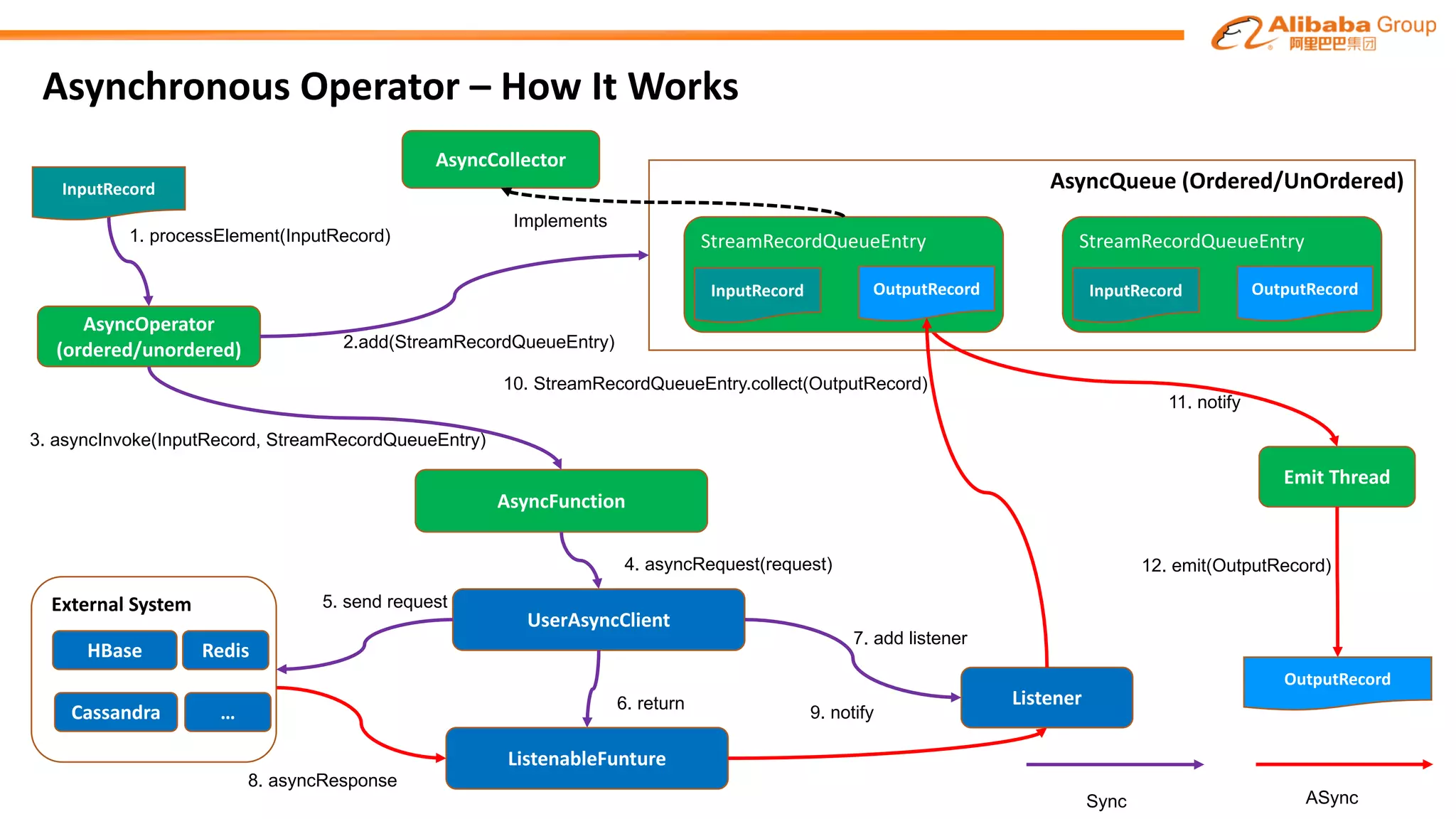
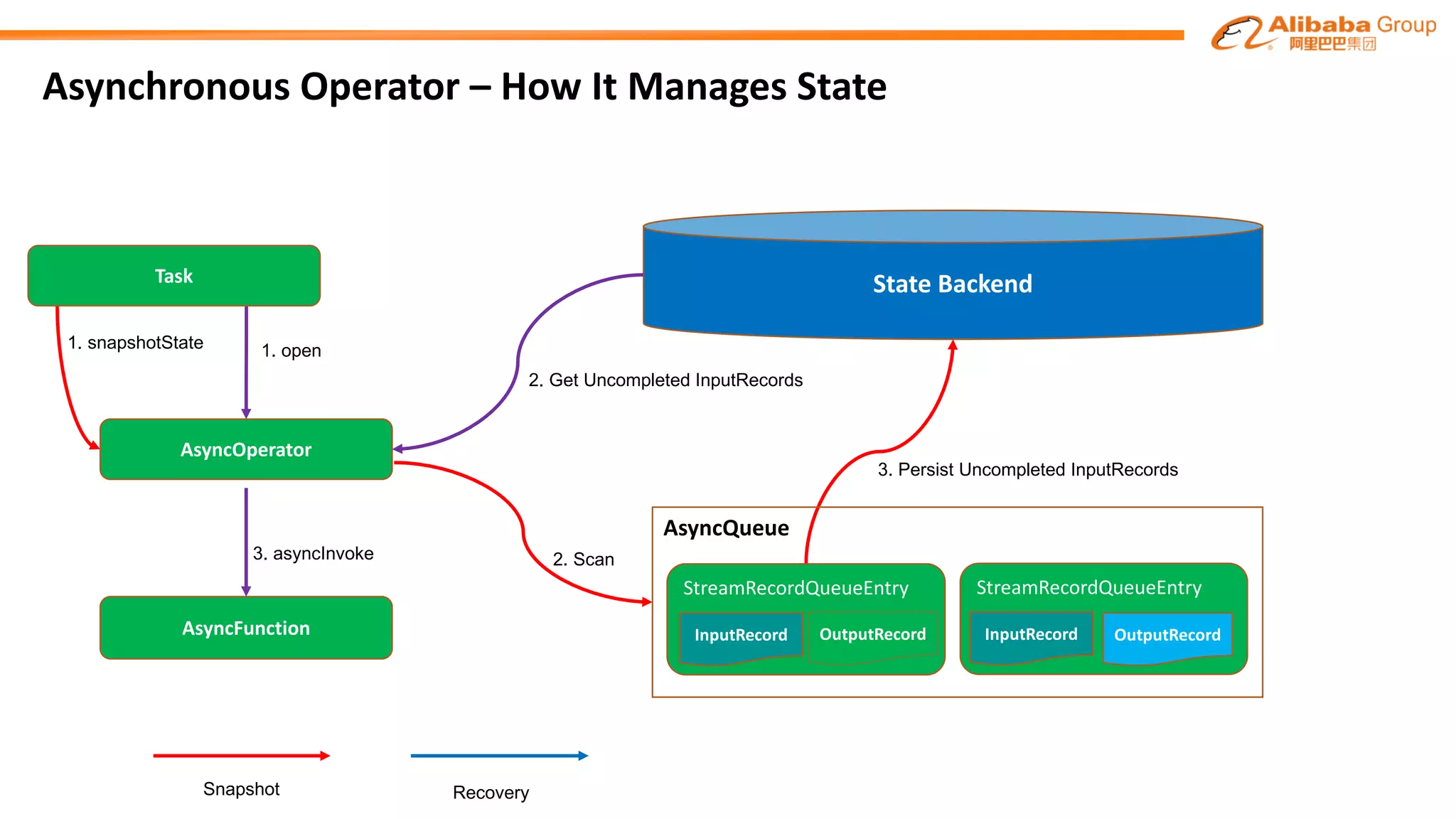
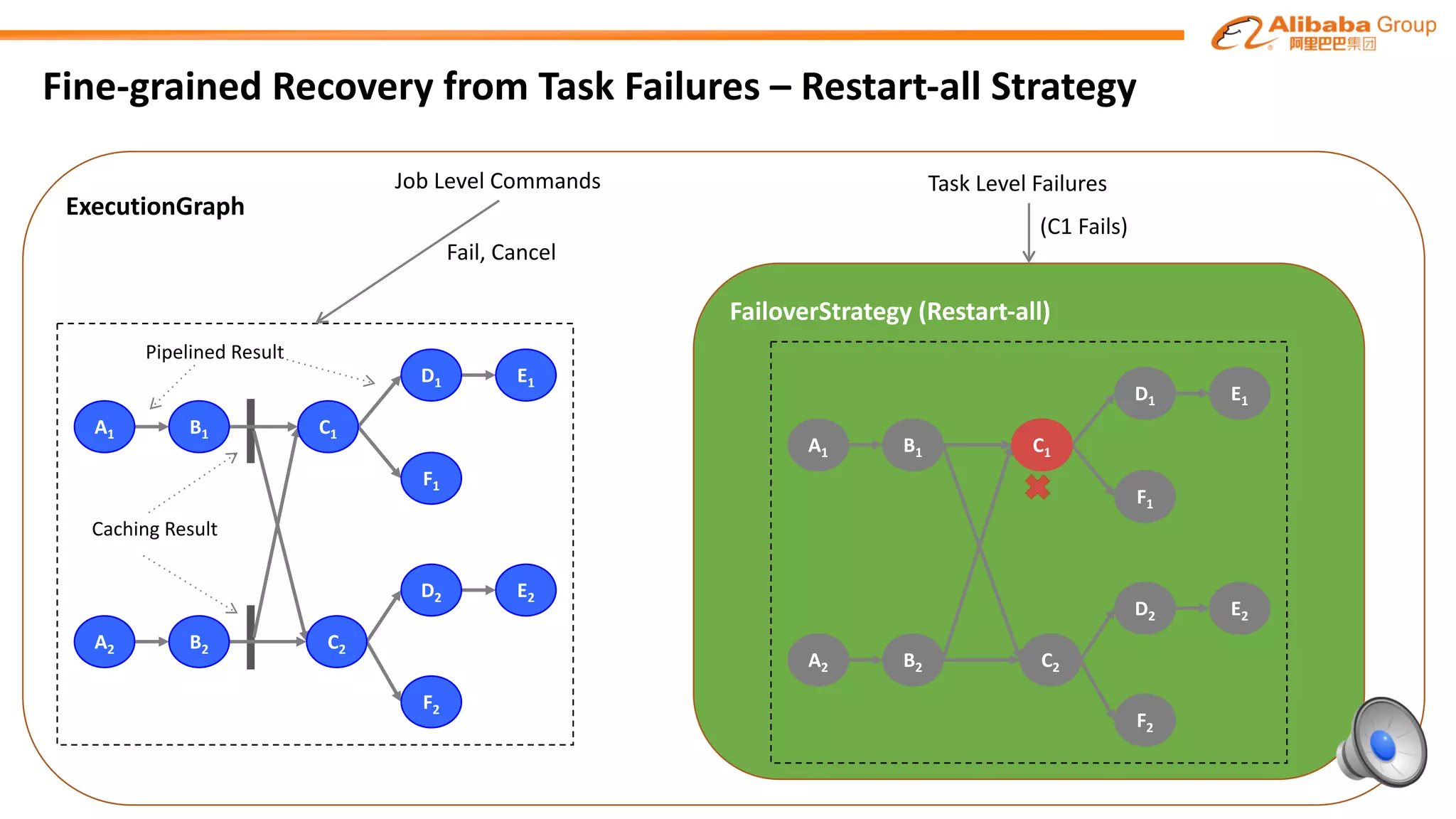
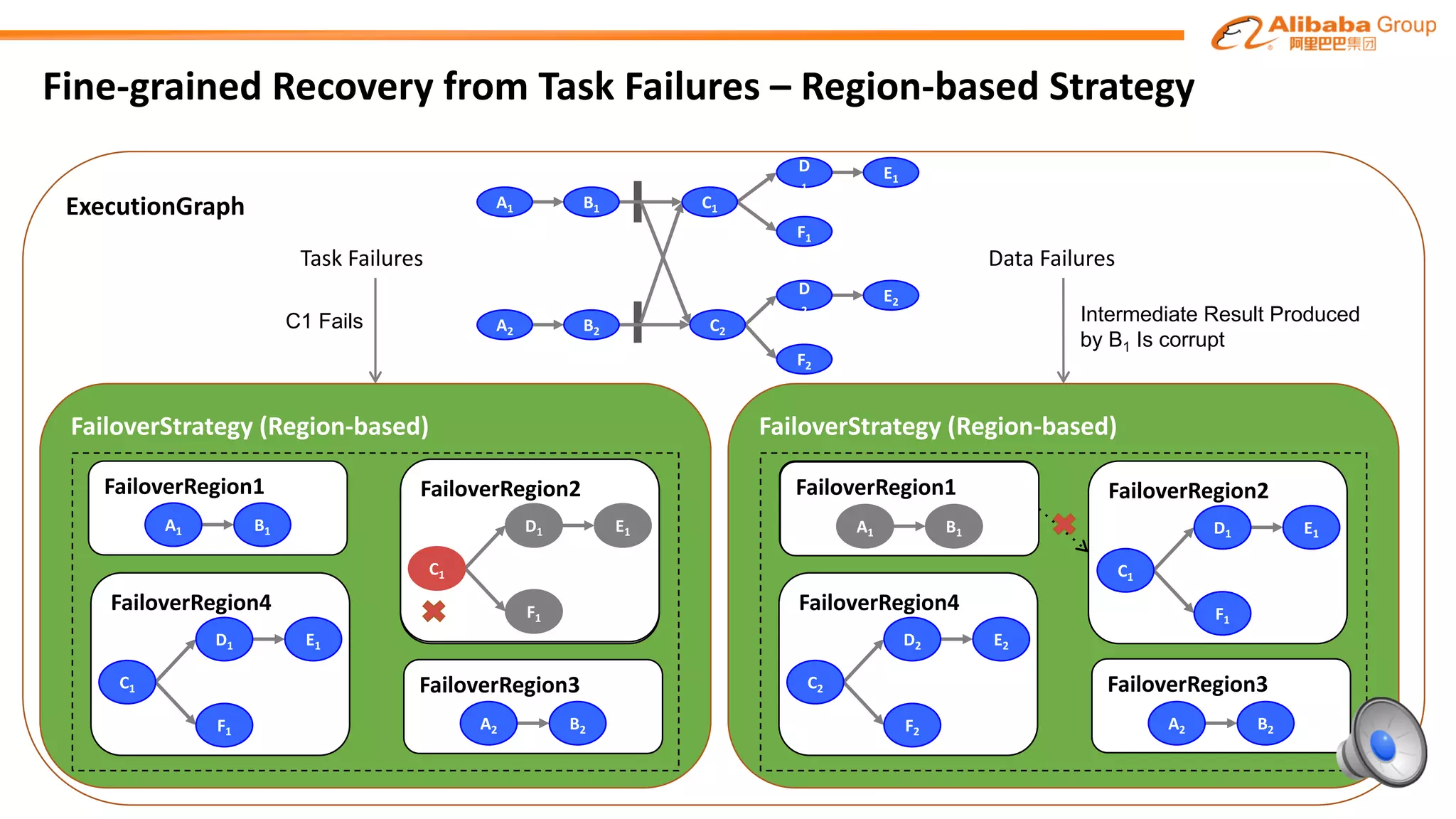
