Embed presentation
Downloaded 314 times



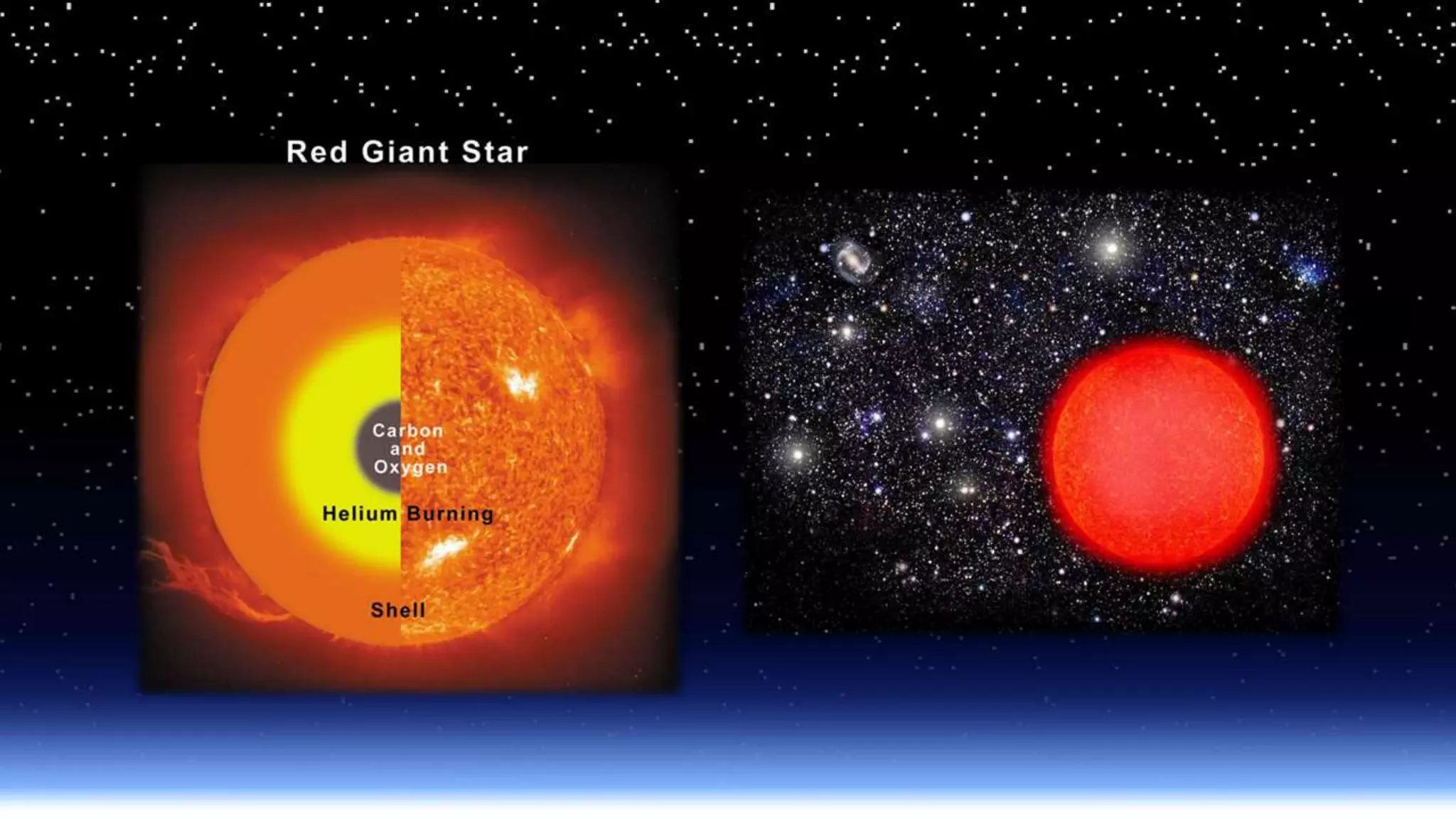







This document describes different stages and types of stars: - Main sequence stars like our Sun spend most of their lives fusing hydrogen into helium in their cores. - Red giants are large, reddish stars that have exhausted hydrogen fusion and begun fusing helium. - Planetary nebulae form when average-sized stars eject their outer layers after becoming red giants, leaving behind dense, hot cores called white dwarfs. - Brown dwarfs are failed stars too small to sustain nuclear fusion. - Variable stars change in brightness over timescales from seconds to years as they evolve. - Binary stars are two gravitationally bound stars that orbit a common center of mass.









