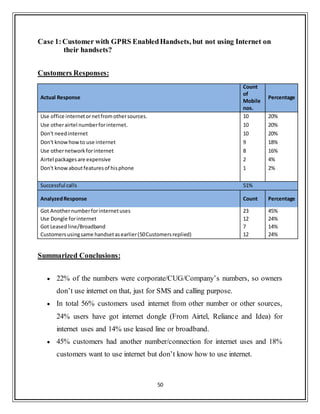
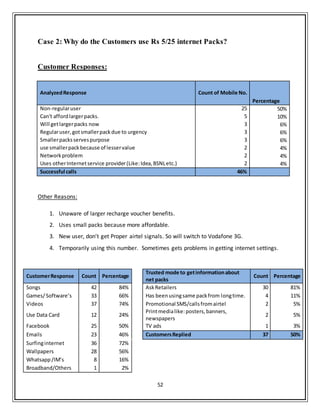
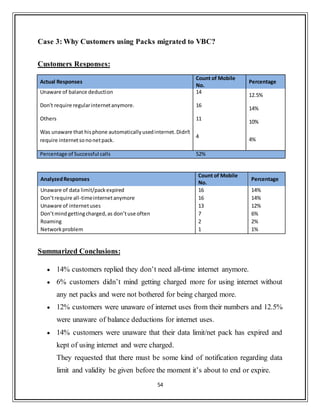
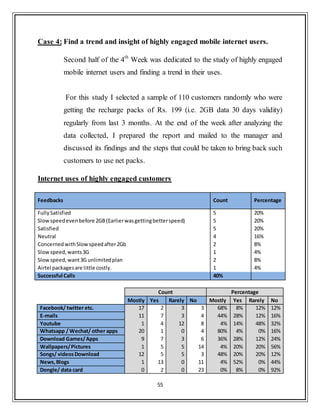
This document provides a summary of an internship report submitted by Anupam Kumar for his Master of Business Administration degree. The 6-week internship was completed at Bharti Airtel Ltd. in Noida, India from May 27th to July 6th, 2013. The report includes insights gathered on data marketing and Airtel Money in Uttar Pradesh - West Circle. It covers company profile, industry analysis, financial analysis and details of research projects conducted during the internship related to customer insights.
![Jaypee Business School
A constituent of Jaypee Institute of Information Technology
(Declared Deemed to be University u/s 3 of UGC Act)
A-10, Sector 62, Noida (UP) India 201 307
www.jbs.ac.in
Insights for
Data Marketing & Airtel Money
(Uttar Pradesh - West Circle)
Corporate Internship Report
Internship Report submitted as a partial requirement for the award of the two year
Master of Business Administration
MBA 2012-14
Name: Anupam Kumar
[Enrollment No. : 9502903]
(Bharti Airtel Ltd, Noida)
CorporateInternship Supervisor Name: Somil Agrawal
JBS-Faculty Supervisor: Dr. Sujata Kapoor
Start Date for Internship: 27th
May 2013
End Date for Internship: 6th
July 2013
ReportDate: 8th
July 2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/80fa71fd-fddb-48b3-924d-bc72e9e97242-161223101529/75/Final_internship_report-Airtel-1-2048.jpg)







![7
the brand as well as their underlying mindsets, moods, motivation, desires,
aspirations, and motivates that trigger their attitude and actions. [2]
Figure 2: Customer Insight, Source: http://www.a-fresh-perspective.com
Customer insights answers to many questions including the important one i.e.:
What is most important to them?
How do they make decisions?
How do they evaluate brands, products and services?
What are their needs, wants and interests?
What are the best ways to communicate with them?
What are key differences among customer segments?
Objective
The main objective of the internship was to interact with as many as possible
customers and retailers and get their insights on mobile internet, internet access
through dongles or devices and airtel money.
