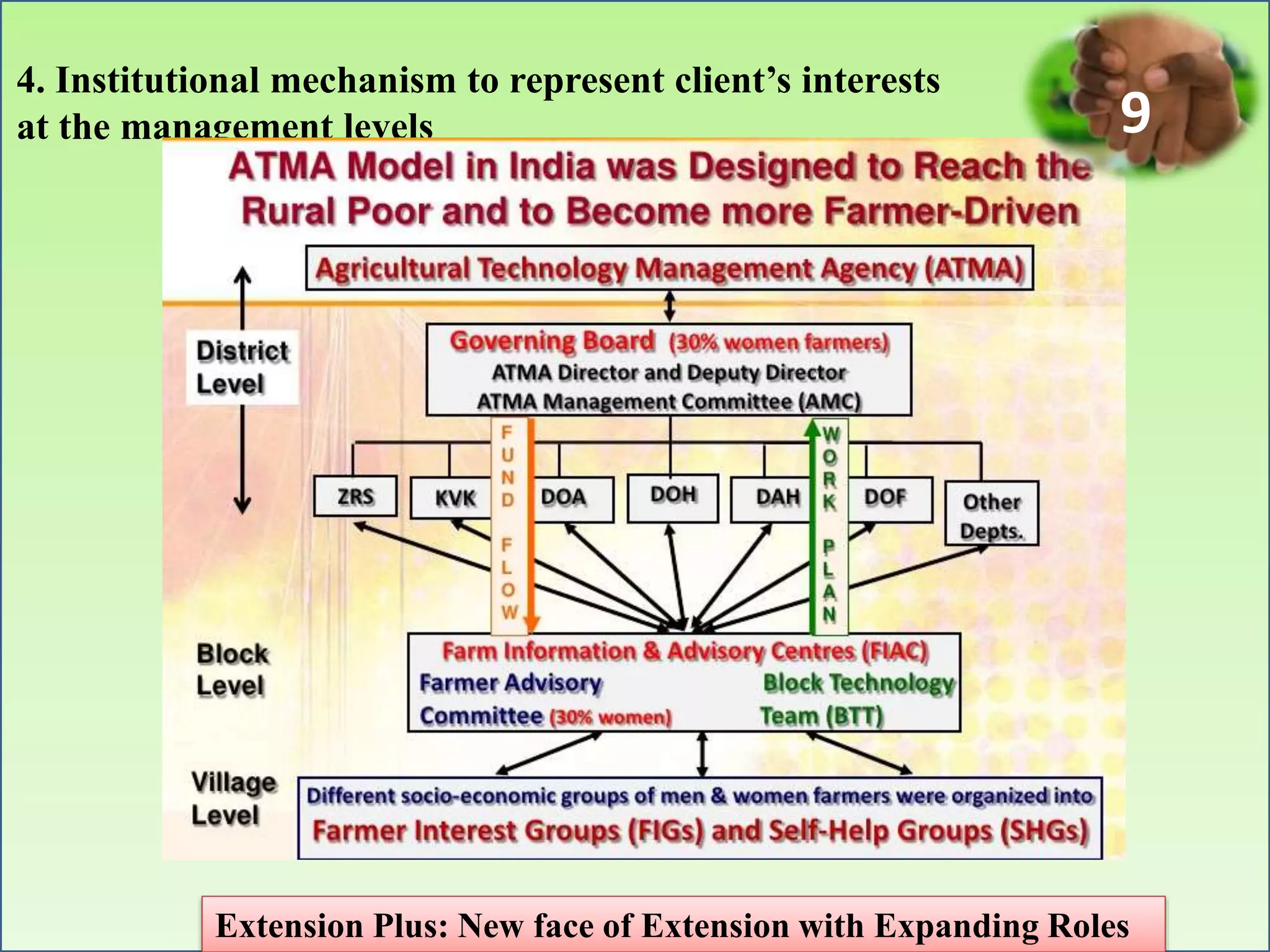
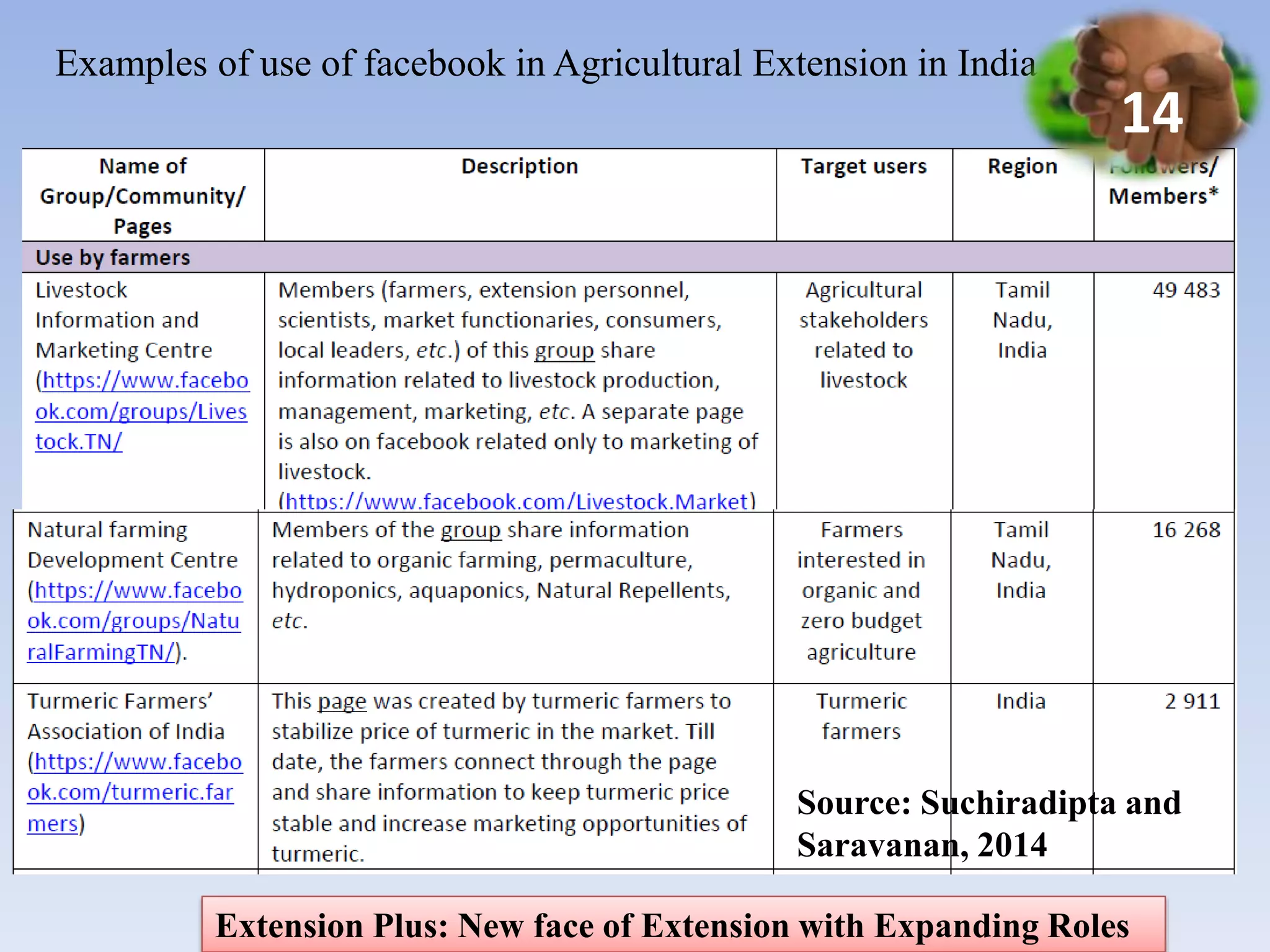
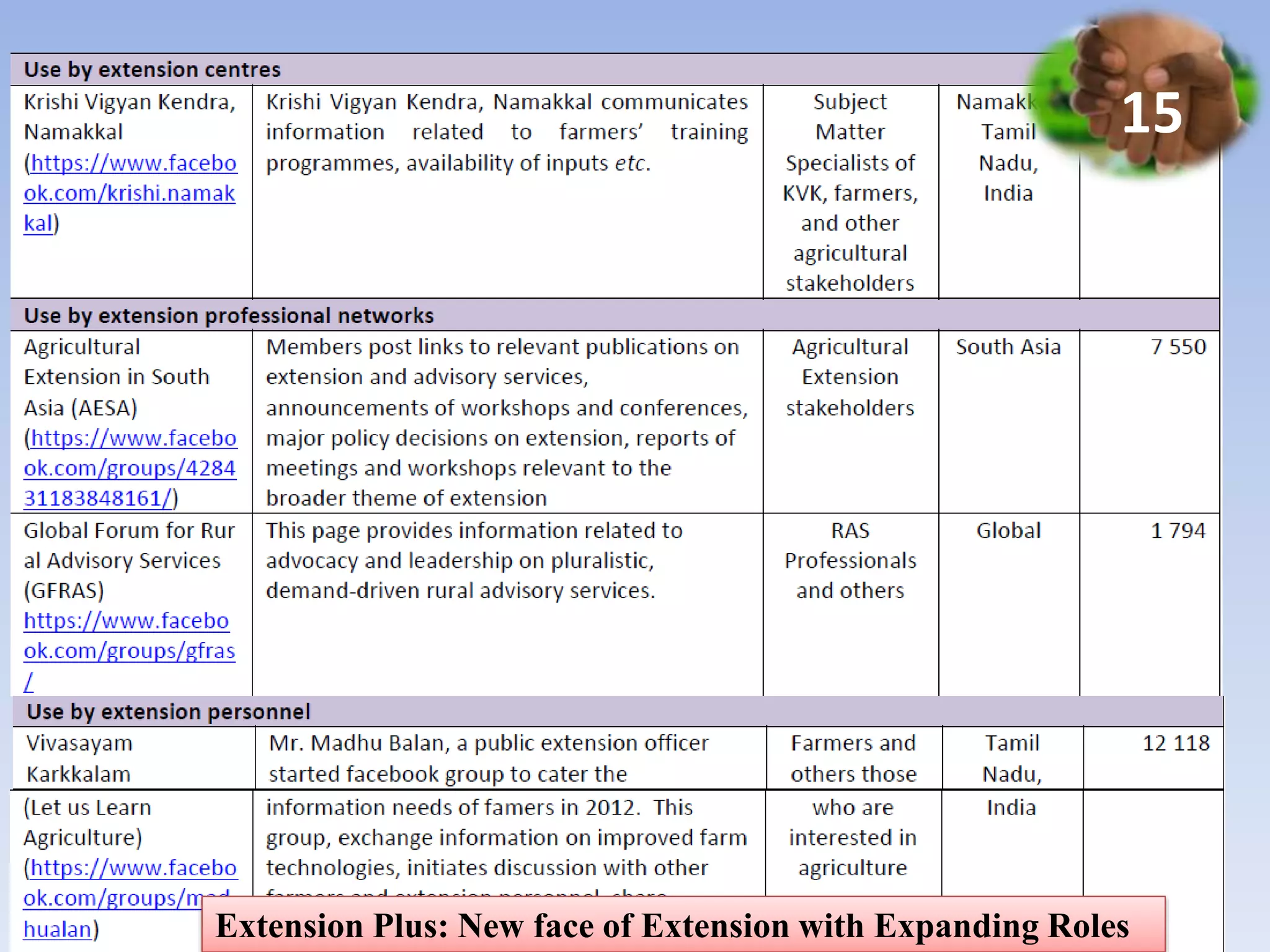
1. The document discusses the need for agricultural extension in India to move from a technology transfer model to an "Extension Plus" approach with expanded roles in linking farmers to markets, reducing vulnerability, and supporting livelihoods.
