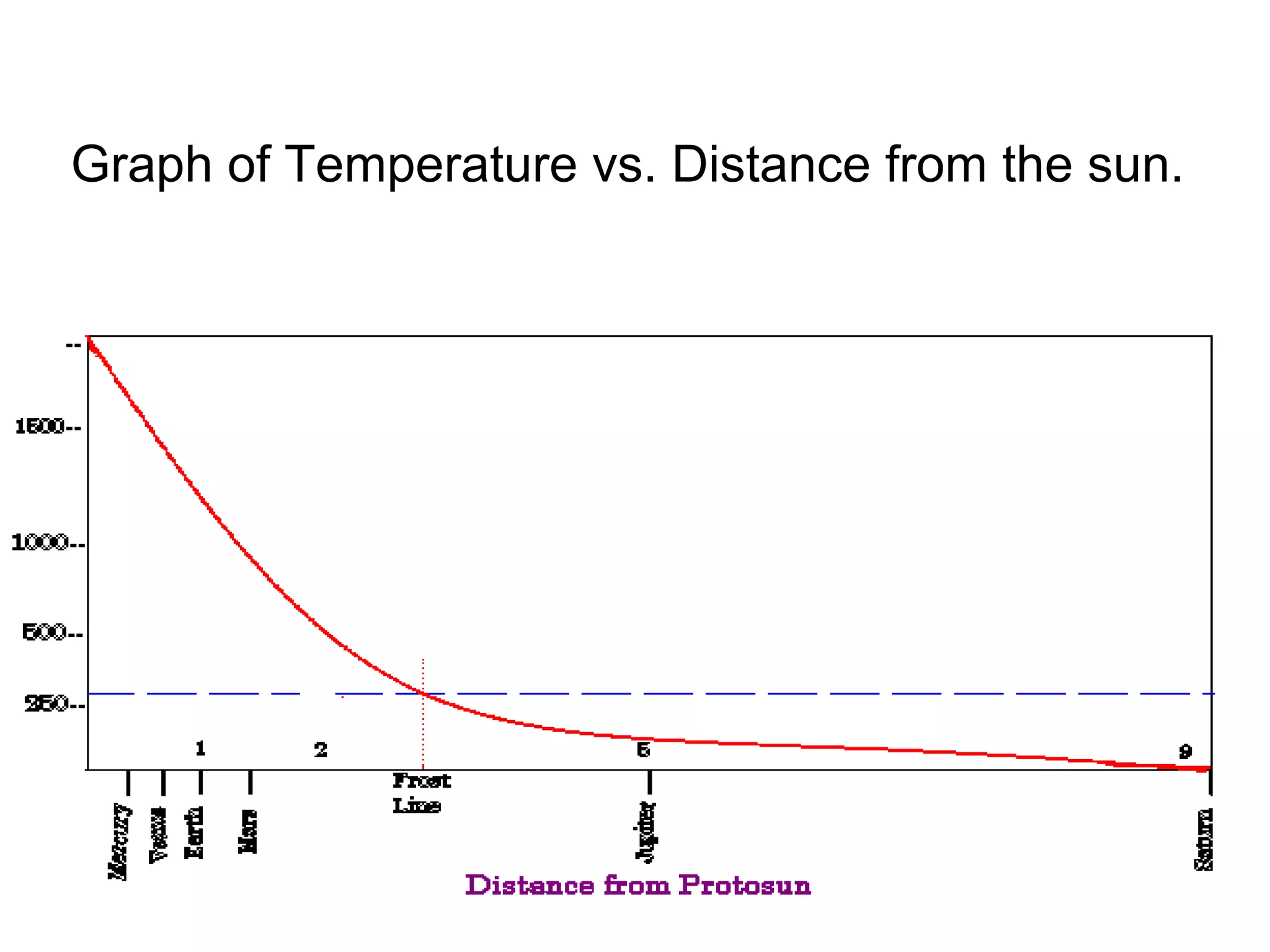
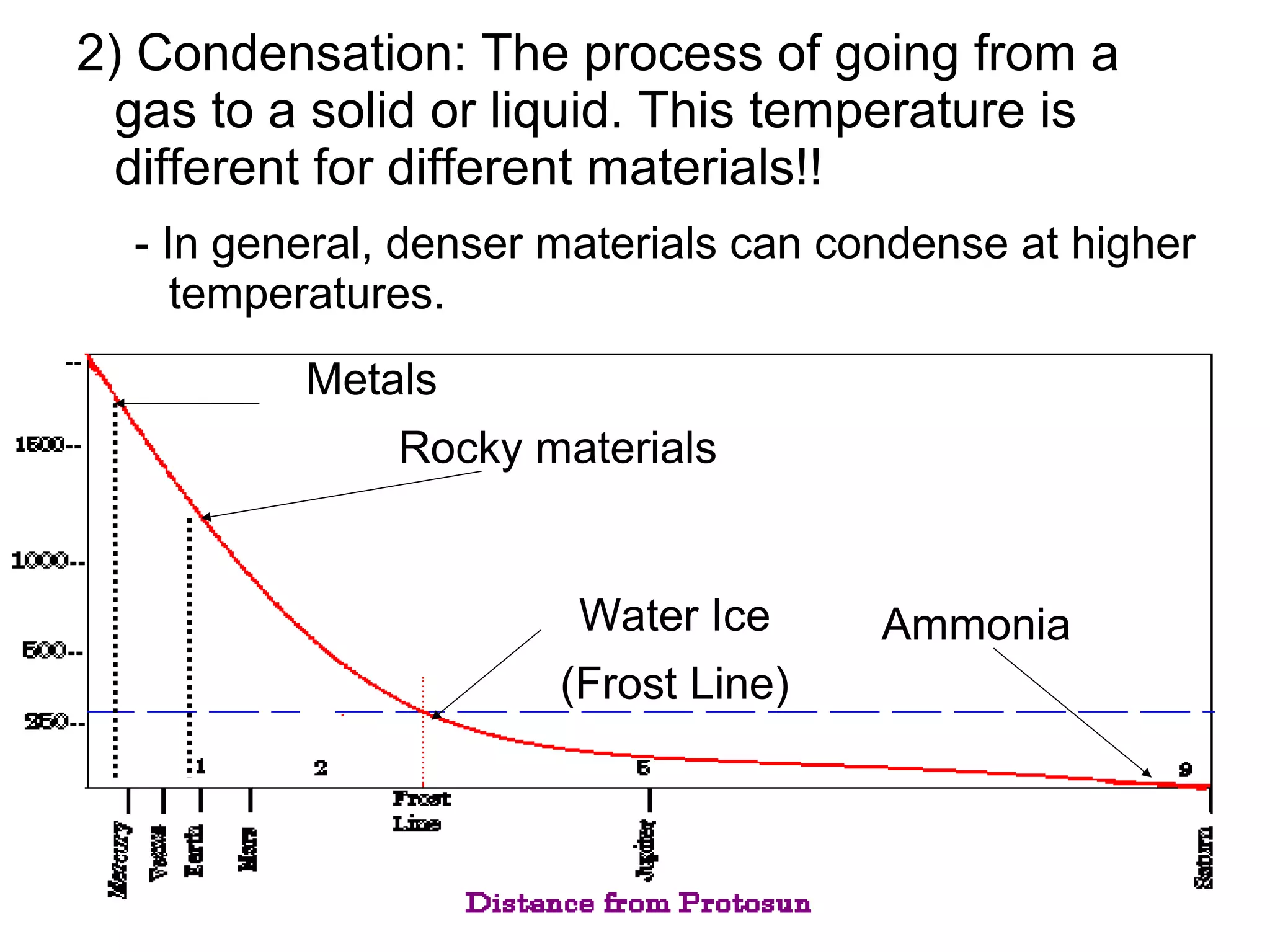
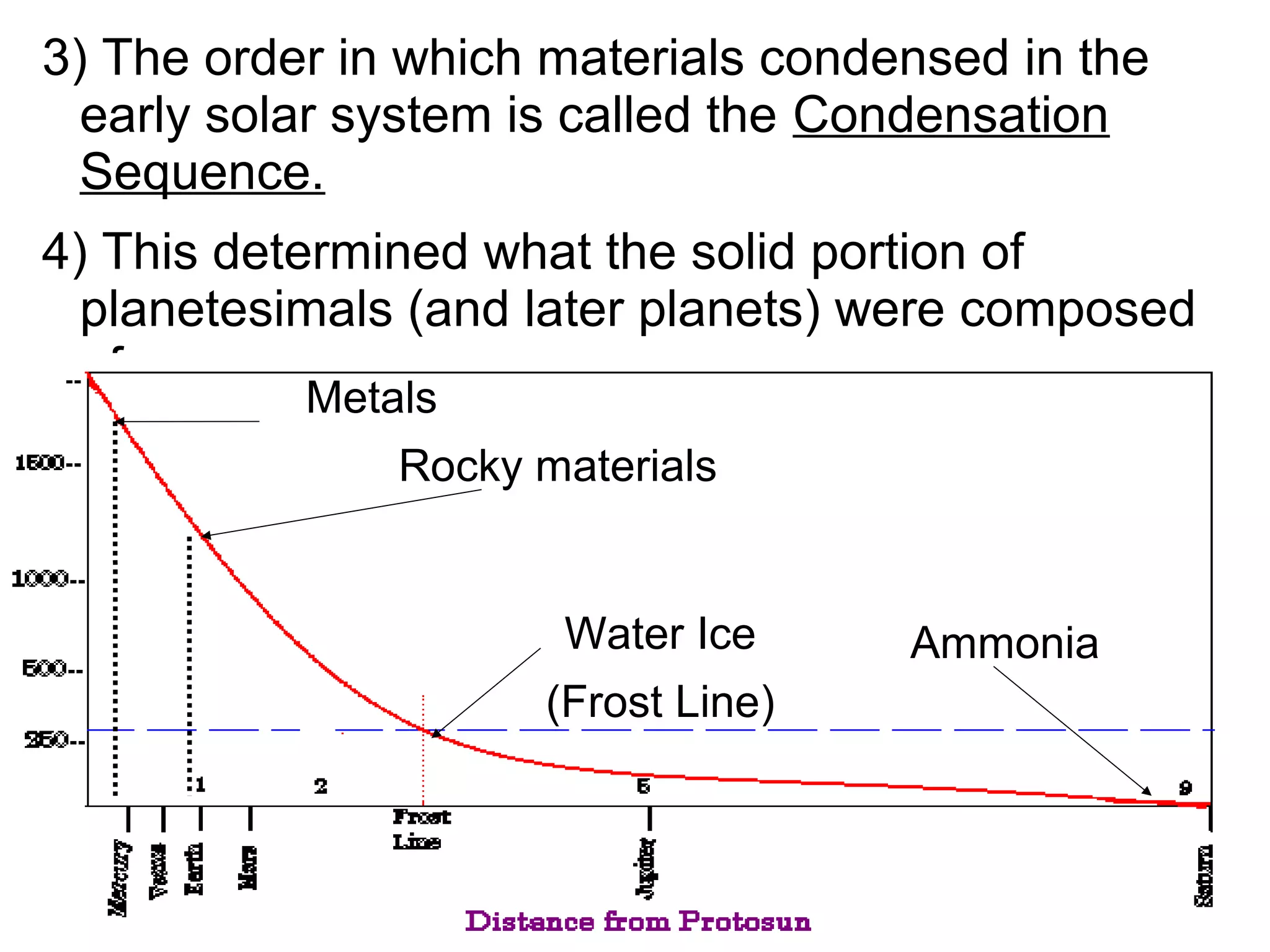
The formation of the solar system began from a large cloud of gas and dust called the solar nebula. As the nebula collapsed due to gravity, it formed a disc with the sun at the center. Planetesimals within the disc collided and accreted to form the planets. The nebular theory explained many characteristics of the solar system but did not account for all observations. The modern condensation theory expanded on this model and better explained features such as the asteroid belt and comets through processes like condensation and fractionation within the early solar system.