The interaction was mainly through tele-calling, visiting to retailers and shops in
person in different areas and taking in-depth interviews through a detailed
questionnaire and recording their answers and feedbacks (secondary research was
also done wherever a data was required). After collection, the data was analyzed
and findings/conclusions are noted and discussed with the supervisor and the
managers along with the recommendations.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/80fa71fd-fddb-48b3-924d-bc72e9e97242-161223101529/85/Final_internship_report-Airtel-11-320.jpg)

![9
1.1 About Airtel
Bharti Airtel Limited is a leading global telecommunications company with
operations in 20 countries across Asia and Africa. Headquartered in New Delhi,
India, the company ranks amongst the top 4 mobile service providers globally in
terms of subscribers. In India, the company's product offerings include 2G, 3G and
4G wireless services, mobile commerce, fixed line services, high speed DSL
broadband, IPTV, DTH, enterprise services including national & international long
distance services to carriers. In the rest of the geographies, it offers 2G, 3G
wireless services and mobile commerce. Bharti Airtel had over 269 million
customers across its operations at the end of March 2013. [1]
The company was founded by its chairman and Marketing director Sunil Bharti
Mittal. Bharti Enterprises is the major shareholder in the company with 52.7%
shares and other important shareholders of this public company are Singtel with
15.57% and Vodafone with 4.4% shares. [2]
1.2 Airtel’s Vision & Promise
“By 2015 airtel will be the most loved brand, enriching the lives of millions”. [1]
“Enriching lives means putting the customer at the heart of everything we do. We
will meet their needs based on our deep understanding of their ambitions,
wherever they are. By having this focus we will enrich our own lives and those of
our other key stakeholders. Only then will we be thoughtof as exciting, innovation,
on their side and a truly world class company."](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/80fa71fd-fddb-48b3-924d-bc72e9e97242-161223101529/85/Final_internship_report-Airtel-13-320.jpg)

![11
bundling across multiple domains (2G, 3G, 4G/LTE & Wi-Fi). It will also offer
flexible multi service charging in geographical redundant mode, making Airtel the
first operator to implement geographical redundancy at such a large scale. [2]
1.4 Company Logo
Airtel‟s unique symbol is an interpretation of the „a‟ in airtel. The meaning of the
logo in company‟s own words is as follows [1]:
“The curved shape & the gentle highlights on the red color make it warm &
inviting, almost as if it were a living object. It represents a dynamic force of
unparalleled energy that brings us and our customers closer.
Our specially designed logo type is modern, vibrant & friendly. It signals our
resolve to be accessible, while the use of all lowercase is our recognition for the
need for humanity.
Red is part of our heritage. It is the color of energy & passion that expresses the
dynamism that has made airtel the success it is today, in India, and now on the
global stage.”
(Figure 3: Logo of Bharti Airtel Ltd.)
(Figure 4: Logo of the Bharti Enterprises)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/80fa71fd-fddb-48b3-924d-bc72e9e97242-161223101529/85/Final_internship_report-Airtel-15-320.jpg)
![12
1.5 Fact Sheet
Name: Bharti Airtel Limited
Established: July 07, 1995, as a Public Limited Company
ISIN INE397D01024
(International Securities Identification Number)
Proportionate revenue: Rs. 204,484 million (ended March 31, 2013-Audited)
Rs. 187,294 million (ended March 31, 2012-Audited)
(As per IFRS Accounts)
Proportionate
EBITDA:
Rs. 64,870 million (ended March 31, 2013 – Audited)
Rs. 62,329 million (ended March 31, 2012- Audited)
(As per IFRS Accounts)
Shares in issue: 3,797,530,096 as at March 31, 2013
Listings: Bombay Stock Exchange Limited (BSE)
National Stock Exchange of India Limited (NSE)
Stock exchange
symbol:
NSE – BHARTIARTL
BSE – 532454
Customer base: India & South Asia:
196,126,000 GSM mobile;
3,283,000–Tele media customers
and 8,100,000- Digital TV
Services
Africa: 63,718,000 GSM mobile customers.
