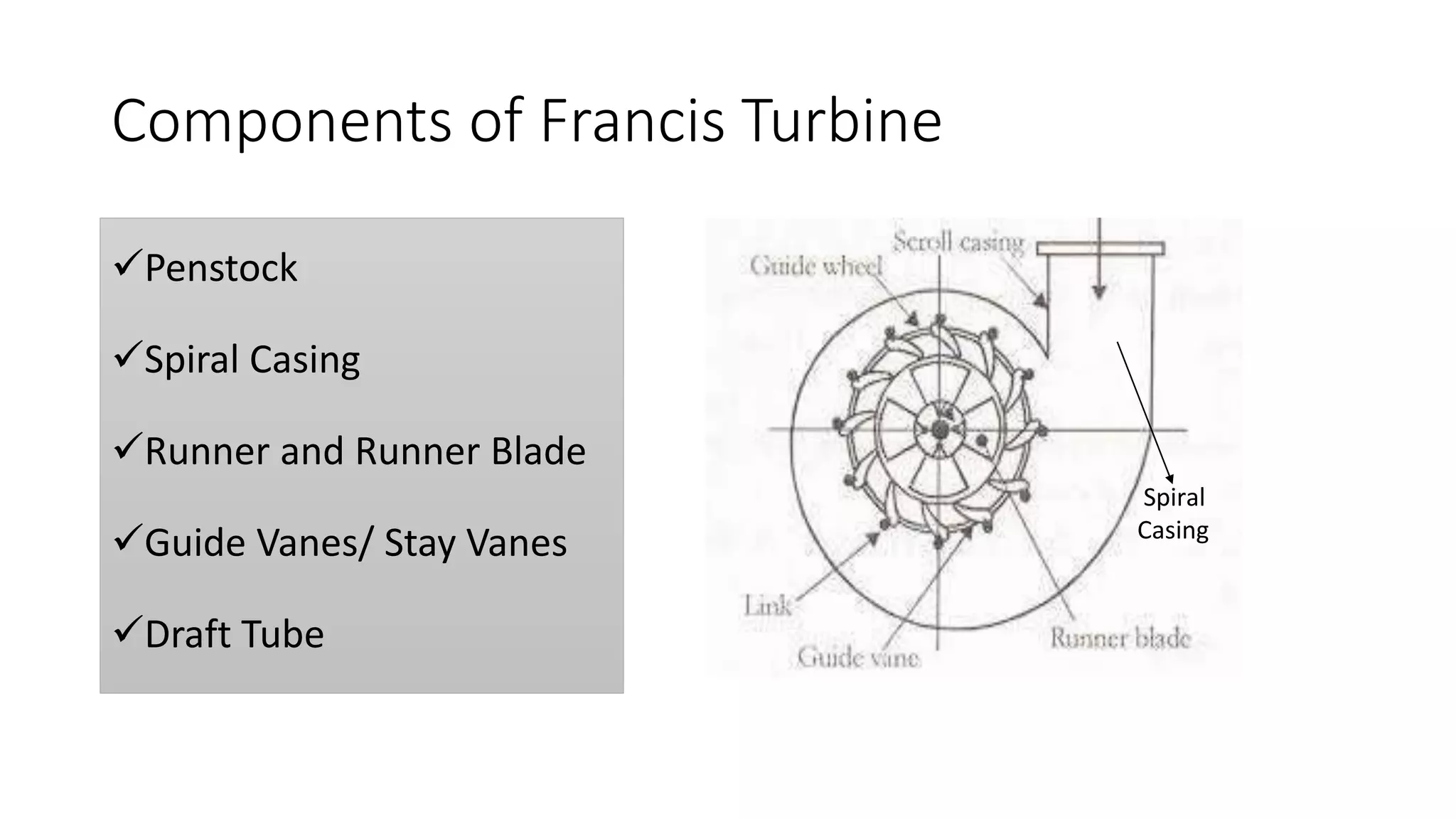
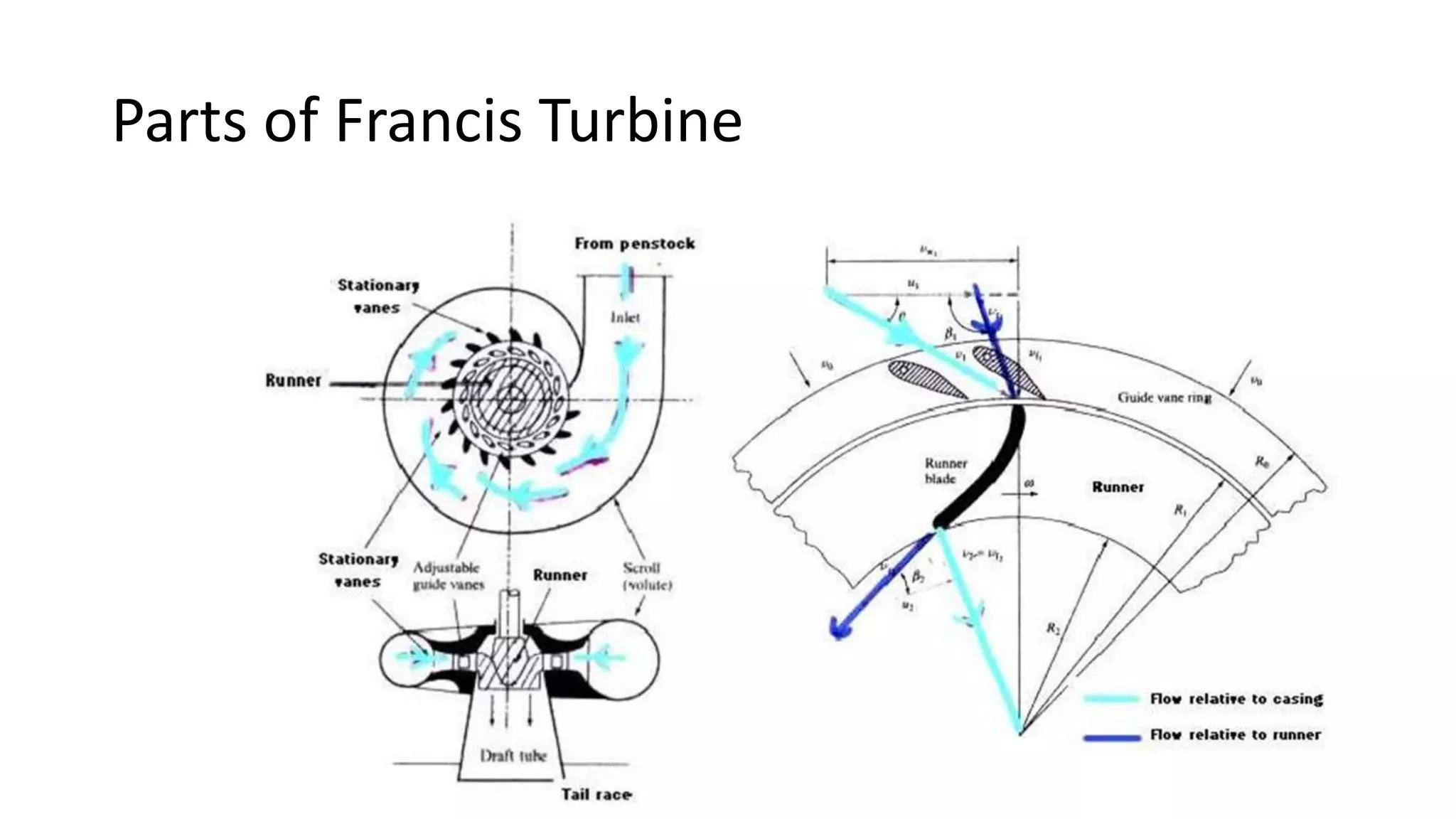
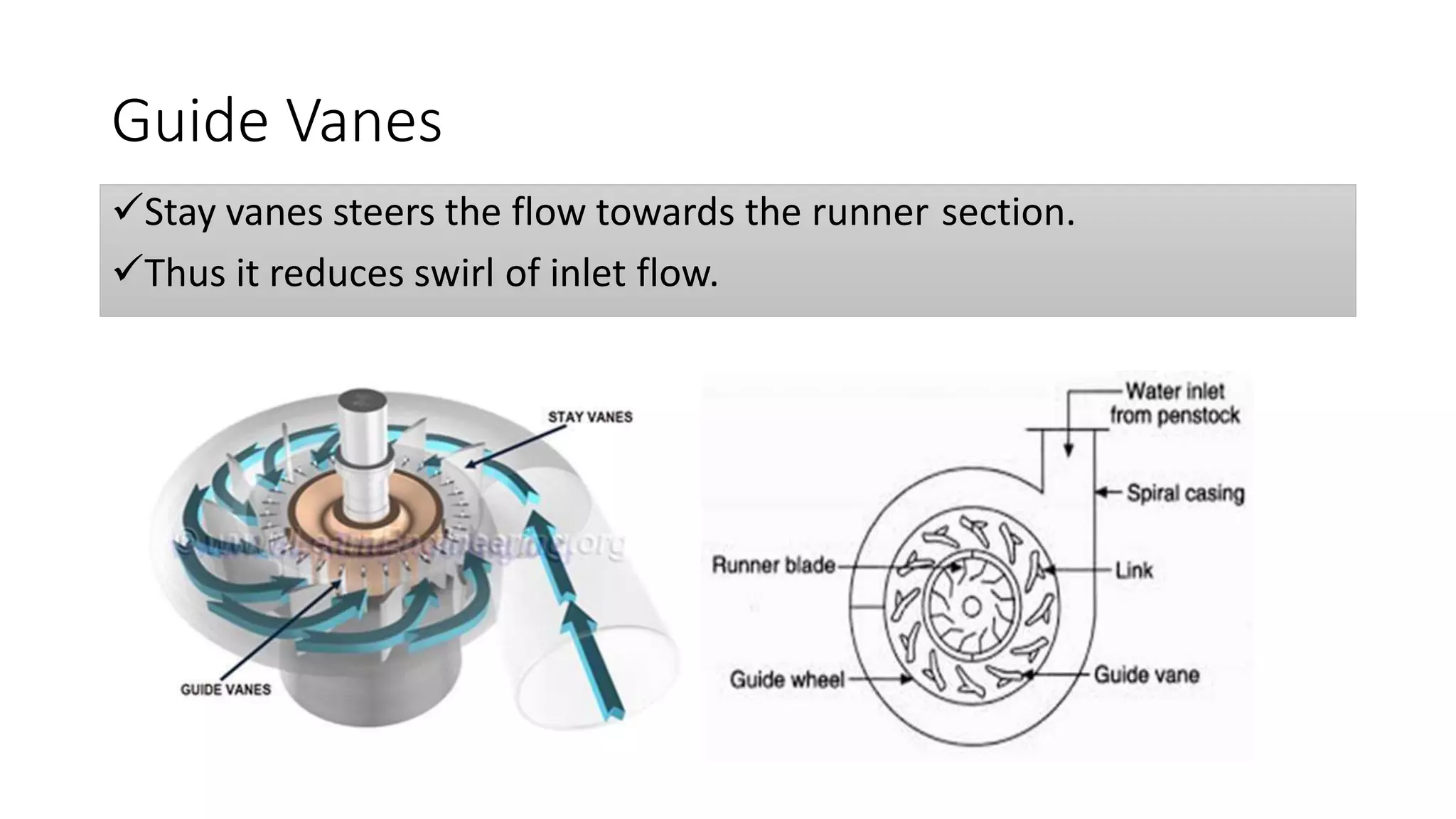
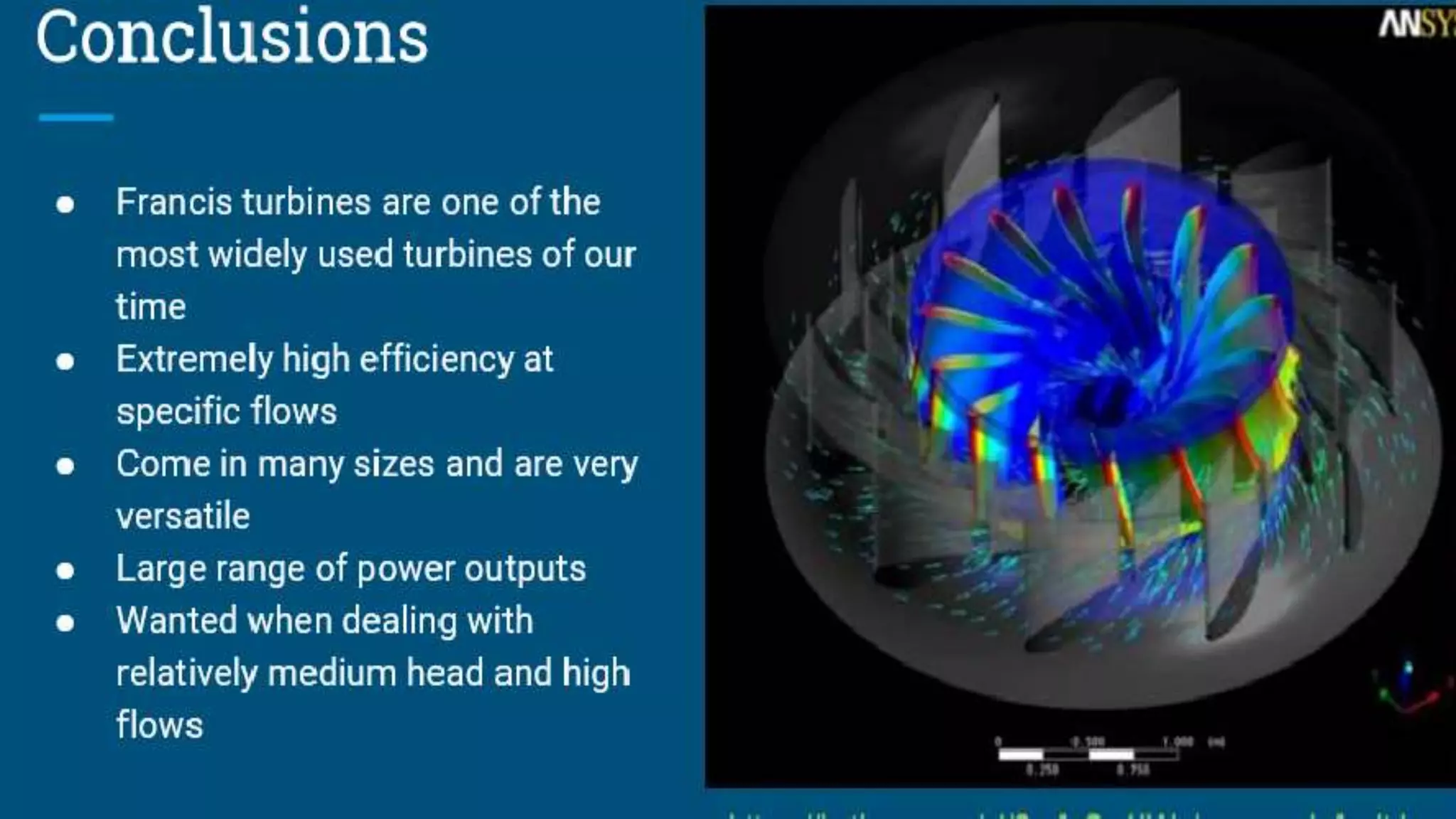
This document provides information about the Francis reaction turbine. It describes the key components of the turbine, including the penstock, spiral casing, runner blades, guide vanes, and draft tube. It explains how the turbine works by converting the kinetic and pressure energy of water flowing through it into rotational energy to power a generator. The turbine is widely used today for power generation due to its high efficiency of around 88%. The document also discusses cavitation issues and recent design advancements aimed at reducing costs and complexity.