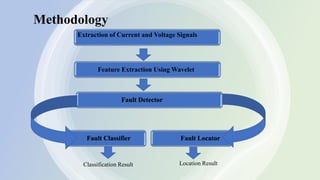
This document presents a presentation on fault classification and location in series compensated transmission lines during power swings. It discusses the importance of accurate fault detection and classification to improve reliability and reduce outage times, highlighting the limitations of conventional methods and the advantages of using wavelet transforms and AI techniques. The objectives include designing simulations, classifying faults using wavelet transforms, and locating faults using traveling waves.




![5
Title Authors Publications year Remark
[1] Transmission Line Fault
Classification and Location Using
Wavelet Entropy and Neural
Network
Aritra Dasgupta, Sudipta Nath
and Arabinda Das
Electric Power Components and
Systems, 2012, 40:15,1676-1689
An expert system based on an artificial
neural network for fault classification and
distance estimation.
[2] Travelling Wave Based Fault
Location Analysis
for Transmission Lines
L. de Andrade, and T. Ponce de
Leão
EPJ Web of Conferences 2012 Review of Fault location methods in
transmission line using travelling wave.
[3] Transmission line fault
classification using discrete
wavelet transform
M. Choudhury and A. Ganguly 2015 International Conference on
Energy, Power and Environment:
Towards Sustainable Growth (ICEPE),
Discrete wavelet transform has been applied
on the fault current and the mean of
approximate coefficients of the phase signals
is calculated.
[4] The Application of Discrete
Wavelet Transform to
Classification of Power
Transmission System Faults
J. Matarweh, R. Mustaklem, A.
Saleem and O. Mohamed
2019 IEEE
Jordan International Joint Conference
on Electrical Engineering and
Information Technology
(JEEIT)
Discrete wavelet transform is adopted to
transform the fault signals in such a way it
can be translated to indicate the fault type.
.
[5] A Comparative Fault Analysis
in Series
Compensated Line during Power
Swing
D. Datta, S. Mohapatra and S. K.
Mohanty
2019 Innovations in Power and
Advanced
Computing Technologies (i-PACT),
Negative sequence component of current is
used for the classification and location of
symmetrical and unsymmetrical fault in a
series compensated line during power swing.
Literature survey](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationonfaultclassification-220918035426-d21e3492/85/Presentation-on-FAULT-CLASSIFICATION-pptx-5-320.jpg)
![6
Title Authors Publications year Remark
[6] Detection of Fault in Fixed Series
Compensated Transmission Line
during Power Swing Using Wavelet Transform
Rohan Kumar Gupta International Journal of Scientific and
Research Publications, Volume 4,
Issue 5, May 2014 1 ISSN 2250-3153
www.ijsrp.org
A support vector machine (SVM) classifier is
employed to distinguish faults from other normal
capacitor and switching transients
.
[7] ANN Based Directional Fault
Detector/Classifier for
Protection of Transmission Lines
Anamika Yadav and A.S. Thoke (IJCSIT) International Journal of
Computer Science and
Information Technologies, Vol. 2 (5),
2011, 2426-2433.
Fault distance and direction estimation based on
application of artificial neural networks for
protection of doubly fed transmission lines
[8] Fast fault detection scheme for series-
compensated lines during
power swing
M. Daryalal, M. Sarlak International Journal of Electrical
Power & Energy Systems, Volume
92,2017.
Likelihood ratio [LR] test is utilized to detect a jump
in the statistical mean of the calculated
forward travelling wave. Finally, a support vector
machine (SVM) classifier is employed to
distinguish faults from other normal capacitor and
switching transients.
[9] A Fault-Location Algorithm for Series-
Compensated
Double-Circuit Transmission Lines Using the
Distributed Parameter Line Model
N. Kang, J. Chen and Y. Liao IEEE
Transactions on Power Delivery, vol.