(Status as on March 31, 2013)
(Source: [1] http://www.airtel.in)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/80fa71fd-fddb-48b3-924d-bc72e9e97242-161223101529/85/Final_internship_report-Airtel-16-320.jpg)

![15
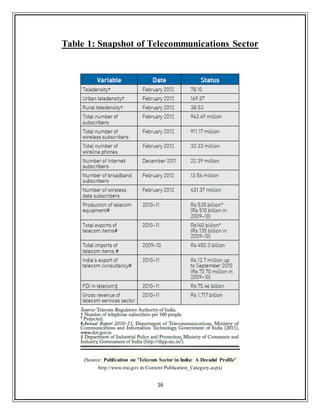
2.1 Brief Overview of the Telecommunications Sector
The subscriber base for telecom services in India is large but skewed in favour of
urban areas. Urban tele-density is 4.4 times that of rural density (Table 1). Further,
wireless phones dominate the market in India and wire-line phone segment
constitutes merely 3.4 per cent of the total subscriberbase. The numbers of Internet
and broadband subscribers are a very small fraction of the population. However,
the number of people capable of accessing the net through mobile phones is
substantially higher, if wireless data subscription through mobile is an indication.
The share of revenue from telecom services is higher than
manufacturing/production of telecom equipment. About a quarter of the domestic
telecom production is exported and the needs of telecom equipment in India are
largely met by imports. Most of the Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) has gone to
the cellular mobile segment. The pace of growth of the telecom sector, particularly
the telecom services has increased its significance to the overall economy in the
past two decades. The share of telecommunication services (excluding postal and
miscellaneous services), as percent of the total GDP, has increased from 0.96 in
2000–01 to 3.78 in 2009–10 (Figure 6 ). [4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/80fa71fd-fddb-48b3-924d-bc72e9e97242-161223101529/85/Final_internship_report-Airtel-19-320.jpg)
![17
2.2 Industry Size and Airtel’s Market Share
GSM continues to be the dominant technology for wireless phones with 87.9 per
cent share. Bharti is the dominant player in GSM segment accounting for 22.35
percent of the market in terms of market subscriptions followed by Vodafone
(18.80 per cent), Idea (13.53 per cent) and Reliance (12.05 per cent) (Figure 7).
There are as many as 14 operators using GSM technology compared to just six
using CDMA. Reliance is the leading player in the CDMA market with 51.32 per
cent share (Figure 8). Tata is the next big player in this market. [4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/80fa71fd-fddb-48b3-924d-bc72e9e97242-161223101529/85/Final_internship_report-Airtel-21-320.jpg)
![18
Figure 9: Airtel and Competitor‟s Market Shares, Source: www.airtel.in
2.3 Comparison with Competitors
Airtel is the market leader in the telecommunication industry with 181.3 million
mobile customers as on March 31st
2012 [1], which makes it the largest wireless
operator in India both in terms of customer base and revenue. As per the latest data
[Table 2] Bharti airtel has the highest sales turnover, market cap. & is the most
profitable telecom operator in India.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/80fa71fd-fddb-48b3-924d-bc72e9e97242-161223101529/85/Final_internship_report-Airtel-22-320.jpg)
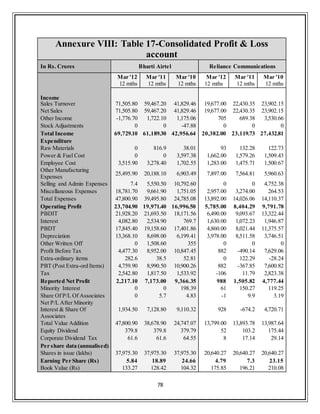
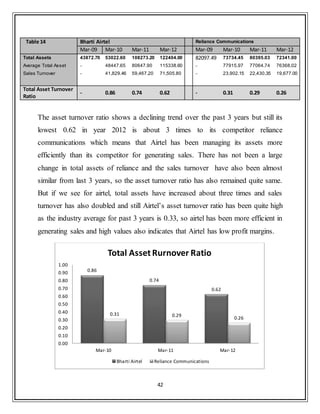
![19
Ranking Name
Market
Cap.
