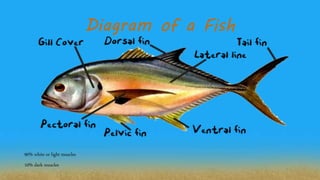
This document categorizes fish and shellfish, describes their characteristics and market forms, and outlines processing methods. It identifies finfish and shellfish as the two major categories. Finfish are vertebrates like bangus and catfish, while shellfish are invertebrates like crabs and oysters. Fresh fish and shellfish are described by characteristics like bright eyes and intact scales. Common market forms include whole fish, fillets, and butterflied fish. Processing methods to preserve seafood include freezing, smoking, drying, curing, and canning.