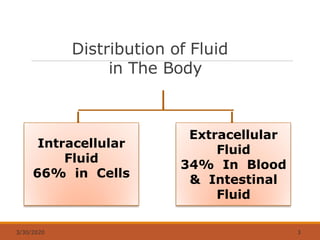
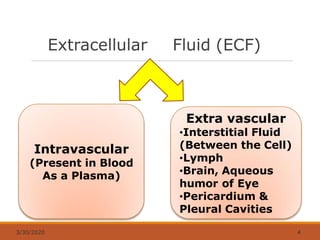
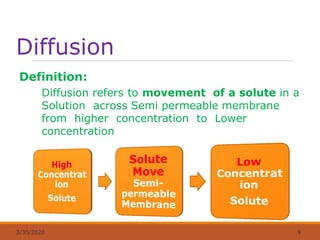
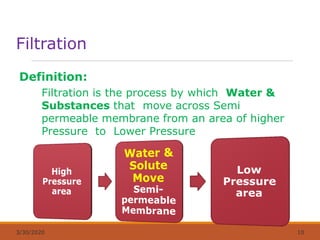
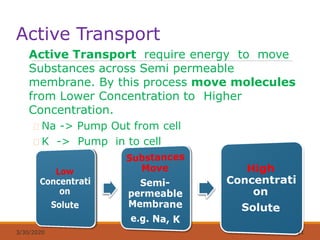
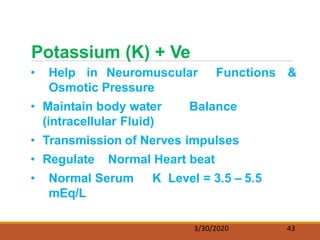
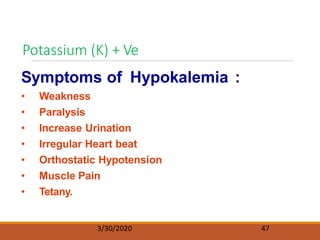
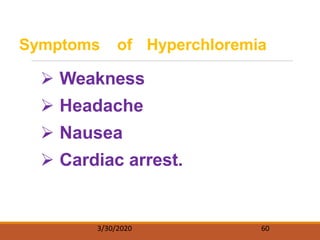
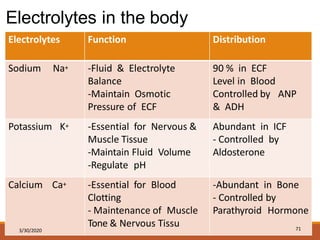
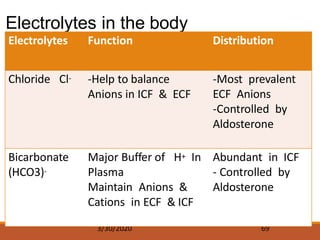
The document discusses fluids and electrolytes in the human body. It covers topics like water distribution and regulation, movement of fluids between compartments, and key electrolytes like sodium, potassium, calcium. Regarding electrolytes, it describes their normal levels and functions and causes and symptoms of abnormalities like hypernatremia, hyponatremia, hyperkalemia, hypokalemia, hypercalcemia and hypocalcemia. The kidneys, hormones like ADH and aldosterone, and osmosis play important roles in fluid and electrolyte balance. Dehydration and overhydration are also covered.