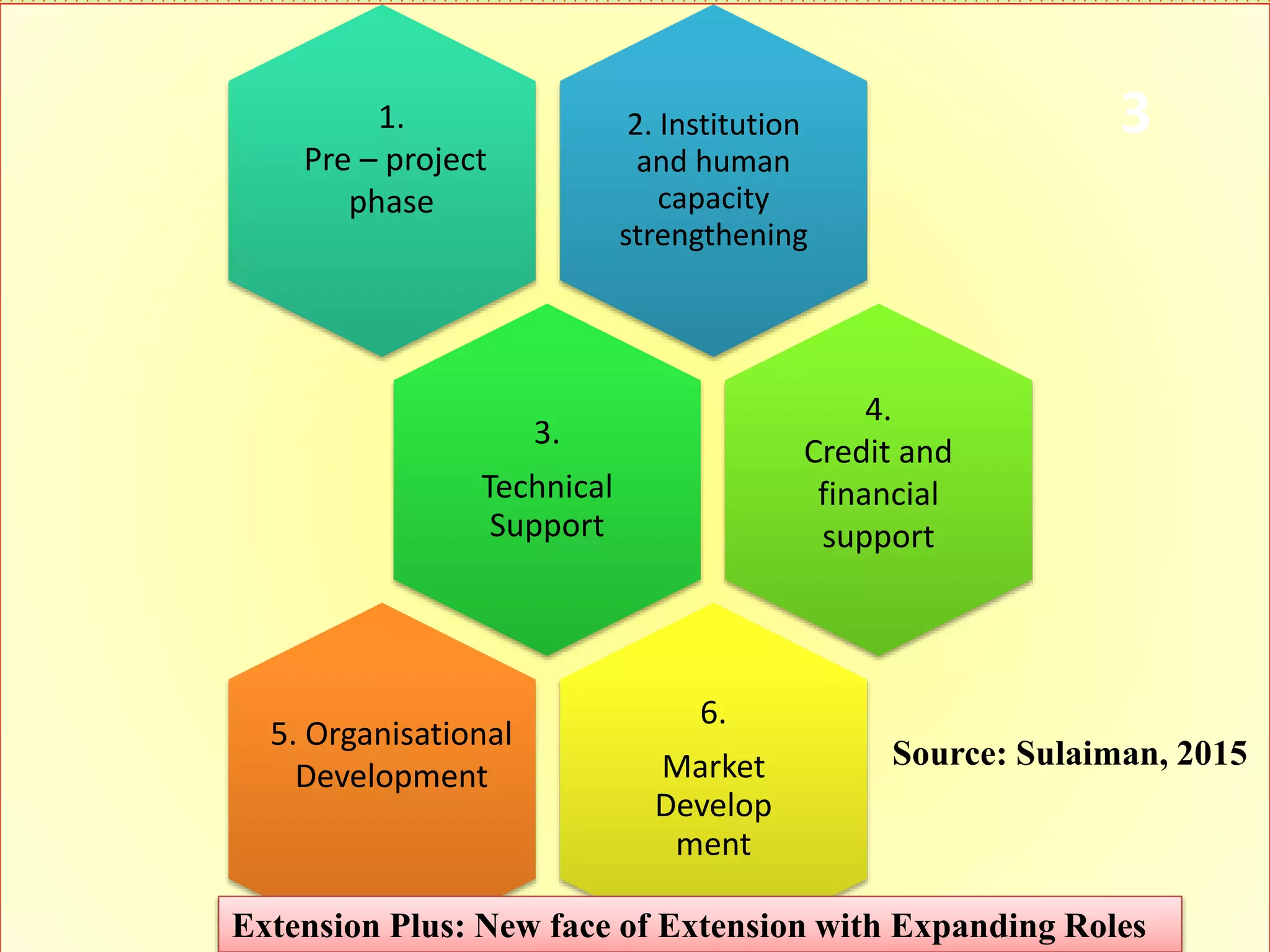
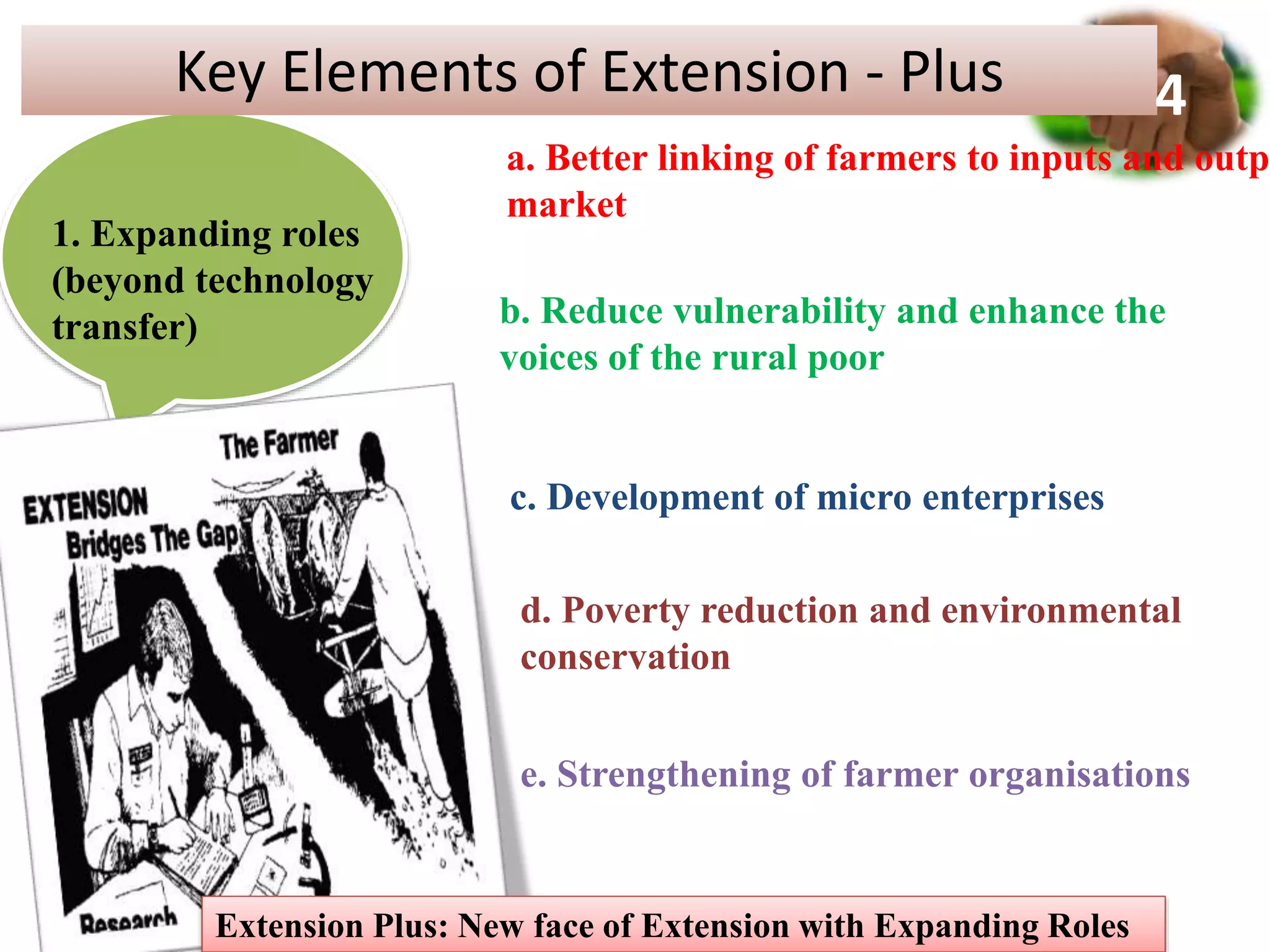
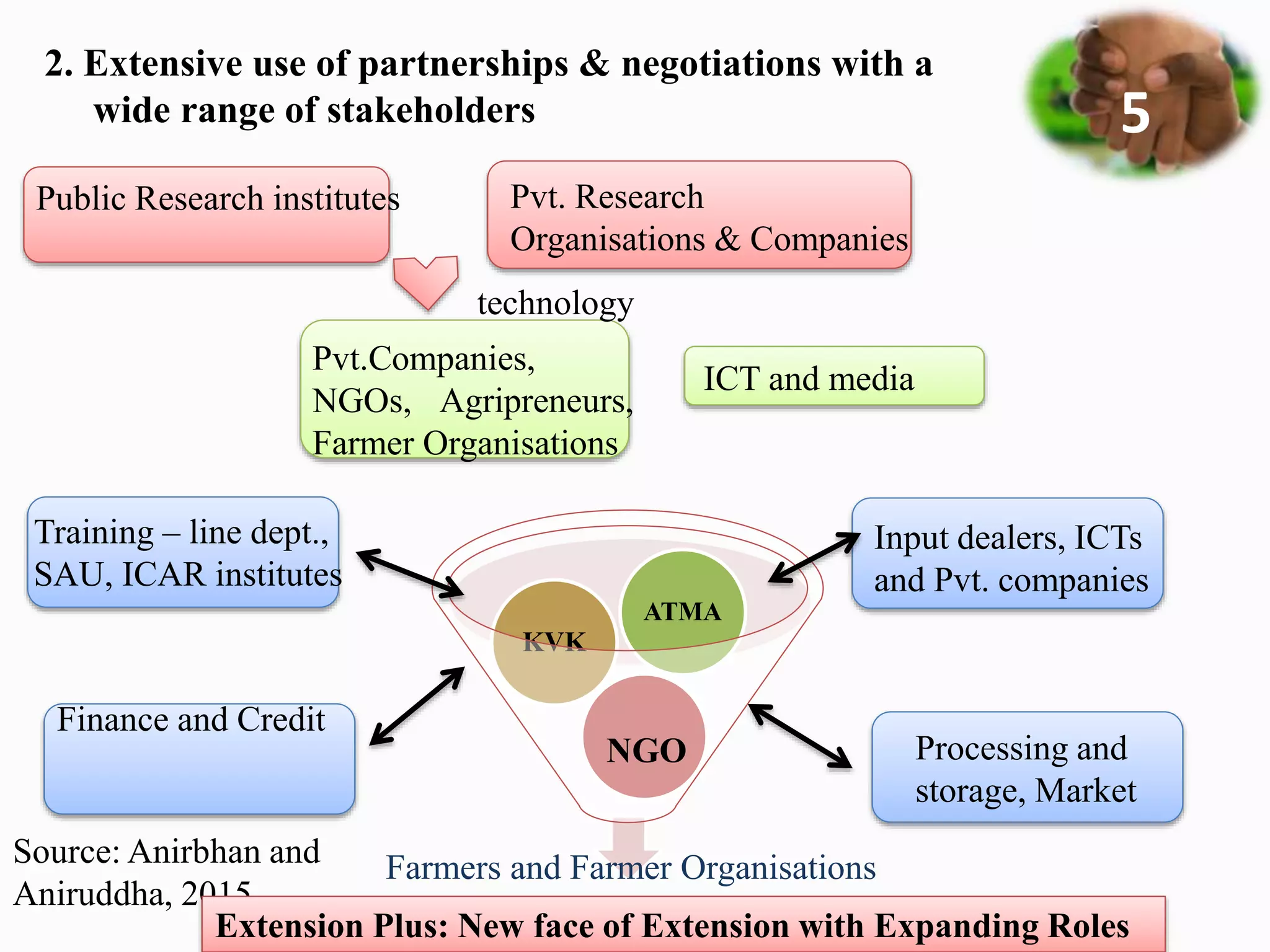
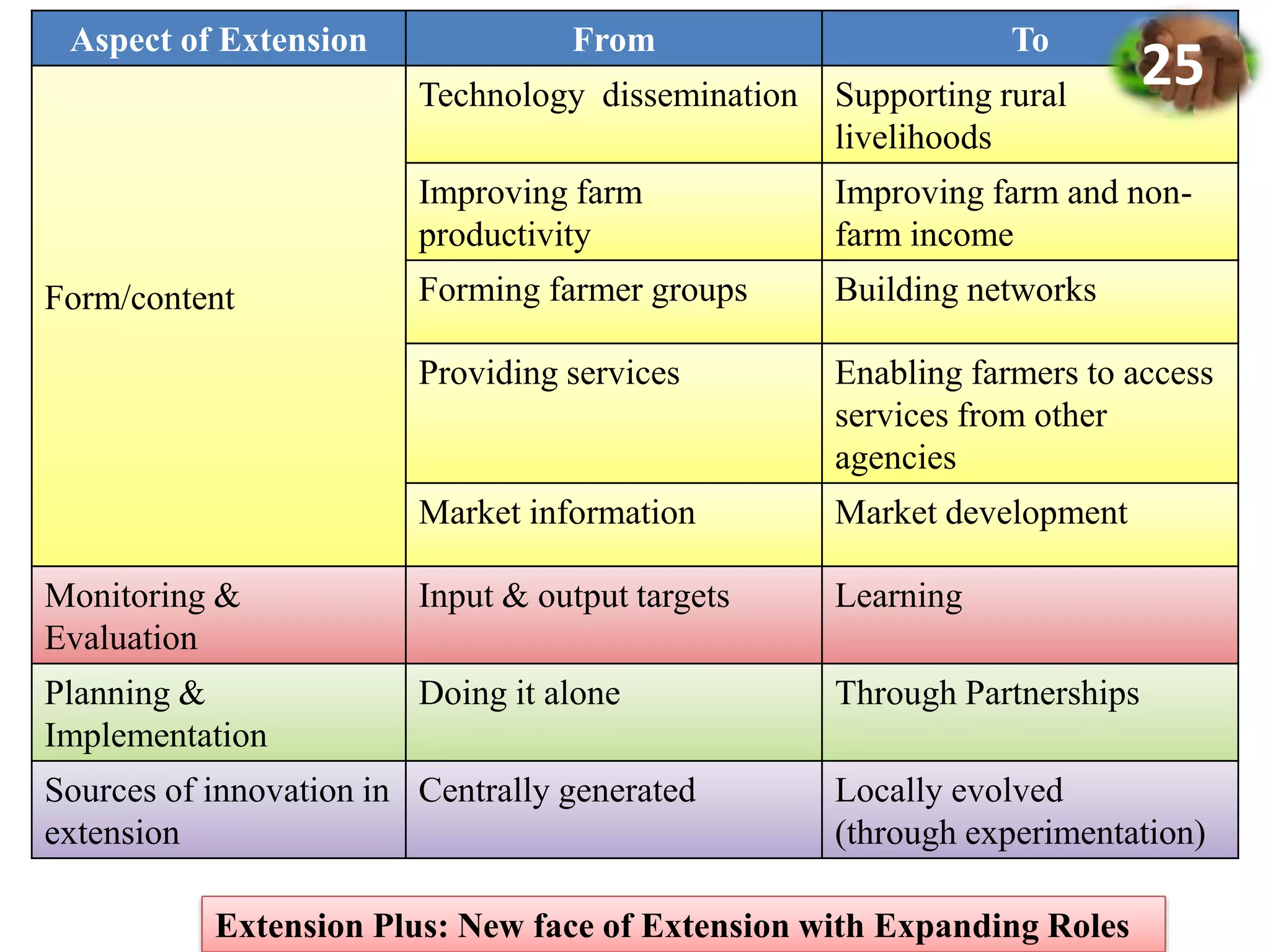
