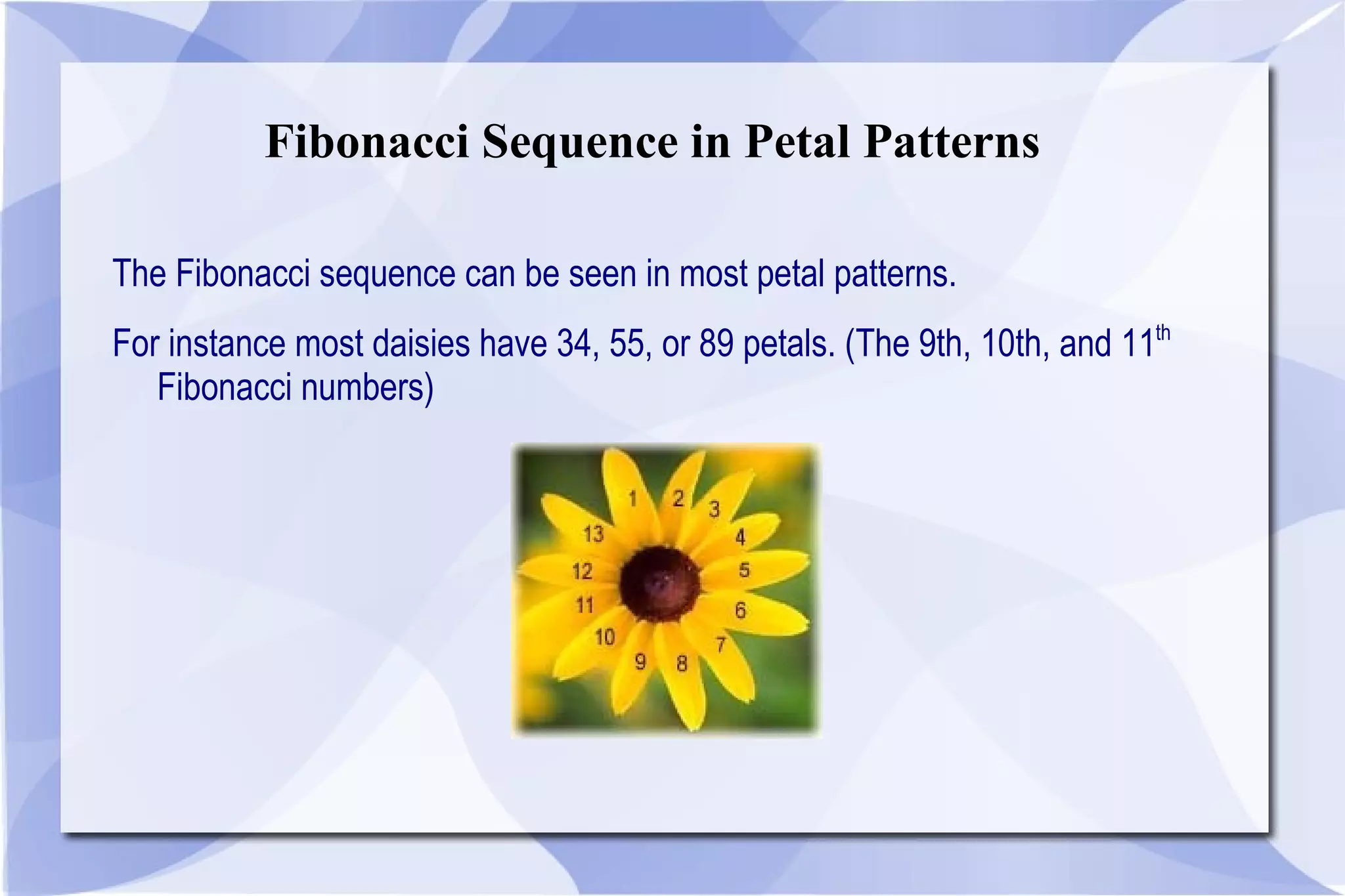
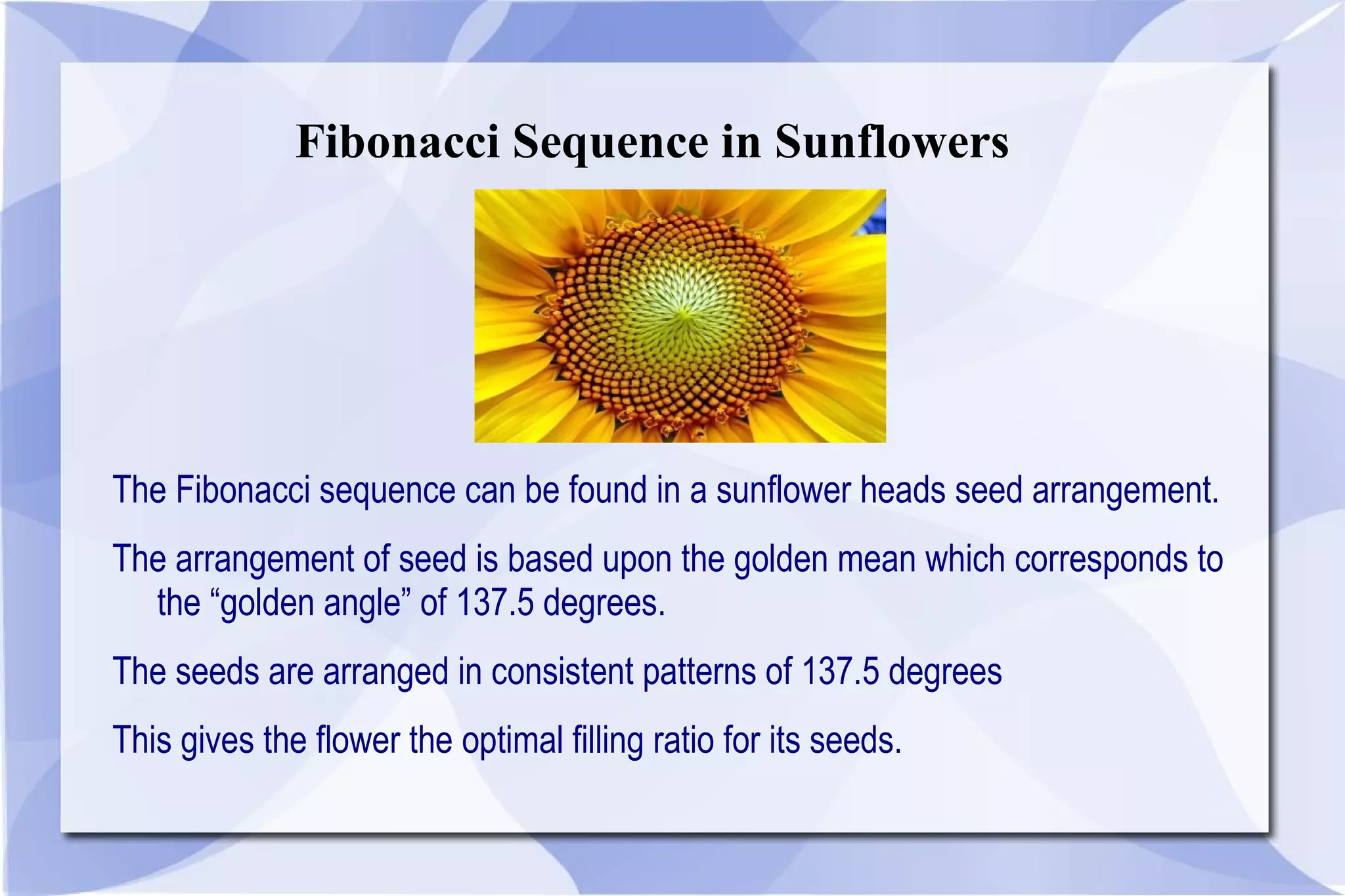
The Fibonacci sequence is a series of numbers where each number is the sum of the two preceding numbers. The sequence begins with 0 and 1 and progresses as 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, etc. This mathematical pattern is found throughout nature, appearing in aspects like petal arrangements, sunflower seeds, and seashell spirals. The Fibonacci sequence was first studied by Indian mathematicians around 200 BC and introduced to Western Europe by Leonardo Fibonacci in 1202 based on patterns in rabbit populations.