Sales
Net Profit Total Assets
(Rs. cr.) Turnover
1. Bharti Airtel 114,685.41 45,350.90 5,096.30 63,559.00
2. Idea Cellular 47,484.83 22,086.87 818.26 23,072.72
3. Reliance Comm 27,451.56 11,267.00 624 73,068.00
4. Tata Comm 4,923.38 4,416.12 475.24 8,087.80
5. TataTeleservice 1,309.07 2,634.54 -658.77 4,237.96
6. MTNL 1,149.75 3,428.66 -5,321.12 12,184.20
7. Tulip Telecom 115.28 945.03 -735 4,115.30
8. Goldstone Infra 38.07 70.07 2.01 109.63
9. Nu Tek India 8.5 119.21 3.94 582.96
(Table 2: Airtel‟s Net Profit comparison with competitors
Source: http://www.moneycontrol.com)
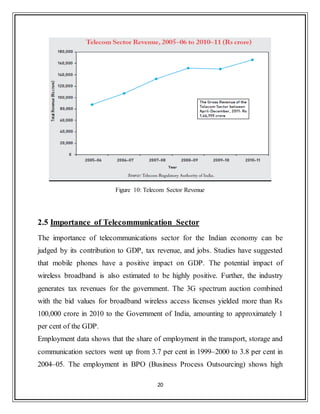
2.4 Revenue of the Telecom Sector
The total revenue trend for the last six years is depicted in Figure 10. The total
revenue (including other income) of the telecom service sector stood at Rs
1,63,067 crore in 2010–11 as against Rs 87,794 crore in 2005–06 showing an
increase of 89 per cent over the last six years. However, revenue from telecom
services is Rs 1,56,657 crore in 2010–11 as against Rs 82,687 crore in 2005–06.
The total revenue of the public sector companies for 2010–11 is Rs 33,971 crore as
against Rs 46,268 crore in 2005–06, showing major decline of 27 per cent over the
last six years. The total revenue contribution from the private sector for 2010–11
was Rs 1,29,096 crore as against Rs 41,526 crore in 2005–06 showing a
tremendous growth of 211 per cent over the period. The share of the public sector
has decreased from 53 per cent to 21 per cent between 2005–06 and 2010–11.
Share of the private sector increased from 47 per cent to 79 per cent during the
same period. [4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/80fa71fd-fddb-48b3-924d-bc72e9e97242-161223101529/85/Final_internship_report-Airtel-23-320.jpg)
![21
rates of growth throughout the 2000s. The mobile telephone industry generated 3.6
million jobs both directly and indirectly. In 2008–09 2.2 million people were
directly employed in the IT–BPO industry with 1.9 million in Tier 1 cities and 0.17
million in Tier 2/3 cities. During the same period the IT–BPO industry employed
7.3 million people indirectly in Tier 1 cities. [4]
The telecommunications sector plays an increasingly important role in the Indian
economy. It contributes to economic growth and the GDP and generates revenue
for the government and generates jobs. In short, telecom sector has a multiplier
impact on the economy.
2.6 Trends in Telecommunications Sector
2.6.1 Tariffs
Mobile cellular prepaid tariffs ranged between US$ 1.3 and 37 per month across
countries in 2008 (Figure 2.2). Average mobile cellular prepaid tariff in the world
is US$ 10.1 per month. Mobile tariffs are the lowest in countries such as
Bangladesh, India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Nepal, Bhutan, and so on. Mobile tariffs in
India are the second lowest (US$1.6 per month) in the world after Bangladesh.
Countries with the highest mobile tariffs in the world include Austria, Venezuela,
Greece, Portugal, Australia, Japan, Spain, Switzerland, France, and Brazil. This
particularly low tariff in South Asia was an innovation (driven by intense
competition, low purchasing power and strict regulatory environments) from this
region called the “budget telecom network model”.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/80fa71fd-fddb-48b3-924d-bc72e9e97242-161223101529/85/Final_internship_report-Airtel-25-320.jpg)
![22
Figure 11: India‟s Position in Mobile Cellular Prepaid Tariffs
This model first emerged in South Asian markets of India, Pakistan and
Bangladesh to cater to “customers who only use a few calling minutes per month.