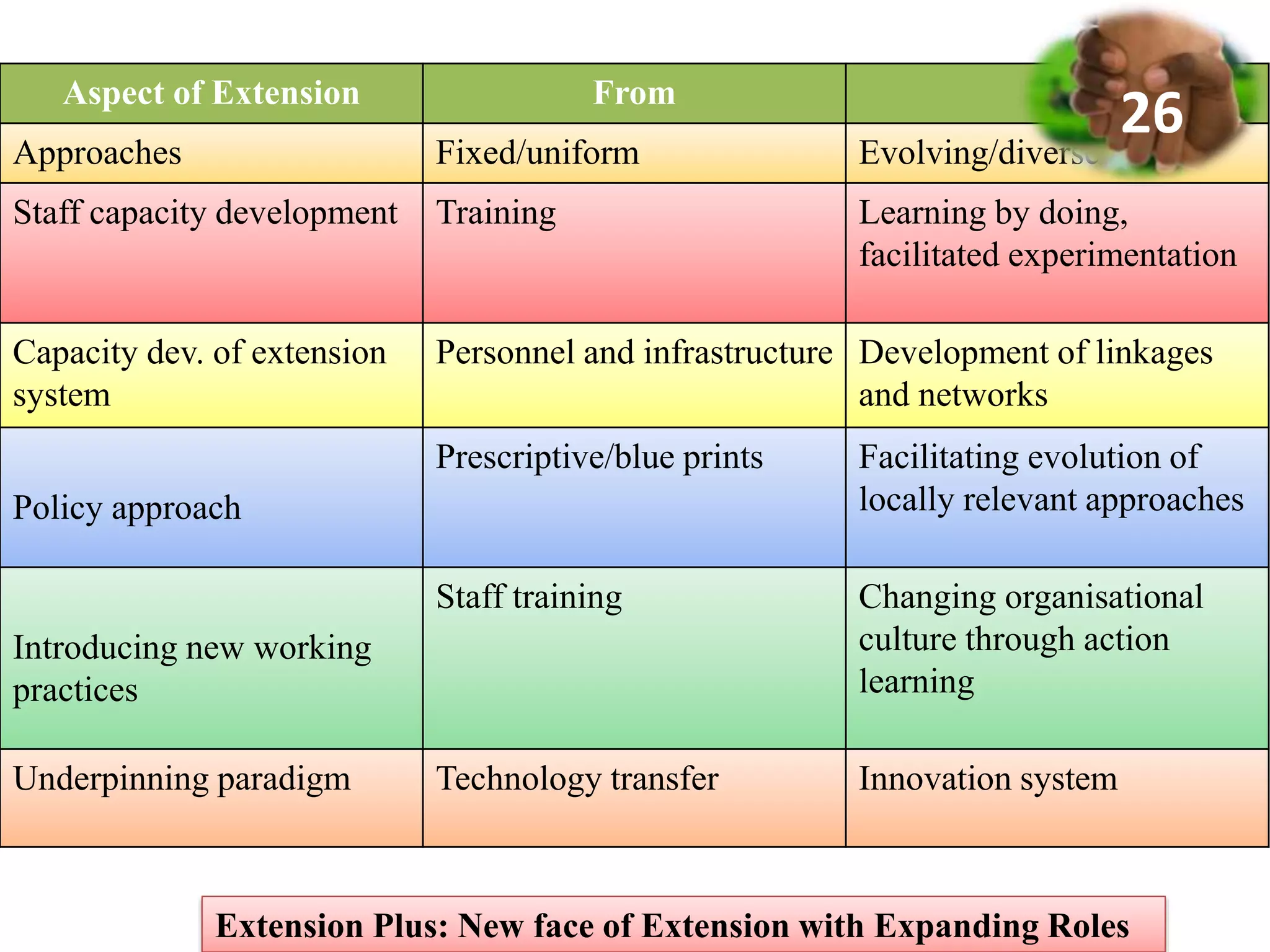
2. It proposes key elements of Extension Plus, including expanding roles beyond technology