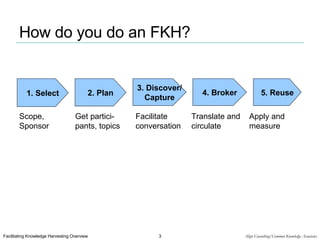
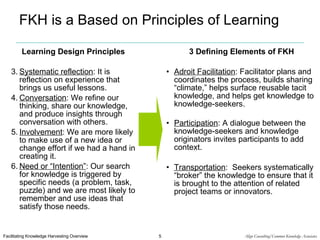
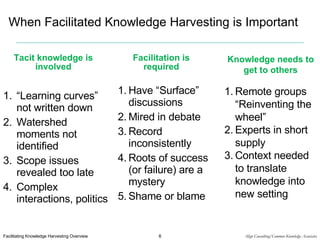
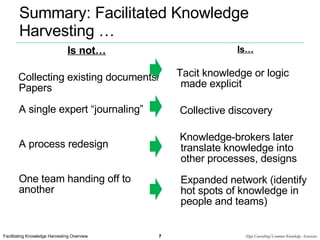
Facilitated Knowledge Harvesting (FKH) is a formal process that uses facilitated conversations between diverse participants to capture tacit knowledge and circulate it to others. The process involves selecting topics, planning the event, facilitating a discovery conversation to surface knowledge, brokering the captured knowledge to relevant parties, and reusing the knowledge. It is useful when tacit knowledge needs to be identified and shared, such as after complex projects or interactions, and involves knowledge originators, brokers, and a facilitator.
![Facilitated Knowledge Harvesting Overview Kate Pugh Nancy Dixon Align Consulting Common Knowledge Associates [email_address] . mit . edu [email_address] .org 617-967-3910 202-277-5839 Align Consulting](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/faciliatedknowledgeharvesting-124033518928-phpapp01/85/Faciliated-Knowledge-Harvesting-1-320.jpg)