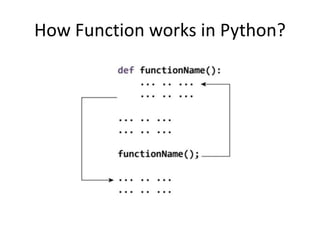
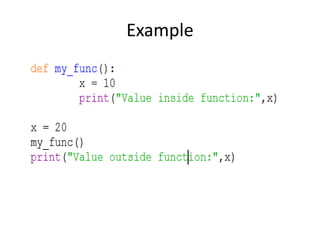
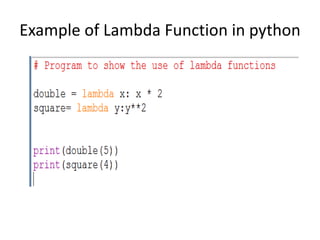
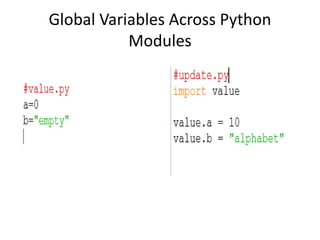
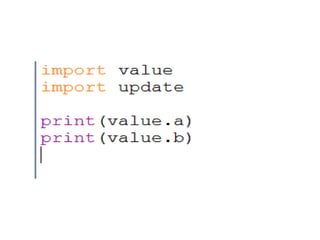
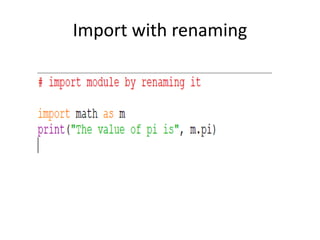
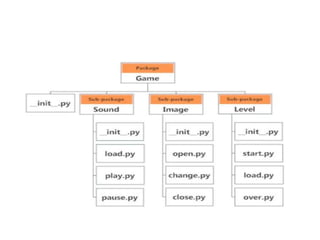
The document provides a comprehensive overview of Python functions, including their definition, purpose, and types like built-in and user-defined functions. It also covers concepts such as variable scope and lifetime, recursion with its advantages and disadvantages, and the use of lambda functions. Additionally, it explains Python modules and packages, detailing how to import them and the structure required for organizing related files.