transfer, extensive partnerships, learning-based approaches, gender responsiveness, use of social media, and climate resilience.
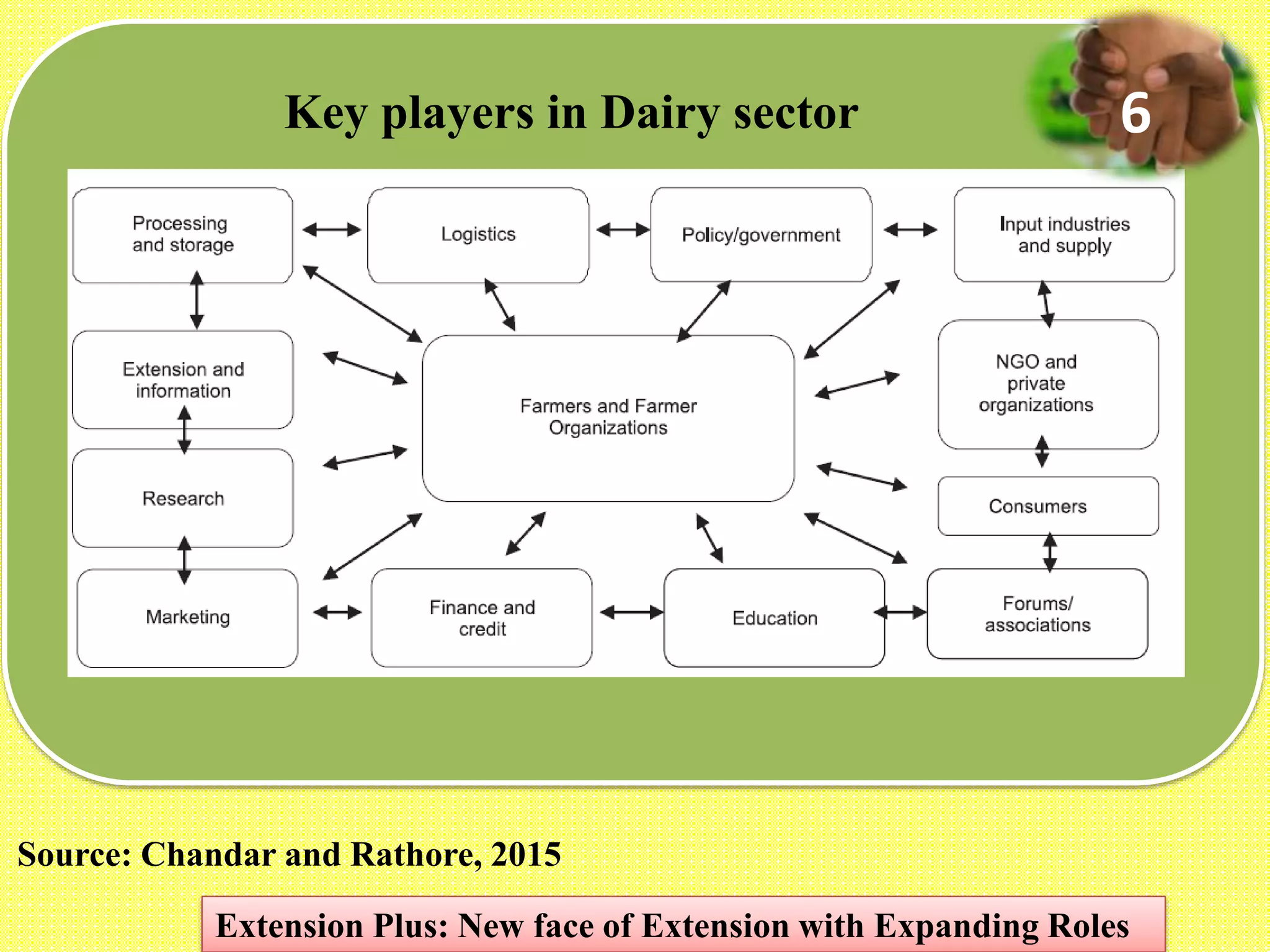