30, no. 1, pp. 360-367, Feb. 2015, doi:
10.1109/TPWRD.2014.2337306
Fault-location algorithm for series-compensated
double-circuit transmission lines utilizing two-
terminal unsynchronized voltage and current
measurements
[10] Power swing protection of series
compensated transmission
line with novel fault detection technique
Saptarshi Roy P. Suresh Babu Green Computing Communication
and
Electrical Engineering (ICGCCEE),
2014
A negative-sequence current–based technique for
detecting presence of fault, classification of fault
occurred, estimating zone and location of the fault
occurred and the fault inception time.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationonfaultclassification-220918035426-d21e3492/85/Presentation-on-FAULT-CLASSIFICATION-pptx-6-320.jpg)


![10
References
[1] Aritra Dasgupta, Sudipta Nath and Arabinda Das. Transmission Line Fault Classification and Location Using
Wavelet Entropy and Neural Network, Electric Power Components and Systems,40:15,1676-1689.
[2] L. de Andrade, and T. Ponce de Leão Travelling Wave Based Fault Location Analysis for Transmission Lines,
EPJ Web of Conferences 2012.
[3] Chengzong Pang and Mladen Kezunovic
http://smartgridcenter.tamu.edu/resume/pdf/cnf/MedPower08_Pnag.pdf
[4] M. Choudhury and A. Ganguly, "Transmission line fault classification using discrete wavelet transform," 2015
International Conference on Energy, Power and Environment: Towards Sustainable Growth (ICEPE), 2015, pp. 1-
5, doi: 10.1109/EPETSG.2015.7510112.
[5] J. Matarweh, R. Mustaklem, A. Saleem and O. Mohamed, "The Application of Discrete Wavelet Transform to
Classification of Power Transmission System Faults," 2019 IEEE Jordan International Joint Conference on
Electrical Engineering and Information Technology (JEEIT), 2019, pp. 699-704, doi:
10.1109/JEEIT.2019.8717394.
[6] D. Datta, S. Mohapatra and S. K. Mohanty, "A Comparative Fault Analysis in Series Compensated Line during
Power Swing," 2019 Innovations in Power and Advanced Computing Technologies (i-PACT), 2019, pp. 1-6,
doi:10.1109/iPACT44901.2019.8960247.
[7] Saptarshi Roy P. Suresh Babu Power swing protection of series compensated transmission line with novel fault
detection technique Conference: Green Computing Communication and Electrical Engineering (ICGCCEE), 2014.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationonfaultclassification-220918035426-d21e3492/85/Presentation-on-FAULT-CLASSIFICATION-pptx-10-320.jpg)
![11
[8]Rohan Kumar Gupta, Detection of Fault in Fixed Series Compensated Transmission Line during
Power Swing Using Wavelet Transform International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications,
Volume 4, Issue 5, May 2014 1 ISSN 2250-3153 www.ijsrp.org
František Janıcek, Martin Mucha, and Marian Ostrozlık. A new protection relay based on fault
transient analysis using wavelet transform. Journal of Electrical Engineering, 58(5):271–278,2007.
[9] S. Lotfifard, J. Faiz, and M. Kezunivic, “Detection of symmetrical faults by distance relays
amidst power swings,” IEEE Trans. Power Delivery, vol. 25, no. 1, pp. 81–87, Jan. 2010.
[10] Power System Relaying Committee et al. EMTP reference models for transmission line
relay testing report. IEEE Power System Relaying Committee,2004.
[11] Aleena Swetapadma, Anamika Yadav A novel single-ended fault location scheme for parallel
transmission lines using k-nearest neighbor algorithm Computers & Electrical Engineering, Volume
69, 2018, pp. 41-53.
[12] Avagaddi Prasad, J. Belwin Edward, K. Ravi, A review on fault classification methodologies in
power transmission systems: Part-II, Journal of Electrical Systems and Information Technology,
Volume 5, Issue 1, 2018,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationonfaultclassification-220918035426-d21e3492/85/Presentation-on-FAULT-CLASSIFICATION-pptx-11-320.jpg)