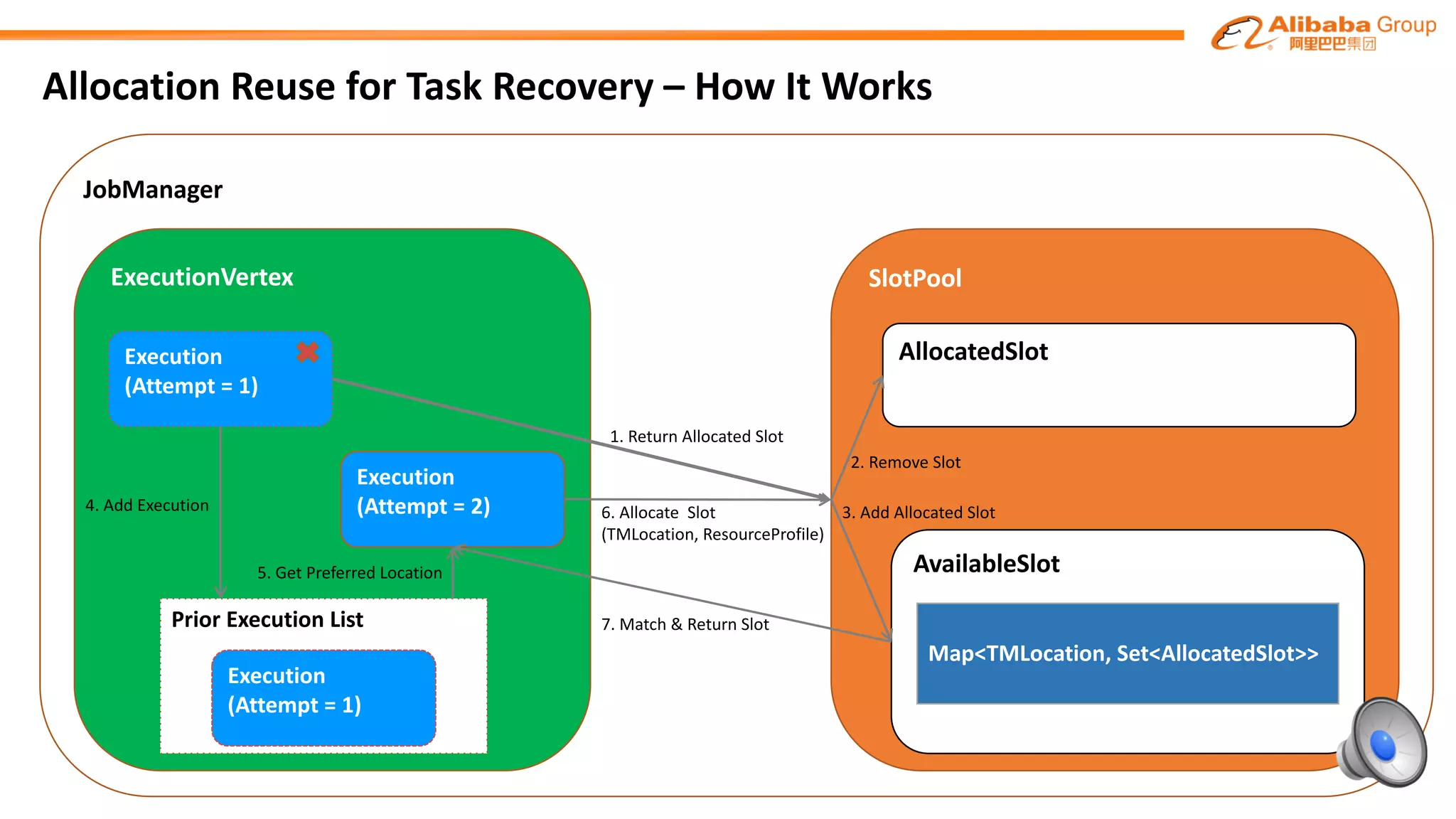
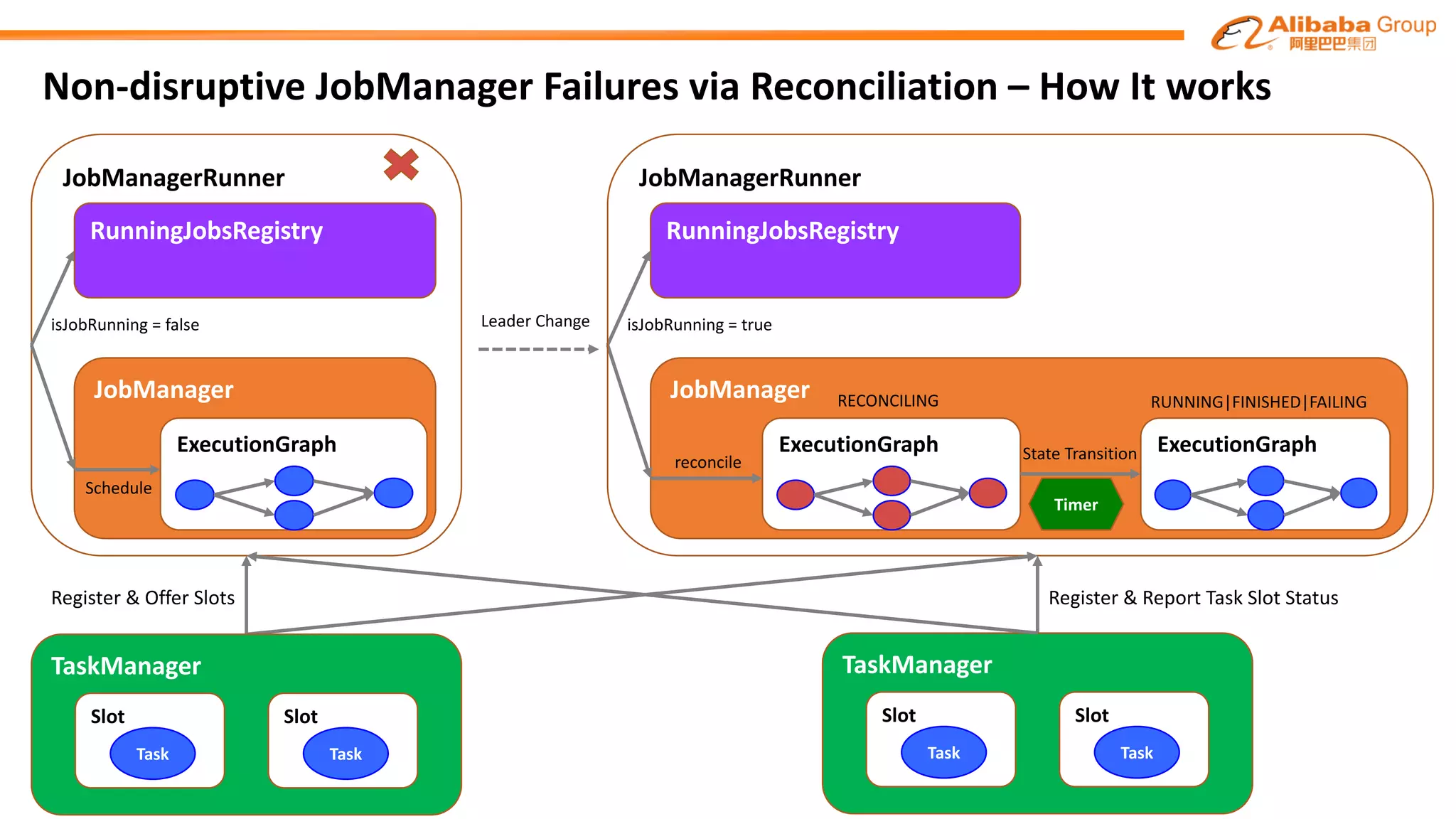
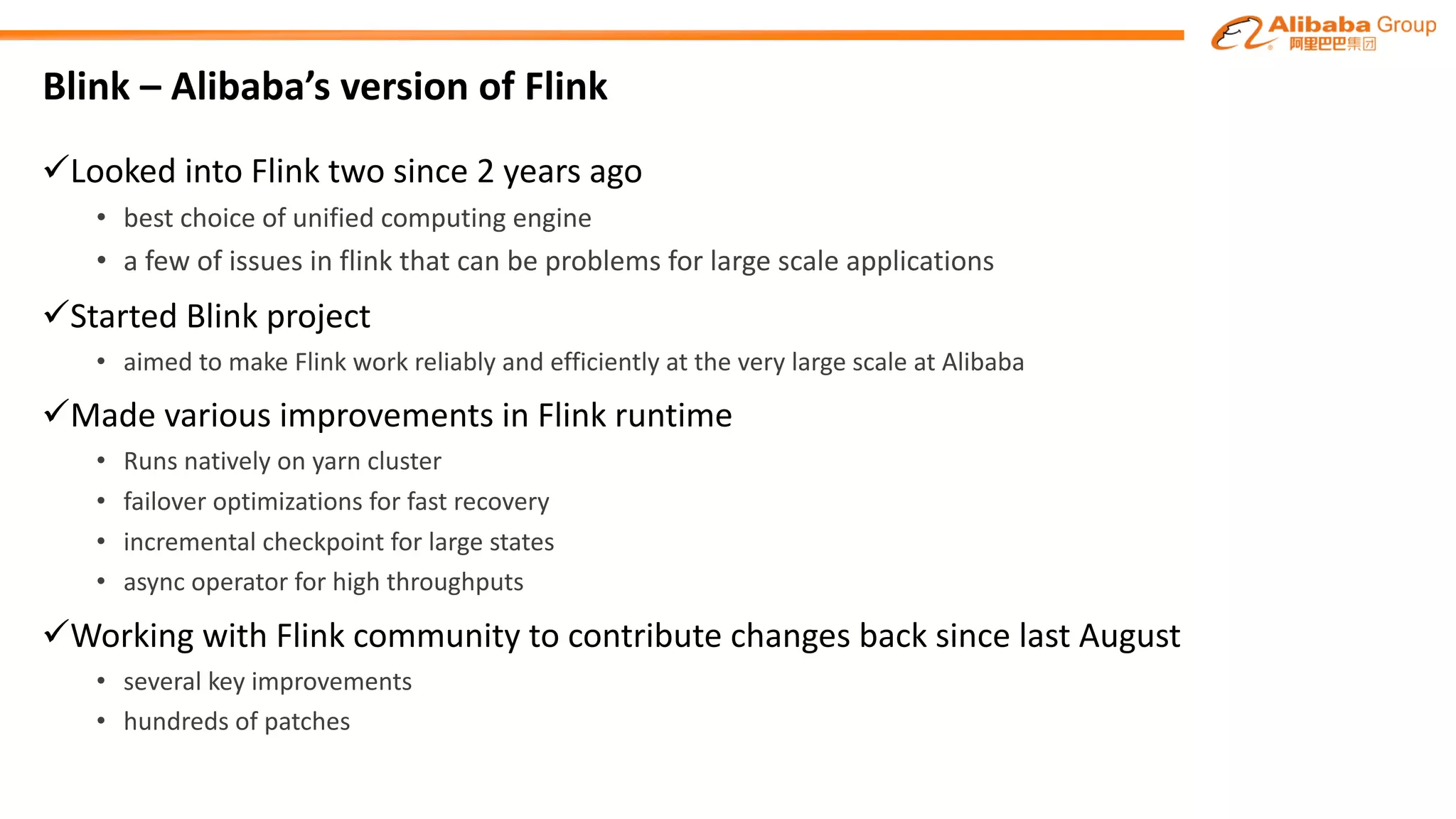
