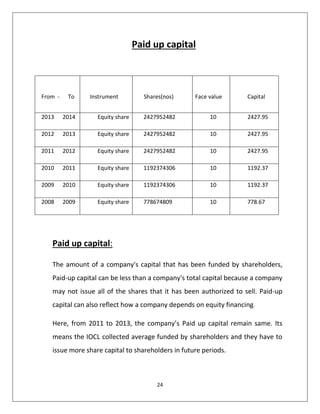
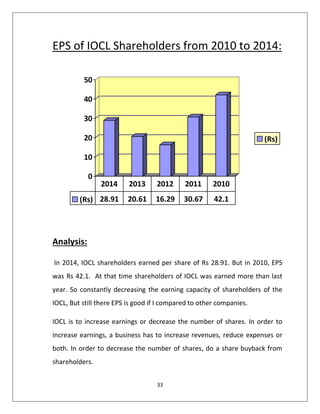
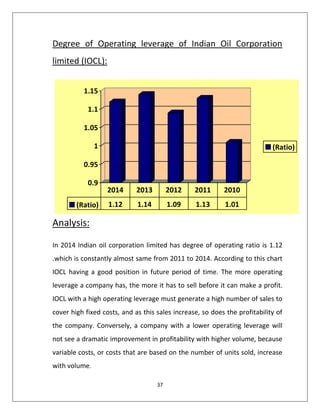
Based on the data provided, here is the analysis of IOCL's paid up capital from 2010-2014:
- The paid up capital remained constant at Rs. 2427.95 crore from 2013-2014, 2012-2013 and 2011-2012. This indicates that during these years, IOCL did not issue any additional shares to increase its paid up capital.
- In 2010-2011, the paid up capital was Rs. 1192 crore. This increased significantly to Rs. 2427.95 crore in the next year. This suggests that IOCL must have issued additional shares and increased its paid up share capital in 2011.
- Overall, the paid up capital increased over the years from Rs. 1192