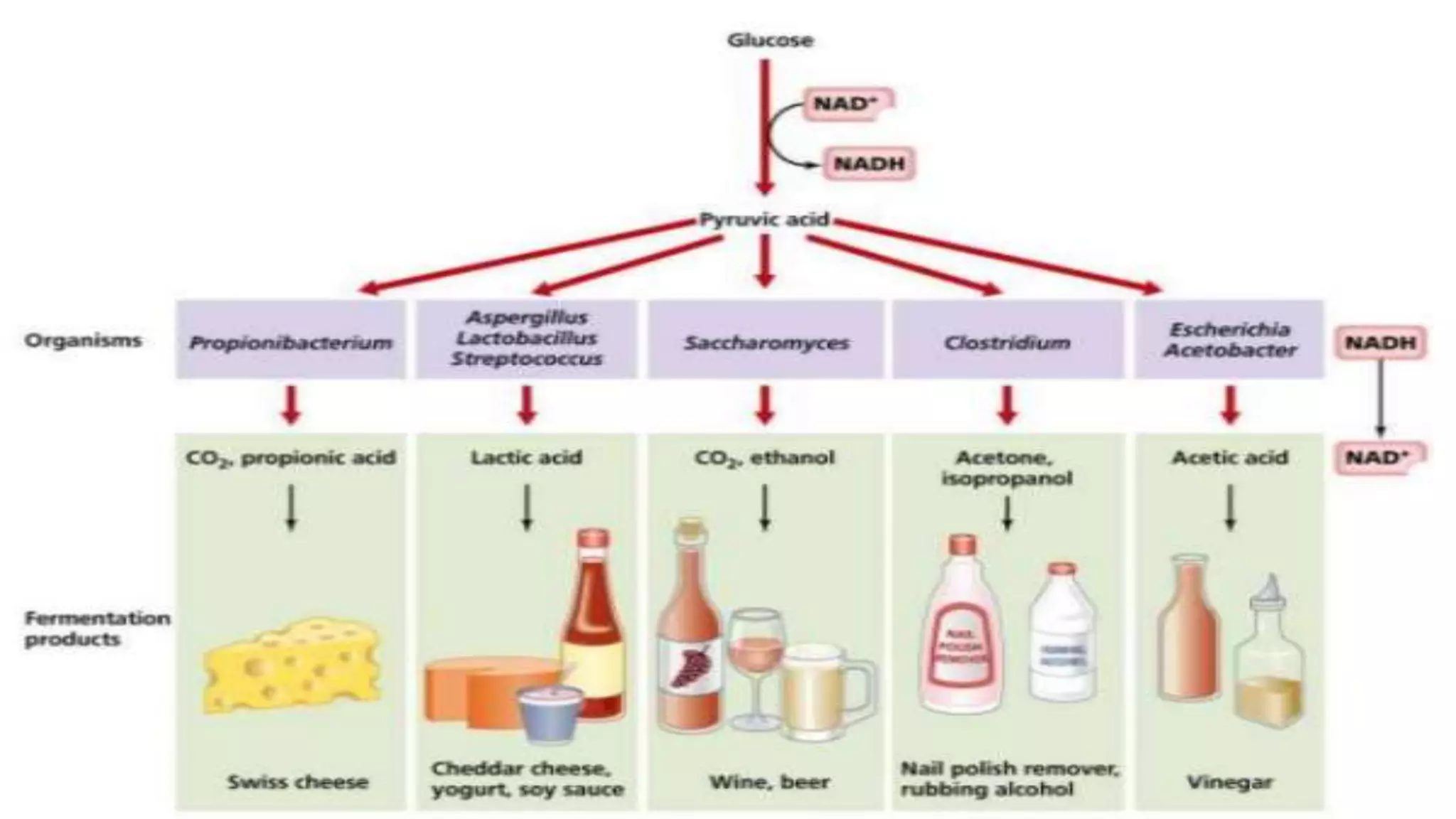
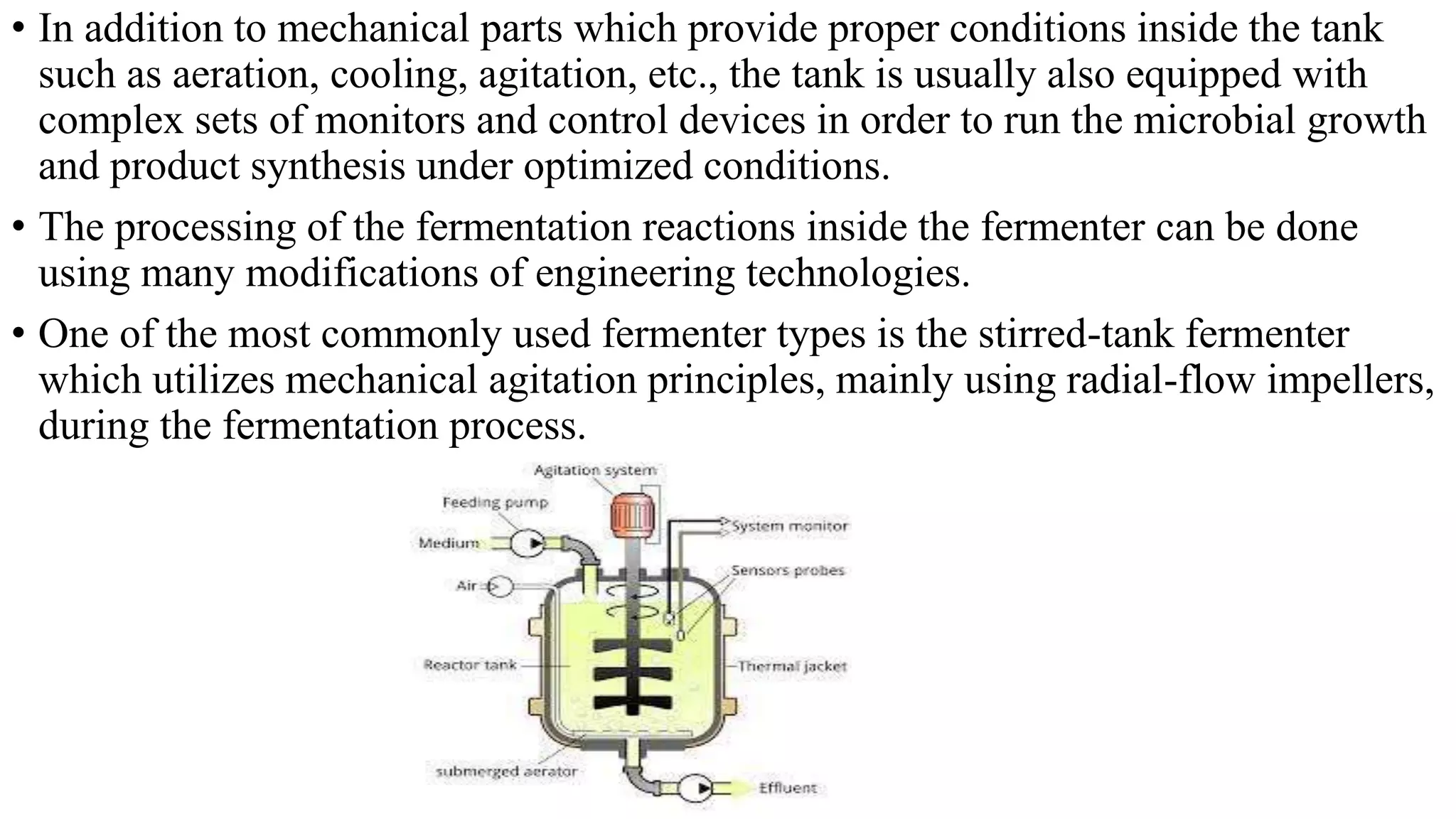
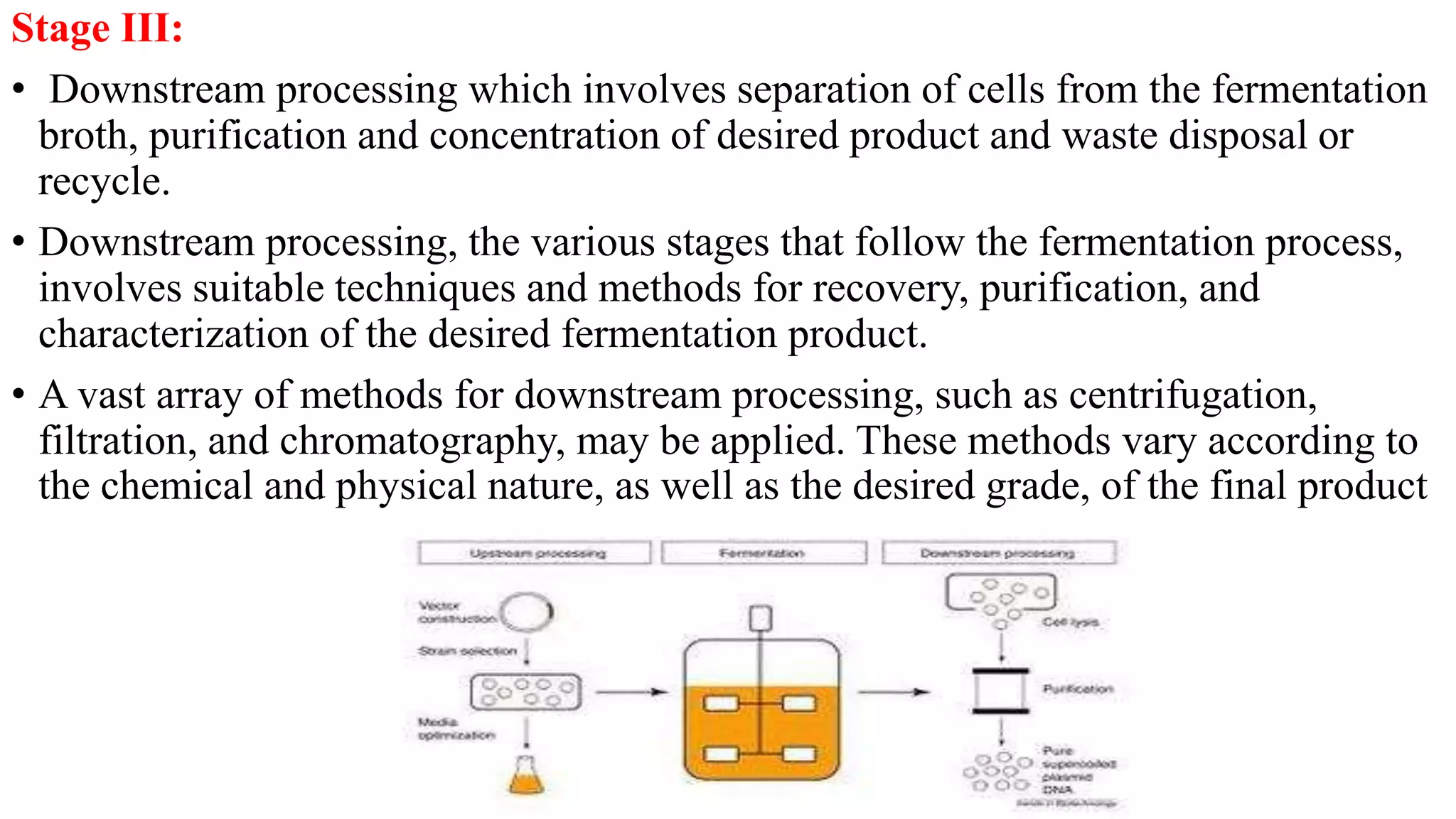
A bioprocess uses living cells or their components to produce desired products through fermentation. Fermentation is an anaerobic process by which cells produce energy without oxygen. It results in less energy production than aerobic respiration. Fermentation can produce products like lactic acid, ethyl alcohol, and carbon dioxide depending on the organism. Bioprocesses are commonly used to produce fermented foods, industrial chemicals, and specialty chemicals. The bioprocess is divided into three stages - upstream processing to prepare the medium, fermentation using microorganisms to produce the product, and downstream processing to separate and purify the product.