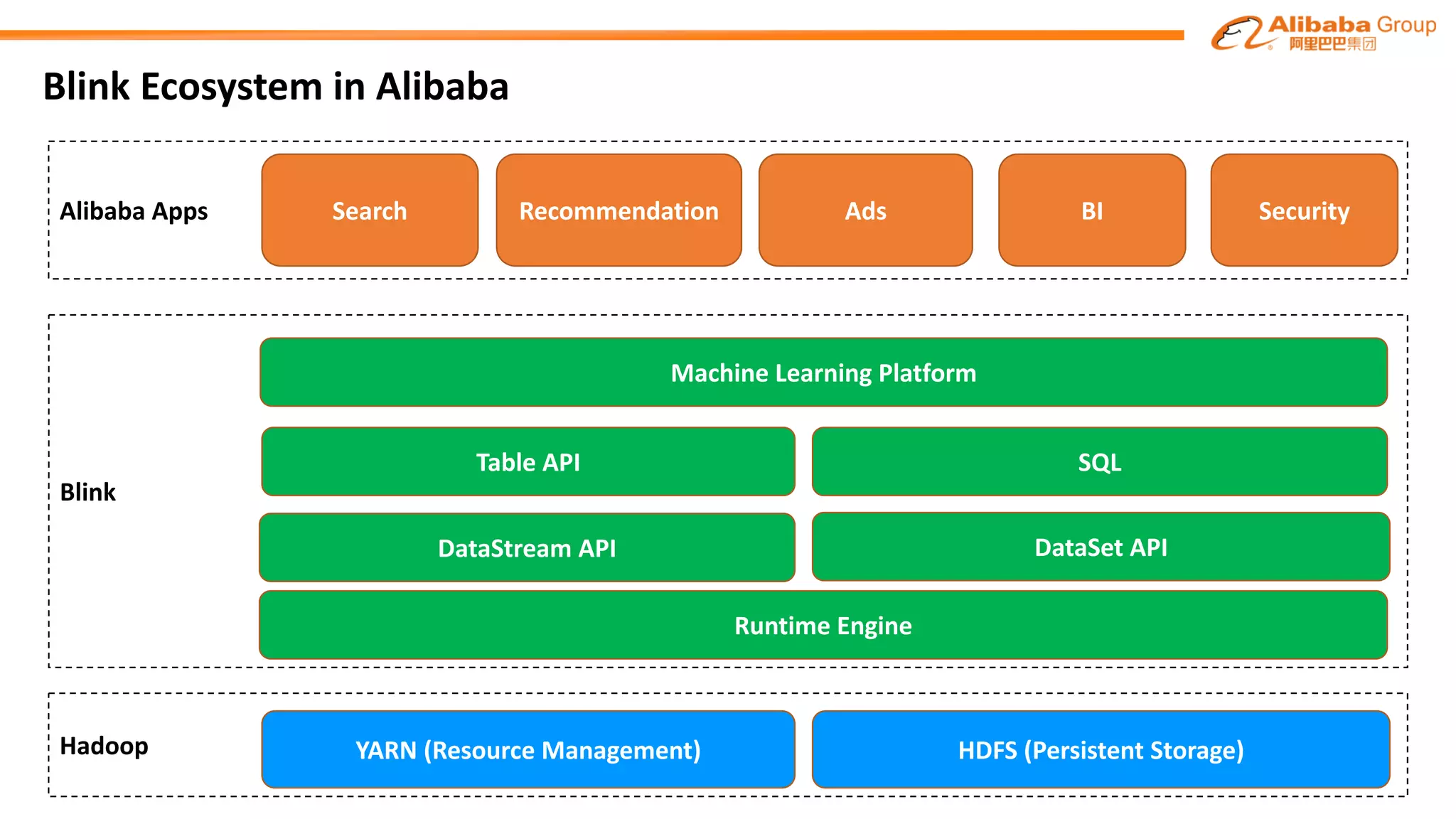
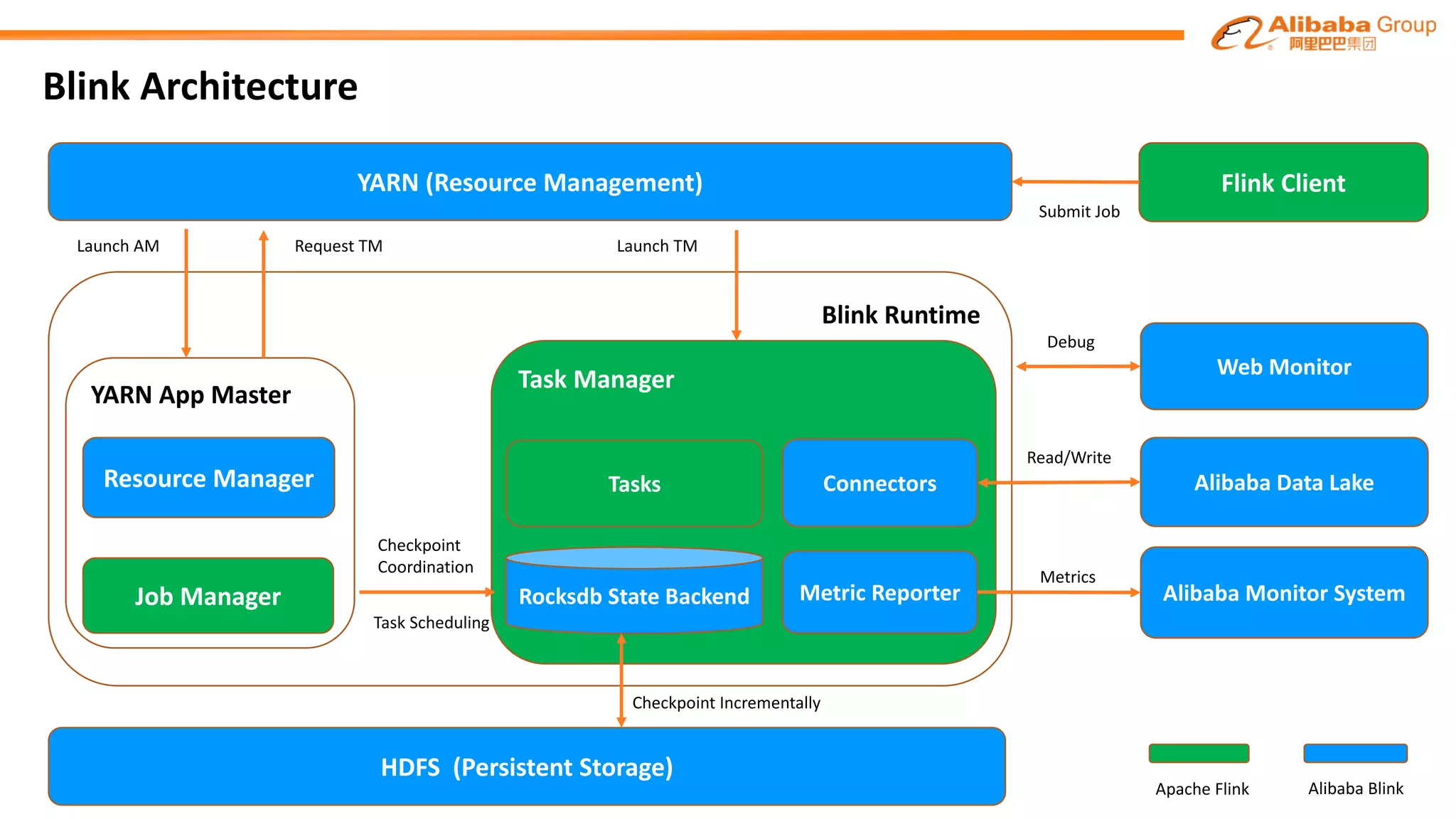
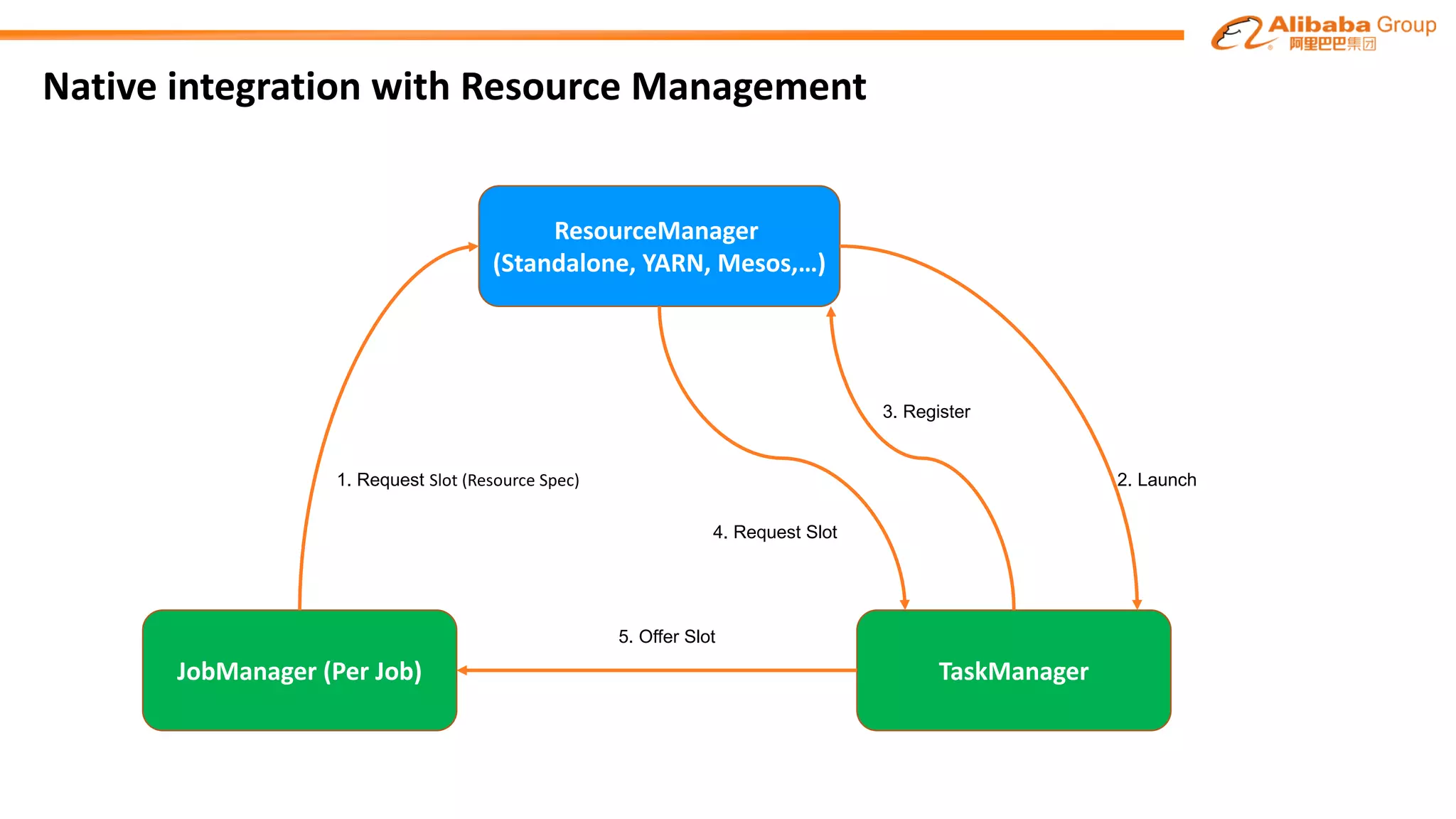
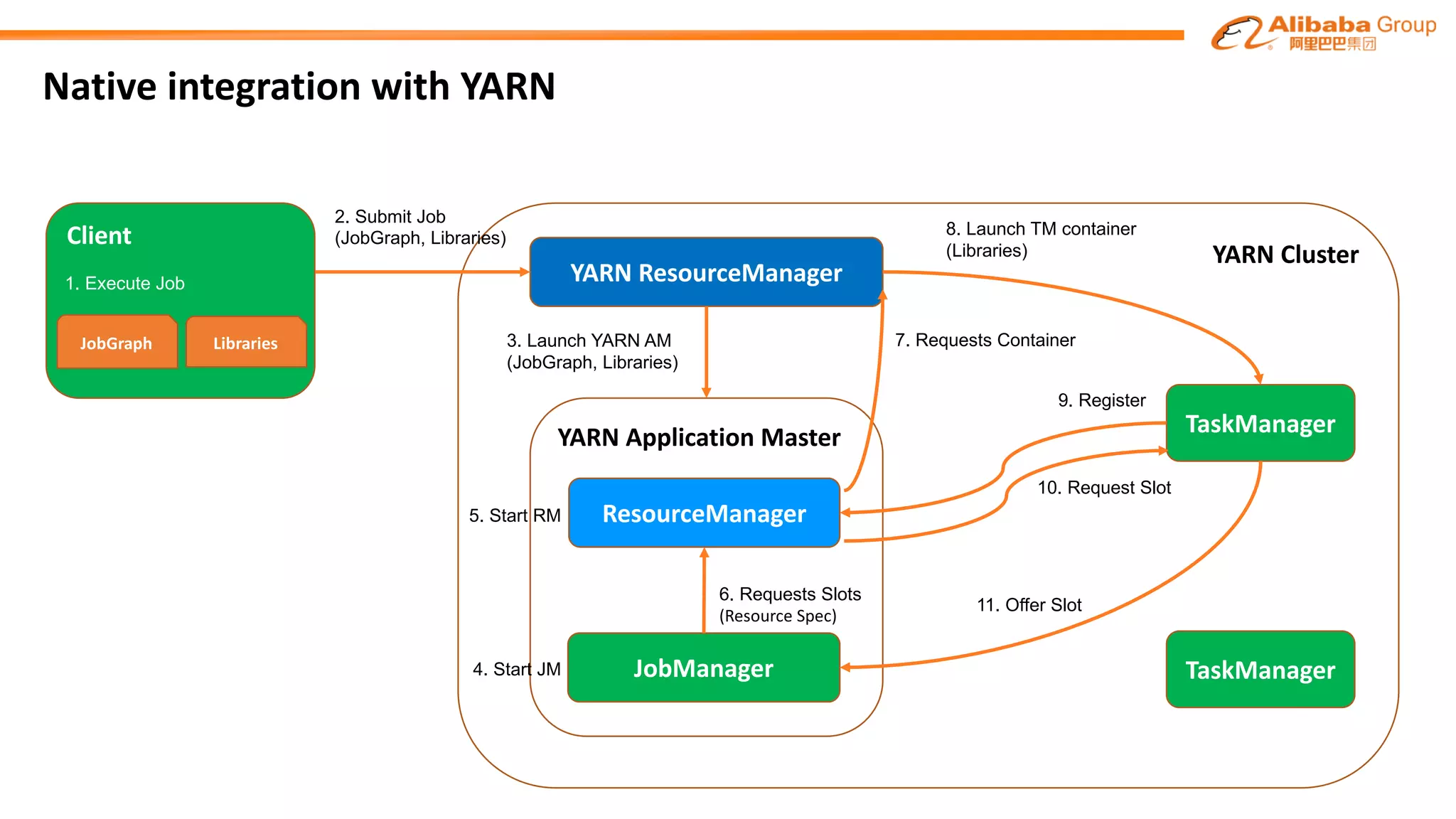
The document outlines improvements made to Alibaba's Blink, a version of the Flink streaming framework, aimed at enhancing its reliability and efficiency for large-scale applications. Key enhancements include incremental checkpointing, failover optimizations, and asynchronous operators, which collectively contribute to better performance in resource management and task recovery. Blink has been successfully deployed in production, notably during major events like China's Single's Day, significantly increasing performance and operational efficiency.








