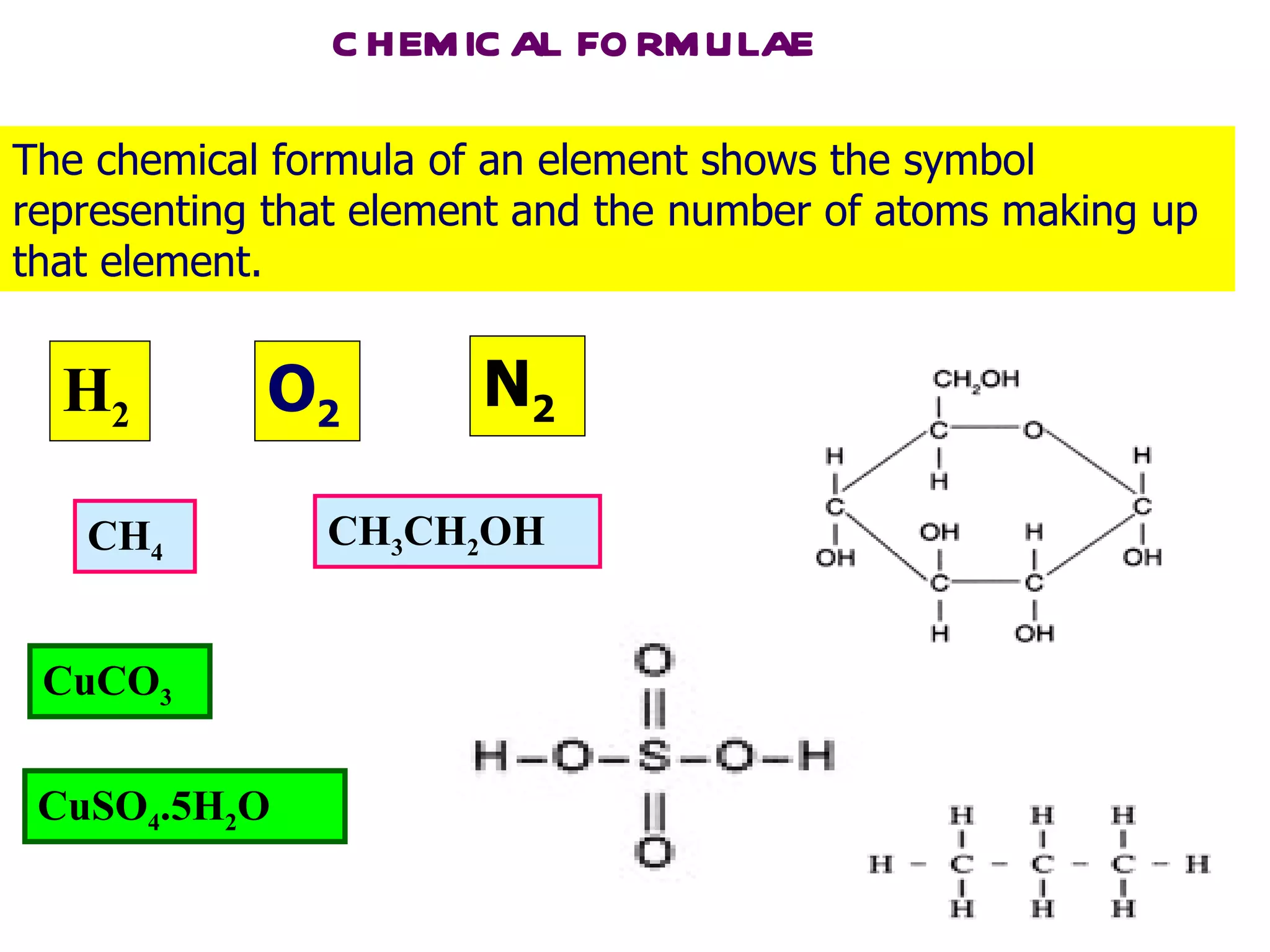
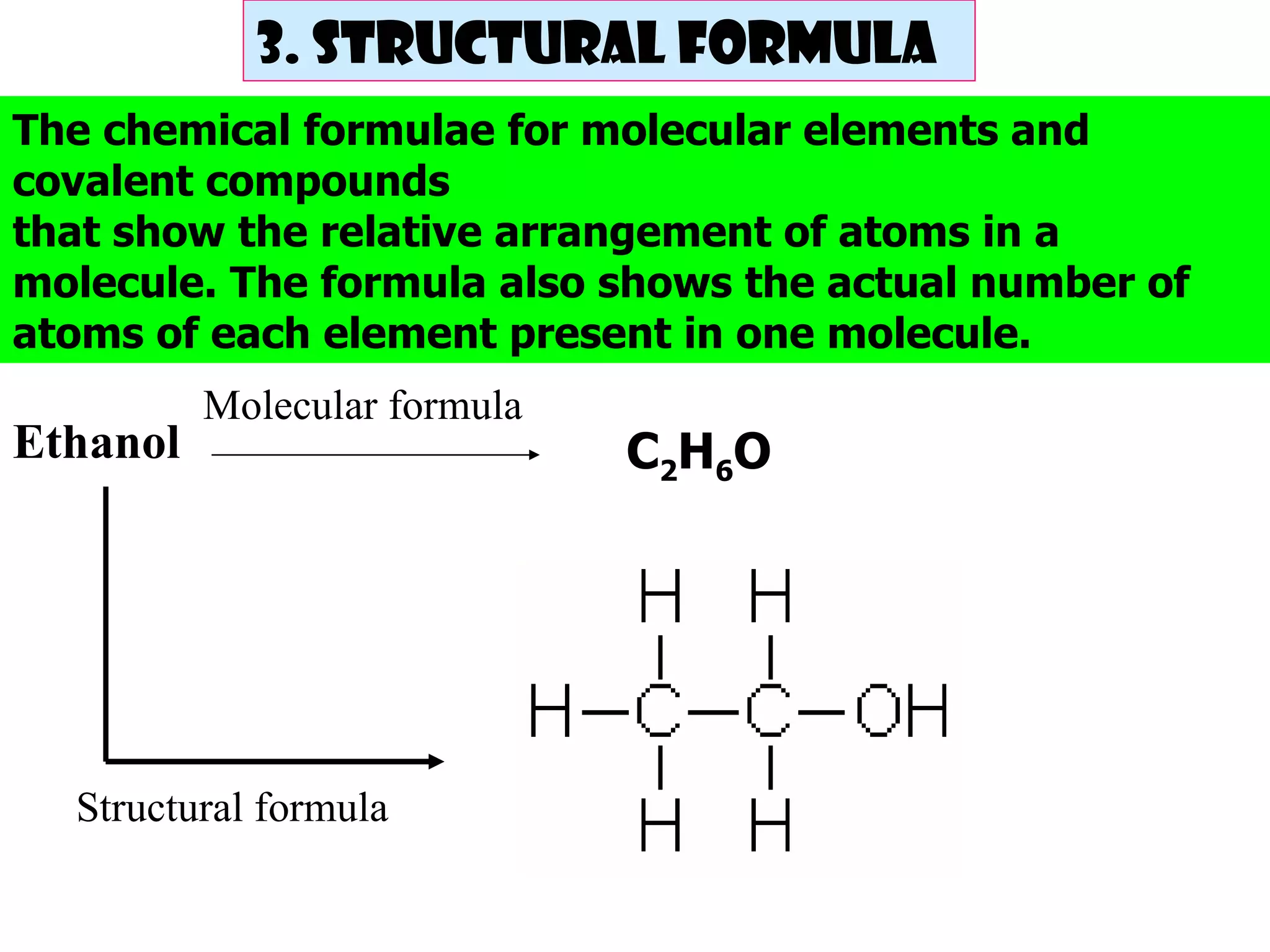
The document discusses chemical formulae including molecular, empirical and structural formulae. It provides examples of formulae for different types of compounds such as ionic compounds, molecular compounds and covalent compounds. It also gives examples of how to calculate empirical formulae from experimental data including mass of elements and relative atomic masses.










![Empirical Formula : Fe 2 O 3 A sample of ferum oxide consists of 1.12 g ferum and 0.48g oxygen.Find the empirical formula of this compound. [Relative atomic mass : Fe, 56 ; O,16 ] 3 2 Ratio of atom 0.03 = 1.5 0.02 0.02 = 1 0.02 Divide by the smallest number 0.48 = 0.03 16 1.12 = 0.02 56 Number of moles 0.48 1.12 Mass, g O Fe Elements](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/formulakimia-120130193752-phpapp02/75/Chemical-Formulae-13-2048.jpg)


![Example 3 The empirical formula of a compound is given as CH 2 . If the RMM of the compound is 56, what is the molecular formula? [ RAM C,12 ; H , 1 ]. ( Empirical formula ) n = RMM ( CH 2 ) n = 56 ( 1x 12 + 2 x 1 ) n = 56 14 n = 56 n = 4 Molecular formula (CH 2 ) 4 = C 4 H 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/formulakimia-120130193752-phpapp02/75/Chemical-Formulae-16-2048.jpg)
![Example 2 A compound CxHyOz contains 40% carbon and 53.3% oxygen. If the relative molecular mass of the compound is 180, finds it molecular formula [ RAM : H , 1 : C , 12 ; O , 16 ] Empirical Formula : CH 2 O 3.33 = 1 3.33 6.7 = 2 3.33 3.33 = 1 3.33 Simplest ratio 53.3 = 3.33 16 6.7 = 6.7 1 40 =3.33 12 Number of moles 53.3 40-53.3 = 6.7 40 Mass in 100g O H C Element](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/formulakimia-120130193752-phpapp02/75/Chemical-Formulae-17-2048.jpg)

