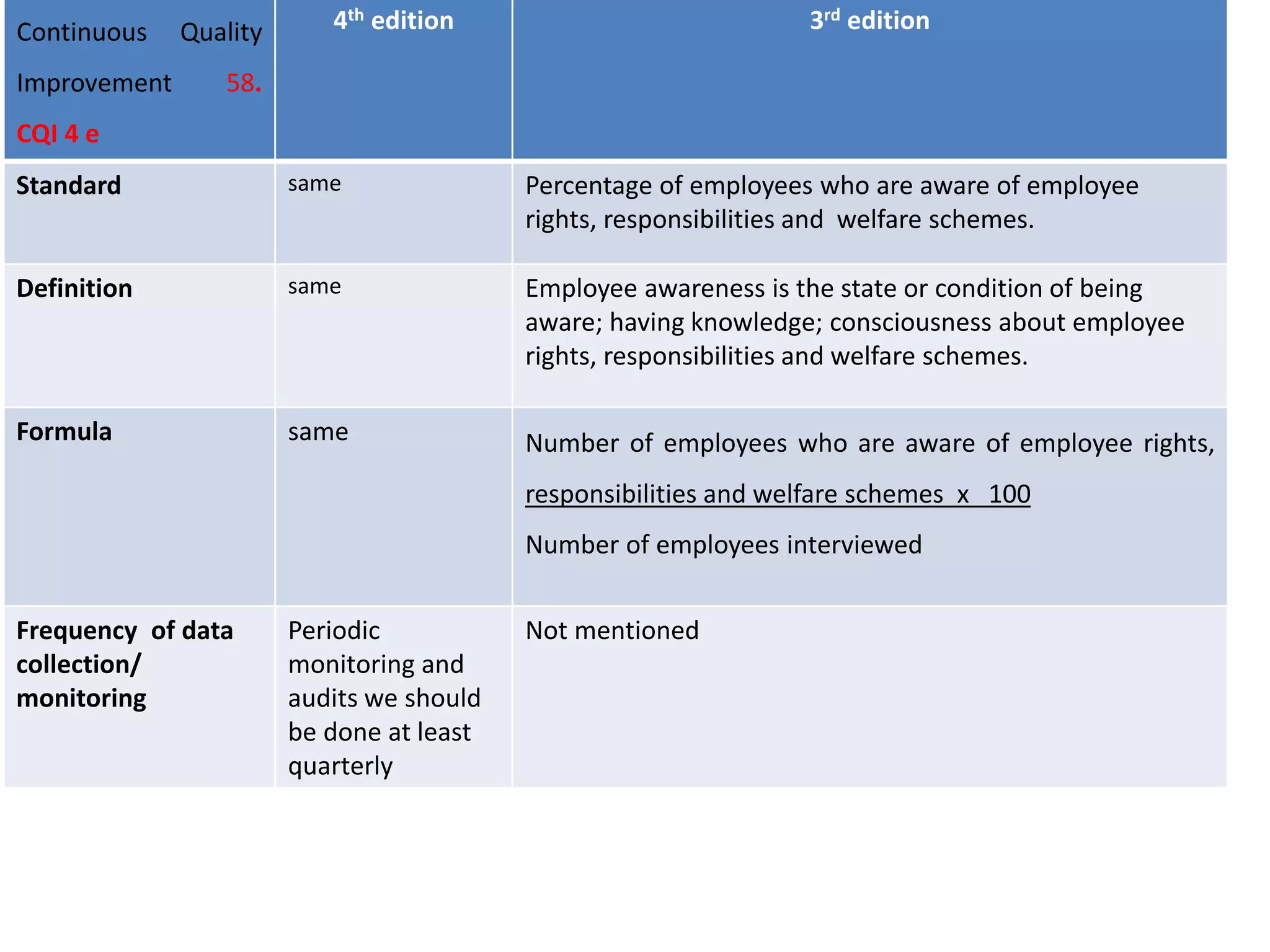
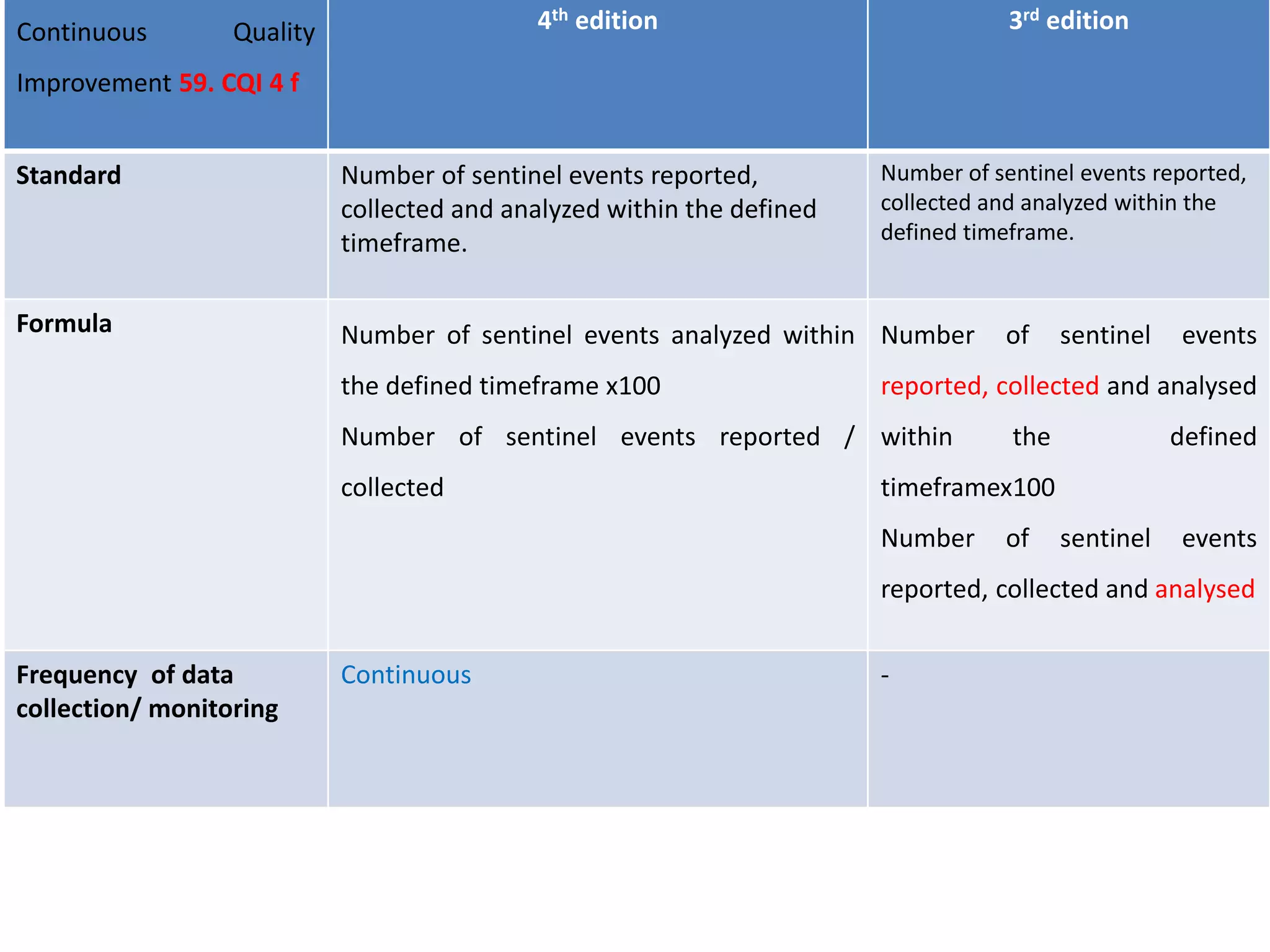
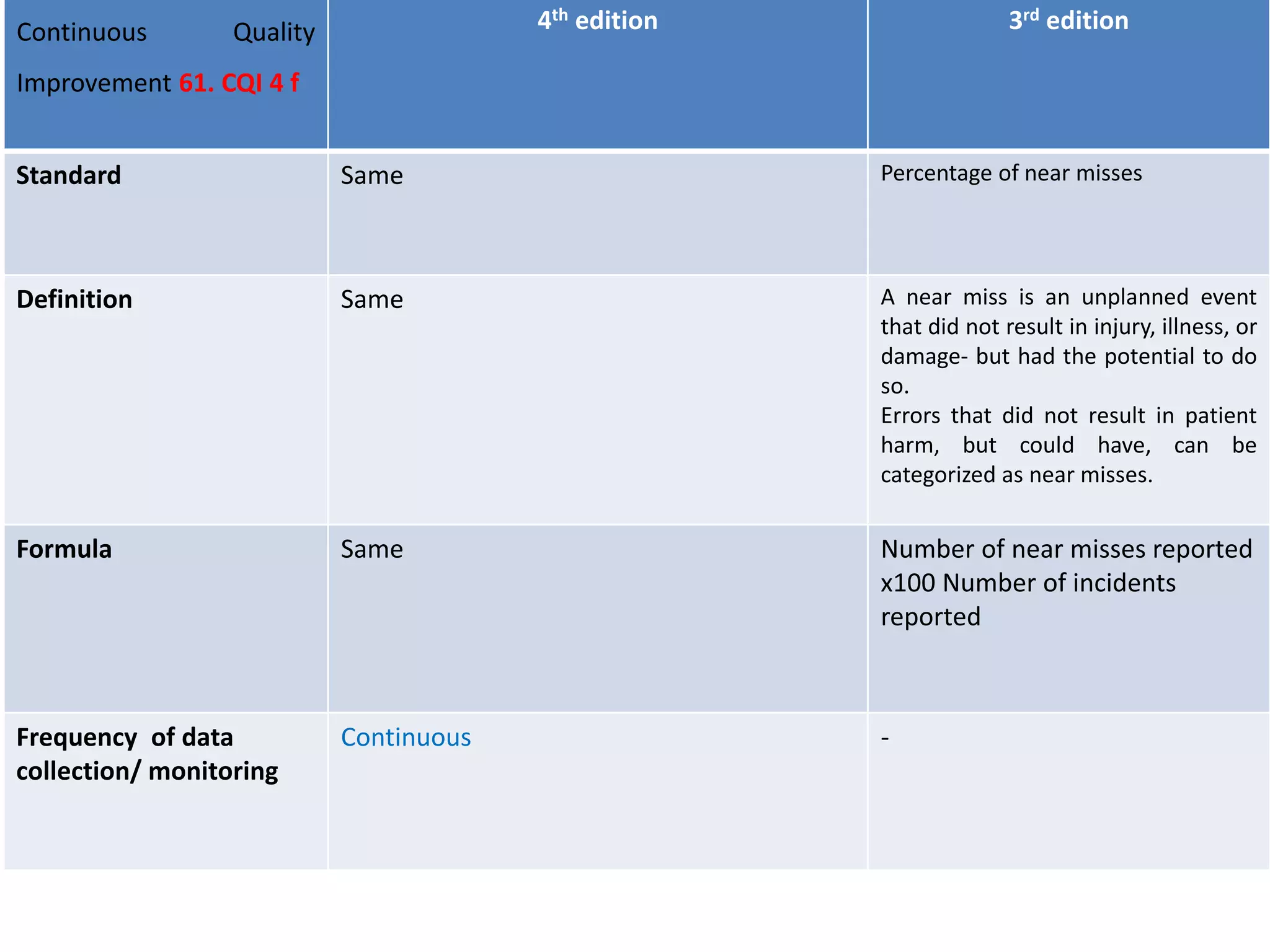