This innovation rests on the reduction of transaction costs of generating and
transmitting a monthly bill for prepaid customers. Low-value recharge cards,
especially electronic reload; give the greatest payment flexibility making this
model work” (OECD, 2009). This model is advantageous for people with low,
irregular incomes, no permanent address and no credit history. Also, these
contracts allow exact monitoring of use. [4]
2.6.2 Internet Users
India is ranked fourth amongst Internet users in the world, accounting for 4.56 per
cent of the world‟s total Internet users in 2010 as shown in Figure 12. Internet
users in India expanded at a significantly high CAGR of 32.27 per cent during the
period 2000–10 while those in the world expanded at an average rate of 17.46 per
cent. However, India ranks low in terms of Internet users per 100 people in the](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/80fa71fd-fddb-48b3-924d-bc72e9e97242-161223101529/85/Final_internship_report-Airtel-26-320.jpg)
![23
world (143 out of 186) with only 7.5 per 100 people using Internet, compared to
the world average of 30.48. The growth numbers in terms of users are dazzling but
as the next section will show, India is still far behind in Internet subscriptions.
Out of the 91.8 million people using Internet in India, there were only 18.7 million
fixed Internet subscribers in 2010 as shown in Figure 13. India was ranked the
seventh highest (out of 214 countries) in this category in 2010. The country
accounted for 3.54 per cent of the world‟s total fixed Internet subscribers in 2010.
The number of fixed internet subscribers per 100 inhabitants in 2010 was 1.53 as
compared to the world figure of 7.73. [4]
Figure 12: Internet Users in India and in the World, 2010
2.6.3 Wireline Subscriptions
Wireline subscriptions increased from 2.3 million in 1981 to 32.44 million in 2000
to reach its peak at 50.18 million in 2006. Thereafter, it started registering negative](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/80fa71fd-fddb-48b3-924d-bc72e9e97242-161223101529/85/Final_internship_report-Airtel-27-320.jpg)
![24
growth. By the end of February 2012, wireline subscriptions came down to 32.33
million. India has followed the worldwide trend where the mobile phone is a
substitute to fixed line phone, through competition has forced the landline services
to become more efficient in terms of quality of services. The landline network
quality has improved and landline connections are now usually available on
demand. [4]
Figure 13: Total number of Wireline Subscribers & Growth Rate in India
2.6.4 Wireless/Cellular/Mobile Phone Subscriptions
Cellular or mobile segment has been the key contributor to record growth in
telephone subscriptions with its wide range of offers of services. It has led the
growth wave of telecom sector in the country. After triple digit growth rate in the
first two years, growth rate reduced to 35.6 per cent in 1998. The annual growth
rate of wireless phones increased again till 2003 and peaked at 159.2 per cent.
Since then the growth rate has tapered down and has averaged around 51.8 per cent
during 2004–11. In 2011, growth rate significantly came down to 18.8 per cent](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/80fa71fd-fddb-48b3-924d-bc72e9e97242-161223101529/85/Final_internship_report-Airtel-28-320.jpg)
![25
(Figure 14). Mobile phones accounts for nearly 96.6 per cent of the total telecom
subscriptions as of February 2012.
Figure 14: Total Number of Wireless Subscribers & Growth in India, 1996-2011
More than 95 per cent of wireless connections are prepaid. In India GSM mobile
system is pre-dominant. There is a clear distinction between the Global System for
Mobile Communications (GSM) and Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA)
technologies. At the end of December 2011, GSM accounted for 87.9 per cent of
the wireless subscriptions and was growing at a faster rate. [4]
2.6.5 Teledensity
With the increase in the number of telecom subscriptions, the total teledensity has
increased from 2.81 in 2000 to 78.10 on February 2012, a CAGR of 31.9 per cent.
