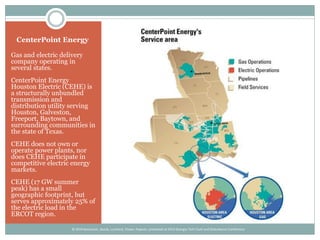
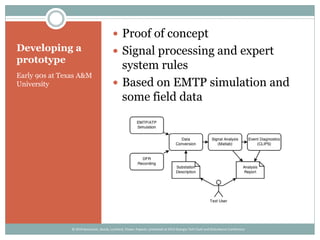
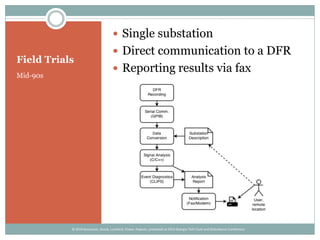
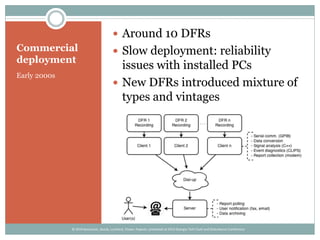
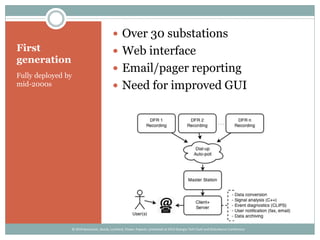
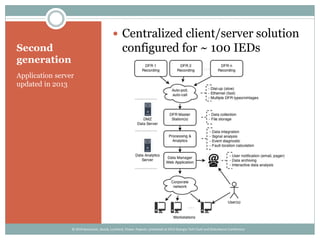
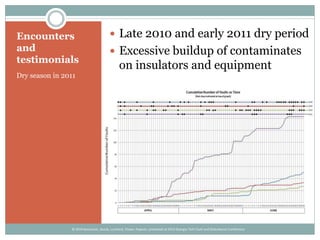
The document details the development and deployment of an automated fault analysis system at CenterPoint Energy over the past 20 years, emphasizing its historical evolution from magnetic tape recorders to modern intelligent electronic devices (IEDs). Key milestones include early prototypes, commercial deployment, and adaptations made in response to reliability issues and new requirements. The effectiveness of this system is illustrated through case studies of significant events, such as hurricanes, showcasing its role in enhancing data utilization and system restoration.