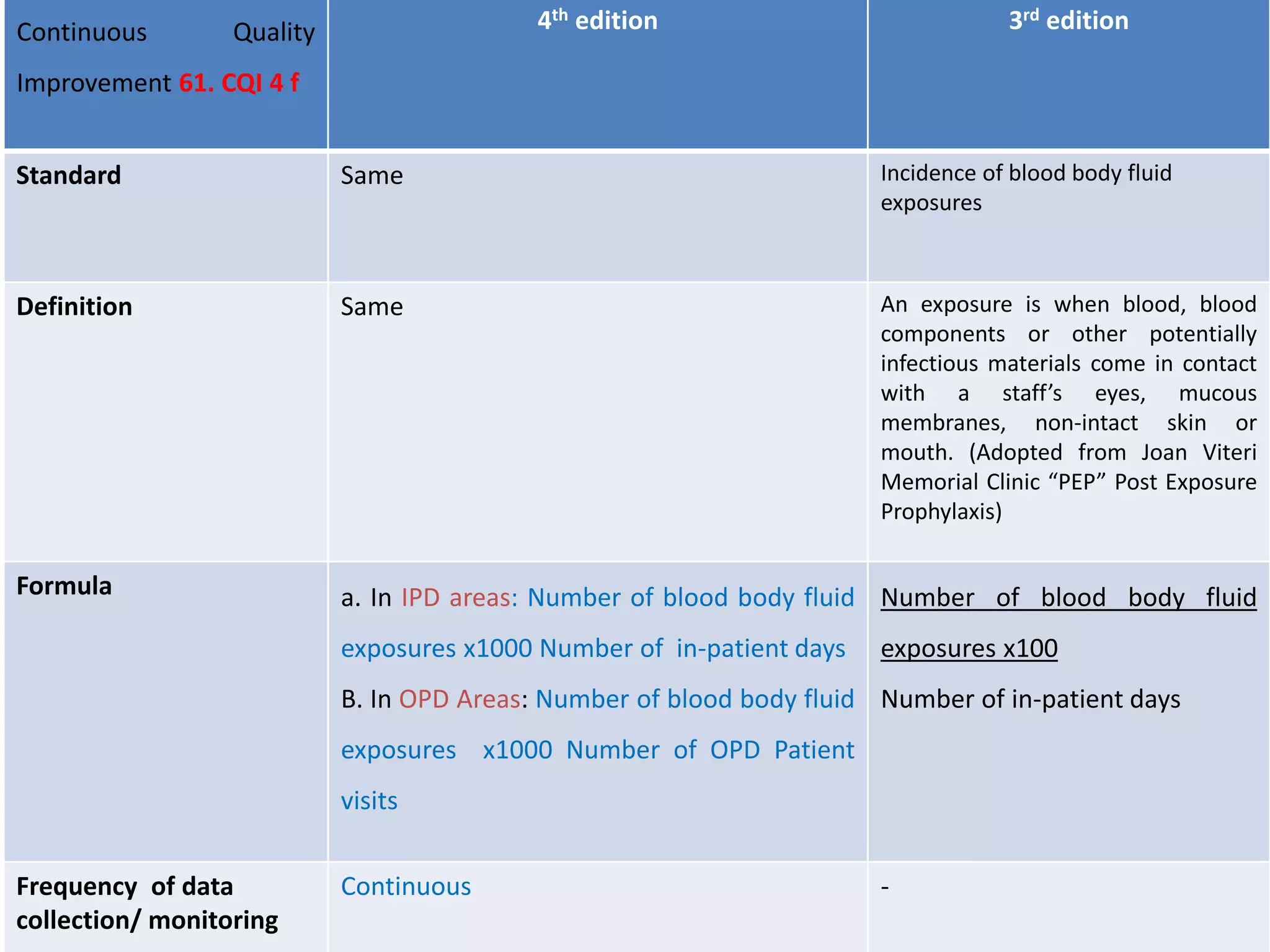
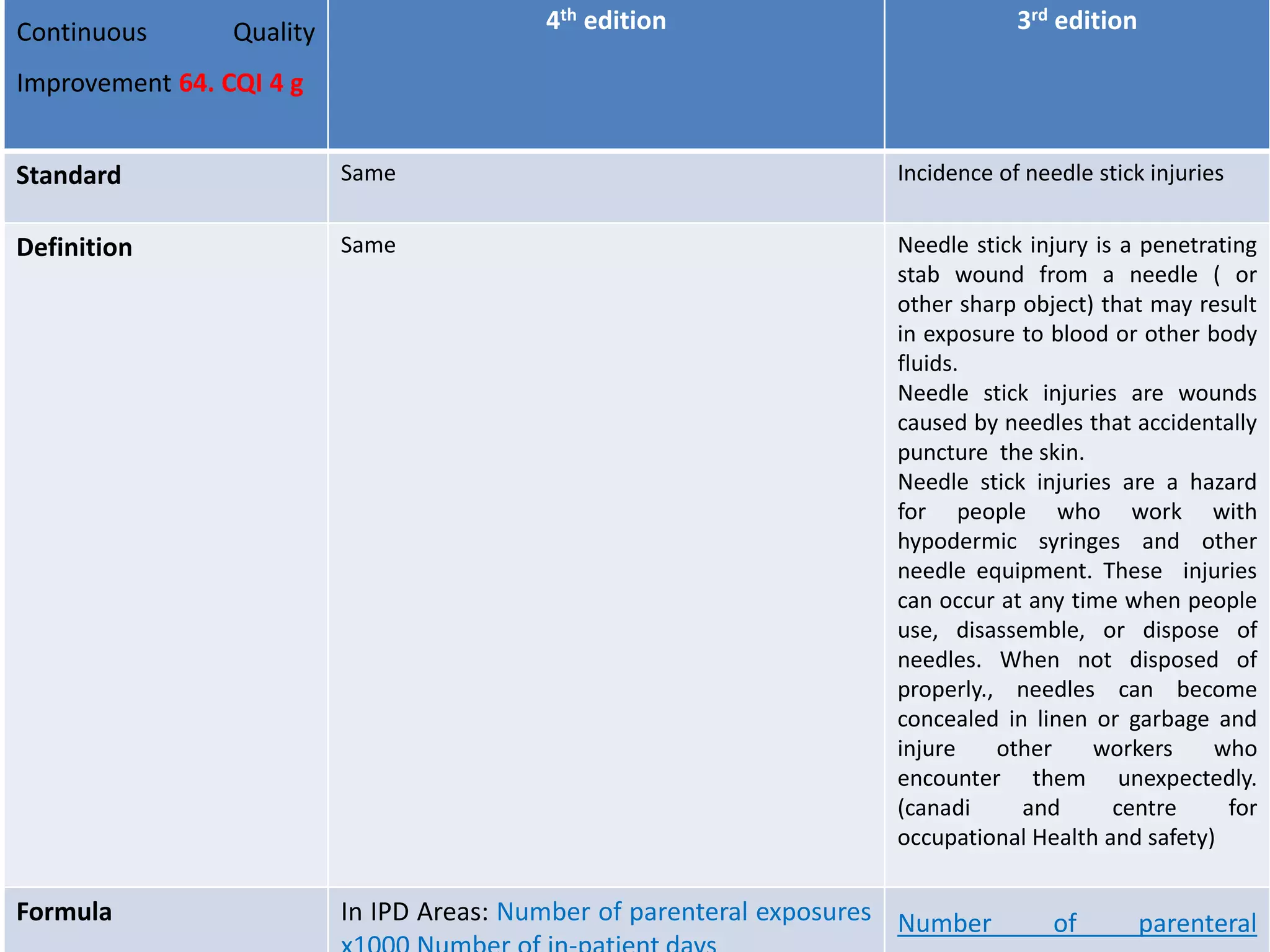
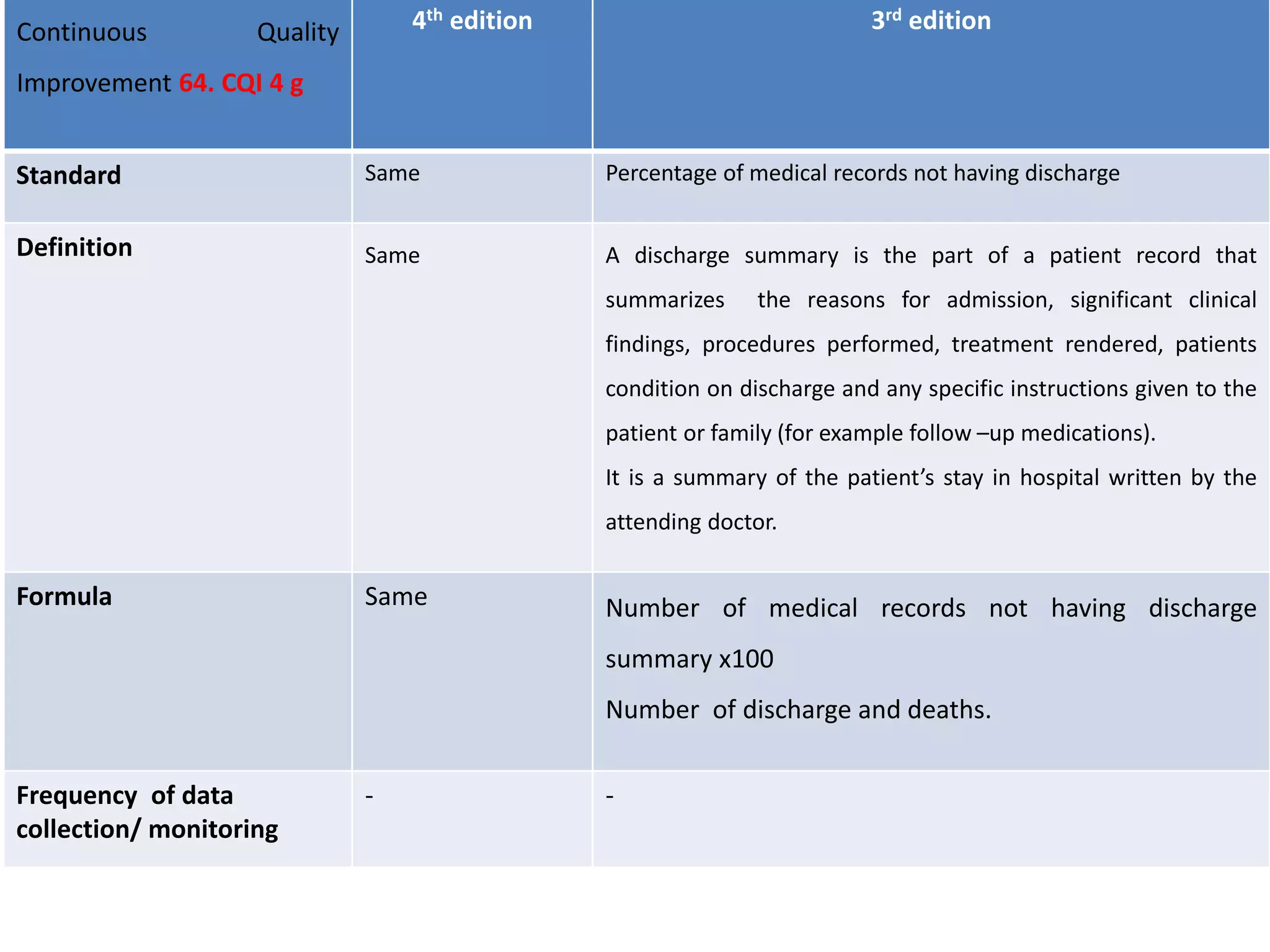