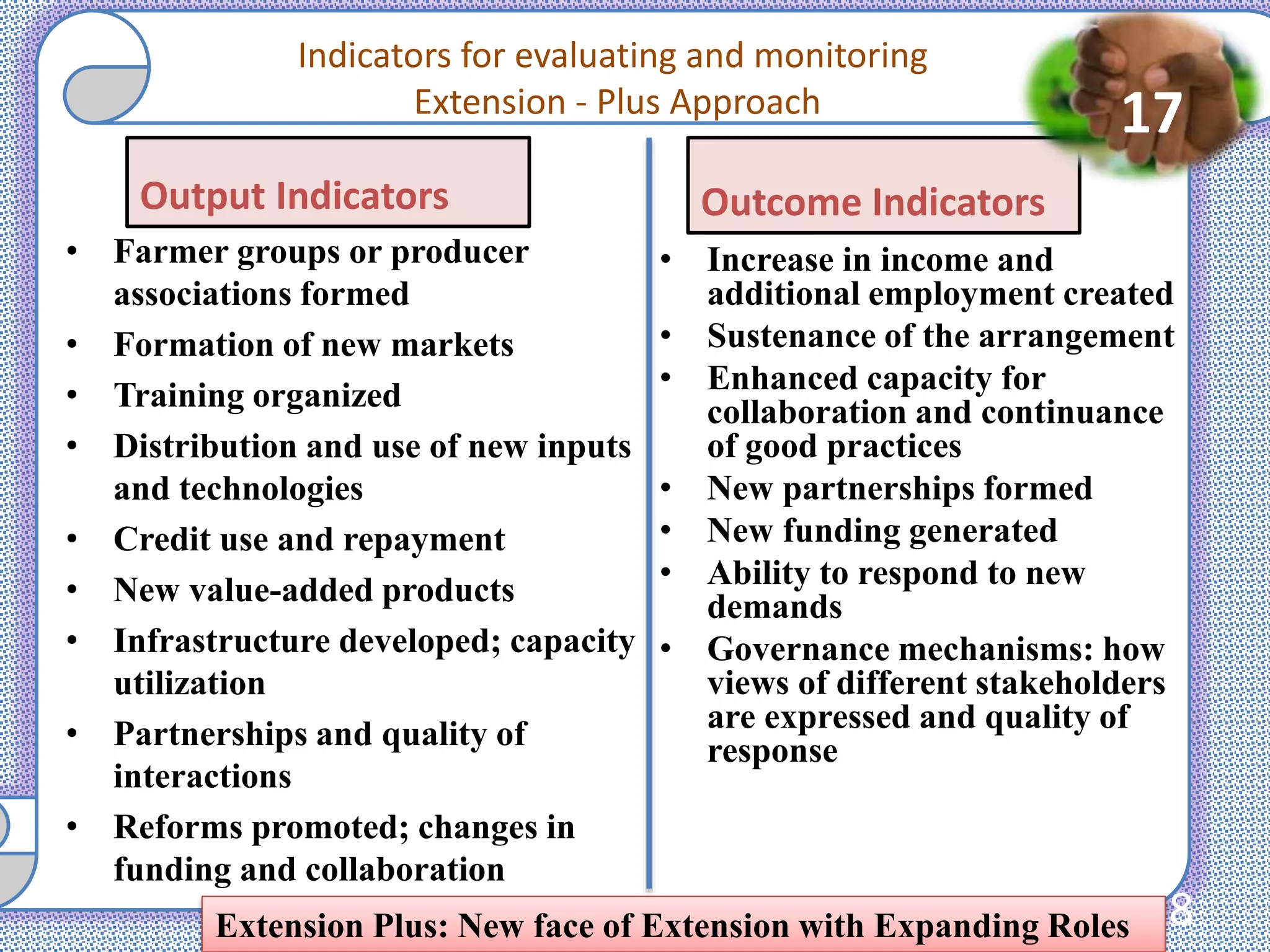
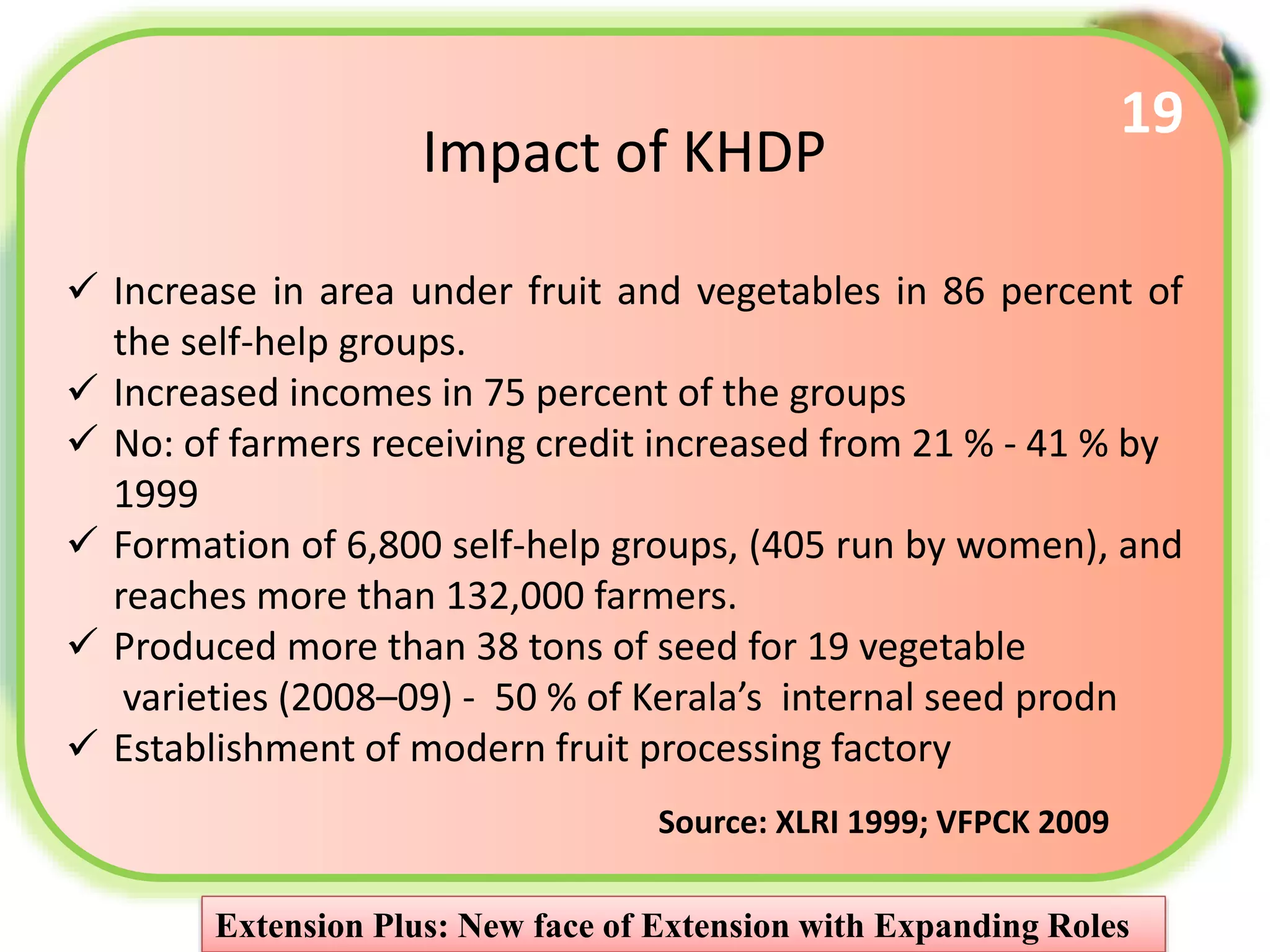
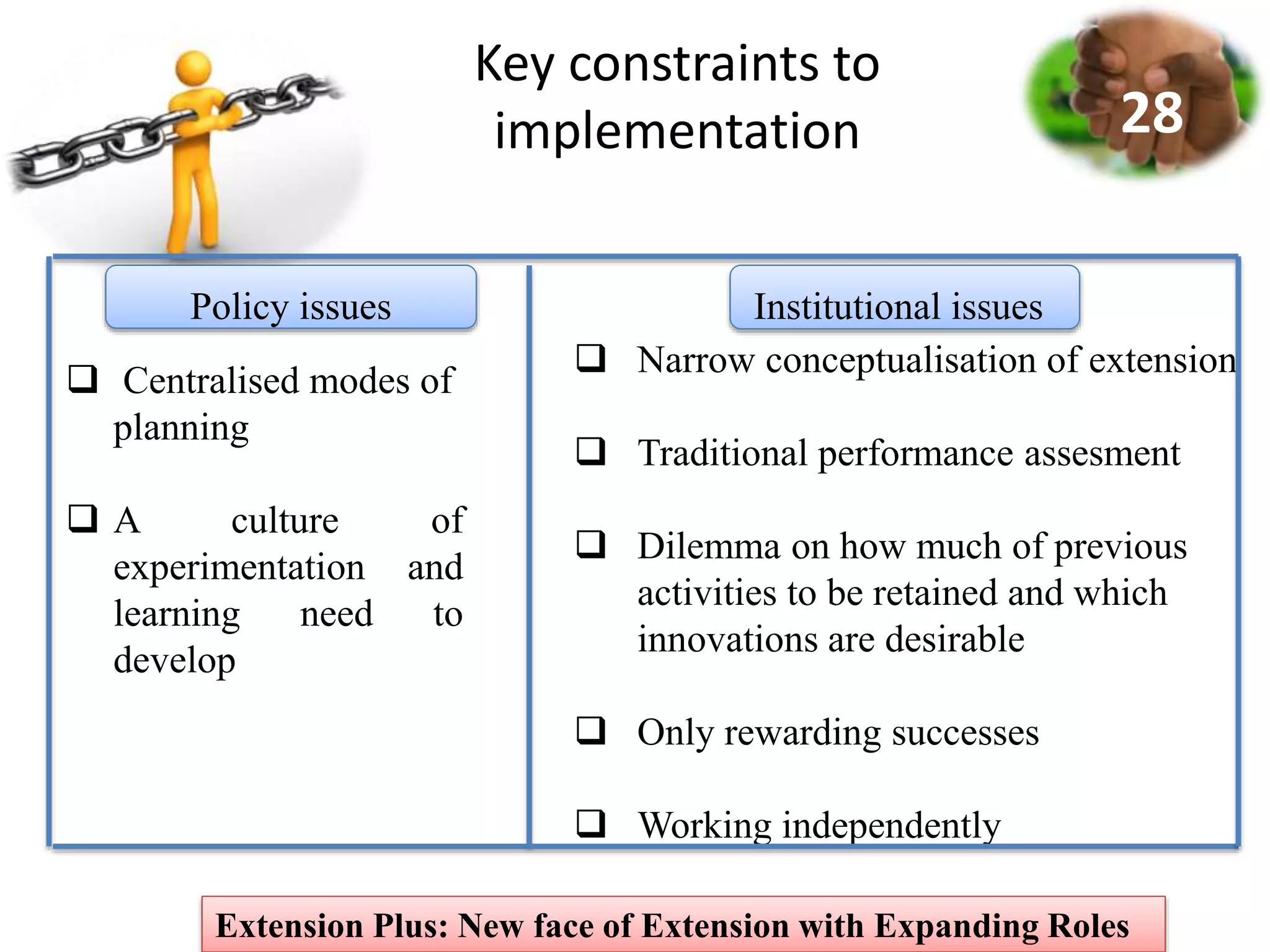
3. Case studies of Extension Plus programs demonstrate impacts like increased incomes, formation of self-help groups and producer organizations, and development of value chains and markets. However, operationalizing Extension Plus fully requires shifts in approaches, policies, and the organizational culture of extension.