This is mainly driven by the increase in wireless density (Figure 15). Wireline
density was higher than wireless till 2004 and then declined after peaking in 2005.
During the period March 2000–February 2012, wireline density increased at the](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/80fa71fd-fddb-48b3-924d-bc72e9e97242-161223101529/85/Final_internship_report-Airtel-29-320.jpg)
![26
CAGR of 0.19 per cent. Wireless density increased at the CAGR of 64.65 per cent
during the period March 2000 to February 2012. [4]
Figure 15: Teledensity, March 2000 - February 2012
2.7 Why Wireless?
The popularity of mobile phones is due to their personal, portable, and digital
nature enabling people to be always “connected”. Further, the budget telecom
network model mentioned earlier and the ultra-low cost of handsets (Figure 16) has
made mobiles ubiquitous. More than a quarter of all handsets sold in India are
second-hand i.e. re-sold and recycled within India. These factors lower the barrier
to entry. On the supply side, it is relatively cheaper to extend mobile connections
than fixed line telephony.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/80fa71fd-fddb-48b3-924d-bc72e9e97242-161223101529/85/Final_internship_report-Airtel-30-320.jpg)

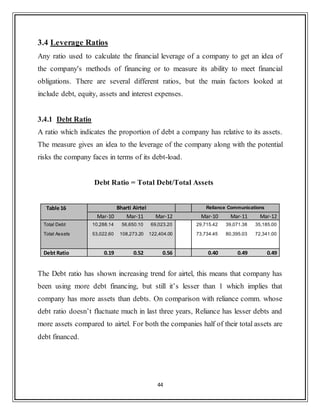
![32
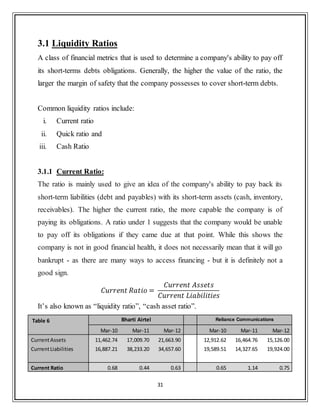
The current ratio has been lesser than 1 for Bharti Airtel from past 3 years which
shows that the company would not be able to pay its short term liabilities with its
short term assets. On the other side its competitor Reliance comm. is healthier in
terms of its ability to pay its short term liabilities. In the year 2011 Airtel had the
lowest current ratio in three years i.e. 0.4, while Reliance was at its best with 1.14
which means the company was able to meet its creditors demand easily. But on
comparison with Industry average over past 3 years, which is 0.46 for telecom
industry [CMIE database] both the companies are doing better than overall
industry in terms of current ratio.
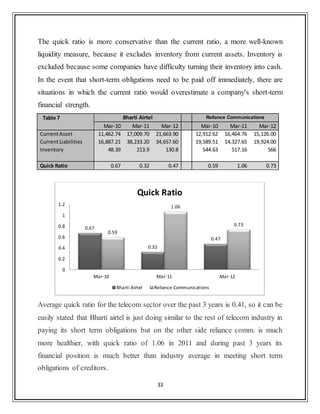
3.1.2 Quick Ratio:
The quick ratio is calculated as:
Also known as the "acid-test ratio" or "quick asset ratio".