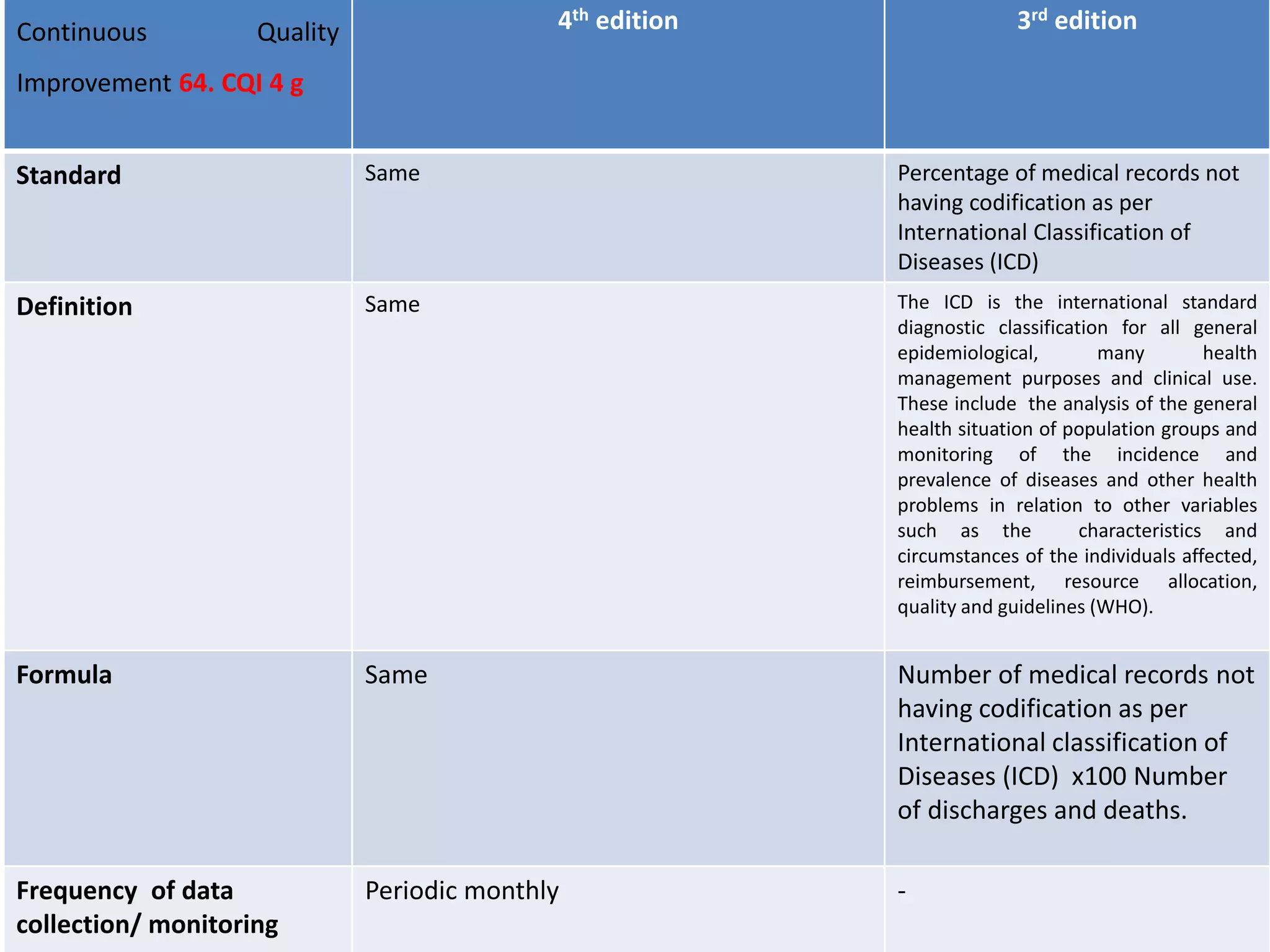
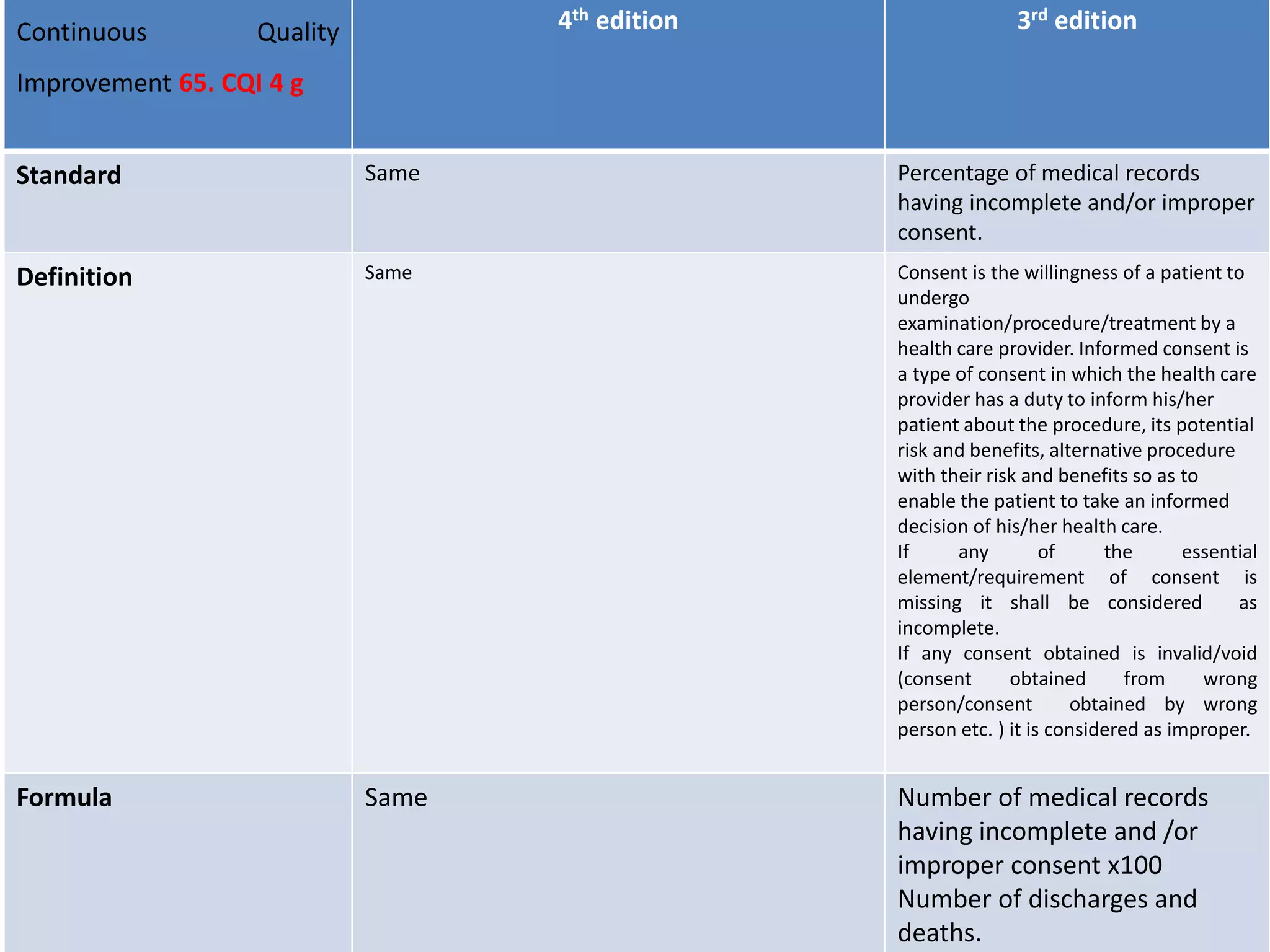
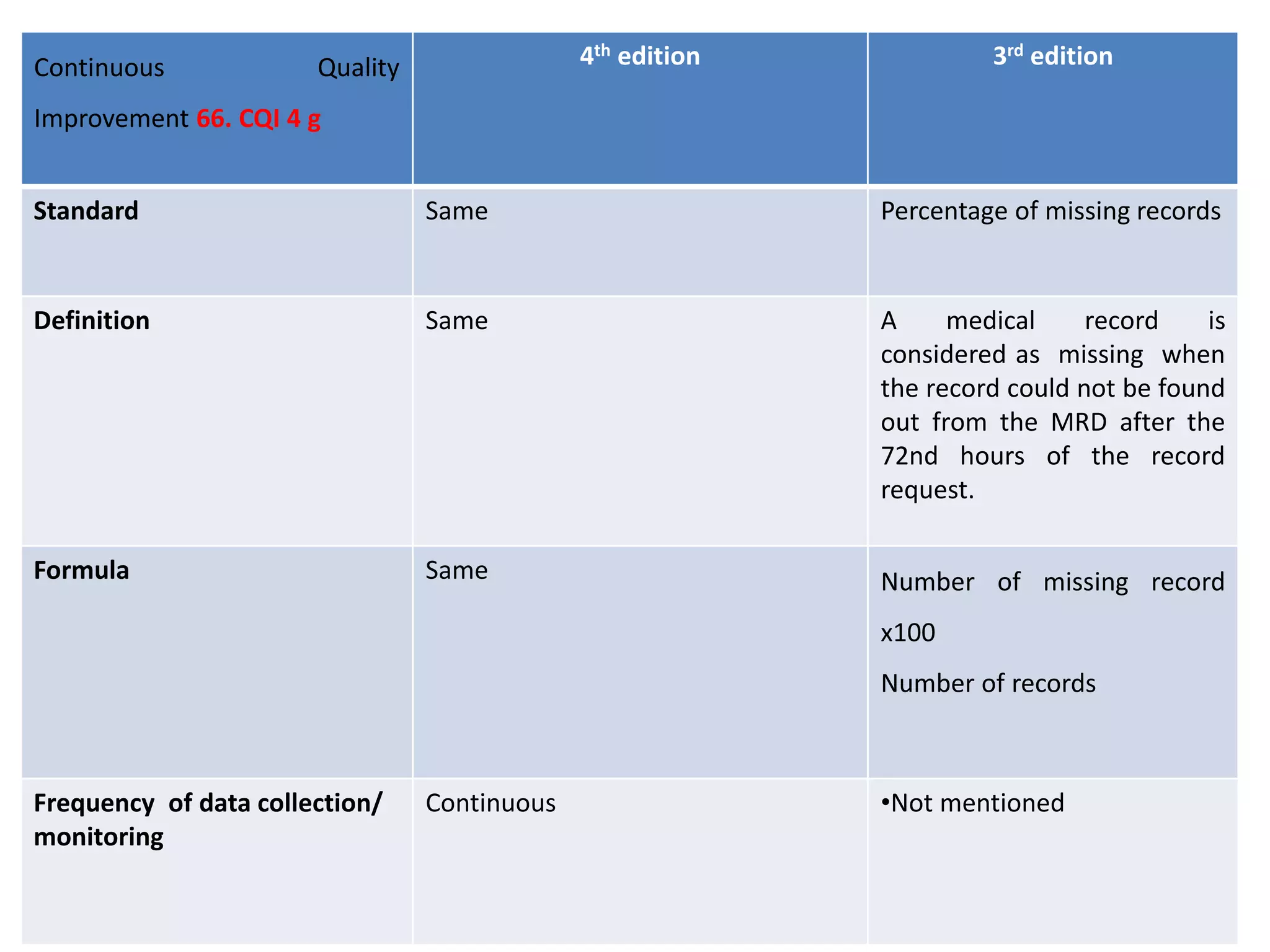