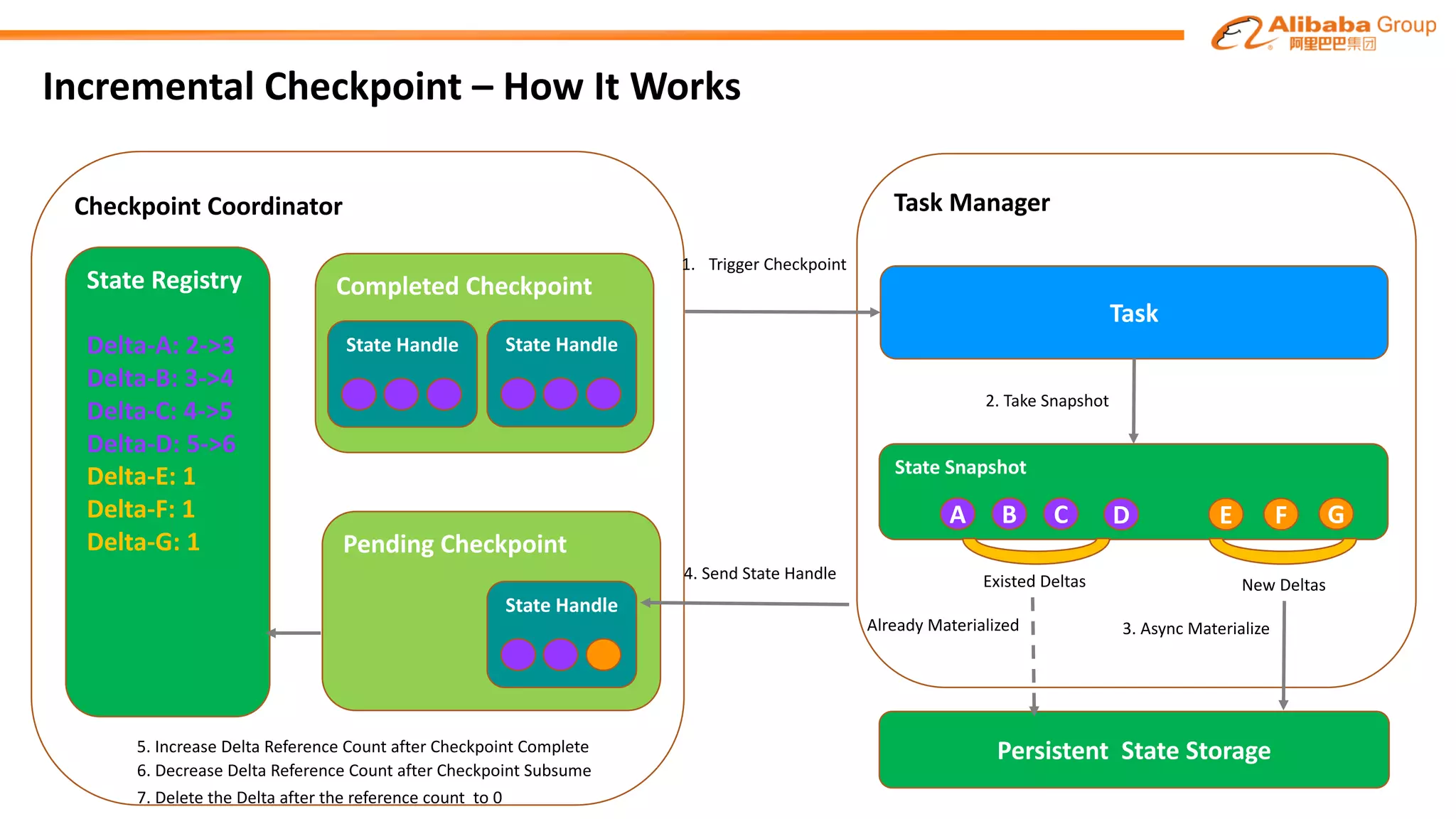
![Incremental Checkpoint - RocksDB State Backend Implementation
RocksDB Instance in TM for KeyGroups[0-m]
.sst .sst .sst
data
1.sst 2.sst 3.sst
chk-1
2.sst 3.sst 4.sst
chk-2
HDFS://user/JobID/OperatorID/KeyGroup_[0-m]
data
3.sst.chk-1 4.sst.chk-21.sst.chk-1 2.sst.chk-1
JobManager
Completed Checkpoint 1
State Handles
Completed Checkpoint 2
State Handles](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flinkforwardsf2017fengwangzhijiangwangruntimeimprovementsinblinkforlargescalestreamingatalibaba-170414104635/75/Flink-Forward-SF-2017-Feng-Wang-Zhijiang-Wang-Runtime-Improvements-in-Blink-for-Large-Scale-Streaming-at-Alibaba-15-2048.jpg)