0.68
0.44
0.630.65
1.14
0.75
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
Mar-10 Mar-11 Mar-12
Current Ratio
Bharti Airtel Reliance Communications](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/80fa71fd-fddb-48b3-924d-bc72e9e97242-161223101529/85/Final_internship_report-Airtel-36-320.jpg)
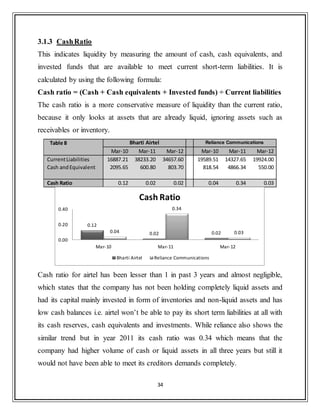
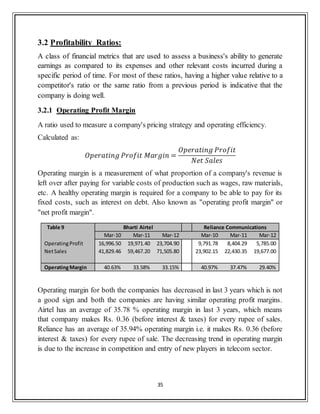
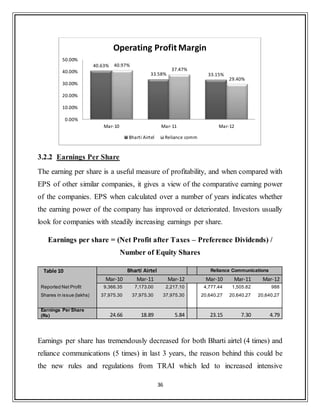
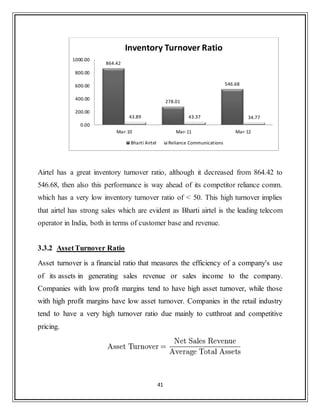
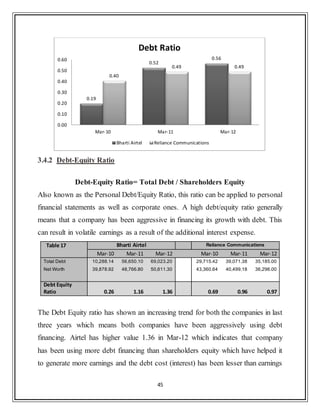
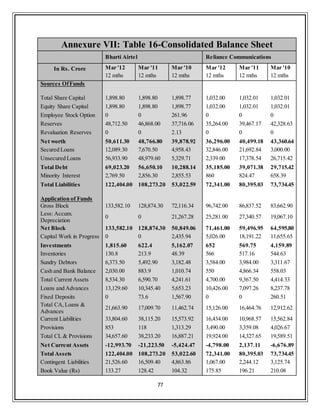
![43
3.3.3 Debtor Turnover Ratio
An accounting measure used to quantify a firm's effectiveness in extending credit
as well as collecting debts. The receivables turnover ratio is an activity ratio,
measuring how efficiently a firm uses its assets.
Table 15 Bharti Airtel Reliance Communications
Mar-09 Mar-10 Mar-11 Mar-12 Mar-09 Mar-10 Mar-11 Mar-12
Sales Turnover 37,352.08 41,829.46 59,467.20 71,505.80 3,961.77 23,902.15 22,430.35 19,677.00
Sundry Debtors 2,899.78 3,182.48 5,492.90 6,373.50 3,961.77 3,311.67 3,984.00 3,584.00
Avg.Receivables - 3,041.13 4,337.69 5,933.20 - 3,636.72 3,647.84 3,784.00
Debtor Turnover Ratio - 13.75 13.71 12.05 - 6.57 6.15 5.20
The industry average Debtor turnover ratio for past 3 years is 4.83 [CMIE databse],
thus it‟s clear that airtel has been very efficient in extension of credit and collection
of account receivables. Reliance comm. has been better debtor turnover ratio than
industry average but lags miles behind airtel. Although this ratio has decreased a
little bit for airtel in last 3 years but still its high values implies that airtel manages
its debtors more efficiently.
13.75 13.71
12.05
6.57 6.15
5.20
0.00
2.00
4.00
6.00
8.00
10.00
12.00
14.00
16.00
Mar-10 Mar-11 Mar-12
Debtor Turnover Ratio
Bharti Airtel Reliance Communications](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/80fa71fd-fddb-48b3-924d-bc72e9e97242-161223101529/85/Final_internship_report-Airtel-47-320.jpg)