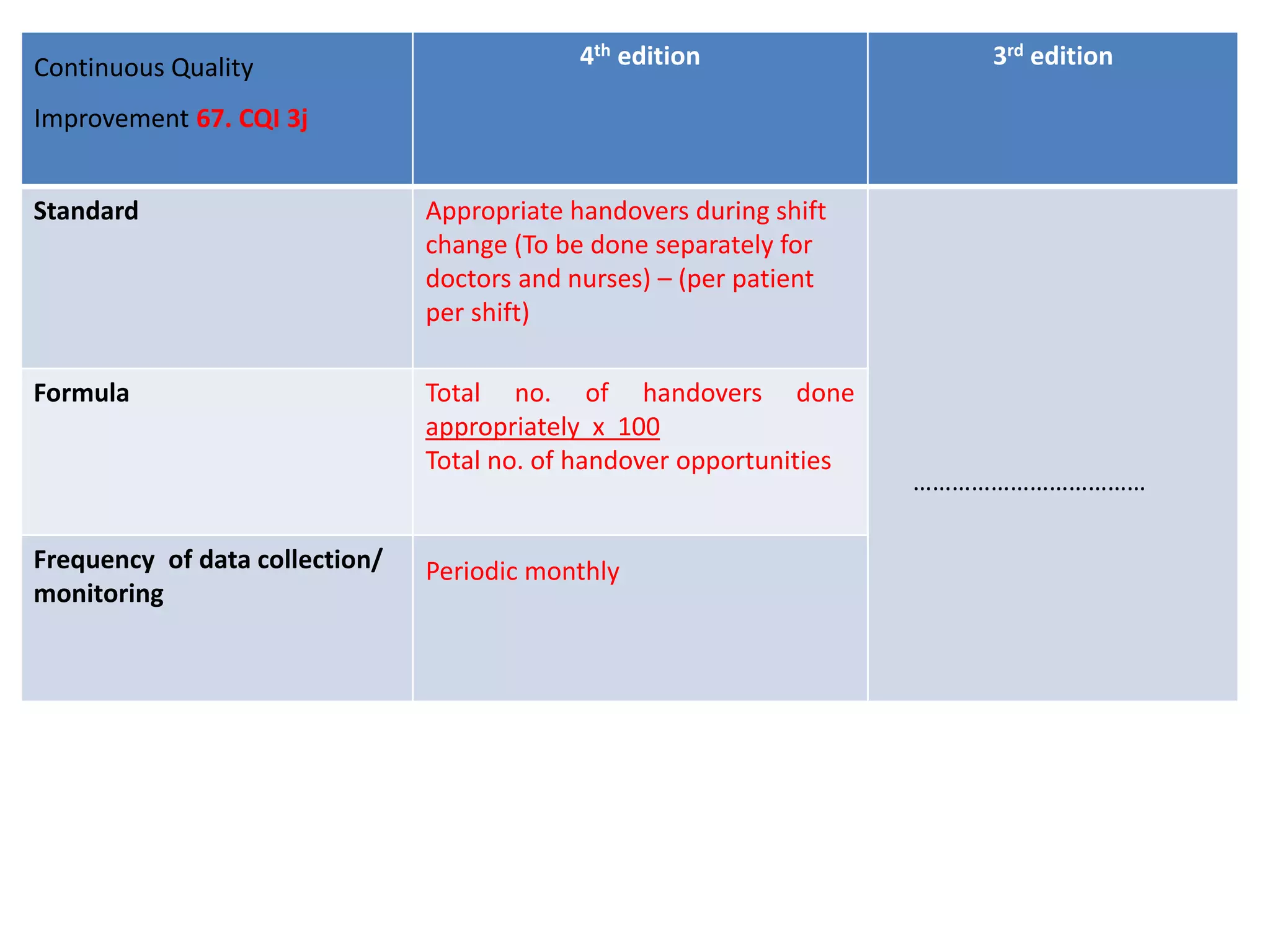
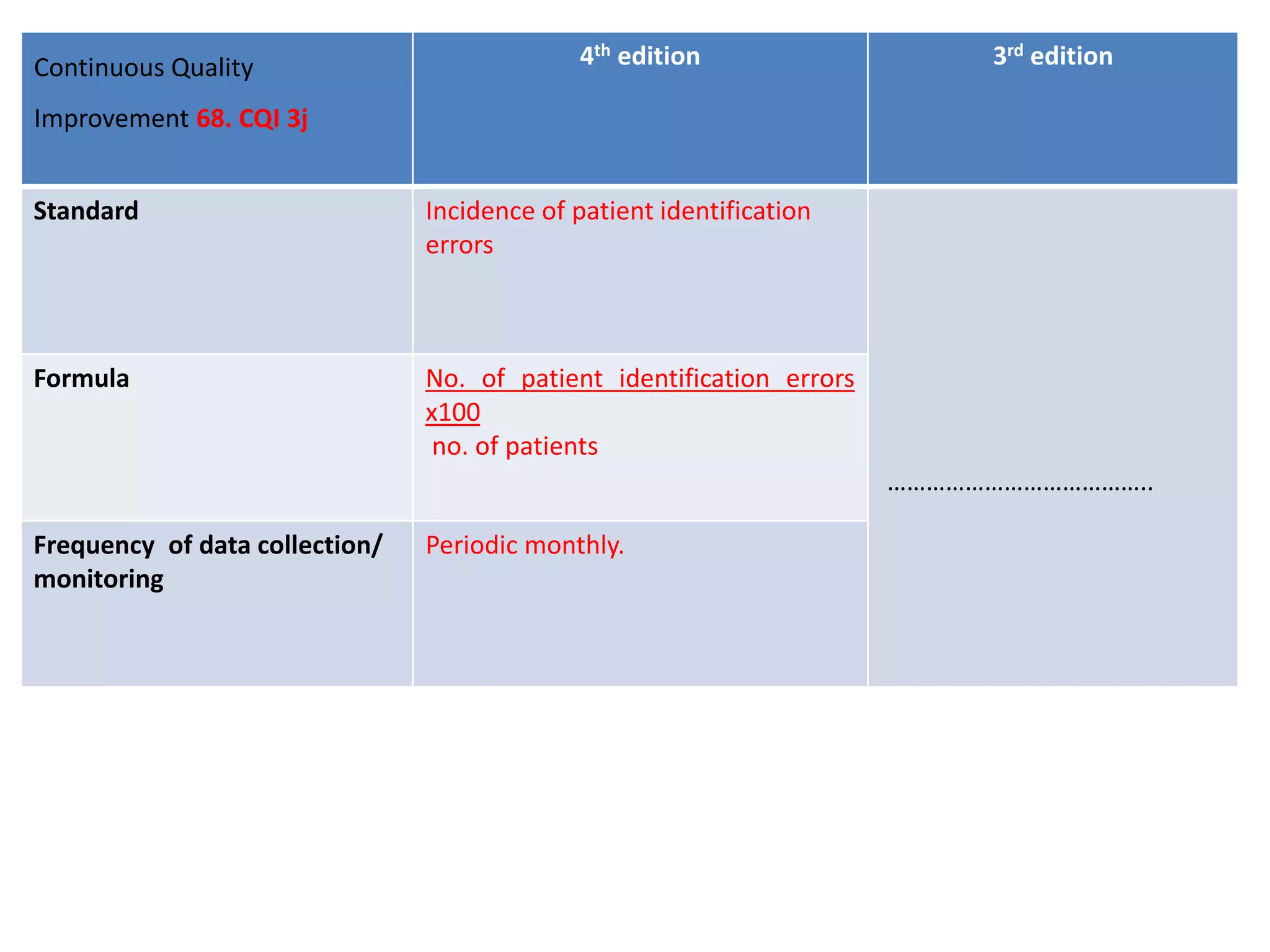
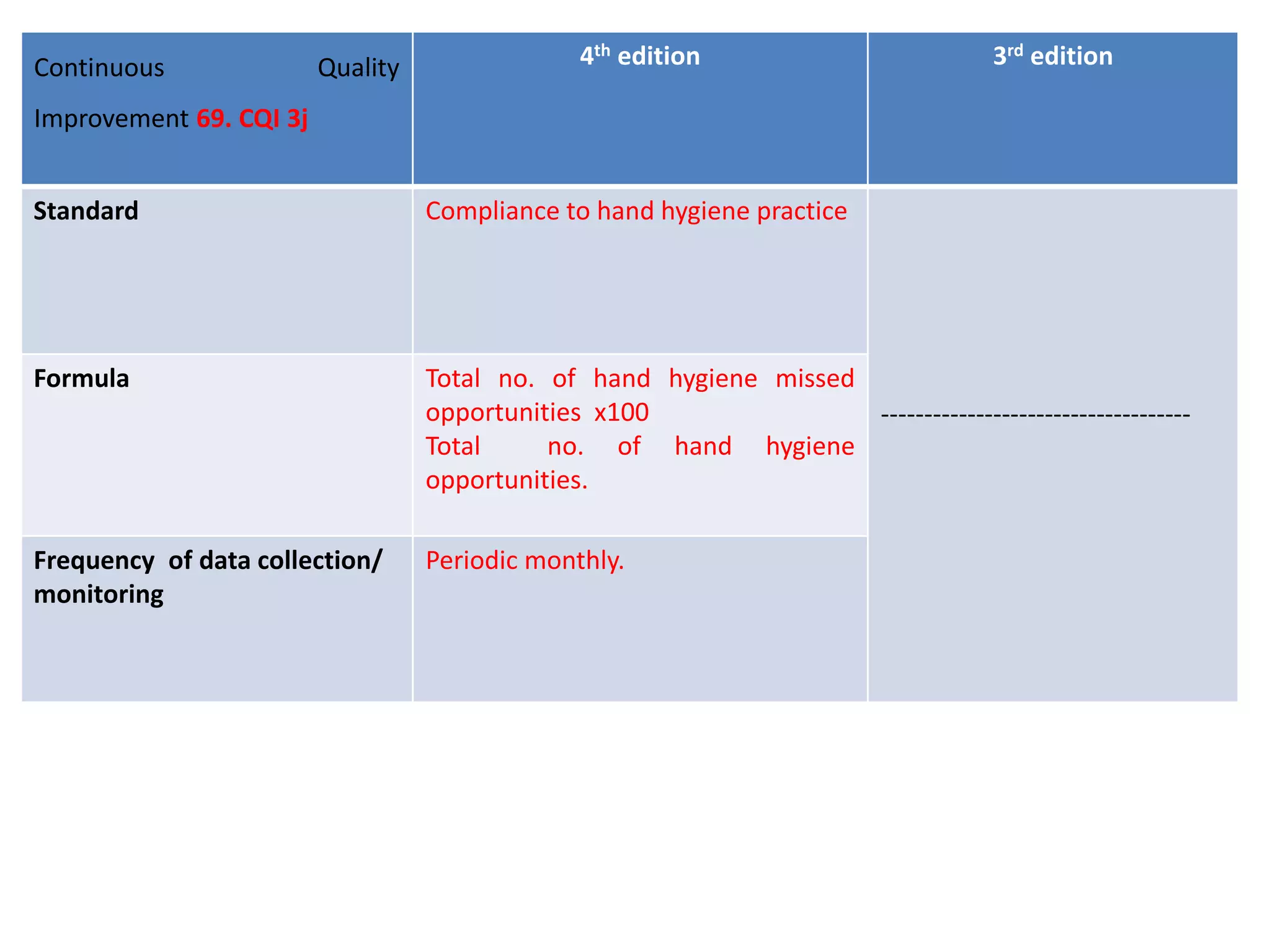
The document provides a comparison of quality indicators between the 4th and 3rd editions of the NABH standards. It summarizes the key changes made to various quality indicators for monitoring access to care, care of patients, medication management, infection control, CQI processes, and other areas. For most indicators, the definitions and formulas for calculation remain the same between the editions, while some new indicators were added and the frequency of data collection was standardized in the 4th edition.